The word “gymnastics” appeared in Russian everyday life thanks to the Greeks. Translated, it means “to exercise”, “to train”. The peculiarity of this sport is that it is suitable not only for women, but also for men. The performances of gymnasts are a beautiful spectacle that fascinates with their dynamism and elegance.
One of the interesting areas of artistic gymnastics is gymnastics on the uneven bars, however, studying this issue in isolation from related ones will not allow us to form a proper understanding of the essence of this discipline.
Basics of artistic gymnastics
This discipline includes several sports areas, namely:
- Exercises on parallel bars. Women train on parallel bars of different heights, while men train on parallel bars. The women's program includes two-way rotations on both the top and bottom bars. The men's program includes dynamic and statistical exercises: swing movements, rotations, handstands.
- Freestyle program. Competitions are held on a special mat, on which athletes demonstrate combinations of several gymnastic elements: somersaults, splits, somersaults, handstands. Ligaments are performed at different paces, and it is not necessary to include all existing exercises in the program. In this direction, it is important to demonstrate a beautiful performance, working out the technique of each movement to the appropriate musical accompaniment.
- Jumping with support. The gymnast picks up speed on a special track, pushes off the apparatus with his hands, and from the bridge with his feet, and makes a jump. The judges evaluate how high and far the athlete jumped, whether he landed correctly, and the technique of performing the jump.
- Beam exercises (women only). Demonstration performance, including dynamic and static elements using a projectile. Gymnasts perform somersaults and other jumps, turns, splits, and runs. Experts evaluate agility, the ability to stand steadily on a log and maintain balance.
- Exercises with a horse (only for men). When performing, all parts of the apparatus must be used. Athletes stand on the apparatus on their hands, make swinging movements and rotations. Horse training requires a lot of effort and time, and is therefore considered difficult.
- Ring exercises (men only). The projectile consists of two movable wooden rings attached to special cables. Athletes perform twists, turns, lifts, thereby demonstrating considerable physical strength, as well as flexibility of the body.
- Barbell exercises (men only). The projectile is a steel rod, which is fixed at a height of just over 2.5 meters. During a demonstration performance, the gymnast must not touch the crossbar with his body. The judges evaluate different types of grips and the technique of transition from one grip to another.
The performances of the gymnasts are assessed by a panel of judges, which includes the chief judge and eight other experts responsible for a specific apparatus. Some judges evaluate the technique of execution, while others evaluate the complexity and presentation of exercises using a system from 1 to 10 points.
How to learn to do push-ups
You shouldn’t just jump right in, you need to start with the basics. It is important to understand which muscles work when doing dips. These are, of course, the pectoral muscles, delta and triceps.
The following exercises will help guide everyone to dips. Completing them will not be difficult!
Reverse push-ups
It is performed with support on a chair, with the body in a hanging position, the support is on the heel bone.
- As you inhale, bend your elbows until a right angle appears between them, and as you exhale, straighten your arms, returning to the starting position.
- You should do this exercise until you can do 3-4 sets of 10-15 repetitions.
- Then you can go to the next level - to the bars themselves!
Jumping dips
These are the so-called negative push-ups. They are easy to implement if you pay attention to the recommendations in the previous paragraph.
To do these push-ups, you need to jump, raising your body.
It is clear that when jumping you should hold onto the bars with your hands. After which you need to slowly lower yourself, then repeat the same thing.
Gymnastic parallel bars: features of the apparatus
The gymnastic beam consists of two poles of different heights, which are connected by special fastenings. The bars are made of wood and their diameter reaches 4 cm.
Everyone, young and old, trains on the parallel bars. This is due to the fact that the gymnast only has to cope with a load that does not exceed his own body weight. Hands must be well trained.
The width of the apparatus is always individual and must correspond to the age and physique of the athlete. Thus, the optimal width between parallel bars is considered to be a value that is slightly larger than the athlete’s shoulders. If you do not follow this rule and make the width smaller or larger, then there is a risk of uneven distribution of the load (only on one muscle group) or even serious injury. Before classes, you should always tighten and adjust the apparatus so that it does not swing. The result of such preparation will be a comfortable and useful training for physical development.
