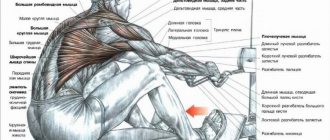
Advantages and disadvantages of linkage
Advantages
- Due to the fact that each lever of the simulator is independent of each other. We can perform rows on each side separately. This will eliminate the imbalance in their development.
- This row allows you to work your back muscles in isolation. This is achieved by resting the chest on a soft pillow with horizontal traction. Thanks to this we get an additional point of support. And in an extended position, the weight of the simulator will not be able to pull us along with it. With vertical traction, we fix our legs by putting them under the bolsters.
- Working in a lever machine, we can achieve a much greater range of motion than in the same block. This will allow more muscle fibers to be involved in the movement. Making our training as effective as possible.
- When performing deadlifts on a lever machine, we have a more stable body position. So we don't have to focus on our sustainability. This will allow you to concentrate entirely on the work of the latissimus muscles. And strengthens the neuromuscular connection.
- The motion vector is set by the simulator itself. Therefore, the exercise takes place in one plane. Consequently, the stabilizer muscles are activated much less than in block and conventional deadlifts. Which gives us the opportunity to perform the exercise only by contracting the lats.
- The lever trainer allows you to deadlift heavy weights.
- Ease of mastering the technique. Which makes lever traction accessible not only to professionals. But also for less experienced athletes.
As you can see, the list of advantages is very impressive. And remembering the previous question about whether a lever trainer is needed or not. I think the answer is obvious. But in order for our understanding of the exercise to be more complete, we need to note its disadvantages.
The pectoral muscles can be divided into the following groups:
- - upper part of the pectoral muscles;
- - middle part of the chest;
- - lower part of the pectoral muscles;
- - inner part of the chest.
For better and uniform development of the pectoral muscles, you should combine the load on different parts.
To do this, during one chest workout, try to use the upper and middle parts, and after a break and muscle recovery - in the next workout, pay attention to the lower and inner parts of the chest
Exercises for the upper pectoral muscles
- Bench press while lying on an incline bench. This exercise involves the clavicular part of the pectoralis major muscle, the anterior parts of the deltoid muscles; triceps, serratus anterior and pectoralis minor muscles.
- Dumbbell press while lying on an incline bench. This exercise is like an intermediate exercise between the incline barbell press and the incline dumbbell fly and primarily engages the clavicular parts of the pectoral muscles.
- Dumbbell flyes while lying on an incline bench. This exercise places the force primarily on the upper portions of the pectoralis major muscle. Along with the dumbbell or barbell pull-over, this exercise is basic for enlarging the chest.
- Reduction of arms in a crossover while lying on an inclined bench. This option of bringing the arms together in a crossover allows you to target and concentrate the load on the upper pectoral muscles. The work also includes the pectoralis major muscle, biceps and forearms.
- Upper block crossovers for the upper chest. This exercise perfectly develops the upper part of the pectoralis major muscle. It also engages the anterior deltoid muscles of the shoulders.
- Bench press for the upper chest. This exercise is great for working the upper muscle fibers of the pectoral muscles. The front deltoids and triceps are also included in the work. Ideal for athletes of entry-level training.
Video: Bench press on a horizontal bench
Exercises for the middle part of the pectoral muscles
- Barbell press lying on a horizontal bench. This exercise develops the entire pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, triceps, anterior deltoid, serratus and coracobrachialis muscles.
- Pushups. In a face-down position, resting your straight arms on the floor, palms shoulder-width apart or slightly wider. Feet together or slightly apart.
- Knee push-ups for chest. The exercise is well suited for those who are just starting to play sports and do not have the opportunity to perform more complex exercises.
- Dumbbell bench press. This exercise is similar to the bench press, except that the exercise with dumbbells has a greater amplitude, which helps to better stretch the pectoralis major muscles.
- Lying dumbbell flyes. This is a basic exercise to increase chest volume and helps increase lung capacity. In addition, it gives elasticity to the muscles.
- Bench barbell row “PULL-OVER”. The exercise perfectly expands the chest. When performing it, use light weights and monitor the position of your torso and proper breathing.
Exercises for the lower chest
- Bench press while lying on an incline bench. This exercise forms the lower undercut of the pectoral muscles. In addition, when lowering the barbell towards the neck, the pectoralis major muscle is stretched, which helps to increase its elasticity.
