Proper nutrition for bodybuilders is half the success. There is not a simple, but a scientific approach to this issue, which allows the athlete to build muscle mass without problems for the athlete’s health. Otherwise, disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system and cardiovascular system are possible.
To build voluminous, strong and sculpted muscles, it is not enough to master various training methods around the world or some personal techniques. Without proper nutrition in appropriate amounts, it is impossible to achieve high results. Nutrients are essential for continued muscle growth after training and full recovery. In other words, in order to increase muscle volume, you need to eat, and eat a lot, but correctly, otherwise it will not be the muscles that will build up, but the fat layer.
This nutrition program is highly effective, progressive and affordable. The thing is that it is based on the most modern advances in the field of nutrition, so it serves as an ideal addition to any training processes that are based on a scientific approach. This approach to nutrition will allow you to quickly increase muscle mass, without gaining excessive amounts of fat.
Some athletes who are “on the mass” suffer from the negative effects of fat in the body and insulin sensitivity, and this slows down the process of muscle growth. Such a diet is free of such drawbacks. Thanks to such a program, it is possible to gradually increase the number of calories consumed by athletes, so that the body has time to adapt to it. In other words, problems such as catabolism and excess fat deposits are left behind.
“Without proper nutrition and in the proper amounts, it is impossible to achieve significant results from training.”
Sample diet before training
A weekly nutrition plan for a person who wants to gain weight looks something like this:
- For breakfast: 1 banana, 2 whole eggs and 3 whites.
- 2 hours after breakfast: 1 banana, 300 grams of yogurt, 50 grams of mixed nuts.
- For lunch: 250-270 grams of brown rice, 160 grams of turkey and ½ part of an avocado.
60-90 minutes before training, it would be correct to organize a small snack consisting of 3 slices of whole grain rye bread, 1 banana and a serving of protein shake (at least 1.5 scoops).
For breakfast, you can use products such as: omelette with tomatoes, shrimp and herbs, oatmeal or barley porridge, low-fat cheese, pears, apples and cocoa.
Lunch may include: stewed lean beef, chicken or turkey with a side dish in the form of durum wheat pasta, brown rice or green peas.
Dark chocolate with a high cocoa content is an excellent source of fast carbohydrates and accelerates the production of endorphins. Therefore, it can be consumed shortly before training as a natural pre-workout.
Gain muscle mass, not fat
No matter what you think of it, the average person eats completely differently than an advanced bodybuilder. And the point is not that the menu of the latter contains various sports nutrition. It is the selection of products in this case that will be very specific.
Let's start with the fact that during training your body experiences extreme stress. Oddly enough, it is a stressful situation that allows us to develop and move forward.
I will give an example that is accessible to anyone. If you fast for a long time, then the moment you start eating normally, the body will try not only to restore what was lost, but also to make reserves for future nuclear times. Therefore, you will begin to gain weight rapidly. This is the main harm of any extreme diet with significant calorie restriction.
Approximately the same processes will occur with your muscles. Imagine that you regularly train and use large working weights, which means you invariably injure your muscle tissue, they stretch and even tear (we are talking about microtraumas).
The natural defense mechanism in this case will work according to the previous principle. The muscles will begin not only to strengthen, but also to increase in volume to protect your body from upcoming overloads. All this is expressed as progress and mass growth.
Therefore, in order to maintain this balance, we need nutrients that will support the body's work, time and strength loads.
As for nutrients, it should be carbohydrates from which we get energy. As well as proteins, which are the main suppliers of amino acids, and from them, in turn, new muscle tissue cells are built.
Another postulate, without which you will not achieve anything, is this: you must receive more than you spend.
Naturally, you and I need some kind of reference point, that is, the number of calories from which we will start. How do we know how much energy is needed for the daily needs and requirements of our body? There are a lot of ways to calculate these numbers, starting with counting the calories of all the food you ate during the day and analyzing your daily weight gain and weight.
And you can end up with complicated formulas that take into account height, age, current weight and even the gender of a person. They will have to be tediously multiplying, adding and squaring.
The simplest equation is your weight multiplied by 30. The resulting figure will be the average amount of calories you need.
