The benefits of swimming for the body are proven and undeniable. This sport has many benefits: it improves health, strengthens the muscles, and is also a type of cardio training. Swimming can help you lose weight quickly.
In this material we will talk about the benefits of swimming and the effect of training on the body. You will also learn how to choose a place to exercise and how swimming affects the fat burning process.
For which organs and muscle groups is swimming beneficial?
Swimming develops the body's muscle complexes, cardiovascular and respiratory systems, and is also an excellent way to quickly lose extra pounds. Let's look at the main benefits of swimming in terms of benefits for the body.
Swimming uses most muscle groups
During swimming, almost all muscles of the body work. Various swimming techniques increase the load on certain muscle groups. During breaststroke, your legs are pumped great - buttocks, calves, thighs. The butterfly stroke uses the shoulder girdle, arms and core. The crawl is the most complex option, in which all muscles are used evenly.
Lung training
Professional swimmers are very resilient. Their respiratory system can withstand enormous loads. This is achieved by developing the muscles of the chest, diaphragm and increasing lung capacity during training.
By swimming, you will not experience problems when running long distances. The respiratory system will be ready for multi-kilometer races and will quickly recover after cardio training.
Development of flexibility
Swimming techniques involve many elements: strokes, flips, dives, etc. All this has a beneficial effect on the flexibility of the body - muscle elasticity and stretching improve.
Do not forget that before training you need to warm up. This will reduce the likelihood of injury during the swim.
Strengthens joints and spine
Another benefit of swimming is strengthening the joints and spinal column. All professional swimmers have a beautiful, sculpted body, and a strong back is the key to a healthy spine.
During training in the pool, the body does not experience shock loads, and the back muscles are actively involved. Due to this, posture is corrected, the spine, joints and ligaments are strengthened.
Stress relief
Swimming, like any sport, helps to take your mind off everyday problems and improve your psychological state. Scientific studies in various countries confirm this fact - people report feeling better after swimming, relieving tension and anxiety.
Coordination and mobility
Correct execution of the technique requires coordinated work of the whole body: limbs, muscle groups, respiratory system. For this reason, swimming can be called a good coordination training, and if you add to it verbal calculation of the number of strokes and breaths, you can develop cognitive abilities well.
Recovery from injuries
Water activities can be used as an alternative to training during recovery. In the postoperative periods, swimming can be the first step in returning to exercise.
There is no shock load, so you can swim even with minor dislocations and bruises.
Activities for people with serious illnesses
There is a special type of water activities - recreational. Limited mobility, arthritis, arthrosis, problems with the spine - in all these cases, exercise in the pool can help cope with the disease or relieve pain.
It is recommended to visit a doctor before starting classes, who will approve your desire to engage in recreational swimming. It is also recommended to train under the supervision of a personal trainer.
Detailed description
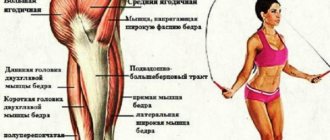
The most important groups that are involved in freestyle swimming were indicated above.
However, in addition to them, many other elements of our muscular system also work, as is clearly visible in this animation:
Torso
The muscles involved in the front of the torso are:
- chest,
- anterior serratus,
- external oblique, as well as rectus abdominis muscle.
Chest Serratus anterior external oblique (abdomen) Rectus abdominis
The following muscles work in the back of the torso:
- Trapezoidal;
- Latissimus dorsi muscle;
- Large and small round;
- Large and small diamond-shaped;
- The erector spinae muscle.
Trapezius Latissimus dorsi Numbers 5 and 6 – teres major and minor: pull and rotate the arm Rhomboids major and minor
Shoulders and arms
Here we are involved:
- Deltoid;
- Shoulder rotators (Rotator cuff);
- Brachioradialis muscle;
- Biceps;
- Triceps;
- Muscles of the palm (thenar - eminence of the thumb, deep flexor of the fingers).
Delta: left - rear view, right - front view Brachioradialis Biceps (front of the arm) and triceps (behind the arm)
Neck
Due to the specific nature of breathing in the crawl, the neck is also involved (the full name of the working part is the sternocleidomastoid muscle):
Pelvis
Here we primarily work the gluteus maximus muscle:
Legs
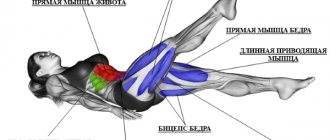
In crawl swimming, the main load is on the thigh, but in general all the muscles of the leg work:
- Quadriceps;
- Hamstring muscles;
- Adductor magnus muscle of the thigh;
- Gastrocnemius;
- Anterior tibial;
- Foot muscles;
- Flexor digitorum brevis.