- Dips. This exercise perfectly stretches the pectoralis major muscles and increases the elasticity of the shoulder girdle muscles.
Video: Dips for chest
Exercises for the inner pectoral muscles
- Bench press with a narrow grip while lying on a bench. This exercise is great for developing the inner definition of the pectoral muscles and triceps.
- Reduction of arms on the simulator. This exercise develops the pectoralis major muscles. As the elbows are brought together, it localizes the force to the inner chest muscles, also developing the coracobrachialis and short head of the biceps.
- Mixing the upper blocks “CROSS-OVER”. This exercise perfectly develops the pectoralis major muscle. By changing the angle of the torso and the trajectory of the arms, that is, by bringing the arms together at different heights, you can use all parts of the pectoralis major muscle.
- Lying overhead dumbbell row “PULL-OVER”. This exercise develops the inner pectoralis major, long head of the triceps, teres major, latissimus dorsi, serratus anterior, rhomboids, and pectoralis minor.
Inclusion in the program
Beginner athletes whose goal is closer to the aesthetics of the body, and not to the development of strength indicators, are recommended to replace the bent-over barbell row with a lever row. This is an acceptable replacement due to the large range of motion and active involvement of the back muscles. The Hummer Lever Row may be the first back exercise for these athletes.
If we are talking about a strength athlete, you can perform lever deadlifts with a moderate weight after deadlifts, and if you are an average athlete whose goal is to gain muscle mass, then second after pull-ups with weights.
The point of the exercise is that it can be performed in a power style. Therefore, it is not worth putting it at the end of the workout, when pumping is performed, and various “injection of injuries” and small muscles.
Recommendations
- The “jerky” style is not acceptable. It is better to gently pull a less significant weight than to sharply push a more significant one;
- If the exercise is performed with both hands at the same time, you need to synchronize their work and avoid “getting ahead” with one hand. This will allow you to avoid problems with muscle imbalances and poor posture;
- It is necessary to master the skill of starting “from squeezing the shoulder blades”, and not from bending the elbows, so that the back muscles are involved in the work, and not the biceps;
- If an athlete has problems with the start, it is worth switching to the “one-armed” deadlift and practicing the skill in turn for each half of the back.
Efficiency Tips
- Strive to stretch your back muscles as much as possible in order to achieve their active contraction in the peak phase;
- Do not neglect static muscle tension in the positive phase, and perform the negative phase more slowly to additionally work the muscles;
- Try not to lift the weight with your arms and don’t focus on your biceps;
- If it is possible to use a machine with unfolding handles, know that palms parallel to the floor will allow you to engage more of the rear deltoids, and palms inward will shift the emphasis to the middle of the back;
- If necessary, you can use the following technique - the weight is lowered twice as slowly as it is pulled up to the belt. This allows you to additionally load your back muscles without using super-high weights. Such techniques are needed when an athlete has reached a plateau in both strength and muscle hypertrophy and cannot achieve good results in the usual way.
Basic mistakes
Too much weight
I have already spoken about this error many times. Athletes greatly overestimate their capabilities. And instead of working with the working weight for 8-10 reps. They prefer to do it 1-2 times, but with a lot of weight, and there is no question of correct technique. And instead of microtraumas, which are a consequence of muscle growth. They suffer serious injuries. Injuring muscles and joints.
Help with your back and legs
This error follows from the previous one. When an athlete cannot cope with the weight, additional muscle groups are activated. These include the lower back and legs. And instead of lat pulldowns, we get an analogue of the leg press and hyperextensions (extensions) in one bottle. To avoid this, choose the right weight.
Performing elbow curls instead of rows
As mentioned earlier, with deadlifts it is very easy to cross the line between working the biceps and the back muscles. Therefore, we definitely need to develop neuromuscular communication. To do this, take enough time to practice the technique. Focus on retracting your shoulder blades and moving your elbows rather than bending your arms.
Correct execution of the exercise
- If you look at the athlete from the side, his forearms move parallel to the floor, in a straight or slightly elliptical path; in the second version, the emphasis is on tightening the elbows to the body, and this version of the movement involves the rhomboid muscles more;
- When performing a deadlift, the arms move at the same speed and do not allow one to get ahead of the other;
- The amplitude of movement should be kept as close to natural as possible. Throwing your elbows over your waist should be avoided so that the work is in the optimal trajectory;
- The support pillow is located at the solar plexus throughout the entire movement; displacement along the axis perpendicular to the spine is not allowed during operation;
- The choice of grip is relevant if the simulator has a flexible handle design. That is, they rotate around their axis, and you can turn your palms inward or parallel to the plane of the floor;
- The main load falls on the latissimus muscles; you should not pull with the biceps;
- Movements with one hand are allowed, but in all technical versions of the exercise it is necessary to pull the shoulder blades towards the spine.
