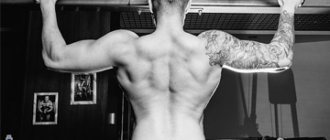
The back is truly important in training, but few bodybuilders give it the attention it requires. Effectively pumping up muscles in this area is the goal of every successful athlete!
Only an experienced athlete can pump up a wide back, because this muscle group is very difficult to work out, so for an excellent result you will need all your skill and a lot of patience. If you have set yourself the goal of acquiring a truly pumped-up wide back, exercises need to be selected carefully and wisely.
No compromises, just work and more work!
The back includes some of the largest muscles in the upper body from the lumbar region to the trapezius muscles (more on the anatomy of the back muscles in the guide to how to build a stronger back). It's involved in virtually every movement we make, from stabilizing the core during the bench press to supporting the barbell during the squat.
You see how important it is to train your back, are you ready to train? If you are already in the gym and ready to start, we recommend 2 programs from our training videos.
Further in the article you will find several more program options.
The first training option is about how to pump up your back. In this video you will learn how to pump up your back, what exercises to do to pump up your latissimus dorsi muscles.
- Lying latissimus dorsi stretch
- Chest row on the upper block, 3x8
- Pull-ups with deviation, 3x8
- Reverse grip lat pull-down, 3x8
- Wide-grip lat pulldown, 3x8
In the next video you will learn the second training option for the back muscles.
Feel free to ask your questions about how to build back muscles in the comments. Our goal is to help you achieve better results in your training.
- Lower back stretch with lunge and twist, 2x5
- Standing mid-back stretch (with body rotation), 2x5
- Rows to the waist on the simulator in support, 3x8
- Pullover on block, 3x8
- Bent-over barbell row, 3x8
- Shrugs with dumbbells, 3x8
Not everyone can boast of a wide, pumped-up back, and this is another argument in favor of the fact that its development deserves special attention. Many athletes do countless sets of chest training, but forget to put equal effort into building a broad back.
Probably one of the reasons is that it is difficult to see your back when standing in front of a mirror. Why train what you can't see, right?
There are so many men in the gym with big pecs, biceps and quads, but few who can show off a wide back, neck or triceps pumped up to the size of powerful horseshoes. Their rounded shoulders project forward because the pectoral muscles push the deltoids forward, giving them a concave appearance.
This means that the back was not trained enough and/or correctly to pull the shoulders back and create a proportionate appearance. The key to this is balance. You must create such a balance of mass and strength to achieve an impressive, muscular, strong and harmonious body. Balance will improve your entire body and help you avoid looking like a “jock” from the outside.
How to create an outstanding back? The presented exercises and workouts are specially selected in such a way as to get the most out of every trip to the gym and build up a broad back for you. Always pay attention to your technique and do not use too much weight for your safety.
Exercises for back width
Wide and narrow grip pull-ups
For the wide grip variation, use a grip wider than shoulder width. Begin the exercise by slightly bending your elbows and pulling them toward your chest, focusing on squeezing your shoulder blades together behind you. Arch your back and contract your muscles, then return to the starting position with your elbows slightly bent again.
This will develop sought-after width and range in the upper back muscles.
Weighted pull-ups
In the narrow grip version, either grab the bar with a parallel grip narrower than shoulder width, approximately six 15 cm between your palms. Pull up as if with a wide grip, and lower down until your hands lock out. This exercise aims to strengthen the lower back muscles and create thickening near the lumbar region, which will help create a visually wider back.
If you have difficulty doing this exercise, there is one good trick. Pick a total number of reps, such as 40, and try to reach that number no matter how many sets you need. You can do 10 reps on the first set, 8 on the second, and 7 on the third. Continue until you have completed 40 repetitions. When you can do 3-4 sets of 10 or 15 reps each, increase your total reps to 50 or more.
Consider other pull-up variations as well.
Rocky Pull-Ups
Grasp the bar with a straight wide grip, bending at the waist. As you exhale, pull your torso up until the bar touches your sternum. Lower yourself and repeat the exercise, only now the bar should go behind your neck.
Rocky Pull-Ups
One arm pull-ups
Drape a rolled towel over the bar. With one hand, grab the horizontal bar with your palm facing you, and with the other hand, grab the towel. Tilt your body back about 30 degrees. As you exhale, pull yourself up until your chest touches the bar. Pause and lower yourself slowly. Switch hands.
One arm pull-ups
Wide grip pull-ups
Grab the bar with a wide grip, palms facing forward. As you exhale, pull your body up until your neck touches the bar. As you inhale, slowly lower yourself to the starting position.
