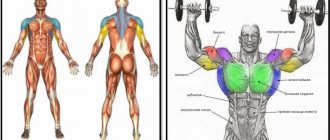
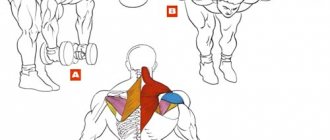
When increasing the volume of different muscles, special attention should be paid to the shoulder girdle. There are many exercises designed to pump it up. When exercising on machines, people forget about the basic movement, which has been proven effective by more than one generation of athletes. It's about lifting dumbbells overhead. This is a basic movement that promotes both mass and endurance in the shoulder girdle. By using it in your program, you will get the wide, rounded shoulders that people crave in gyms.
We recommend reading: Program for gaining muscle mass 3 times a week in the gym
Correct technique and exercise variations
The exercise can be performed both sitting and standing. But in both cases, movements should be smooth, without jerking. Do not straighten your elbows all the way so that the main load goes to your shoulders and not to your triceps. Keep your back straight.
Sitting
This option is safer, since the spine is supported by the back of the bench. But the back must be vertical (90 degree angle). When you bend back, the load goes to the upper chest muscles and begins to resemble a chest exercise - an incline bench press.
Our goal is deltas, so keep your body vertical.
- Starting position (i.p.) – dumbbells slightly above the shoulders, palms facing forward and elbows to the sides. The back is pressed against the bench, and the legs rest on the floor.
- As you exhale, press the projectiles upward.
- As you inhale, lower the projectiles to IP.
standing
- Take dumbbells and lift them up to your ears (elbow angle is about 90 degrees). Palms face forward and elbows to the sides. Feet shoulder width apart. The abs are tense, the pelvis is slightly pulled back so that a slight deflection forms in the lower back.
- As you exhale, lift the weights up and hold for a couple of seconds, feeling maximum muscle tension. In the top position, the projectiles should not hit each other.
- As you inhale, slowly lower the dumbbells towards your ears.
- Do all repetitions in the same way.
Squat with press
This option allows you to comprehensively work out the main part of the body. Well suited for experienced athletes to diversify their workouts. After all, if you do the same exercises for a long time, the muscles get used to the load and begin to grow poorly.
For beginners, a squat with a bench press will be difficult to perform, since in addition to the movement of the arms, you also need to coordinate the movements of the legs and body.
- The starting position is the same as for a standing press, only the elbows point forward and the hands hold the dumbbells with a neutral grip.
- Moving your pelvis back and bending your knees, gently squat until your thighs are parallel to the floor or slightly lower. At the same time, make sure that your knees do not move forward further than your toes.
- Then stand up and lift the weights above your head.
All these options can be performed not only with dumbbells, but also with kettlebells. Just perform the exercise with even greater caution due to the shift in the center of gravity of the weights.
Morning exercises with dumbbells for children
Doing morning exercises is recommended for everyone without exception. This process will tone your muscles after sleep, cheer you up and fill your body with energy for the whole coming day. Often, exercise is also actively used as a preliminary workout to strengthen the muscular system. This is why, in addition to classic gymnastic and warm-up exercises, strength complexes using dumbbells are also introduced into the charging process. All this is true for both adults and children. This issue is especially relevant for those who seek not only to strengthen their body, but also to achieve initial preparation for playing sports at a professional level. However, it is important not to overdo it in this matter. Otherwise, such charging may cause more negative consequences than positive results. First of all, you need to pay attention to the working weights. You shouldn’t dramatically increase the weight of dumbbells or start right away with equipment that is large by children’s standards. For the first classes, a pair of dumbbells of half a kilogram each is enough.
Example workout
The shoulder joint is easily damaged, so warm up for 12-15 minutes before training. Also, before each exercise, do a warm-up approach with a weight of 0.5-0.7 of the working weight.
At home
- Dumbbell press sitting or standing - 3 sets of 12 repetitions.
- Dumbbell rows to the chin – 3 to 12.
- Bent-over dumbbell raises – 3 to 12.
In the gym
- Barbell press – 3 sets of 12.
- Pulldown to the chin on the lower block – 3 x 12 repetitions.
- Lateral arm raises in the crossover simulator – 3 to 12.
- Finish your workout with breathing exercises and deltoid stretches.
What muscles work
A basic exercise involves working several muscles when performing it. Along with the bench press and squat, this exercise targets 3 additional muscle groups , thereby giving that mass gain that everyone is talking about. When performing this movement, the anterior and middle bundle of deltoid muscles are included in the work; as mentioned above, this is not the only muscle group that is involved during the execution. In addition to the shoulders, the triceps, trapezius muscles and stabilizer muscles are involved.