The main mistake of beginning gymnasts is that when performing exercises on the poles, they train only a specific muscle group. This is incorrect, since a gymnastic bar is not a horizontal bar: the load should be distributed evenly across all muscle groups. This is why warming up is so important before starting a lesson.
Training for beginners
If you're just starting to build muscle, parallel bars are a great push-up tool for all bench exercises like the bench press, dumbbell press, etc.
- If classic push-ups from the floor are not easy for a beginner, then start doing push-ups from your knees, or put your hands on a raised surface. Thus, the load on the muscles will be less.
- Once you have mastered the classic push-up and built up enough strength, then you can confidently step onto the platform and begin lifting the bars. If you have done a few repetitions, even with difficulty, then you have already won. Either way, don't be embarrassed to do a few reps with shaky hands.
- If a beginner cannot do one repetition on an instrument, this is, of course, sad, but not critical. You should not rush to widely advertised steroids. There is another way out of this situation: you need to start with simple push-ups. It is better to do fewer push-ups, but in more sets.
- Perform several sets once or twice, increasing the number over time.
Many aspiring bodybuilders went through this parallel bars training program when they were small and weak.
Projectile evolution
In the middle of the last century, the distance between the poles was very small. This prevented athletes from performing complex elements and even compositions of several simple exercises on the beam. Only by the beginning of the 70s the distance between the crossbars was increased by using a new method of attaching the poles (stretching method). This way the gymnasts were able to show a greater range of skills. But the evolution of the projectile did not end there. In the 80s of the 20th century, the decision of the international federation established that the poles should be spaced even further apart. This innovation had several advantages:
- the ability to perform high speeds;
- use of male exercise techniques;
- complicated flights from one pole to another;
- the exercise techniques have become as complex as with the bars for men.
However, there were also negative sides. In particular, some elements disappeared from the athletes’ arsenal, since they became impossible to perform with such a width of the poles.
What are the benefits of gymnastic bars?
Constant training with the use of such a projectile contributes to better pumping of the upper muscle corset and correction of posture. Also, gymnasts, performing exercises on the uneven bars, form the abs and beautiful shape of the buttocks.
But it is very important to do everything correctly. The pace and number of approaches do not play a major role. Athletes work on the purity of the technique of performing movements and the depth of muscle development. This may sound paradoxical, but the slower the gymnast performs the exercise, the faster the result will appear and the body will become more defined.
Working muscles
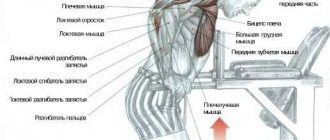
Bars are used for different types of movements and this determines which muscles are pumped during their execution.
We list the main ones:
- Push-ups work the chest, shoulders and triceps
Indirect load falls on the forearms, lats, abs and small stabilizer muscles of the torso.
- Australian or horizontal pull-ups activate the lats, biceps and forearms
The trapezius (back, back), shoulders and abs are indirectly loaded.
- Leg raises engage the rectus abdominis, while lateral raises focus on the obliques.
In static mode, the forearms, triceps and shoulders work.
In fact, with the help of different movements on one apparatus, the main muscle groups of the upper body are pumped - chest, shoulders, triceps. As well as biceps, lats, trapezius and abs.
Classification
Depending on the installation location, the beams are divided into street and home. What are the differences?
- at the installation site;
- in design;
- in appearance.
Street beams are dug into the ground. These are 4 vertical posts on which crossbars about 2.5 meters long are located. The distance between the posts is from 1.4 to 1.5 meters. The height of the structure should be no more than 2.5 meters. Some outdoor versions of the bars have two additional poles.
Equipment for indoors (at home or gym) differs in appearance from outdoor ones only in the lower bars that connect the racks. They are needed for stability, because a home projectile cannot be dug into the ground. The slats are parallel. Beginner bars are made entirely of steel. They may vary in size as they are not intended for professionals. Experienced athletes train on standard-sized equipment. These bars have a steel frame and a carbon fiber pole. These structures are attached to the floor with guy wires.