So, let's say you multiply your weight by 30 and get the number you're looking for. We add 500 kilocalories to it on top. This will be nutrition for a surplus or excess of calories. If this is not enough, then add more. If you continue to gain weight even with this schedule, then we remove the excess.
You will definitely have to make allowances for genetic data, that is, take into account your metabolism. If you are an endomorph (see
article on how to pump up an endomorph), whose metabolism (what is metabolism) is naturally slow, then you will have your own adjustments. And a completely different nutrition plan can be for an ectomorph with a high-speed metabolism that can cope with large volumes of food without loss.
Answers to basic questions
- How many meals should a bodybuilder's diet consist of?
The standard diet of the average person (breakfast, lunch, dinner) is not suitable for a bodybuilder. A fan of this sport should have a food intake system consisting of 5-7 meals a day. With this routine and diet, the athlete’s body does not experience hunger.
Hunger is the main enemy of a bodybuilder, since it begins the production of necessary substances from the body’s reserves and the muscular system. Muscle loss continues throughout the fasting period and only stops after eating. For healthy nutrition, you need to increase the number of meals, but make the portions more moderate. A bodybuilder's diet should be frequent, but not dense.
- What foods are needed for proper nutrition?
To answer this question, you need to understand the basic principle - that a bodybuilder’s food should consist only of natural foods! An athlete’s diet cannot contain doshirak, expired foods, or harmful food additives; it must consist of 80% meat, fish, vegetables and fruits.
Only on a natural basis can you build a proper muscular system. The bodybuilder’s body is subjected to constant stress; only products of natural origin, which must be included in the daily diet, can help to endure them painlessly.
“Proper” foods also include those that are grilled or steamed, without adding oil, or boiled. The correct method of cooking will provide an enriched diet of beneficial microelements and vitamins for a bodybuilder.
- What protein ratio does a bodybuilder need per day?
A bodybuilder's menu should consist of a huge amount of protein (natural protein found in pure meat and nuts); this element is the foundation for muscle building. To provide progressive sports nutrition, you must consume 2 grams of protein per 1 kg of live weight. Only this ratio will ensure a rapid gain of muscle mass and constant progress. To ensure your diet is rich in protein, you should include the following foods in your diet:
- Boiled or grilled chicken breast.
- Boiled eggs.
- Skim cow's milk.
Summing up
After reading the answers to the questions, we can conclude that an athlete’s diet should consist not only of natural products, but also contain a lot of protein. Only such nutrition will ensure a qualitative increase in muscle mass.
Bodybuilding Basics
Bodybuilding differs from powerlifting or Olympic lifting in that the athlete is judged on appearance rather than physical strength.
Thus, bodybuilders strive to develop and maintain a well-balanced muscular physique without excess body fat.
To do this, many bodybuilders start with an off-season followed by a seasonal eating pattern called the bulking phase and the conditioning phase, respectively.
During the bulking phase, which can last from several months to several years, bodybuilders eat high-calorie, protein-rich foods and gain weight intensively with the goal of building as much muscle as possible (1).
The next proportion improvement phase focuses on losing as much fat as possible while maintaining the muscle mass developed during the bulking phase. This is achieved through specific changes in diet and exercise over 12 to 26 weeks (1).
Summary:
Training and diet in bodybuilding are usually divided into two phases: gaining mass and improving proportions. The goal of the bulking phase is to build muscle mass, while the bulking phase is designed to maintain muscle while losing fat.
Nutrition rules
The bodybuilding diet is designed for a minimum of 6 meals, but to achieve serious results you should eat 8-10 times a day. Fractional nutrition is necessary to constantly replenish the muscles with energy and protein, since if there is a lack of building material, muscle mass will not be able to grow, and we need good results.
In the first half of the day, it is necessary to give the body a boost of energy in the form of slow (complex carbohydrates), and the second half of the day should be rich in protein. This means that in the morning you should eat a lot of carbohydrates and a small amount of protein, and in the evening, on the contrary, more protein and less carbohydrates. This rule is justified by the fact that in the morning you need to get energy, which will be spent throughout the day, and after training, the muscles need protein, it will strengthen damaged muscle tissue. Since in the evening there will be no place to spend energy, you should not consume carbohydrates.
