How to eat and not get fat? Lose weight or gain weight? Speed up metabolism? Get rid of gastrointestinal diseases and just be healthy? KBJU answers all these questions. This article will tell you how to calculate KBZHU - the daily intake of calories and nutrients.
What is KBJU? This is an abbreviation for the words calories, proteins, fats, carbohydrates. The system seems like a rebus. (At first glance, this is so.) But having solved it, you get the key to a healthy, harmonious body.
You need to count KBZHU to maintain body weight at the desired level with the help of a balanced diet. This system is universal. It is suitable for both those who want to lose weight and those who cannot gain weight.
This is not a diet, but a lifestyle, a discipline. There are other similar nutritional systems, but most of them are based only on calorie counting without taking into account the correct ratio of nutrients.
What data is needed for calculations
Do not use other people’s calculations; calculate the daily norm of KBJU specifically for yourself. You will need the following data:
- age;
- floor;
- lifestyle (sedentary, active, heavy physical activity, etc.);
- metabolism;
- Goal: lose weight, gain weight, maintain body weight.
How to calculate KBJU once? It is impossible to calculate the norm of KBZHU and use it all your life. The initial data will change and the norm will change along with it. Carry out calculations at least once a year, the success of the final goal depends on it.
You Will Need More Protein If...
Older adults can also include protein in their diet. As we age, our body produces less protein. Over time, a lack of protein can lead to decreased muscle strength, as well as loss of muscle mass and strength. Exercising and eating at least 1.2 grams of protein per kg of body weight will help you stay toned even into your golden years.
Vegetarians and vegans should also consider the amount and type of protein in their diet. Besides soy and quinoa, vegetarian and vegan sources of protein are considered incomplete because they do not contain all nine amino acids needed for protein synthesis.
By consuming 1.5-2.0 grams of protein per kg of body weight along with an expanded diet that includes legumes and grains, vegans and vegetarians will be able to obtain sufficient amino acids for muscle growth and repair.
You may have heard that consuming too much protein can lead to kidney damage, kidney failure, or osteoporosis. In fact, there is no evidence that increased protein intake can have a negative impact on human health.
How to calculate calories correctly
First of all, the metabolic rate is determined. Men count according to their formula, women - according to theirs.
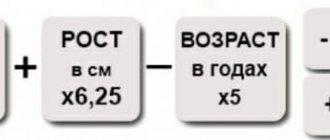
- Men : Metabolic value = weight in kilograms X 9.9 + height in centimeters X 6.25 – number of years X 4.92 + 5
- Women : Metabolic value = weight in kilograms X 9.9 + height in centimeters X 6.25 – number of years X 4.92 – 161
The result will show the number of calories needed per day without physical activity. But you will find out your norm by multiplying the result by the activity coefficient:
- 1.2 (zero activity);
- 1.4 (classes in the gym 2 times/week);
- 1.46 (4-5 workouts/week or active work);
- 1.55 (workouts up to 6 times/week);
- 1.63 (daily training);
- 1.72 (2 daily workouts);
- 1.9 (high-intensity training, heavy physical labor).
So now you know your normal. But this is the number of calories you need to consume to keep your weight at the same level. Therefore, if you want to lose weight or gain weight, when calculating the KBJU, reduce or increase calories by 10%.
In any case, we recommend not to force yourself into strict limits. At first, when eating according to this system, it is better not to cut calories or add 10% of calories to the diet so that the body gradually gets used to the new norm. This will help avoid health problems and prevent you from gaining extra pounds in the future.
What is the best time of day to consume protein?
Bodybuilders are still trying to establish the optimal time to consume protein. Should you take it before, during or after a workout? Should it be consumed daily before or after meals? What is important here is the amount of protein consumed per day, and not the time of its consumption.
Whether it's an omelet in the morning, a protein shake after a workout, or cottage cheese before bed, your priority should always be the daily requirement mentioned above.
The rate of muscle protein synthesis remains elevated for 3-5 hours after protein consumption. By consuming about 20 grams of protein 3-4 times a day, you stimulate protein synthesis while simultaneously promoting protein breakdown. Research has shown that consuming more than 20 grams of protein per meal does not provide any real benefit.
However, this doesn't mean that consuming more protein is a complete waste. While extra protein won't speed up protein synthesis, it can minimize muscle breakdown and also be stored in your amino acid store for later use or serve as an energy source during long, intense workouts.
We calculate the norm of proteins, fats and carbohydrates
Calculations are made to maintain the balance of nutrients. Again, the ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates specifically in your case depends on the result you are achieving.