Tips for implementation
Sets and reps
To develop endurance, perform 4-5 sets of 20-25 repetitions.
To increase muscle volume, do 3 sets of 8-12 repetitions, and to develop strength, do 3 sets of 6-9 repetitions.
I recommend that women train their endurance so as not to hypertrophy their shoulders. It’s better for men to do weight training to increase the width and volume of their shoulders.
Dumbbell weight
The shoulder joint can be easily injured when using heavy weights or using incorrect technique. Therefore, take a weight with which you can do all the repetitions in the set without distorting the correct trajectory of movements.
Equipment
Use bandages or wristbands to secure your hands. To prevent the projectiles from slipping off your hands, wear gloves.
When doing the standing press, it is advisable to use an athletic belt to avoid damaging your lower back.
Why overhead press?
The overhead press is renowned for its profound impact on strength and its apparent simplicity. You just need to lift the barbell or its closest relatives - weights or dumbbells - above your head until your arms are completely straightened.
This is how the bench press can be described in a nutshell, and the pleasant fruit of hard work will be the unsurpassed development of the shoulder girdle and upper back.
Of course, the strength development of the standing overhead press extends far beyond the shoulders and arms. Whole body involvement increases full body strength. The standing overhead press strengthens the abdominal wall and pelvic muscles and improves leg stability.
But we can't forget the main target: shoulders, upper back and triceps. Search through the mountains of information, and you will not find another exercise that develops the shoulders and upper back as successfully as the overhead press.
The overhead press is very simple to describe, but in fact it is a fairly complex press that needs to be approached with understanding, training and honing the technique. Here's how to do it.
Common mistakes
- No warm-up
The muscles and joints are not prepared for hard work, which will sooner or later lead to injury.
- Performing a one-arm press
The spine is overloaded, which can lead to injury.
- Improper breathing
Don't hold your breath. Muscles need a constant supply of oxygen.
Raise the weight as you exhale and lower it as you inhale. If you breathe in reverse, intra-abdominal pressure will increase (leading to hernias), and the muscles will not be able to contract properly.
- Snatches, cheating, walking elbows and back
Elbows should move strictly in a vertical plane. Walking elbows reduce the effectiveness of the exercise and increase the risk of injury.
Keep your body vertical so as not to overload your spine. There is a little secret to keep your back straight. You need to look forward or even a little up. If the body is rocking back and forth, reduce the weight of the projectile.
- Overtraining
The deltoids work not only on the day of shoulder training, but also on the day of chest training. Therefore, they can easily be overtrained and damaged. In order for deltas to grow, you need to give them proper rest.
Finally, watch these videos to fully understand the exercise.
Next steps.
So where do we go next? If you pass all tests, you are fully qualified to perform the overhead press. If you pass the scapular tests but fail the overhead raise test, you can lift dumbbells or kettlebells in other positions—such as on one or two knees—until you improve. We'll talk about these options a little later.
If you fail the scapular tests, you lack the mobility to safely perform the overhead press. Perform overhead presses with kettlebells and dumbbells and incorporate stretching into your workout routine.
Tags
Exercises Variations of the exercise varyThen the exercise is appliedperform exercises on this exercise.This exercise is performedThis exercise is performed Exercises forperform the exercise technicallyin the exercise on and chest muscles.pectoral muscles.pectoral muscles.muscle strength. Shoulders and upper arms. volume of the shoulders and shoulder muscles should to the shoulders correct shoulder muscles and for the shoulders. and the shoulders remain to the shoulders by taking in the shoulder and removing the stomach Women's fitness
bicepsprogramsarticlemediumnutritionbodybodybuildingfitnessnoncommentarytrapezeweightlosspump up
Video
Let's look at the correct technique for performing the exercise:
Fitness trainer, group exercise instructor, nutritionist
Provides general consultations on nutrition, selection of a diet for pregnant women, weight correction, selection of nutrition for exhaustion, selection of nutrition for obesity, selection of an individual diet and therapeutic nutrition. Also specializes in modern methods of functional testing in sports; athlete recovery.
On the calendar 29
April, which means that today we have a technical note and we’ll talk about lifting dumbbells in front of you. After reading, you will learn what benefits lifts offer and how to perform them correctly, we will also get acquainted with some practical information regarding the injury risk of shoulder exercises and the degree to which they are better.
Please everyone sit down, we are starting.
Standing or sitting.
Although the movement itself is largely independent of whether you are sitting or standing, there are significant differences between variations of the exercise. The standing barbell press is more effective at developing full-body strength than the seated bench press because it requires more trunk stability and tension in the legs and glutes.