Pre-workout nutrition
It is necessary to eat 2 hours before strength training, the food should consist of complex carbohydrates and proteins to provide sufficient energy and material for muscle growth. Half an hour before class, you need to drink a protein shake; it can consist of milk and cottage cheese, or you can buy special protein drinks.
During training, drink non-carbonated mineral water and, if possible, add 5 g of amino acid to it.
After training, you can replenish your energy reserves with fast carbohydrates within 30 minutes, or wait an hour and eat a full protein meal and slow carbohydrates.
Before going to bed, it is necessary to give the body a good portion of proteins, since during sleep the substances necessary for the muscles will not be supplied.
How much protein is needed for muscle growth?
During training, there is a huge load on the body and muscle fibers are damaged, so a bodybuilder's diet should contain a lot of proteins and carbohydrates, in other words, you should consume more than you spend. This approach to muscle building will help you achieve maximum results.
After training with metal, it is necessary to strengthen damaged tissues, where protein will go. Restoring muscles requires time and materials that must be regularly supplied to the body, all bodybuilders should know this.
What to eat (about the ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates)
In addition to excess calories in the diet, many athletes make another mistake: they do not consume enough protein, but instead lean on fatty and sweet foods. Naturally, this will negatively affect both the figure and the quality of training.
The ratio of nutrients is approximately as follows:
- carbohydrates: 50-60%;
- fats: 10-20%;
- proteins: 20-30%.
Basic constants:
- 1 gram of protein – 4 calories;
- 1 gram of carbohydrates – 4 calories;
- 1 gram of fat contains 9 calories.
As for protein, the main muscle-building “component”:
- to maintain weight: take 1.4 grams of protein per 1 kilogram;
- to “dry”: take 2-2.2 grams of protein per 1 kilogram;
- to gain weight: take 3-4 grams of protein per 1 kilogram.
As for carbohydrates - the source of “fuel” for activity:
to “dry”: take 2-3 grams of carbohydrates per 1 kilogram.
Regarding fats:
- We calculate daily calorie intake (DAI).
- We calculate protein and carbohydrate intake (PBU).
- We subtract the PBU from the SPK. As a result, we get the remainder, which should be fats (F).
- F 9 = amount of fat in grams you should consume.
Products for muscle growth
When creating a menu for weight gain, it is important to take into account that for the complete absorption of proteins, they must be properly combined with amino acids. Carbohydrates play a leading role in nutrition aimed at weight gain, since if they are deficient, the body will “eat” muscle tissue during periods of increased physical activity
Products containing protein
Proper nutrition in bodybuilding is unthinkable without protein-rich foods. These include:
- Nuts;
- Beans, chickpeas, lentils and other legumes;
- Low-fat cheese, cottage cheese;
- Lean varieties of meat and poultry.
Soy is the record holder for protein content (about 36 grams per 100 grams of product), but it contains a high percentage of female hormones phytoestrogens, which slow down muscle growth.
High fat foods
To gain muscle mass, your weekly diet must include foods rich in unsaturated fats. Fats are considered the most readily available source of energy, but if saturated fats are overused, health problems appear such as: decline in immunity, wrinkled skin, increased wear and tear on joints and destruction of muscle tissue. Foods rich in unsaturated fats include:
- Hazelnuts, pistachios, almonds;
- Wheat sprouts;
- Sunflower seeds;
- Soya beans;
- Soy cheese (tofu);
- Seafood.
Fats, despite their high energy potential, are characterized by a long process of breakdown, therefore they make the body lethargic and reduce vitality. Proper nutrition consists of food that is prepared without frying in butter or vegetable oil. It is preferable to steam or bake products in the oven.
Carbohydrate-rich foods
The diet of a natural bodybuilder for mass should include predominantly complex carbohydrates
Therefore, you should pay attention to the following products:
- Oatmeal, buckwheat, corn and pearl barley;
- Rice (roughly processed);
- Asparagus, green beans;
- Raisins, dates and other dried fruits;
- Durum wheat pasta.
Fruits and vegetables are a source of carbohydrates, as well as useful fiber, necessary for the high-quality digestion of animal proteins. In addition, they contain a lot of vitamins, microelements and amino acids, without which one can only dream of gaining muscle mass.
Nutritional supplements
Most modern sports involve the use of special supplements that are useful for both girls and men.