AND A FEW MORE EXERCISES TO PUMP YOUR BACK MUSCLES
Stretching the latissimus dorsi muscles - standing swinging your arms. Stretching the latissimus dorsi muscles - standing swinging your arms. Photo - Women: Rows from the lower block to the chest. Rows from the lower block to the chest. Photo - Women Crossover rows from upper blocks Crossover rows from upper blocks. Photo - Women Gironde pull-up with a reverse grip (to the chest) Gironde pull-up with an overhand grip (to the chest). Photo - Women Stretching with kneading the latissimus dorsi muscles while lying on the floor Stretching with kneading the latissimus dorsi muscles while lying on the floor. Photo - WomenStretching the latissimus dorsi muscles while standing with support on a wall.Stretching the latissimus dorsi muscles while standing with support on the wall. Photo - Women Stretch of the lats hanging on one arm. Stretch of the lats hanging on one arm. Photo - Women Stretching the back muscles with a partner Stretching the back muscles with a partner. Photo - Women Pull-ups on the bar with a medium overhand grip - classic Pull-ups on the bar with a medium overhand grip - classic. Photo - WomenRocky pull-ups - to the chin - behind the neckRocky pull-ups - to the chin - behind the neck. Photo - Women Pull-ups on the bar with lateral movements Pull-ups on the bar with lateral movements. Photo - Women Stretching the back muscles while lying on the floor on your side Stretching the back muscles while lying on the floor on your side. Photo - Women Straight arm rows from shoulder level from the top block Straight arm rows from shoulder level from the top block. Photo - WomenReverse grip rows from the upper block while seatedReverse grip rows from the upper block while seated. Photo - Women: V-shaped chest rows from the upper block. V-shaped chest rows from the upper block. Photo - Women Pull-ups with a V-shaped grip Pull-ups with a V-shaped grip. Photo - Women Seated wide-grip chest rows from an upper block Seated wide-grip chest rows from an upper block. Photo - Women: Neck rows with a wide grip from the upper block while sitting. Neck rows with a wide grip from the upper block while sitting. Photo - Women Stretching the latissimus dorsi while hanging on a bar with a wide grip Pull-up on a bar with a wide grip. Photo - WomenAlternating bent-over kettlebell rowsAlternating bent-over kettlebell rows. Photo - Women Alternating rows of weights in a lying position Alternating rows of weights in a lying position. Photo - Women: Barbell rows to the stomach in a half-tilt. Barbell rows to the stomach in a half-tilt. Photo - WomenT-bar rows with one handT-bar rows with one hand. Photo - WomenT-bar row with two handsT-bar row with two hands. Photo - Women Bent-over dumbbell rows. Dumbbells along the shoulder line. Bent-over dumbbell rows. Dumbbells along the shoulder line. Photo - Women Bent-over dumbbell rows. Dumbbells along the body. Bent-over dumbbell rows. Dumbbells along the body. Photo - Women: Barbell rows to the chest on an inclined bench. Barbell rows to the chest on an inclined bench. Photo - Women Barbell rows with a curved bar lying on a bench, face down. Barbell rows with a curved bar lying on a bench, face down. Photo - Women T-bar rows in a chest-rest machine. T-bar rows in a chest-weight machine. Photo - Women Shrugs with dumbbells lying on an incline bench. Shrugs with dumbbells lying on an incline bench. Photo - Women Stretching the back muscles - Standing body turns. Stretching the back muscles - Standing body turns. Photo - Women Pull-ups on the bar with mixed grip Pull-ups on the bar with mixed grip. Photo - Women Pull-ups on the bar with one hand - reverse grip, the other with a grip on the towel. Pull-ups on the bar with one hand - reverse grip, the other - with a grip on the towel. Photo - Women Bent-over dumbbell rows to the chest with emphasis. Bent-over dumbbell rows to the chest with emphasis. Photo - Women Bent-over kettlebell row Bent-over kettlebell row. Photo - Women Bent-over barbell rows with a reverse grip Bent-over barbell rows with a reverse grip. Photo - WomenStretching the middle part of the back - rhomboid muscles - lying down with a rollerStretching the middle part of the back - rhomboid muscles - lying down with a roller. Photo - Women V-shaped grip rows to the stomach from the lower block V-shaped grip rows to the stomach from the lower block. Photo - Women: One-handed rows to the stomach from the lower block. One-handed rows to the stomach from the lower block. Photo - Women Bent-over barbell rows on a Smith machine Bent-over barbell rows on a Smith machine. Photo – Women Spinal stretching. Side crunches while sitting on a chair. Spinal stretch. Side crunches while sitting on a chair. Photo - Women: Bent-over rows of two weights to the stomach. Bent-over rows of two weights to the stomach. Photo - Women Stretching the back muscles while standing with clasped hands. Stretching the back muscles while standing with clasped hands. Photo – Women