There are options for wall bars: stationary, removable, folding. These are two pipes installed at a distance of about half a meter from each other. They can be adjusted in width, which makes them universal for both beginners and pros (the latter have a large muscle corset). The bars are equipped with handles and soft cushions. All this contributes to the safe and comfortable performance of gymnastic exercises. However, not every room can accommodate such a projectile. Usually it is bolted only to a brick or concrete wall. An undoubted advantage is the ability to secure the bars at any height.
For those athletes whose premises do not have enough space to install a simulator, corner bars are provided (attached to two walls) or removable. The latter are attached to the wall bars with special hooks. They are convenient to store and transport.
Main characteristics of beams for the home and tips for selecting them
Home exercise equipment can vary significantly in length, height, and size (portability). These criteria are important for any projectile. In order to perform basic exercises on the beam, you need a sufficient length of the structure. To correctly determine it, it is necessary that the arm from the hand to the elbow fits freely into the distance between the handle and the base of the simulator. Manufacturers of home parallel bars claim that they are designed more for strength exercises than for gymnastics.
Another factor that you should pay attention to when choosing beams is height. So, when purchasing a home equipment, you should give preference to those designs that are height adjustable. This way you can adjust the projectile to your own height. And if two people systematically train on the simulator, then the height is selected individually for each athlete.
For people who, due to necessity, often transport beams, another important parameter is the possibility of trouble-free transportation. In this case, you should give preference to compact models - they do not have to be assembled and dismantled from scratch every time. The downside is that small beams cannot withstand heavy loads.
So, what is important to consider when buying gymnastics bars for home workouts?
- Material. It is better not to skimp on it, otherwise the simulator will not last for a long time. You only need to buy shells made of steel, not alloys. The crossbars should be well polished, with an anti-slip coating.
- Reliability of fastening. Exercises are safe only if the structure is strong and securely fixed.
- The weight that the projectile can support. If you plan to use additional weight-bearing equipment when performing strength training, this should also be taken into account.
- For beginner gymnasts, you can choose simpler models. Professionals use bars of standard sizes, which are more reliable and allow for all sorts of combinations.
- Price. In order not to buy parallel bars for each type of training, it is better to give preference to multifunctional exercise machines. The cost of any timber depends not only on the manufacturer, but also on the functionality and design features.
Home equipment will help the athlete keep in shape outside the gym.
Techniques for working out different muscle groups
- If the body is straight and the legs are straight when lifting, the weight falls on the triceps.
- If the elbows are turned to the side, the pressure shifts to the pectoral muscles.
- Compound exercises are always more effective for gaining mass and increasing strength. Parallel bars work the muscles of the upper body: pectoral muscles, triceps and deltoids. The load can be adjusted by the tilt of the body, the position of the arms and the distance between the “crossbars”.
- If you press your elbows as close to your body as possible, the load will be transferred to the triceps.
- When the body leans forward, all the weight falls on the chest. For maximum effect, bend your knees
Structural groups of elements on bars
All combinations begin with attacks. They are divided into simple and complex. Examples of jumps: hanging on one pole, somersault, jump into a handstand.
Groups of elements can then be executed in any order:
- back swing turns;
- "jumpers";
- big turns;
- stands;
- revs in the rack.
The first group includes standing jumps (with or without rotation), somersaults from the lower to the upper pole, and Comaneci somersaults. “Jumping” in professional jargon refers to revolutions without touching. This class of elements is performed on one crossbar or with their change, for example, Shaposhnikova’s flight. This also includes hangs and supports.
Elements with a large swing are performed back and forth with incomplete rotation. They can be performed on only one pole or on two with a flight. “Stalders” are rotations with swings, which are performed from a bent-over hanging position, transitioning to a handstand.
The last group of elements is quite extensive. Includes rotations while standing, with emphasis on the stomach, with or without swings. Even famous athletes with world titles rarely perform rear hanging exercises.