- With the help of high-quality whey protein, you can increase your muscle mass gains.
- Gainer is a super-calorie mixture consisting of carbohydrates and easily digestible proteins. You can consume it either immediately after training or during your first meal.
- Creatine doesn't need much introduction as it is one of the most popular muscle building supplements. You can take a few grams of it both on training days and during rest.
- Vitamin-mineral complexes accelerate metabolic processes and have a positive effect on the process of weight stabilization.
An excellent student from Moscow has invented a fat burner! 12 cm in the waist goes away in a week if mixed with kefir... Read more
Revolutionary technology for losing weight at home. Lose excess weight without dieting or training! In just 23 minutes a day. Buy
Age-related fat does not come from food! You will lose 22 kg of fat in a week if you drink 150 ml of hot water on an empty stomach... Read more
Summarize
- In bodybuilding, proportionately developed large muscle mass together with a small amount of fat on the body is assessed, and not athletic performance.
- Achieving the desired look of a bodybuilder requires regular training and special attention to diet.
- A bodybuilding nutrition program is typically divided into a bulking phase and an improvement phase, during which your calorie intake will change while your macronutrient ratio remains the same.
- Your diet should include nutrient-dense foods and 20-30 grams of protein with every meal and snack.
- You should also limit your intake of alcohol, heavily fried foods, and foods high in sugar.
- This ensures that you get all the important nutrients your body needs to build muscle mass and improve your overall health.
Body-building
Why is bodybuilder nutrition so important for gaining muscle mass?
To effectively grow muscles and increase strength, a bodybuilder's sports diet should consist of plentiful amounts of protein and calories, as well as trace elements and vitamins. For example, for visible muscle growth, an athlete must consume at least 2 g of protein per 1 kg of body weight per day. Carbohydrates are especially important, without which an actively training body will not have enough energy for effective recovery. Moreover, without getting the required amount of calories, the athlete will quickly get tired during weight training.
The more calories consumed, the higher the food costs. Protein-rich foods are especially expensive. Yes, and vitamin food has a hefty price tag. Even if you save on useless food (fast food, smoked foods, sweets, etc.), it is not always possible to provide the required level of nutrition for muscle growth. Prices for poultry, meat and fish will still remain high. Preparing a balanced and varied diet for weight gain every day will not only allow you to get the right amount of proteins, carbohydrates and vitamins, but also save money.
Calculate your protein needs[edit | edit code]
Calculation of protein needs
Protein requirements vary depending on energy intake and exercise goals. Although menu plans presented in foreign articles give food volumes in grams per pound of body weight, you can easily convert kilograms to pounds by multiplying your weight by 2.2. Make sure your body is getting the amount of protein it needs by following all four bodybuilding nutrition strategies. If you're vegan, add an extra 10% protein to each plan.
- Maintenance of muscle mass: 1.4 g per kilogram of body weight per day.
- Muscle building: 3.5-4 g per kilogram of body weight per day.
- Nutrition for relief: 2.2 g per kilogram of body weight per day.
- Fat burning: 2.3 g per kilogram of body weight per day (2.2 for those who prefer mainly vegetarian dishes).
Individual nutrition plan for a bodybuilder[edit | edit code]
As your weight changes, you must recalculate the amount of energy and nutrients you need. With the help of Body Expert, you will receive information on calorie needs, this is a necessary condition that allows you to create the correct nutrition for a bodybuilder for an individual, taking into account the individual parameters of the body.
Bodybuilder nutrition to maintain muscle mass.
Men who exercise five or more times per week need to consume 42 calories per kilogram of body weight per day (3,444 calories per day for an 82-kg man). Women who exercise five or more times per week will be able to increase muscle mass by consuming 44 to 50 calories per pound of body weight per day (2,950 calories per day for a 59-kg woman) and maintain muscle mass by consuming approximately 38 to 40 calories per day. kilogram of body weight per day (2360 calories). The larger and more muscular a woman is, the more calories she should consume to maintain her muscles.
Petite women may need less than 38 calories per kilogram of body weight per day to maintain muscle mass. For women, you learn a lot by trial and error, since all scientific experiments were done on men, and activity levels can vary greatly between individuals. For other parts of the nutrition plan, women should generally choose smaller portions. This diet is great for bodybuilders, weightlifters, powerlifters, and amateur strength athletes. Beginners must follow special instructions.