BJU ratio for weight loss
- Carbohydrates - 40%
- Proteins - 30%
- Fats - 30%
The given percentage is considered ideal for weight loss.
BZHU ratio for weight gain
- Carbohydrates - 45-55%
- Proteins - 30-35%
- Fats - 25-30%
When calculating, keep in mind that:
1 g protein = 4 kcal
1 g fat = 9 kcal
1 g carbohydrates = 4 kcal
Daily Protein Recommendations
Governments in many countries have set their daily protein intake standards, as well as vitamins, minerals, fiber, fats and carbohydrates.
For the average person, the daily value of protein is 0.8 grams per 1 kilogram of body weight, but this figure increases with increasing activity level.
For most people, this norm is not enough. If you run or go to the gym, you will need more than the average to speed up the muscle recovery process. Almost all studies show that an athlete, unlike the average person, needs to consume twice as much protein.
There are different recommendations for daily protein intake. Often this norm per unit of body weight is overestimated. The more intense your workouts, the higher your protein intake should be within the above range.
For more active people, increasing the daily protein intake promotes tissue repair and replenishes the amino acids needed for intense activity. Strength training not only increases muscle protein synthesis, thereby stimulating muscle growth, but it also breaks down muscle tissue, especially when you exercise in a fasted state, because you break down more protein than your body produces. Eating protein post-workout promotes a balance between muscle breakdown and growth. Separately, the amino acid leucine stimulates the influx of cells responsible for muscle growth.
And a few more tips
- No matter what your calculations are, eat at least 35 grams of fat daily.
- Complex carbohydrates - yes, simple - no.
- As a result of calculations, your protein intake should fit into the gold standard - from 0.7 to 1.3 g per 1 kg of weight. However, focus not only on these numbers, but also on yourself. If there are a lot of muscles in your body, then they consume more protein, so feel free to increase it to 1.5 g. Conversely, if you do not play sports and do not plan to be physically active, then 0.7-1 g will be enough.
If you have been counting and counting and nothing has worked out, you are confused or want to check your result, use online calculators on the Internet, applications and programs for smartphones. Some of them are free.
Now you know how to calculate the KBJU and will definitely achieve your goals!
Characteristics of BZHU and list of products
All that remains is to talk separately about proteins, fats and carbohydrates and figure out which products contain them. This is necessary to create a menu with the correct ratio of these macronutrients.
Squirrels
Proteins perform many functions in the human body: build new cells (including blood vessels, hair, muscles), carry oxygen to all tissues, strengthen the immune system, balance hormonal levels, etc.
The daily protein intake will depend on many factors: age, gender, weight, height, level of physical activity. On average, it is believed that a person needs about 1.5 g of protein per 1 kg of weight per day.
You can determine the exact number by calculating your body mass index (BMI):
BMI = weight (kg) / height² (m)
For example, for a girl weighing 60 kg and height 177 cm, BMI = 60 / 1.77² = 19.15.
Now you need to refer to the table, which shows the protein requirements per day (in grams) for women and men, depending on height and BMI.
| BMI | Height (cm) - women | Height (cm) - men | ||||||
| 147-153 | 154-163 | 164-173 | 174-183 | 154-163 | 164-173 | 174-183 | 184-193 | |
| 19 | 54 | 66 | 80 | 93 | 82 | 97 | 107 | 126 |
| 20 | 56 | 70 | 82 | 95 | 84 | 98 | 113 | 130 |
| 21 | 56 | 72 | 85 | 97 | 86 | 99 | 115 | 132 |
| 22 | 59 | 73 | 85 | 100 | 87 | 102 | 118 | 133 |
| 23 | 61 | 74 | 88 | 102 | 89 | 104 | 119 | 137 |
| 24 | 61 | 76 | 89 | 104 | 92 | 106 | 122 | 140 |
| 25 | 62 | 77 | 92 | 106 | 92 | 107 | 125 | 141 |
| 26 | 63 | 78 | 94 | 108 | 93 | 110 | 127 | 143 |
| 27 | 66 | 81 | 97 | 110 | 95 | 110 | 129 | 147 |
| 28 | 66 | 82 | 97 | 113 | 97 | 114 | 131 | 149 |