Any combination ends in dismounts. This class includes spins, somersaults, arcing and stall jumps. The element is complicated by a flip or counter-rotation.
World champions in parallel bars
- 1954 - Agnes Keleti, Hungary 1958 - Larisa Latynina, USSR 1962 - Irina Pervushina, USSR 1966 - Natalya Kuchinskaya, USSR 1970 - Karin Janz, East Germany 1974 - Anne-Laure Zinke, East Germany 1978 - Patricia Frederick, USA 1979 - Maxi Gnauk, East Germany 1981 - Maxi Gnauk, GDR 1983 - Maxi Gnauk, GDR 1985 - G. Feinreich, GDR 1987 - D. Silivas, Romania and D. Thümmler, GDR 1989 - Fan Di, China 1991 - Kim Gwan Suk, DPR 1993 - Shannon Miller, USA 1994 - Lu Li, China 1995 - Svetlana Khorkina, Russia 1997 - Svetlana Khorkina, Russia 1999 - Svetlana Khorkina, Russia 2001 - Svetlana Khorkina, Russia 2003 - Holly Wiese and Chelsea Memmel, both USA 2005 - Nastya Liukina, USA 2006 - Elisabette Tweddle, Great Britain 2007 — Ksenia Semyonova, Russia 2009 — Hyo Kesin, China 2010 — Elisabette Tweddle, Great Britain
Get text
The evolution of gymnasts' combinations on uneven bars
In the 50s of the last century, combinations were simple and low-dynamic. This was due to the fact that the poles were located close to each other. After 10 years, the distance between them increased, which provided gymnasts with more opportunities to show their abilities. The arsenal of elements has been expanded 2-3 times, and the combinations have become more complex. The pauses between parallel bars exercises disappeared, and the athletes moved continuously during their performances. New achievements of this period are the mastery of the transition from the lower pole to the upper one, the adjustment. Changes have also occurred in the dismounts: now it is a forward arc from a standing rotation.
But the development of gymnastics did not end there. In the 70s, a very complex element appeared - the “Korbut Loop”. It is a downward somersault from a rack on the top pole to a hanging position on the same crossbar. This exercise was subsequently banned due to the increased risk of injury. Another innovation is the “Radokhly Somersault”, which is performed with your back to the top pole. Over time, athletes began to perform handstands on uneven bars, which served as another impetus for the development of gymnastics. Exercises with the flight phase have also undergone changes for the better: the rotation in the training began to reach degrees. The girls tried to perform all the elements through a handstand, and the small distance between the poles made the task more difficult.
Since the 80s, the width between the crossbars has become even greater. Since then, girls began to perform handstands not only on the top, but also on the bottom pole. Increasingly often in the gymnasts' program there was a turn without touching in the rack. The champions began to master the most complex elements that other athletes had adopted. For example, Tkachev’s flight became the norm in a demonstration performance within a couple of years. Yeager and Delchev somersaults became mandatory exercises. Female athletes tried to adopt male techniques used on the bars, especially for dismounts. During this period, not many new elements appeared, but the quality of existing ones became better. Pounces and elements with changing poles (for example, Pak somersault) have become more difficult.
In the 90s, the uneven bars discipline continued to develop at a rapid pace. This was facilitated by the fact that the poles were spread even further. Another innovation made it possible to work on elements that were performed in a big swing. In combinations, they began to pay attention to the combinations of exercises with each other, even if these were simple transitions. Svetlana Khorkina showed good results, using several combinations at once during her performances. All outstanding gymnasts had two flight phases in their program. The dismounts became more difficult, and now this somersault was performed with a backward tuck with a 360-degree turn.
Recommendations for training
Bars are a fairly simple sports equipment, but any exercise on it requires compliance with certain rules. They will help achieve the fastest possible progress in muscle development and reduce the risk of injury to zero.
Warm up before class
Before performing exercises, be sure to do a light warm-up. This is especially true for push-ups and pull-ups. These movements put a lot of stress on the fragile shoulder and elbow joints and ligaments.