Wide grip pull-ups
Barbell row
These machines help build mass for overall muscle density, working toward our goal of a toned, broad back. To lift the barbell, hold the bar shoulder-width apart. Bend over, keeping your back in line with your hips and parallel to the floor, transfer your weight to your stomach and contract your muscles. Slowly lower the bar and repeat.
Bent-over barbell row
If you experience discomfort when lifting the barbell, attach a wide handle to the cable of the lower pulley and pull it instead of the barbell, holding it with a shoulder-width (or slightly wider) grip.
T-bar row
When lifting a T-bar, follow the same rules, but be careful not to drop the weight or arch your back. Keep your back straight and let your back muscles do the work, not your lumbar region.
T-bar row
If you lack mass in your upper back, try doing barbell curls with a wider grip and pull the weight toward your lower chest. In this case, you will have to reduce the weight in order to perform this wide back exercise correctly without getting injured.
Belt row on the block
To really gain mass in your lower back muscles (if you're interested in a wider back, of course), try one of these exercises.
To perform the pulley lift exercise, take your starting position: sit and tilt your upper body forward, knees slightly bent. At the same time, pull the handle and straighten your body perpendicular to the floor. Squeeze your shoulder blades together and pull the handle towards your abdominal muscles. Return to starting position and repeat.
Belt row on the block
Belt row on the machine
An undeniable advantage of rowing in the simulator is that you can work each side separately. Use the principles above and make sure to contract the muscles as you return to the starting position.
Belt row on the machine
Parallel and wide grip rows
For a wide-grip row, grab the bar with an overhand grip and lower it to your upper chest. Return the bar to the starting position, controlling the weight with your shoulders and keeping your elbows slightly bent. In terms of pumping quality, this exercise perfectly replaces pull-ups, creating the desired volume and width of the back.
Wide-grip lat pulldown
Pulldown of the upper block (pullover)
Nothing works the teres muscle better than parallel grip rows.
Pulldown of the upper block (pullover)
Grab the bar with a grip slightly wider than shoulder-width and bend your elbows slightly. Lower the bar to the middle of your chest and contract your muscles. Return to the starting position, feeling the weight force your back muscles to work upward and outward.
When performing any downward pull, try to return the shoulder girdle to its original position. Drop your shoulders back slightly and arch your chest forward. This will allow you to fully engage your back muscles.
Dynamic stretching of the back muscles
To stretch your back muscles, stand in front of a back row machine (or other machine with a cable running overhead). Take the bar with a shoulder-width grip and hold it at approximately eye level, tensing your back muscles. This is the starting position.
Dynamic stretching of the back muscles
With straight arms, lower the weight to your hips and contract your back muscles. Return the bar to the starting position and repeat. Variations of this exercise can be used as a warm-up before working the entire back. Three quick sets of moderate reps will do the trick.
Deadlift
The ancestor of all back exercises is the deadlift. A healthy, strong, wide back loves this exercise.
Deadlifts are essential for overall core strength from head to toe, but deadlifts are especially beneficial for your back. Place the weight on the bar on the ground and take a shoulder-width grip with your knees bent, keeping your back straight.
Overhand grip deadlift
Lift the weight off the ground using your legs first, and then begin to straighten your back until you stand completely straight. Return the bar to the ground, performing the movements in reverse order.
If you have trouble deadlifting from the floor, try partial deadlifts. It is distinguished from the usual deadlift by its starting position: here the barbell begins to move not from the floor, but from the level of the athlete’s knees, for example, in a power rack or from a bench. Set the bar at this level and then simply follow normal lifting principles. This will relieve your back a little if you are tall or want to engage your leg muscles in the exercise.
For beginners, we recommend the option with a trap bar
Deadlift with trap bar
Why you need to strengthen your back muscles
The back muscles are responsible for the health of the spine, its correct position, and, therefore, affects the overall health. When performing special gymnastics, the prevention and treatment of pathologies is carried out, the result will be the disappearance of pain and discomfort.
The aesthetic perception of a strong and sculpted back is also important. Those with an even posture, graceful gait and squared shoulders attract the attention of the opposite sex and give the impression of a successful person.
Strengthening your back is also important because:
- The muscular frame allows you to bend, twist, and bend.
- When support weakens, osteochondrosis develops, and the intervertebral discs undergo degenerative changes.
- Thanks to strong back muscles, metabolism and energy improves. An oxygenated body is less susceptible to fatigue.
- Trained muscles alleviate the increased load on the spine associated with upright walking.
- If the muscular frame of the back is weak, then the intervertebral discs experience increased pressure and lose elasticity. The joints in the spinal column wear out faster, wear out and become covered with growths.
Exercises to strengthen the spinal muscles make the spine resistant to stress and serve as a prevention of degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs.