The seated press does not require such balancing because the body is stabilized by the support of the bench. However, in the seated press, as a rule, you can lift a little more weight due to the stability that the back support provides.
Safe transition to the barbell press.
Most of you have experience with standing overhead presses. However, if you are just becoming familiar with this exercise, start with simplified versions, such as dumbbell or kettlebell presses while standing on two knees or on one knee.
When you feel that you have mastered them perfectly, lift dumbbells and kettlebells while standing. Once you have learned to perform these variations with absolute confidence, grab the barbell.
Start with light weights and focus on technique. At first, leave 5 reps in each set and focus completely on each lift.
For example, if you choose a weight that you can do 10 technical reps with, do no more than five. If you feel your back arch during the press, or you can't complete the rep with your hands in the same plane as your ears, the load is too high.
Read also: Simple training for deltoids.
Progress by adding 2.5 kg per week to the bar. Your body will adapt to such an increase without risk. Aim for a total of 15-25 repetitions. This number is the sum of repetitions in all working approaches.
Muscle atlas
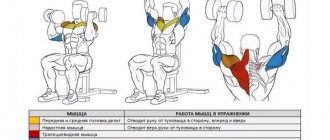
In different variations, the standing military dumbbell press can engage a huge number of small muscle groups.
| Muscle group | Load | Types of exercises |
| Extensor arm triceps | Significant accent | Standing Dumbbell Press, Military Press, Shung Press, Standing Arnold Press |
| Lateral head of triceps | Slight emphasis | Standing dumbbell press, military press |
| Wrist muscles | Static loading | Standing Dumbbell Press, Military Press, Shung Press, Standing Arnold Press |
| Upper delta | Dynamic basis | Standing Dumbbell Press, Military Press, Shung Press |
| Anterior delta | Slight emphasis | Arnold Press |
| Collar | Basic load | Arnold Press |
| Upper bundle of pectoral muscles | Slight emphasis | Army press |
| Muscles of the lumbar region | Stabilizing load | Standing Dumbbell Press, Military Press, Shung Press, Standing Arnold Press |
| Thigh muscles | Blasting load | Shung press |
| Quadriceps | Blasting load | Shung press |
In its basic variation, this exercise primarily involves:
- Upper deltas.
- Triceps.
- Lumbar region.
As can be seen from the muscle atlas, this exercise is multi-joint, but its load is not enough to generally shock the body and increase the level of anabolism. That is why it is included in split programs, and not added to the classic “press-dead-squat” trio. At the same time, if we are talking about functional lifting strength and impact force, then a better exercise than the dumbbell upward press has not yet been invented.
How to intelligently build a microcycle for the development of deltas
If you already have a couple of years of training experience, but your deltoids are still lagging behind in development, here is a basic scheme on how to cheer them up. She personally helped me a lot.
Four-day split:
- Monday: legs (3-4 exercises).
- Tuesday: pectoral (2-3 exercises) + anterior delta (1-2 exercises - military press or dumbbell press, lifting dumbbells in front of you with a hammer grip).
- Wednesday: rest.
- Thursday: back (3-4 basic exercises) + rear delta 1 exercise (any of your choice from the above).
- Friday: triceps (two exercises) + biceps (1-2 exercises, after all, when working on the back it was already loaded) + middle delta (2 exercises - barbell rows to the chin, dumbbell swings to the sides).
The meaning, I think, is clear - together with the pectoral muscles, the anterior delta is well loaded and it is enough to finish it off with 1-2 exercises. The rear delta is loaded along with the back, and one exercise at the end is enough to finish it off. Plus a couple of exercises for the middle delta on arm day.
Three day split
If you don't have the time or desire to do four strength training sessions a week, then add one basic triceps exercise to your chest day. For example, close grip bench press or French press. On your back day, add one or two biceps exercises (PSB and/or dumbbell biceps curls while sitting on an incline bench). On leg day, after training your lower body, do middle deltoid exercises (barbell rows and standing dumbbell swings).
A specialized version of the microcycle with an emphasis on the upper body
I practiced this option for four months from October last year to January of this year inclusive. The idea is to visually increase your upper body without having to add much muscle mass. To do this, we make the back more lumpy (emphasis on training its inner part), prominent trapezius, more powerful deltoids, plus pecs.
Excellent specialization is obtained if the desired muscle group is trained a couple of times a week. In my case, I did four strength training sessions a week, during which I worked separately on the thickness (bulge) and width of the back, hammered the deltoids a couple of times and the pecs a couple of times. The exercises below are just an example, you can use any of your choice. Two or three warm-up approaches, two working sets.