| 29 | 67 | 84 | 98 | 115 | 98 | 115 | 132 | 151 |
| 30 | 69 | 84 | 102 | 117 | 99 | 118 | 135 | 154 |
| 31 | 71 | 87 | 103 | 119 | 102 | 119 | 137 | 157 |
| 32 | 72 | 89 | 105 | 121 | 104 | 120 | 139 | 159 |
| 33 | 74 | 91 | 106 | 124 | 105 | 122 | 141 | 162 |
| 34 | 74 | 93 | 109 | 126 | 107 | 125 | 143 | 162 |
| 35 | 76 | 95 | 110 | 128 | 109 | 127 | 146 | 165 |
| 36 | 77 | 96 | 113 | 129 | 110 | 131 | 148 | 169 |
| 37 | 80 | 97 | 115 | 131 | 111 | 131 | 150 | 171 |
| 38 | 80 | 99 | 117 | 133 | 114 | 132 | 151 | 173 |
| 39 | 82 | 102 | 118 | 136 | 116 | 135 | 153 | 176 |
| 40 | 83 | 103 | 120 | 138 | 117 | 136 | 155 | 177 |
| 41 | 85 | 105 | 122 | 141 | 119 | 139 | 159 | 180 |
| 42 | 86 | 106 | 125 | 143 | 120 | 140 | 161 | 183 |
| 43 | 86 | 108 | 126 | 146 | 122 | 141 | 163 | 185 |
| 44 | 88 | 109 | 128 | 148 | 125 | 143 | 165 | 187 |
| 45 | 89 | 111 | 130 | 150 | 127 | 146 | 168 | 191 |
There is another way to determine the daily protein requirement: depending on gender, age and nature of work. The activity groups used are the same as above:
- I - knowledge workers;
- II - work involving light physical labor;
- III - work involving moderate labor;
- IV - work associated with heavy physical labor;
- V - workers engaged in very heavy physical labor.
| Labor category | Age group | Women | Men | ||
| Daily value of protein (g) | Including animal protein (g) | Daily value of protein (g) | Including animal protein (g) | ||
| I | 18-29 | 78 | 43 | 91 | 50 |
| 30-39 | 75 | 41 | 88 | 48 | |
| 40-59 | 72 | 40 | 83 | 46 | |
| II | 18-29 | 77 | 42 | 90 | 49 |
| 30-39 | 74 | 41 | 87 | 48 | |
| 40-59 | 70 | 39 | 82 | 45 | |
| III | 18-29 | 81 | 45 | 96 | 53 |
| 30-39 | 78 | 43 | 93 | 51 | |
| 40-59 | 75 | 41 | 88 | 48 | |
| IV | 18-29 | 87 | 48 | 102 | 56 |
| 30-39 | 84 | 46 | 99 | 54 | |
| 40-59 | 80 | 44 | 95 | 52 | |
| V | 18-29 | — | — | 118 | 65 |
| 30-39 | — | — | 113 | 62 | |
| 40-59 | — | — | 107 | 59 | |
It is also worth saying that the daily dose of protein per kilogram of weight will differ for athletes exercising to achieve different goals:
- for muscle building - 1.5-2 g;
- for weight loss - 2-2.2 g;
- for drying (reducing fat while maximizing muscle preservation) - more than 2.2 g.
List of protein products:
- meat and poultry (pork, beef, chicken, turkey, etc.);
- fish and seafood (tuna, salmon, shrimp, squid, etc.);
- eggs;
- dairy products (milk, cottage cheese, cheese, etc.);
- nuts (peanuts, walnuts, almonds and others);
- legumes (beans, chickpeas, lentils, chickpeas).
These are the main sources of protein. They must be included in your diet to have a good figure and good health.
Fats
Many people consider fats to be harmful to the body and try to completely eliminate them from their diet. But this is absolutely forbidden.
Fats are necessary for humans for thermoregulation, maintaining the stability of the cardiovascular system, strengthening hair and nails, and maintaining the health of the nervous system.
All fats can be divided into:
- saturated;
- unsaturated (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated);
- trans fats.
Saturated fats are found in butter, milk, meat, lard, etc. They can lead to weight gain if you overeat. But within reasonable limits they should be included in your diet.
Unsaturated fats are the healthiest for the human body. They contain essential fatty acids (Omega-3,6,9), which can only be obtained externally. Monounsaturated fats are found in olive and peanut oils, avocados, black olives, etc. Polyunsaturated fats are found in fatty fish, nuts, and seeds.
But trans fats should be avoided. They clog blood vessels and do not provide any benefit. Such fats are formed during deep-frying, frying in vegetable oils, etc.
In addition, all fats can be divided into animal (milk, cheese, egg yolks, fish, meat) and vegetable (oils, nuts, seeds).
The daily fat intake is about 30%. The need for this nutrient is approximately 1-1.5 g per kilogram of body weight, depending on body weight. Moreover, two-thirds of the daily dose should be animal fats, and one-third should be vegetable fats. Older people should adhere to a different ratio: 50% animal fats and 50% vegetable fats.