September 2, 2015 Admin Home page » Biceps
The technique of lifting the biceps from the lower block, the muscles being trained and the starting position, important tips for avoiding mistakes, as well as a video for performing the exercise correctly are described.
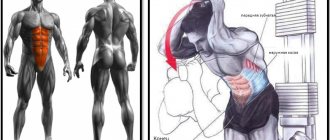
This type of isolated exercise loads equally short and long sections of the biceps, and is performed in a special simulator where a cable with a handle is located.
Benefits and disadvantages of exercise
The crossover biceps curl is a movement that has many different variations. It has a number of advantages and disadvantages compared to the classic barbell lift. Therefore, it is worth considering these exercises as complementary and not replacing each other.
The main advantages of curling your arms on a block:
- The ability to change the degree and focus of the load using different grips, handles, and performing with one or two hands.
- Helps to master the correct technique and ideal execution of the motor pattern.
- It creates tension even at the starting point due to the tension of the cable, because of this, the working muscles are constantly under load.
- Ideal for safe pumping, multi-repetition techniques, static dynamics and other techniques.
- Consistently increases the volume and strength of the biceps.
Disadvantages when working with the lower block:
- Poorly suited as a main “mass-building” exercise, inferior to working with free weights (dumbbells and barbells).
- The gym may not have a crossover (or the right handles).
What types of grips are there?
The horizontal block row can be performed with different grips through the use of different handles. This opportunity allows you to “target” focus on individual areas of the back, thereby forming the desired volume or relief.
There are straight-grip and reverse-grip rows, each of which allows you to distribute the load on the synergist muscles in its own way. As a rule, it is performed with a straight handle.
At the same time, you can still pull in different directions, which opens up the possibility of creating a precise and subtle load on certain areas of the back. Let's take a closer look at grip variations.
Lower block rows with direct and reverse grip
The ability to change the grip allows the horizontal handle, which can be taken with both a neutral and reverse grip. Due to this, the load on the muscles is redistributed. Let's take a closer look at which muscle groups, in addition to the latissimus, are involved in the grip:
- Straight grip. Works most of the rear delts and the middle trapezius. Similar to the bent over row.
- Reverse grip. Involves the rhomboids and lower trapezius, including the biceps.
By varying your grips, you can equally target different muscle groups, achieving symmetry and balance.
Close-grip lat pull-down
Seated rows with a narrow grip can be performed on various handles, both horizontal and V-shaped. The second handle option is classic for the simulator.
The horizontal row with a narrow grip allows you to focus on the lats, as well as the middle and lower back. In this case, the biceps are actively involved in the work:
- If you do it with a narrow parallel grip (palms facing each other) on a V-shaped handle, then the middle part of the latissimus dorsi muscles actively works.
- When performed with a narrow closed grip on a horizontal handle, the middle and lower back are involved in the work.
- If you take the same horizontal handle with an open grip, then in addition to the middle and lower back, the biceps will actively work.
Wide grip lat pulldown
In these variations, you can use either a regular horizontal handle or the same one, but with special handles, thanks to which you can perform horizontal block rows with a wide grip and a parallel grip (when your palms are parallel to each other).
A wide grip slightly limits the range of movement, making it smaller. But, at the same time, the load on the biceps is reduced. It also allows you to engage the rear deltoids, trapezius and mid-back.
Let's take a closer look at which muscle groups are involved with this variation:
- When using a regular horizontal bar, wide grip rows allow you to pump the upper part of the latissimus dorsi muscles. If you change your grip to an inside grip, then naturally your biceps will engage.
- By using a bar with curved ends, you can engage the outer lats, creating a V-shaped back.
What muscles work
When performed correctly, biceps curls are classified as isolating exercises, since only one pair of joints (the elbows) is involved in the work. The main burden falls on:
- Biceps (mostly short head).
- Brachial muscle.
- Brachioradialis muscle.
If an athlete feels tension in other muscles (for example, triceps or trapezius) when performing a cable curl while standing, this indicates incorrect technique or a lack of neuromuscular control in the target area.
Anatomy
The lat pulldown allows you to work absolutely all areas of the latissimus muscles, but you should not try to pump them all in one workout. From an anatomical point of view, as mentioned above, this exercise is very convenient, it allows you to perform the movement for which evolution has been preparing the latissimus muscles for centuries, so achieving hypertrophy will not be at all difficult, just show patience and perseverance.