Attempts to exercise on unheated muscles, as a rule, end in an unpleasant injury.
So don't skip the warm-up. It is your guarantee of athletic longevity and rapid muscle growth.
Perform several swinging or rotating movements for each muscle group. Also add some light dynamic stretching without too much pressure. The whole process takes from 5 to 10 minutes .
Load change
Muscles adapt very quickly to strength training. They get used to the same type of load in just 2-3 weeks, and this leads to a significant slowdown, and then to a complete stop of progress.
To prevent this type of addiction, regularly challenge yourself . This is done in different ways:
- increasing the number of exercises per muscle, approaches and repetitions
- weight gain
- reducing rest pauses between approaches, etc.
Another way to vary the load when doing dips is using loop fitness bands. For example, expanders or elastic bands.
If the tourniquet is secured to the handles so that the middle of the rubber hangs down, you can place straight legs or knees on it (depending on the length of the rubber), making it easier to perform. The rubber will help push your torso up.
This option is suitable for beginners with a low level of physical fitness or for beginner girls.
If you fasten the edges of the tourniquet to the handles, or another stop at the bottom, and throw the middle over your shoulders, you will have the opposite effect.
In the bottom position, the movement is performed as usual. But the higher the body rises, the more resistance will have to be overcome due to the tension of the rubber. And the more muscle effort you will have to apply.
This method is suitable for well-trained men for whom regular dips become too easy.
Rest between sets and workouts
Depending on your goals, rest between sets and workouts will differ.
When exercising to increase muscle mass and strength, do it no more than 2 times a week.
Remember that muscles grow during the rest period between workouts. And if the load is too frequent, they will not have time to recover, and therefore increase their volume.
Mass training involves the use of heavy and medium additional weights. Therefore, during this period, rest pauses are 2-3 minutes.
If you are a beginner athlete, progress in muscle growth will come from minor loads. At first, they hone the movement technique. Only when the athlete performs 15 or more push-ups without much effort is additional weight used.
When training on relief, exercises on the uneven bars are performed up to 3 times a week.
Here they mainly use their own body weight, without additional weights. Therefore, they try to reduce the pauses between approaches to a minimum (30-60 seconds).
When training for strength endurance, flexibility and coordination, train exclusively with your own weight. The frequency of classes for amateurs is 4-6 times a week.
Depending on the type of motor quality being developed, rest pauses range from 30 to 120 seconds.
About the role of technology
Like any other exercise, we try to do all movements on the uneven bars as correctly as possible, observing all the technical requirements for a specific exercise.
Only with the correct technique will you work the target muscles as much as possible and get the desired result in a minimum period of time without injury.
Competition rules for the uneven bars section
Gymnast competitions are held in six disciplines for men and four for women. Each athlete’s program consists of compulsory elements with the addition of optional ones.
Nature of the competition
All artistic gymnastics competitions in the uneven bars section are divided by nature into:
- Personal. Only the athlete’s personal achievements are taken into account.
- Team. A gymnast can represent his team and perform alone, but the jury gives a score not to him personally, but to all members of the group.
- Personal-team. Depending on the discipline and rules of the competition, both personal and team achievements influence the final result.
Competitions are also divided into:
- classification;
- non-classifying.
The difference is that the former are carried out according to general rules, following one program, while the latter are carried out under special conditions.
Introduction
Uneven bars
Uneven bars
- a sports equipment used in women's artistic gymnastics. For men, parallel bars are used. They are two poles of different heights. In essence, they are a double crossbar from men's gymnastics, connected to each other by special fastenings. The difference between the bars and the crossbar also lies in the diameter of the pole, and also in the fact that the pole is wooden, not steel.
- Height of the upper pole - 241 cm Height of the lower pole - 161 cm Diameter of the pole - 4 cm Length of the pole - 240 cm Diagonal distances between the poles: 130-180 cm
Graduation of athletes by age
In the uneven bars section of artistic gymnastics, the following age categories are distinguished:
- Children (6–8 years for girls, 7–10 years for boys);
- Girls up to 12 years old, and boys up to 13 years old;
- Juniors (14–17 years old for males, 13–15 years old for females);
- Adults (women over 16 years old, men over 18 years old).