Nutrition for building muscles and gaining mass
. This plan requires consuming 44-52 calories or more per kilogram of body weight per day, depending on the intensity of the activity (4264 calories or more for a man weighing 82 kg); 2596-2950 calories for a 59 kg woman. Start with a minimal amount and add calories as needed. As noted earlier, for women looking to build muscle, 44 calories per kilogram of body weight per day will be enough. Petite women should consume slightly fewer calories at the beginning of a workout program and add more as their muscle size increases. This diet is suitable for all competitive strength athletes and amateurs. Beginners must follow specific beginner instructions.
Diet for terrain
(10-12 weeks of pre-competition diet). In order to reduce the fat component and start working on muscle definition, you should consume 35-38 calories per kilogram of body weight per day (3116 calories for a man weighing 82 kg; 2065 calories for a woman weighing 59 kg). Because it is more difficult for women to lose fat than men, they should consume a minimum amount of calories and increase aerobic activity to burn 300-400 calories per day. Again, petite women will require fewer calories. This recommendation applies mainly to female bodybuilders. Beginners follow the instructions for beginners.
Fat Burning
(maximum 7-14 days). This plan calls for consuming 29 calories per kilogram of body weight per day for women (1,711 calories for a 59-kg woman) and 32 calories per kilogram of body weight per day for men (2,624 calories for a 82-kg man). For smaller women following a reduced-calorie diet, this may also include reducing the number of recommended calories. Use this method only in extreme cases. This diet is only suitable for bodybuilders or competitive athletes gaining pounds for their weight class, but not for powerlifters (strength lifters) or Olympic weightlifters.
Powerlifters and weightlifters
gaining muscle mass for their weight category. Once you've followed a muscle-building diet, you'll need to go back to a maintenance diet for two weeks before you get into shape. This diet will allow you to get rid of subcutaneous fat without losing muscle mass, strength and endurance. This technique is also a good basic diet for high-impact strength athletes who are trying to lose subcutaneous fat.
We create a basic diet for a bodybuilder
Let's start by creating a basic diet. Due to individual differences in each person's metabolism and activity level, I prefer not to use equations to calculate calories. Instead, I think it's more effective to start by determining the number of calories you currently consume and gradually adjust it.
This program requires you to track your exact calories and macronutrients for the next 6 weeks. If this approach is new to you, look for information about it on the Internet and spend time learning about it.
If you don't know how many calories you consume, keep a diary or use special programs to record everything you eat in the first 3 days of your diet. Some smartphone apps will help you calculate your average calorie intake over this period.
To speed up the process of gaining muscle mass, you will need to add 300 kcal to your baseline intake. Over the next 2 weeks, monitor your body weight by measuring your chest, neck, arms, etc. Also monitor your fat levels using a caliper and follow these guidelines:
- If you are gaining weight without excess fat, add another 300 kcal to your daily diet.
- If weight gain does not occur, add 500 kcal.
Repeat this process every 2 weeks, adding more and more calories.
Nutrition for bodybuilders to gain muscle mass
This mass-building diet is perfect for lean men who want to build muscle while training in the gym.
Norm: approximately 3000 Kcal, 300 g carbohydrates, 225 g protein, 100 g fat
Please note that this meal plan is suitable for those who go to the gym in the afternoon. If you train in the morning, it's enough to switch up your meals so that you eat starchy foods during your pre- and post-workout snacks. Next, stay away from starchy carbohydrates throughout the day.
Meal schedule
- Dish 1: Starchy-carbohydrate
- Meal 2: Low/No Carb
- Meal 3: Low/No Carb
- Meal 4: (Post-workout snack) Starchy-carbohydrate
- Dish 5: Starchy-carbohydrate
- Dish 6: Starchy-carbohydrate
Recommended Recipes
Dish 1: Scrambled eggs with cheese and shallots
- Eggs (source of Omega-3) – 3
- Egg whites – 4
- Cheese (cheddar) – 1/4 tbsp.
- Shallots – 2
- Ezekiel bread – 2 pieces
- Apples – 1
- Protein powder (vanilla flavor) – 2 servings
- Blueberries – 1 tbsp.
