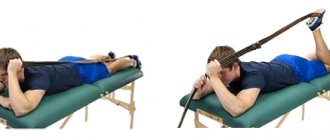
Muscle pain after training is a sure sign that the training was not without success. Without pain there is no muscle growth and progress, but this only applies to those cases where the pain is caused by excess lactic acid in the muscles during intense work. This type of pain is completely harmless and does not require treatment. However, it happens that training is not without injuries. These two types of pain can be distinguished by the following signs:
| “Correct” muscle pain in the lower back after exercise | Low back pain due to injury |
| Associated with lactic acid accumulation | Associated with trauma to muscle fibers, especially small muscles |
| Starts the next day | Begins immediately after traumatic movement |
| The pain is dull | The pain is sharp |
| It hurts only in the area where the load was placed | The pain may radiate to another part of the body |
| It is felt only during movement, but goes away completely when at rest. | Feels both in motion and at rest |
| Gradually weakens and goes away completely after a couple of days | Does not go away for long, may even get worse |
If everything is quite clear with muscle pain in the arms and legs, then the lower back deserves special attention as a very delicate and capricious organ. During training, lactic acid is released in the lumbar muscles, just like in others, after which pain appears the next day. This is absolutely normal. But if discomfort begins immediately after the exercise, or even during it, then this is a signal that an injury may occur.
A psoas muscle injury is not necessarily a serious injury. Microtraumas occur much more often, which can be caused by too much weight lifted, fast and sudden movement, incorrect technique of performing the exercise, or exercising on cold muscles without warming up. It happens that the pain is caused by spasm of the lumbar muscles, as well as small intervertebral muscles, for example, after hyperextension is performed too intensely.
What does “strained my back” mean?
This is usually said about nagging back pain that occurs after excessive physical exertion. “In medical terminology, the condition of “straining your back” is called dorsalgia,” says Grigory Zhezha the SportMedica clinic , exercise therapy and sports medicine doctor, and rehabilitation specialist .
There are many reasons for this condition. “There can be many reasons for pain, and it’s difficult to say which one provoked it at one time or another,” comments Alexander Kolesov, head of the rehabilitation department of the MEDSI Clinical Diagnostic Center on Krasnaya Presnya, sports medicine doctor, physical therapy doctor, manual therapy doctor . “But if you don’t expect any serious damage, then most often it’s a muscle spasm.” If the pain is felt somewhere in the depths, then, most likely, we can talk about overstrain of the deep stabilizers of the spine - the multifidus, interspinous and intertransverse muscles.”
Many fitness professionals do not consider the phenomenon of “ strained lower back during training ” to be something serious and continue to exercise despite the discomfort. But this is wrong, doctors say. “The concept of “muscle strain” does not exist,” explains Alexander Kolesov. — A muscle can either spasm until a trigger point forms, or become injured, and this is, at best, a microtear, that is, a mechanical rupture of a large and small part of the muscle fibers. Both the deep, small muscles, which we mentioned earlier, and the superficial, large ones can be affected: the erector spinae muscle, the upper or lower trapezius, the quadratus lumborum muscle and others.”
Causes and possible consequences
Muscle strains usually occur when lifting heavy weights or improper strength training.
Injuries occur under the following conditions:
- Hard physical work.
- Physical inactivity causing weakening of the muscle frame.
- Injuries caused by a fall or blow.
- Sudden increase in weight.
- Lifting weights with a bent waist.
Muscle tissue has the ability to recover . They contain many blood vessels that supply the muscles with oxygen and nutrients. This explains the rapid recovery.
Muscle tissues are able to recover and their stretching does not pose a threat. Spraining ligaments is more complicated. Bradytrophic muscles are not provided with oxygen and other useful elements . Therefore, it takes more than one month to restore ligamentous damage.
With any sprains, neighboring muscles are also affected, since tears cause a reflex reaction.
Sprained spinal muscles do not pose a threat to the functioning of internal organs . This disease poses a threat to people who work physically, as they will have to limit their professional activities, which entails material losses.
A stretched or torn muscle sometimes leads to severe pain that even painkillers cannot relieve. Inflammation often occurs, causing lymphatic stasis, that is, the outflow of lymph is disrupted. Because of this, swelling appears.
At first, a febrile state is possible, this is how the victim’s immunity responds.