Upper hummer thrust
The row in a vertical machine is very similar to the row of the upper block. This version of the exercise is considered more “advanced”, since in a lever simulator the exercise can be performed with one hand. If you compare the work of the muscles, there is no difference in the exercises, and the pull-down of the upper block can also be done with one hand. This traction option is suitable for those athletes who cannot perform pull-ups. The technique of execution is absolutely the same as when performing lat pull-downs.
- While performing the movement, your back should be kept straight and your lower back should be arched.
- Exhale while pulling the weight down.
- And inhale while returning the load upward.
To further engage the latissimus dorsi, you can lean your torso slightly forward.
How to Develop Back Width: Vertical Hummer Row
The second exercise in the training, in order to develop the width of the back, it is necessary to perform a vertical hammer row with a narrow position of the arms in order to involve the lower part of the latissimus muscles, which are closer to the spine, into the work.
During the movement, bend back to eliminate the work of the biceps, and concentrate on working the lower part of the lats. Perform 4 sets of 6 reps, also increasing the weight on each set. To be more effective, finish the last set with a drop. That is, after 6 repetitions of 4 sets, drop the weight and do another set without rest.
What is so special about vertical rows for women?
Classes in the block simulator are suitable for both men and women.
For girls, regularly performing vertical rows helps:
- gaining enough strength to perform more difficult exercises (for example, pull-ups or push-ups);
- achieving the desired result in the shortest possible time, regardless of the specifics of the goal itself (vertical traction is effective both in increasing the relief of the body and in improving strength indicators, as well as endurance of the muscles of the shoulder girdle);
- visual transformation of the décolleté area (by strengthening the pectoral muscles when performing exercises in a block design, the breast shape is tightened and slightly changed for the better).
Don't miss the most popular article in the section: Body drying for girls. Training program, detailed nutrition menu for the month by day.
Effective lat training on a vertical block
There is no point in performing a large number of exercises on a vertical block, since approximately the same muscles work.
You need to choose two types of traction from those we talked about. For example, wide-grip and narrow-grip rows, or overhead rows and one-arm rows. The main thing is that the exercises affect different areas of the back!
An example complex might look like this:
- Wide grip rows – 3-4 sets of 8-12 reps.
- Close grip rows – 2-3 sets of 8-12 reps.
After completing the complex, you can perform stretching exercises.
Features of traction in a hummer with one hand
Lever pull machines allow you to work with one hand. Sometimes working with one hand will be more important due to the performance of more concentrated movements. When performing deadlifts with one hand, you need to fix the position of the body with your free hand. Pay attention to the fixation of the hand in the peak position of the amplitude. Typically, when performing an exercise with one hand, the body rotates following the movement of the hand, thereby engaging the biceps and serratus muscles.
Technique for performing exercises on a vertical machine
Strict adherence to the technique of performing exercises in a vertical simulator will help minimize the likelihood of injury to the athlete.
The generally accepted algorithm consists of successive stages:
- Set the required number of blocks that you plan to use during the exercise. Take the starting position, sitting on the supporting part of the structure and clasping the handrails of the simulator with your hands. The legs must be fixed in special bolsters.
- As you exhale, pull the handle down until it is level with the area slightly below the back of your head. During exercises, the elbows move in a perpendicular plane. The back remains consistently straight.
- Hold the position for 5 seconds.
- Slowly relax the muscles and return to the original position.
The direction of muscle development depends on the grip at the time of performing a vertical row.