With poorly developed muscles, the condition is aggravated by congenital or acquired curvature of the spine. Excess weight, abdominal weakness, and spinal injuries have a negative impact.
If back pain is already present, then consult your doctor about performing strengthening and stretching exercises; it is important to establish a diagnosis and determine the permissible load.
For pain caused by muscle weakness, rest is prescribed, but due to lack of movement, the muscles will weaken even more. Therefore, light physical exercise is acceptable, but with a gradual increase in load.
Gymnastics at home helps prevent pain and spinal injuries.
Upper back training program
Pull-ups
- a total of 30-40 repetitions
- Body Part: Lat Equipment: Bodyweight
Bent-over barbell row
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body Part: Press Equipment: Barbell
Pull-down of the upper block behind the head
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body part: Lat Equipment: Block
Quick box squats using expanders
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body part: Quadriceps Equipment: Barbell
Add to Calendar * Add to My Workouts * Print Workout
* — The service is in beta testing
Survey
The lateral part of the latissimus muscle forms the dorsal border of the axilla. When the arm is adducted with force, it contracts. The latissimus muscle attaches anterior to the tuberosity of the humerus. To improve visualization of the latissimus muscle relative to the torso, the patient can be asked to flex the arm approximately 90 degrees and hold it in this position against pressure applied from below. Doctors may palpate for muscle contractions by pinching the posterior axillary fold between the index finger and thumb and asking the patient to cough.
Training program for muscle growth
Smith Machine Bent Over Row
- 3 sets of 6-8 reps
- Body part: Middle back Equipment: Exercise
Deadlift
- 5 sets of 4-8 reps
- Body part: Quadriceps Equipment: Barbell
Wide grip pull-ups
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body Part: Lat Equipment: Bodyweight
Pull-down of the upper block behind the head
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body part: Lat Equipment: Block
Add to Calendar * Add to My Workouts * Print Workout
* — The service is in beta testing
Lower back training program
Pull-down of the upper block behind the head
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body part: Lat Equipment: Block
Downward pull of the upper block
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body part: Lat Equipment: Block
Smith Machine Bent Over Row
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body part: Middle back Equipment: Exercise
Lying barbell row
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body part: Middle back Equipment: Barbell
Add to Calendar * Add to My Workouts * Print Workout
* — The service is in beta testing
Training program for total mass and muscle growth
Pull-ups
- a total of 30-40 repetitions
- Body Part: Lat Equipment: Bodyweight
Bent-over barbell row
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body Part: Press Equipment: Barbell
Wide grip pull-ups
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body Part: Lat Equipment: Bodyweight
Deadlift
- 3 sets of 6-10 reps
- Body part: Quadriceps Equipment: Barbell
If you have trouble deadlifting from the floor, try a partial deadlift. Place the weight on the bar on a bench just below your knee and then simply follow normal lifting principles. This will relieve your back a little if you are tall or want to engage your leg muscles in the exercise.
Add to Calendar * Add to My Workouts * Print Workout
* — The service is in beta testing
A wide and pumped back is the dream of every man, especially if nature did not endow him with it in the first place. But it is precisely due to a wide back that a bodybuilder looks strong and impressive, and the daily worries of life become significantly and literally easier.
How to practice
If you're working your entire body in one workout, choose an exercise for each muscle group. If you prefer splits, take two exercises from each point and add them to your back day or deadlift day.
Some of the exercises described in the article pump up several muscle groups at once. Take this into account when creating your program. For example, you can choose one that will work both your upper and lower back well, or work these areas separately.
Select the weight of the equipment in such a way that the last repetitions in the approach are difficult, but without compromising the technique. The number of sets and repetitions will be indicated for each exercise.
If the movement is performed with body weight, do it as much as you can.
Training program for pumping up a wide back
Pullover with barbell
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body part: Lat Equipment: Barbell
Pull-ups
- a total of 30-40 repetitions
- Body Part: Lat Equipment: Bodyweight
Pullover with barbell
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body part: Lat Equipment: Barbell
Bent-over barbell row
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body Part: Press Equipment: Barbell
Lying barbell row
- 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Body part: Middle back Equipment: Barbell
Add to Calendar * Add to My Workouts * Print Workout
* — The service is in beta testing
To avoid going to the gym empty-handed, pay attention to concentration and technique. Engage only the necessary muscles to build a really wide back!
Always pay attention to your technique and do not use too much weight for your safety. Be sure to warm up before your workout and stretch after!
Sports nutrition will help speed up the process of gaining muscle mass - protein, creatine, gainer, arginine, BCAA, amino acids. These supplements are specially designed for athletes and fitness-active people of different fitness levels. Such drugs are completely safe, and their effectiveness has already been proven.