Video: “Sprained muscles and ligaments”
Broke my back during training: causes of pain
Dorsalgia, according to doctors, can occur for a number of reasons. This:
Predisposition to exacerbations of dorsalgia. “In this case, it can be associated with training or even occur without it,” notes Grigory Zhezha.
Overtraining and muscle decompensation. Due to fatigue, some muscle groups “transfer” the load to others, causing discomfort.
Reflex muscle spasm. “This occurs if we ignore stretching after training,” says Grigory Zhezha. “What is necessary for normal muscle nutrition.”
No warm-up. Moreover, this applies not only to training, but also to everyday movements. “In everyday life, you can break your back if during motor activity, for example, lifting a heavy object from the floor, the back muscles - the extensors - are not prepared and suffer with any contraction,” says Ilya Frank, the X - martial arts direction in Russia .
Incorrect execution of the exercise. Especially if you are doing the movement from the wrong starting position. “For example, when doing crunches from a supine position or standing rows. In this case, the large muscles take the entire load on themselves, and the biomechanics of the body will not work fully. This can cause minor injury and reflex spasm,” explains Grigory Zhezha.
Flat feet. It leads to the fact that the back muscles receive an asymmetrical load, a reflex spasm occurs
Problems with intervertebral discs. “Most often they are caused by physical inactivity and the age factor - the nutrition of the discs deteriorates over the years,” explains Grigory Zhezha. — Let’s say, if a 30-year-old person sits in the office for 8 hours and then goes to the gym 2-3 times a week, it is quite expected that he will experience dorsalgia. You can ensure normal nutrition of the discs with daily exercises, which, by the way, will be an excellent prevention of protrusions and hernias.”
Spondyloarthrosis. This disease is associated with changes in the joints of the spinal column, which causes pain along it.
Excessive load when performing a particular exercise.
Why are the lumbar muscles injured?
From a physiological point of view, there are three main predisposing factors to injury: 1) heavy load, 2) weak muscle in 3) a state of stretch. If the range of motion is within physiological limits and the brain does not send signals to lift too much weight, then injury will not occur. However, if you try to lift more than the loaded muscle can, you run the risk of tearing the fibers and causing severe pain.
Another mechanism for the appearance of pain is that under high loads, part of it is taken over by small intervertebral muscles, which are not adapted for this type of work. This model works most often in the case of incorrect exercise technique, when a smaller and weaker muscle works instead of a large one. And a weaker muscle is much easier to injure.
If you train without warming up, cold muscle fibers respond much less well to the load. Not only their strength decreases, but also their ability to stretch, which significantly increases the likelihood of injury. That's why the best prevention of lumbar pain and injury during exercise is:
- Always warm up the muscles you are going to train - a couple of approaches with light weights.
- Maintain proper technique.
- Do not take a weight that you are not used to.
What exercises are at risk of breaking your back?
Breaking your back in training
can be done in almost any exercise. However, doctors consider only a few situations to be the most dangerous. “Incorrect performance of squats, deadlifts or crunches leads to tension in the lumbar spine,” says Alexander Kolesov. — An imbalance occurs in the muscles that stabilize the lumbar spine, when the back muscles are in spasm, and the gluteus maximus and abs are, on the contrary, stretched and weakened. This causes pain. Also, performing a rotation with a barbell on the shoulders with limited rotation in the thoracic spine results in an increased load on the lower back. This will cause inflammation in the facet joints of the spine and, as a result, back pain.”
Doctors generally associate lower back pain with physical inactivity. “Injuries to the lumbar region are associated with low physical activity (we don’t walk fast enough) and a long forced static position, for example, sitting at a computer,” says Alexander Kolesov. “In this regard, the muscles responsible for the stability of the spine cease to function adequately, which leads to injuries. The hardest part is getting them to work organically again. To activate them, there are exercises using balancing pads, as well as aerobic training: fast walking with wide strides, climbing stairs every two steps, exercising on an elliptical. It is fast walking that is effective; regular walks do not work in this case.”
Painkillers
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or NSAIDs, are a pain reliever for athletes and people who are injured. This class of medications includes ibuprofen, including Advil and Motrin, naproxen (Aleve), celecoxib (Celebrex), and aspirin. Tylenol is not considered an NSAID because the active ingredient, acetaminophen, is only a pain reliever.