Monday (pectorals + trapezius + deltoids):
- Two chest pressing exercises for 10-12 reps (for example, bench press, 30° dumbbell press, or hummer press).
- Shrugs with dumbbells or barbell (15-20 reps) + T-row with emphasis on the chest or lever row (10-12 reps).
- Military press or standing dumbbell press.
- Row in the cable handle block to the chest.
Tuesday (Legs + Abs):
- 3-4 leg exercises to pump up all muscles (barbell squats, leg extensions, deadlifts, platform presses, lunges - 8-12 reps) + lower leg (20-25 reps).
- Ab crunches and reverse crunches (20-25 reps, 3-4 sets).
- Neck (so as not to be skinny against the background of broad shoulders) - raising the head with a pancake on the forehead and/or on the back of the head.
Thursday (back width + deltoids):
- Three or four favorite exercises for the width of the back (pull-ups, rows in a hammer or barbell/dumbbells, rows of a vertical block to the chest, pullover, etc. - 10-12 repetitions).
- Pull the barbell to the chin and swing dumbbells to the sides (10-12 repetitions, swings can be done for 12-15 repetitions).
Friday (arms + chest for tone):
- One rigorous basic chest exercise for three working sets of 12-15 reps. In my case, these were chest dips with a weight on the belt.
- A couple of basic biceps exercises (for example, PSB, seated dumbbell curls) + a couple of basic triceps movements (close-grip press, French press, cable extensions, etc.) for 10-12 repetitions.
Supersets
A superset is when an athlete performs two muscle exercises in a row without rest. Examples of antagonist muscles are the biceps and triceps: the first flexes the arm at the elbow joint, and the second extends it. The pectoral muscles push the arms, and the latissimus dorsi muscles pull them.
Technically, doing a superset is easy: you just need to combine two exercises into one and perform it without rest. When one super series comes to an end, you need to take a short break and then start a new super series.
Examples:
- After performing the biceps curl, you can immediately begin performing arm extensions on the block. This is an example of a superset on antagonist muscles.
- After bench press, you need to immediately start lifting the dumbbells while lying down. This is an example of working the same muscle group.
When you perform multiple supersets on one muscle system, your arm muscles will increase in volume and become stronger.
This will be observed only at first; soon they will decrease to the previous volume that was before they were pumped.
Why use supersets
The main reasons for using supersets in training:
Muscles recover more quickly during exercise. This happens because in a superset all antagonist muscles are activated. Scientists believe that when a tired muscle receives a small load, it recovers faster. More active supply of muscles with nutrients. In the process of stopping the load, blood begins to move away from the muscle, and with it oxygen and nutrients. But with the assistance of this moment, the blood continues to actively supply nutrients. Supersets are a great way to make changes to your training routine. They also help save time
Their presence is especially important when you do not have a lot of time and you intend to conduct classes quickly but effectively
How to properly use supersets in training
When performing a superset, you don’t need to chase weight. In any workout, you can choose a weight that will help you technically complete all repetitions and approaches. Volumetric training will provide your muscle mass with new growth stimulation and force you to adapt in a new way. It is not recommended to do supersets frequently.
They won't work well. For one muscle group, you can perform a superset once a week or once every two weeks. You and your muscle mass need to have a period of time to recover, as increasing the intensity of your training using these methods will place significant stress on your muscles and nervous system.
In training, supersets can also be used at the stage when you are trying to lose weight, burn excess fat, as well as during the stage of gaining muscle mass and increasing strength. When cutting, you need to force the body to burn more calories than it takes in. An important element in this is diet and training.
Including supersets in your workout program will help you use energy efficiently, as you will train more productively, without pauses. Between exercises in a superset you need to take breaks and rest.
A classic superset is an option without rest between exercises. But you should still take short breaks of 30 seconds. This is necessary because during rest the muscles have time to recover. This increases the effectiveness of the workout.
Before exercising in a superset, you need to do warm-ups lasting ten minutes. It consists of classes with light weights, and also includes rotations of the body and arms, as well as other movements to warm up.
In conclusion, I would like to give some useful tips aimed at achieving maximum results without exhausting the body:
- Training should take place according to the described system. It is not recommended to exercise to failure. The selected working weights should be such that the athlete is able to perform 1-2 more repetitions to the optimal number within the session.
- Supersets are used to increase the effectiveness of the result. It should be noted that they are very energy depleting. Therefore, it is recommended to take energy drinks and isotonic drinks during classes.
- After training you need recovery. It is necessary to take a protein shake to replenish the nutrients in the body.
- You should exercise regularly. In addition to training, nutrition should be regular and balanced.
By performing various of the above exercises and following useful recommendations, you will achieve the desired result without overload and other negative consequences.