- Almonds – 28 g
- Almond milk – 1 tbsp.
- Water – 1 tbsp.
- Ice – 3-4 pieces
Dish 3: Steak with tomato and bean salad
- Steak (grilled flank steak) – 170 g
- Tomatoes – 1
- Half a cucumber (sliced)
- Chickpeas – 1 tbsp.
- Olive oil – 1 tbsp. l.
Meal 4: Post-Workout Snack
- Chicken meat – 170 g
- Quinoa – 1/3 tbsp.
- Walnuts – 2 tbsp. l.
- Raisins – 2 tbsp. l.
Dish 6: White fish with yams and parmesan
- Tilapia – 170 g
- Parmesan cheese – 2 tbsp. l.
- Yams – 2 (medium size)
- Butter – 1 tbsp. l.
- Broccoli – 1 tbsp.
- Egg white substitutes: 2 slices turkey bacon, 2 small chicken sausages, 2 slices Canadian bacon or 1/4 cup. canned salmon
- Shallots can be replaced: 2 tbsp. l. salsa, 1/4 tbsp. chopped onion, or 2 tbsp. l. chopped sun-dried tomatoes.
- Blueberry alternative: 3/4 cup. frozen mango
- Instead of chicken fillet: 170 g pork tenderloin, 141 g buffalo ribeye, 141 g beef upper thigh
- Quinoa analogue: 1/3 tbsp. couscous, 1/4 tbsp. brown or black rice
- Substitution for tilapia: 141 g tuna steak, 198 g cod, 170 g shrimp
- Yams are replaced: 1/3 tbsp. agaric, wheat or pearl barley
The concept of “proper nutrition” for an athlete means eating exclusively those foods that contribute to the growth of muscle tissue. But it is better to exclude other foods that have little benefit from the diet. These products include carbonated drinks, sweet foods, baked goods, as well as unhealthy, fatty and fried foods.
Food purchased at markets is truly healthy, since it has not been subjected to special treatments that deprive the food of vitamins and microelements. In addition, they do not fry foods, but steam them, grill them, etc., without adding animal fats.
Increasing the number of calories
It is necessary to increase the caloric intake exclusively according to the above method.
As a rule, after increasing the number of calories, fat begins to be deposited. Subsequent actions may be as follows.
First of all, you should avoid increasing the number of calories, although there is another option proposed by Lane Norton. Its essence is to add not 300 kcal every two weeks, but only 50.
These calories will be burned throughout each day, but after a couple of months the body will begin to receive a sufficient amount of calories, which will lead to an increase in the required body weight.
This amount of calories should be distributed over 3-4 doses, consuming them every 4 hours. The task can be simplified if you make the portions the same in volume, with the exception of the portion that is taken immediately after training. This portion should contain about 20% more calories than other portions.
Well, now it’s time to figure out the type of calories that are best consumed.
Squirrels
Proteins should be consumed at the rate of 1.5-2 g per 1 kg of human body weight during the first 6 weeks. This amount differs from that consumed by some bodybuilders to a lesser extent. The most important thing here is to eat only high-quality products.
Some athletes believe that this is not enough, but studies show that when taking 1.5 g of protein per 1 kg of body weight, muscle volume increases. Each serving should contain at least 30 grams of protein, which is found in a variety of sources.
For example:
- in chicken thighs;
- in chicken breasts;
- in turkey breasts;
- in salmon;
- in mussels;
- in tuna;
- in shrimp;
- in lean beef;
- in pork tenderloin;
- in chicken sausages;
- in turkey bacon;
- in eggs;
- in whey protein;
- in casein protein;
- in Greek yogurt;
- in the curd mass.
Fats
You should only consume dietary fat, which has a number of functions. First of all, it is a form of concentrated energy. Some fats affect the secretion of hormones. To maintain a healthy body and ensure growth in the first 6 weeks of intense exercise, it is necessary to consume the optimal amount of fat.
After determining the basic level of calories, you need to decide on the consumption of fats, which should occupy up to 30% of the total diet. As your training intensity increases, this percentage will increase. When increasing caloric intake by 300 kcal, the fat level should be about 150 kcal. The energy value of 1 g of fat is about 9 kcal, therefore, each time you add 300 kcal to the diet, you should add 15-17 g of fat. If the diet increases by 50 kcal, then 5 g of fat should be added.