Some NSAIDs are available over-the-counter in pharmacies, while others are available by prescription only. Check with your doctor if you are unsure how to take NSAIDs or other pain medications.
The benefits of taking NSAIDs included not only overall improvement, but also a reduction in the need for any type of pain medication.
However, the side effects of COX-2 inhibitors are sometimes very serious and even fatal.
Advil and other NSAIDs with ibuprofen as an active ingredient may also increase the risk of fatal cardiovascular events.
Muscle spasm provides protection for damaged or unprotected joints; the immobility it provides limits further tissue damage.
But this limitation can hamper all of your physical therapy efforts. Left unchecked, spasms can also create an imbalance in flexibility throughout the body. Imbalance affects your posture, causes pain, and will likely affect your competitive advantage in your chosen sport.
For these reasons, injured athletes sometimes turn to skeletal muscle relaxers for help.
Several studies have shown that muscle relaxants may be effective for the treatment of nonspecific low back pain. However, the authors remind us that there are side effects associated with this class of medications and that caution should be exercised when using muscle relaxants.
Symptoms of a broken back
The main sign that you have strained your back during training is a pulling or sharp pain in the lumbar spine or along its axis. In this case, you must complete the lesson and take emergency measures. “First aid for a torn back is to limit movement in the injured area. You can use a corset, warming or cooling ointments (here it all depends on the characteristics of your body), if the pain increases or does not go away for more than 2-3 days, you need to consult a doctor,” comments Alexander Kolesov.
First aid
A sprained back muscle can happen to anyone at any time. In this case, you need to know how to properly provide first aid. It consists of the following actions:
- The patient needs to ensure maximum rest for the injured muscle, regardless of whether it is located in the neck or in the lower back. You should once take a horizontal position on a hard, flat surface.
- Apply ice to the area of maximum localization of pain. It is advisable to first place it in a clean natural fabric to reduce discomfort upon contact with the skin.
- Apply anesthetic ointment to the site of inflammation. “Finalgon” or “Apisatron” are perfect for this.
- Take a painkiller tablet, for example, Solpadeine or Diclofenac.
If someone has pulled a muscle and doesn’t know what to do, these tips will prevent the situation from worsening and help reduce the discomfort that appears in the first few minutes after the injury.
How to treat a torn back?
Only a doctor can prescribe adequate treatment after examination. “To treat back pain, it is better to consult a specialist - a neurologist or a sports doctor if you are actively involved in sports. Only they will be able to correctly determine the cause and give competent recommendations. In the simplest cases, I use kinesio taping; this method is accessible and effective; it is also useful to perform myofascial release using a roller or tennis ball. Anti-inflammatory or painkillers should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor, since there are serious contraindications to their use, for example, stomach ulcers and even simple gastritis, says Alexander Kolesov. — Physiotherapeutic treatment is often effective for back pain, but it is prescribed by a physical therapist. Surgical treatment is indicated only in the most difficult cases, prescribed by a neurosurgeon and only when other treatment methods have proven ineffective.”
Strengthen your core muscles
The traditional approach to strengthening the back is to pump it up using special exercise machines and in different “boats”. But isolated strength work is not only ineffective, but can also be harmful. The core muscles are not only back extensors: together they form a ring around the lower back. On top of this ring there is a “lid” - the diaphragm, and on the bottom - the pelvic floor muscles. The core muscles work as a team to solve the difficult task of stabilizing the lower back. Therefore, you need to train a movement, not a specific muscle. When all muscles are equally strong, the load is applied evenly, and a very strong structure is obtained.
The role of these muscles is not to create force, but to transmit it along the floors of the body: from legs to arms and vice versa, preventing the lower back from moving. These are exercises to resist movement in the back - statically and dynamically.
The core is divided into 4 types, resulting in four groups of exercises that need to be included in your training:
Front core:
Rear:
Side:
"Rotary" (rotary core):
Therapy methods
Back strain is treated by a vertebrologist, traumatologist or surgeon. Therapy is carried out comprehensively and involves several stages. Cold should be applied on the first day. Heat will cause swelling and worsen the condition. If the vessels are damaged, bleeding will occur, leading to the formation of a hematoma.