Even though the lower block row is performed while sitting, nevertheless, since the athlete leans forward and straightens, pulling the bar towards himself, the spine receives a load. This load especially increases when they try to “cheat”. In this case, when the muscles no longer pull the weight, the athlete begins to sway and, due to inertia, gets the opportunity to simulate performing a deadlift. Never do this if you value your spine.
Other exercises
Bend the arms on the lower block
The crossover version from the lower block is a classic version of the exercise. However, there are three popular variations that use different handles. Each of them has its own characteristics.
Classic technique with straight handle
- Approach the machine half a step. Take the handle in your hands and stand straight, feet shoulder-width apart.
- Bend your arms until your fist is level with your front deltoid.
- Stay in this position for 0.5 seconds, then at a slower pace, straighten your arms until your elbows are completely straight.
To more effectively perform the movement on the lower block, it is recommended to do a long delay of 1 second. Exhale while bending your arms, inhale while extending your arms.
The straight handle version is the most common. Main advantages:
- Load on the short head of the biceps.
- The option is as convenient as possible even for beginners and does not require much preparation.
- Allows you to set the highest weights in the simulator, which makes it one of the most promising for increasing strength indicators.
Bending in a block with a rope
Main features and differences when working with a rope handle in a crossover:
- Having your hands in a neutral grip (palms facing each other) puts more stress on your forearms. This is especially true for those who are lagging in this muscle group.
- To place even more stress on the forearms when performing bending, the athlete can turn the hand to the sides (so that the palms are facing upward at the top point). This helps not only strengthen the tendons, but also thicken the muscles in the forearm area.
- This technique is considered an analogue of hammer bends and switches the focus of the load from the short to the long head.
- Due to its flexibility, the rope creates less stability, forcing more stabilizer muscles to come into play.
Curls with EZ-handle
Cable curls with an EZ handle are very similar to the Scott Bench movement. Main differences:
- The load falls more on the lower part of the biceps.
- Due to the lack of triceps fixation and barbell position, more muscle fibers are involved in the work.
- You can perform the movement with a wide grip, which will partially shift the load onto the long beam.
Bending from the lower block with each hand separately
Performing the movement with one hand allows you to more specifically load the biceps and eliminate other muscles from working. However, for the exercise to be effective, it is important to follow the basic rules:
- Always do the same number of reps on each D-handle arm.
- Securely fix the body (hold the frame with your free hand) to eliminate inertia and swaying.
- Perform the movement at a slow pace (raising your arm slightly faster than lowering it).
Seated dumbbell curls
Briefly about the mechanics of the exercise
The main function of the biceps brachii muscle is to flex the arm at the elbow joint and supinate the forearm—rotate it outward, clockwise. When performing a dumbbell biceps curl, both heads receive the maximum possible load, since the movement combines both bending the arm and rotating it in the forearm. Thus, the entire biceps is fully tensed, as well as the muscles of the forearm.
Correct execution of the exercise
- We accept the starting position. Let's take a bench with a back - the most successful option for a beginner, allowing you to concentrate only on performing the exercise. We sit down straight, our legs are brought together, our arms with dumbbells are lowered down, our palms are directed inward.
- Begin bending one arm at the elbow joint, and at the same time rotate your forearm clockwise until the biceps contracts completely. Perform bending and turning at the same time - when the dumbbell rises to shoulder level, the palm should be directed towards the athlete’s face.
- Squeeze your biceps and forearm as much as possible, holding for a short period of time.
- Smoothly lower your hand to the starting position, while simultaneously turning your forearm inward.
- Repeat the movement for the other hand.
Basic Rules
When lifting dumbbells for your biceps, remember the following basics of proper technique:
The bending and turning of the arm should be done evenly. The spine should always be straight - to do this, press your lower back and upper back into the bench. The option of using a bench without a back will complicate the task. During the exercise, only the elbow joint should be involved. A very common mistake made by beginners is to bring the elbow forward to help complete the repetition by engaging the anterior deltoid muscles in the work.
This reduces the load on the biceps and forearms, so in this case it is better to take less weight
Calculate your ideal sports weight!