Fat intake depends on carbohydrate intake, compared to protein intake, which has a constant component. If you eat foods rich in carbohydrates, then the amount of fat should be reduced and vice versa.
There are 3 main types of fats: polyunsaturated, monounsaturated and saturated. A more optimal option is when all types of fats are consumed, rather than just one. Sources of healthy fats include:
- olive oil;
- canola oil;
- almond;
- avocado;
- pistachios;
- walnuts;
- macadamia nuts;
- linseed oil;
- butter;
- Coconut oil;
- cheese.
Carbohydrates
This last component leads to some confusion. To understand this problem, it is better to divide carbohydrates into 2 groups.
Starchy carbohydrates
Starchy carbohydrates that are quickly absorbed by the body and contain a sufficient amount of calories and include:
- regular potatoes;
- sweet potato;
- quinoa;
- white and brown rice;
- sprouted grain bread;
- tortilla;
- kamut.
Fruits and vegetables
They contain fiber, which is somewhat more difficult to digest. Fruits and vegetables are lower in calories and contain fewer carbohydrates. Legumes can also be included in this group.
The following group can include the following products:
- blueberries;
- raspberries;
- strawberries;
- apples;
- oranges;
- pears;
- spinach;
- cabbage;
- broccoli;
- cucumbers;
- pepper;
- Brussels sprouts;
- lettuce leaves and greens;
- green beans;
- carrots;
- green onions;
- mushrooms;
- bulb onions;
- tomatoes;
- lentils;
- black beans;
- beans;
- chickpeas
The only challenge is to use these products correctly. There are a number of recommendations that will help you do this, for example:
- Fruits and vegetables should be consumed with every meal.
- It is better to eat starchy carbohydrates in the morning and after training.
- When you eat few starchy carbohydrates, you need to introduce more fats, as well as fruits and vegetables, into your diet.
At the same time, the amount of protein will be at the same level, and the remaining calories are distributed between fats and carbohydrates.
The energy value of 1 g of carbohydrates is about 4 calories, therefore, increasing the calorie content of food by 300 kcal, it is necessary to add about 35-40 g of carbohydrates. When just 50 kcal are added, that's about 12 grams of carbohydrates.
Proper nutrition in bodybuilding, or preparing food for the whole day
Nutrition for the Beginner Bodybuilder
Now you know how to prioritize and distribute calories and nutrients in your diet. Now let's calculate an approximate nutrition plan using an example.
No widgets added. Why doesn't it turn out like in the picture? It turns out that this is only halfway. Where did she come from? It turns out that to work with heavy weights, you need a lot of strength, and to work with very heavy weights, you need a lot of strength. When the required mass has been gained, the athlete reduces the amount of energy consumed, reduces the amount of strength training and adds more cardio training.
They allow you to burn more fat.
Not only beginners, but also professionals may not immediately choose the right nutrition for a bodybuilder to achieve great shape. Below, the proposed fundamental principles of menu design in bodybuilding will take you to the level of a professional. If you want to build muscle, lose fat, or get in shape, you will need a specific nutrition strategy, which will depend on your chosen goal.
It is also important to drink plenty of fluids to effectively remove waste products. To ensure the body works, it must receive a sufficient amount of carbohydrates
Moreover, their quantity should cover energy consumption with a slight deficit. This will allow you to effectively lose weight without harm to your health, this is what is called: nutrition for bodybuilders: diet for losing weight and muscles.
Proteins will predominate in the diet, but fats and carbohydrates should be in the minority. This will provoke weight loss. But the problem is that muscle tissue is easier to break down than fatty tissue and the body will inevitably lose the muscles built up with such hard work.
Proper nutrition for a bodybuilder
To avoid this, they need to be regularly exercised and their metabolism stimulated. Therefore, mass training is replaced by endurance training and cardio training. After this stage, subject to the rules, the thickness of the fat layer will become noticeably smaller, and the muscles will be much more prominent.
But not everyone is able to properly organize and calculate the menu. This is indeed a difficult task, requiring knowledge in the field of dietetics and sports nutrition, but there is a solution.