Under the influence of heat, an inflammatory process or abscess will begin. The patient will require surgery, antibiotic therapy and a long hospital stay.
Traditional remedies
Complex therapy includes the following group of drugs:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs are used (“Diclofenac”, “Ortofen”, “Nimesulide”).
- Analgesics (“Lornoxicam”) are prescribed.
- Creams and ointments are used (“Menovazin”, “Troxevasin”).
- Muscle relaxants are prescribed to relieve muscle spasms (“Mydocalm”, “Baclofen”).
- Chondroprotective drugs are prescribed if, based on the results of the examination, the doctor has diagnosed a disease (osteochondrosis). The patient is prescribed “Alflutop”, “Teraflex”.
- B vitamins are used in tablets or injections. They help muscle fibers recover faster.
If a muscle tissue rupture occurs, the patient is indicated for surgical intervention. Back injuries can be dangerous and should not be self-medicated. A qualified specialist will determine the cause of the injury and tell you what to do if you have strained your lower back.
Exercise therapy
During therapy, patients are recommended to exercise and perform special gymnastics every day. It stretches muscles, speeds up the process of restoration of damaged ligaments, preventing ruptures.
Examples of effective exercises if you have strained your lower back:
- The patient lies with his back on a flat surface. Raises his leg, bends it at the knee and presses it to his stomach. Lowers the leg and repeats the exercise with the other limb. 10 approaches are enough.
- The patient lies on his back. Feet should be placed with your feet on the floor, knees bent. As you inhale, raise your back. Do not lift your shoulders and legs off the floor. As you exhale, lower your back. Perform the exercise for 3-4 minutes.
- The patient lies on his back. It is necessary to bend your knees and turn them in different directions. It is important to touch the floor as much as possible and stay in this position for 1 minute.
Prevention
Back strain can be prevented by remembering the helpful recommendations of specialists. Prevention allows you to strengthen the spine and muscle corset. More elastic muscles are less exposed to external risks and can withstand physical activity more steadily.
To avoid injury, just remember the following rules:
- If you have spinal diseases, you need to sleep on a hard surface and use low pillows.
- It is important to monitor your weight and prevent extra pounds. This is an additional load on the spinal column.
- In cold weather, wear a warming belt on the lower back.
- Experts recommend dancing, swimming and fitness. Exercises will help strengthen the muscle frame.
- Before physical activity or lifting weights, you need to warm up.
- You should avoid working with long bends; it is better to squat and keep your back straight.
- It is not recommended to lift objects that are too heavy without a supportive corset or belt.
- Avoid overcooling your back muscles.
It is important to monitor your health, lead an active lifestyle, exercise and follow simple advice from doctors. It is not recommended to lift heavy objects yourself. It is better to ask for help from relatives and friends to move them together. The load on the spine will not be as strong. You can also use a special orthopedic corset.
Signs of stretching
What are the main symptoms of a back strain?
- localized pain in the damaged area (most often the lumbar region);
- increased pain when massaging and palpating the damaged area;
- pain occurs suddenly, usually during or after a heavy approach (when working on pumping, pain may occur much later, when the blood has left the muscles);
- When the back muscles are completely relaxed, the pain goes away.
It is important to distinguish between pain when the back muscles are strained and pain caused by a microdislocation. Stretching pain is a pulling pain that intensifies with any movement. The pain during a breakdown is acute, comparable to an internal cut (it feels).
Note: the article does not cover the case of muscle connection rupture. It can be identified by a suddenly formed hematoma, and the only help that can be provided to the athlete in this case is to call an ambulance and send him to the surgical table immediately!
© LMproduction — stock.adobe.com
Make single-leg exercises your main focus
Single-legged exercises should be the basis of the program; they allow you to load the target muscles just as well, but put much less strain on the lower back. Two-legged exercises - with light weights and only after working the lower body in one-legged exercises.
Select 1-2 hip-dominant and 1-2 knee-dominant exercises in each of three groups: single leg, split set, two legs.
This results in a matrix like this:
- Single leg pelvic dominance exercise here, here and here
- Pelvic dominance exercise in split position here and here
- Pelvic dominance exercise on two legs here, here and here
- Single-leg knee-dominant exercise here, here, here
- Knee Dominant Split Exercise here, here and here
- Knee dominant exercise on two legs here, here