Grip width
The most commonly used exercise in this exercise is:
| Type of grip | Short description |
| Straight grip | The backs of the palms are turned forward. It is recommended to use for the best pumping of the latissimus dorsi muscles. |
| Reverse grip | The backs of the palms are directed back. To work your biceps, you need to pull the block towards your chin. |
| Neutral grip | Used when working with heavy weights. |
| Wide grip | Most effective for strengthening the muscles of the shoulder girdle. The hands are located slightly wider than the shoulders. |
| Narrow grip | The hands must be placed on the handle of the block structure at a distance less than the distance between the shoulders. When performing the exercise with a close grip, the elbows are slightly moved to the sides. |
The difference between rows and pull-ups
The main difference between rows and pull-ups is the technique of performing the exercises. If in the first case the athlete is required to pull the block-structured handrail down (the working weight is determined by the fitness instructor), then when doing pull-ups the person works with his own weight.
Vertical rows in the simulator differ from pull-ups in that in the second case you can only work with your own weight. The weight on the machine is adjustable.
Vertical rows are included in the training program if the athlete has contraindications for pull-ups or does not have sufficient strength.
How many repetitions should women perform?
To avoid injury while performing vertical rows, athletes must strictly follow the fitness trainer's recommendations regarding the number of sets and repetitions. For women just starting to practice strength training, 3 sets of 10 repetitions would be optimal. In this case, the “working weight” should not exceed 15 kg.
As the muscle corset adapts to a given level of load, the number of approaches can be increased to 4, and repetitions to 12. If a girl has previously been involved in sports and is now recovering after a long break, the initial load for her will be 4 sets of 15 repetitions.
Weight for women when pulling a block
The initial working weight for women when performing exercises in a block simulator should not exceed 15 kg. After 3-4 weeks of active sports, it is recommended to increase the total weight of the blocks used to 20.
Further weight gain should occur as the muscle corset adapts to the given level of load (but not more than 5 kg in 2-3 weeks).
Technical errors
The most common mistakes that prevent you from achieving maximum results from regularly performing vertical rows are:
Scroll:
- stooped position of the shoulders during the exercise;
- curved spine due to incorrect position;
- lifting the buttocks from the supporting surface while relaxing the muscles;
- shifting the load (from the back to the arms, in particular the biceps);
- incorrect selection of “working weight”, which prevents compliance with the exercise technique.
The above mistakes are made not only by beginners who have not previously dealt with power loads, but also by experienced athletes who do not pay due attention to the technique of performing the exercise in question.
Contraindications for use
Contraindications to starting work on working out the pectoral muscles are related to the characteristics of specific cases:
- It is forbidden to work with your own weight in cases where the spine has been injured, ligament tears, or joint injuries have been recorded. In this case, work on simulators should be carried out only after the recommendations of a specialist.
- Work on the simulator is excluded for nursing mothers or mothers who are at the end of feeding.
- Working on the simulator is not recommended for women with artificial implants that were installed under the muscle.
- Those who experience fluctuations in blood pressure should consult a doctor before starting work.
Horizontal thrust in a hummer
This exercise is similar to a horizontal block row. Of course, pulling in a hummer is much more convenient to perform, and the athlete does not receive stress on the spine thanks to the support that fixes the torso.
In order to perform the exercise correctly and get the maximum effect from the deadlift, you should set up the machine correctly. To perform the exercise, you need to take a sitting position. The seat depth should be adjusted so that your hands are at the level of the elbow joint when moving. If the hands are higher during the movement, the biceps will be involved in the work.
- The chest support is located at the level of the solar plexus.
- The lower back should be in a natural arch, as should the upper back.
- While performing the exercise (pulling the levers towards you), you exhale, while you need to bend the thoracic region and bring the shoulder blades closer to each other.
- The elbows should be pressed as close to the torso as possible during the pull. This nuance will ensure maximum load on the latissimus dorsi muscles.
- You should return to the starting position slowly. The stretch of the latissimus muscle should be maximum - with the arm straightened at the elbow joint. There is no need to return the lever to its support. Inhale while returning the levers.
Features of the simulator
The machine can be adjusted according to the height and length of the athlete’s arms.
The main difference between the machine and free weights is its high safety. When working with free weights, the possibility of deviation from the correct amplitude always remains. The risk is especially high if you are overweight. In the simulator, the trajectory is determined by the design and remains unchanged under any load.