Perform the exercise with each hand in turn, focusing your attention as much as possible. Start bending your second arm only when the first one reaches its starting position.
Do not lean towards the hand that is performing the movement. Choose a weight that allows you to perform the movement smoothly and complete at least 5-7 repetitions. Don't lift your elbows away from your body.
What are the benefits of the exercise?
As mentioned above, lifting dumbbells for biceps while sitting is equally useful for both athletes who have extensive experience in bodybuilding and beginners who have recently learned what bodybuilding is and have recently begun the difficult path to building an ideal body. For people who are taking their first steps in bodybuilding, this exercise is effective for the following reasons:
- Sitting on a bench reduces the additional stress on your lower back, leaving you with more energy to perform the exercise.
- The biceps are involved in many other exercises, so additional stimulation of them will quickly increase the results of the entire workout.
- The exercise very quickly forms the “correct” biceps, increasing its thickness and visually separating it from the deltoid muscles. In addition, the forearms also grow in width.
Alternatively, curling your arms can be done at the same time - this way you can ensure that they move along the same path. This will also help to avoid involuntary bending towards the working arm.
Now you know how to pump up your arms, or more precisely your biceps, with the help of dumbbell curls for biceps while sitting. I would like to remind you that there are still many articles on the blog about how to pump up your arms.
Bending arms in a crossover from the upper block
The biceps curl on the upper block is a complex technique, so when working in this style it is recommended to use a light weight.
Technique:
- Place the D-handles into the upper blocks of the machine. Stand in the middle and grab them with your hands. Feet shoulder-width apart, back straight.
- Begin to bend your elbows, trying to bring your hands as close to your shoulders as possible.
- Pause briefly at the peak point and extend your arms until your elbows are straight.
- The biceps is always parallel to the floor.
- Also, when performing it, it is important to ensure that the elbows are directed to the sides (bringing the elbows together is a technical error).
Pull the block down with straight arms[edit | edit code]
Characteristics
:
Pulling the block down with straight arms
- Assistance exercise focusing on stabilizing muscles
- Isolating one joint when pulling a block down with straight arms
- Traction movement
- Closed kinetic chain
- Using weights
- For intermediate and advanced levels
This exercise is aimed at working the stabilizing muscles of the trunk, in particular the abdominal muscles, serratus anterior and lower trapezius muscles. The quality of the exercise in this case is more important than the magnitude of the load.
Pulling the block down with straight arms
Recommendations
- Technique and smooth execution without jerking in this movement are more priority than the weight of the projectile.
- Try to place the movement at the end of your workout, after heavy exercises like barbell curls.
- It is optimal to perform 10-12 repetitions per set (12 for each hand when performed alternately). Also, the exercise “responds” well to a multi-repetition training regimen, 12-20 repetitions.
- Try to do no more than 3-4 working sets of curls per week.
How to choose a working weight
The optimal mass of weights for effective muscular hypertrophy is determined by the sinking method. It involves initially performing deadlifts with light weights and gradually increasing the number of weights on the machine.
Small weights are added until the maximum level of external resistance is reached, at which it is possible to do 10 repetitions without breaking the technique. Further work continues with this weight.
This method will provide improved strength results and a noticeable increase in muscle mass. You should not sacrifice the technique of performing the exercise for the sake of increasing the total working weight of the weights. This will lead to a shift in the main load to other muscle groups and loss of training effectiveness.
Superset: French press + close grip bench press
These exercises will perfectly pump up your triceps.
French press
Technique:
- We lie down on a bench and take a barbell with a curved bar with a narrow grip.
- We hold the barbell with straight arms, and then begin to bend our elbows, lowering the bar to the top of our forehead.
- In the upper phase, the bar should be slightly tilted back so as not to load the joints.
Close grip bench press
Technique:
- We lie down on a bench and take a barbell with a curved bar with a narrow grip.
- With a powerful movement we push the barbell up.
- We move our elbows along the body, lower the barbell onto the solar plexus, and not onto the chest.
It is recommended to do four supersets and perform each exercise 8-15 times.
How to gain muscle mass if you eat and don’t gain weight?
We pump up the back and biceps. Training for those taking their first steps in fitness