Hip structure
How many calories does swimming burn?
Cardio training is considered the best workout for weight loss. The fat burning process begins 20-25 minutes after monotonous exercise, and swimming just involves prolonged physical activity with moderate intensity. While running, for example, a person experiences many irritants and distractions - sweat, sun, shock loads on the feet. Swimming does not have such disadvantages, and fatigue during training will come much later than during running.
The process of losing weight when exercising in water depends on the anthropometric data of a person. A person weighing about 70 kg will spend 400 calories per hour of moderate intensity training. If you try hard and increase the pace, you can burn up to 750 calories per session.
If we compare swimming with other low-intensity cardio exercises, we get the following picture:
- Elliptical – up to 370 calories per hour;
- Walking – up to 300 calories;
- Yoga – up to 200 calories.
Read more in the article How many calories does running burn?
It turns out that swimming wins noticeably. And if you consider that when exercising in water, a person not only loses calories, but also pumps up many muscle groups, the choice becomes even more obvious.
Movement technique
The back crawl technique consists of the following elements:
- the body is in a horizontal position and elongated. In the process of swinging your arms, your shoulders make slight turns;
- the head is always motionless, the gaze is directed upward;
- legs are straight, slightly bent at the knee and make scissor-type movements;
- arms are straightened, moving above the water in a “semicircle” trajectory.
For a better understanding, let's study each point separately.
Body position
To make it easier to maintain a straight and high body position, your gaze is always directed upward. Also keep your stomach pulled in - this allows you to create the desired arch in your back. While moving, the body makes turns, due to which the speed of movement increases.
Please note that the swimmer must glide through the water. To do this, the legs should not be bent at the hip joint.
How to hold your head
After you have assumed a horizontal body position, you should check your head and neck.
Relax your muscles, achieve a horizontal position of your head so that your ears are submerged under the water and the water line runs in the middle of your cheek. Lift your chin up. You can experiment with this by raising it higher or lower. 3-5 centimeters will be enough.
You should not turn your head from side to side - this can cause you to lose your balance and correct body position.
Hand movement
In backstroke swimming, the arms act as the main engine, so proper movement technique is the key to speed. The cycle performed by hand consists of 4 phases:
- Influx. The palm is tightly closed, the hand is immersed, starting with the little finger, and turns in the water perpendicular to the body.
- The main element is the elbow turns back and down, the arm straightens at the hip.
- Exit from the water. The hand is quickly raised with the little finger up. At this moment, the body turns, following the shoulder.
- The carry is carried out with a completely straight hand at an angle of 180 degrees above the water.
It is necessary to work out the cycle until it is fully automatic.
Leg movement
Let's study in detail the technique of leg movement. She must comply with the following rules:
- The legs move alternately, the strongest blow occurs when the leg moves from bottom to top. At this moment she fully unbends.
- When moving the limb from top to bottom, it is almost completely relaxed and straight.
- The leg bends when it is below the body.
From the outside it may seem that your legs help push water out. But in fact, by performing this cycle, they help push the body out of the water, after which it glides along the surface thanks to powerful arm movements.
The benefits and harms of swimming in the pool
You can swim both in open water and in a pool. In large cities you can find several good swimming complexes for training. What are the benefits of swimming in a pool?
- Improvement of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Swimming improves the functioning of the heart muscle, has a beneficial effect on blood circulation and normalizes blood pressure. The volume of the lungs increases, the diaphragm and chest are pumped;
- Improved muscle and respiratory endurance. Swimmers are some of the toughest athletes. It will not be difficult for them to immediately run several kilometers, and at the end of the distance you may not even notice signs of fatigue on their face;
- Strengthening the skeleton and bones. In water, the load on joints is much less than when playing other sports. Buoyancy supports body weight and reduces the force of gravity. Swimming is often used as a preventive measure for diseases associated with the musculoskeletal system;
- Losing weight. As mentioned above, swimming is a good way to lose weight. In an hour you can burn from 400 to 900 calories, depending on the style and intensity of the workout;
- Improved sleep. The US National Sleep Foundation conducted a study, the results of which show that water procedures directly affect the quality of sleep. Those who visited the pool are 2 times more likely to report sound sleep and have almost no insomnia or sleep paralysis;
- Increased mood. During exercise in water, happiness hormones are produced - endorphin and serotonin;
However, despite all the advantages, swimming in a pool can be harmful to the human body.
- Infections. The public swimming pool is visited by many people every day. Most pools require certificates to enter, so choose a swimming place with verified certificates and good reviews.