In addition, Hammer line has other advantages:
- The athlete performs the exercises in a sitting position. At the same time, it rests on a support, which reduces the load on the spine.
- The amplitude of the lever simulator is slightly larger than the block one. The deadlift is performed with the maximum possible stretch of the muscle, and this allows you to better work the muscles.
- In the simulator you can pump half of your back and arms together and separately from each other.
- The weight is easy to adjust and within fairly large limits.
The advantages of the design in certain circumstances become disadvantages:
- The parameters of the simulator vary within certain limits. It is impossible for athletes of small stature and short arms to train in it.
- Performing the exercise along a strictly defined trajectory excludes the participation of stabilizer muscles. On the one hand, this is safer, on the other hand, such a movement is far from natural and makes it difficult in the future to synchronize muscles when performing deadlifts or deadlifts with a barbell and dumbbells.
- The safety of the hummer often provokes beginners to use maximum weights and not pay attention to technique. This is fraught with injuries and sprains.
There is another major drawback: the price of the Hummer is quite high. They buy expensive equipment for expensive and famous halls.
Execution technique
Before you start performing vertical or horizontal traction, you need to determine your working weight from the weighting blocks. Loads should be increased gradually. It is also necessary to first warm up the body by doing a set of exercises to prepare the cardiovascular system and joints for stress. To prevent injuries, you must strictly follow the recommendations of your fitness trainer. As you adapt, you can increase the load, as well as the duration of the exercises. Lever traction in a sitting simulator is done in a vertical position with the knees secured under special bolsters. The legs rest firmly on the floor. When performing horizontal lever traction, support is placed in the thoracic region; for this purpose, special pillows are installed on the simulators.
To perform a hummer row on your back, you need to try to relax your hands. If you strain them too much, the biceps will be activated. Exercise technique:
- Prepare the simulator and adjust the seat to your height.
- Sit down and rest your chest against a vertical surface. Extend your arms and grab the handles of the machine. The spine is straight, the elbows are pressed.
- Pull the handles towards you, bringing your shoulder blades together at the end point of the movement. It is important not to lean back and avoid turning the body.
- Lower the weight, but do not return it to the support.
Features of execution with different hand positions:
- with a reverse grip - position with your palms facing you, the load falls on the lower halves of the latissimus muscles;
- with a straight grip - palms turned away from you, the upper areas of the “wings” are trained;
- with a neutral position - the hands are turned towards each other, the central part of the latissimus muscles is worked out.
For a good result, it is recommended to alternately use all types of grip, and also experiment with its width.
Reverse grip
Straight grip
With neutral position
How to avoid injuries - useful tips
Here we will consider contraindications and typical mistakes of beginners. If you have a sore lower back, it is not recommended to do deadlifts, but if you really want to, use an orthopedic belt. Your task is to protect the sacrolumbar region from excessive loads. The lats should be pumped up - this is your main goal. Typical mistakes include:
- round back (your lower back suffers);
- the main load is on the arms (the lats should bear the weight);
- jerking and swaying (danger to your spine);
- deep bends forward (do not become like a pendulum);
- pushing away with your feet (this is what inveterate cheaters do).
The occurrence of injuries can be prevented by proper technique - this is the only way to protect yourself. Technical violations over time lead to torn muscles, sprains and lumbar osteochondrosis. The gym should develop your body, not cripple it. By proving something to friends or casual acquaintances, you risk facing serious problems in the future. Health comes first.
Technical characteristics of the Hammer simulator:
- The frame of the Hummer simulator is made of thick-walled profile pipe 40 x 80 mm.
- The rotation units are closed ball bearings.
- The load on the simulator is provided using Olympic or training discs with a mounting hole diameter of 51 mm.
- The upholstery is made of vinyl artificial leather with a high-strength nylon base.
- The soft elements of the strength training device are filled with foamed polyurethane foam.
- The base for the pillows is multi-layer plywood on a steel base.
- The coating of rubbing and guiding parts is complex galvanic (chrome + nickel).
- The supporting parts of the machine are steel legs with holes for fastening to the floor.
- Permissible load on the moving part of the overhead pull simulator: 350 kg.
- Dimensions: 1700x1385x2000 mm.
- Weight of the strength trainer: 115 kg.
- The Hammer exercise machine lever pull from above on free weights has no limit for athletes in terms of height and weight.