These companies specialize in preparing and delivering meals tailored to athletes of various sports.
For example, the Grow Food company offers a menu for weight gain, cutting and functional training, as well as simply two options for balanced diets.
Bodybuilding is a fairly popular sport among men and women and is a process of body modification by increasing the hypertrophy of muscles in general, and individual muscle groups in particular, as well as the formation of body relief by reducing subcutaneous fat. We do not consider issues of the training process; these issues are covered on specialized web resources with videos and in specialized literature. It is generally accepted that diet for bodybuilders, along with strength training, is the basis of bodybuilding. Moreover, it is a properly selected diet when training in the gym that allows you to solve specific problems that athletes face - gaining muscle mass, increasing strength, burning subcutaneous fat. Generally speaking, the main nutritional goals for bodybuilders are:.
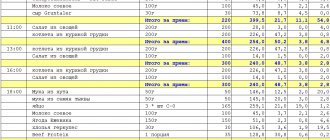
Let's look at the menu for drying. It is implemented for 5 and 7-day meals.
Stick to your meal plan[edit | edit code]
For this entire system to work effectively, you must strictly follow your strength nutrition diet. Add your favorite foods to your diet. Use the sample menus presented in Chapters 12–15 to create your own personalized meal plan. If you don't like the foods suggested, you won't be able to follow this plan. If you take liquid supplements, try different brands and flavors to find the right products for you.
Listen to your body and adjust your diet to the time when you usually feel hungry. You may prefer to vary your meal times rather than sticking to a set schedule. But also remember your actual food and drink needs; Sometimes we confuse the feeling of thirst with the feeling of hunger. Wherever you go, try to always keep some kind of drink and something to eat on hand. Most successful strength athletes carry a backpack full of food and drinks with them everywhere they go. This way, they will always be able to stick to their eating schedule. And if they get hungry, they won't be dependent on vending machines or other quick food sources that are high in fat and sodium.
When you are trying to lose fat, you may have difficulty visiting restaurants and especially traveling. If you do find yourself in this situation, try to find a restaurant that specializes in healthy eating and can easily accommodate your custom order. But don’t forget to ask for the recipe for the dish. Menu descriptions of items may be incomplete or inaccurate. You can even order food not listed on the menu - restaurants like this should probably accommodate your requests.
Remember to always calculate the number of calories you need based on your current weight. If you gained weight during the muscle-building phase and now want to lose those extra pounds, start with your current weight.
No one will do this for you. You know that in order to become fit and strong, you have to work hard on your body. Your muscles also need nutrition to grow. Plan your diet and stick to it constantly. You will be shocked by your excellent health and appearance and also by your athletic results.
Take a break
Every bodybuilder has experienced this at one time or another: your schedule is so busy that you miss a couple of workouts in a row. To your great surprise, you are not losing weight, but seem to be growing. Why? Recovery!
Taking time off, along with adequate nutrition, allows the body to overcompensate and recover more fully from recent workouts. The same applies to nutrition.
It is recommended to have a cheat meal every 10-14 days and eat, in addition to what you usually eat, some foods that are not included in a typical bodybuilder's menu: ice cream, cakes, fatty cuts of steak, pizza, fried foods.
Should you overdo it? Absolutely not.
But taking one day and switching to fattier cut steak, eating a few muffins at dinner and ice cream for dessert won't hurt. Having a cheat day actually helps in terms of muscle growth. Of course, the next day you will need to return to a cleaner diet.
Take that, Atkins!
Clearly, carbohydrates are a big part of Jay Cutler's off-season diet. He eats about 200g at breakfast and at least 300g after training. If there are two workouts per day, then after the second one, 200-250 g of carbohydrates are also provided. Bodybuilders knew about the "secret" of weight control with carbohydrates long before the general public began buying low-carb foods. An ordinary person would have been treated for obesity long ago if he ate such a huge amount of carbohydrates. But don't forget: Jay trains hard - sometimes twice a day, not counting cardio training. In addition, one should take into account the huge amount of muscle already built, which turns his body into a perpetual fat-burning engine. Thanks to them, metabolism and fat burning continue even during rest. It seems that Jay, even just sitting on the couch, processes more calories than the average person does during a daily run.