You need to make sure that the place where you will go will only benefit your body.
Breathing function
During crawl swimming, breathing is performed while overcoming the following difficulties:
- exhale through your nose into the water;
- short inhalation time;
- water pressure on the chest.
As a result of this, crawl swimming, in addition to the above parts of the body, also pumps our respiratory system :
- the respiratory function of the lungs is being worked out ;
- the ability to consume oxygen improves .
How to choose a place to swim
Almost every city has several large water sports complexes. Some are used by professional athletes, while others are available for public visitation and use. There are also swimming pools on university campuses and in some schools.
Some tips to help you choose a place to swim:
- Find out about all the available public swimming spots in the city. Compare prices, read reviews;
- Pay attention to sanitary and epidemiological standards - most swimming pools should require a certificate from a doctor stating that the person does not have skin or other diseases;
- If you are going to swim short distances, a 25 meter pool will be enough. If you want to practice professionally, you will need a 50-meter pool;
- Sign up for trial lessons at a few pools you like. Evaluate the interior, water quality, cleanliness of showers and locker rooms;
- If you want to work out with a trainer, call ahead or visit the gym's website to see if they offer personal trainer services. Swimming can also be done in groups.
Swimming is one of the most accessible sports: it does not require special physical training or expensive equipment. Almost anyone can learn to swim. All you need is desire and free time.
In addition to pleasure, swimming improves health, relieves stress and tension and improves mood. By combining business with pleasure, you can simultaneously pump up your muscles, lose weight and become more resilient.
The cardiovascular system
Swimming by its nature is an aerobic exercise, and the advantage of the crawl is that:
- here the legs work non-stop, on which very large muscles are located, constantly consuming oxygen and energy;
- the shoulder body and arms also make constant cyclic movements over a wide amplitude.
Thanks to this, perhaps, of all the swimming methods , crawl can probably be called the most aerobic - the mechanics of its movements are such that there is a constant, cyclical and significant consumption of oxygen, which provides a corresponding load for the heart.
At the same time, it is important to monitor your pulse so that it does not go beyond acceptable limits, otherwise such training will not be beneficial, but harmful.
More information about what the pulse should be can be seen in this video:
Read also
- Can walking be considered a sport? Does it help you lose weight? How many kilometers a day should you walk?
- How much do tennis lessons cost? How much will it cost to rent a court and use a coach? How to choose a racket?
- What is canicross? What dog breeds are best for competitions? What do you need to get started?
- What is crossfit: history of origin and who is this sport suitable for?
- The benefits of cycling - losing weight and developing muscle strength
- Nordic walking is very useful. We talk about the correct technique and how to choose poles for Nordic walking
- Workout: what is it and how to start doing it? What exercises are suitable for a beginner?
- Zorbing: what kind of entertainment is it, who is it suitable for and how to prepare for it
- Windsurfing for beginners - answers to questions about riding a board with a sail
- Bungee or bungee jumping. Is it sport or entertainment? How is it different from rope jumping?
Common Mistakes
Let's look at common mistakes that prevent you from learning to swim on your back.
- Incorrect body position, which causes the pelvis to sink too low. Most often this happens due to excessive flexion at the hip joint, which causes the pelvis to sink deeper. In order for the body to take on a streamlined shape, we stretch out horizontally and “lie down” on the water.
- The body loses balance and drowns if the work of the arms stops. To prevent this from happening, practice the technique of leg movement: feet straight, toes pointing inward, ankle mobile.
- When working with your hands, water gets on your face - this problem occurs if the hand does not move in a straight line and enters the water incorrectly. Remember: hand immersion begins with the little finger.
- The swimmer's movement is too slow. Most often the reason is a lack of core work. Add more spins when swimming.
There is one "but"
Even a 5 kilogram dumbbell can work wonders for a beginner! This is because even this load will be unusual for the muscles and will create microdamages. This trick won't work with a professional athlete: the muscles won't grow without a bet on growth.
The conclusion is simple: if you decide to take up swimming from scratch and have no training experience behind you, you will see the result in the form of increased muscle mass. There will be an effect, but you can improve the situation only if you start going to the gym and increase the load or... And we’ll tell you about “or” now.
Why do muscles grow after strength training?
In general terms, the whole process looks like this. You take a good weight, press, your muscles experience overload, microdamages appear in the muscle tissue. During the recovery phase, your body begins to patch up holes, starting the regeneration process. Muscle tissue gains volume to withstand increasing loads.
The result is an increase in lean muscle mass, the growth of which was caused by its damage. Well, the cause of damage is critical loads .