In some cases, the age category for juniors and juniors is stated to be up to 25 years old. An athlete's career begins with the first youth sports category. You can become a master of sports in this area from the age of 14 for girls, and from 16 for boys.
Costume requirements
Athletes are required to perform in gymnastics costumes. For men, this is gymnastics tights and a T-shirt. Women perform in gymnastic leotards or overalls. At the request of the participant, the swimsuit can be with or without sleeves. It is allowed to wear leggings that match the color of the swimsuit.
For shoes, gymnasts wear socks or slippers. If athletes perform as a team, then their gymnastic costumes must be the same.
Judging system
The competition participants are assessed by a panel of judges (GC), which consists of the chief judge, judges of teams D and E, and assistant judges. The main panel of judges is formed by the federation that organizes the event.
The chief judge organizes the preparation of the competition site, equipment, reviews applications from athletes, and holds organizational meetings before the competition. He also checks how well trained doctors are, controls the availability of places for reporters, and prepares a report to the organization under whose auspices the event is being held. His deputy forms judicial teams and exercises control over them.
The chief secretary and his deputy are involved in drawing up documentation, checking protocols, and maintaining a table of gymnasts’ results. The secretary prepares lists of participants, issues them numbers, and contacts the press center.
Judging panel D consists of two people. They evaluate how difficult the gymnast performed an element and enter the final result into the computer. According to the rules, jury members have the right to deliberate among themselves. If they cannot come to a common opinion, they turn to the appeal commission for an independent assessment. The judges set certain requirements for the compositions and add points for connections.
Judging Panel E consists of five jury members. They are responsible for assessing artistry and identifying mistakes that were made by the gymnast while performing combinations, and keeping a record of all exercises. It is their scores that are the basis for summing up the final result.
Assistant judges are appointed during the draw. This group includes judges:
- timekeepers;
- those responsible for musical accompaniment;
- informants;
- with the participants.
It is worth noting that no less requirements are imposed on the selection of judges than on the participants. A judge may be rewarded for a job done competently, but if they perform their duties incompetently, they may be fined or even deprived of their judicial license.
Grading system
For each discipline in gymnastics, there are two grade options: D and E. The first is given for the content of the element being presented, and the second is for the overall composition, performance technique, and the ability to present oneself during a performance.
Judges evaluate participants using a ten-point system, with deductions and bonuses in the form of tenths of one point allowed. To arrive at the final score, the jury members add up the scores of the D and E judges and then apply deductions.
Federation
The International Gymnastics Federation (IFG) is the most important organization preparing global sporting events and developing performance rules. The Federation organizes competitions in several gymnastic disciplines, including uneven bars. It is worth noting a number of additional areas of work of the federation in addition to artistic gymnastics - these are rhythmic gymnastics, sports aerobics and acrobatics, trampolining.
The European Gymnastics Union was founded in the 80s of the last century, unites federations of European countries (48 organizations in total), and represents the interests of the states of this continent at international competitions. Engaged in the preparation of competitions in artistic and rhythmic gymnastics.
The Russian Artistic Gymnastics Federation was founded in 1991 and unites federations from more than 70 regions of Russia. The organization coordinates the development of this sport in our country, assists in creating conditions for the popularization and accessibility of artistic gymnastics among children and adolescents, and strengthens the prestige of our gymnasts on the world stage.
History of artistic gymnastics
In Ancient Greece, athletes performed various gymnastic exercises before participating in the Olympic Games. Due to such training before competitions, athletes developed not only strength and agility, but also endurance. However, over time, namely towards the end of the ancient era, this sport faded into the background. In the 15th century they remembered gymnastics, and oddly enough, it was the military. Many commanders were concerned with issues of physical training, and therefore, in the intervals between aggressive campaigns, the leadership forced the soldiers to do gymnastics.
However, these actions did not lead to a significant increase in the popularity of artistic gymnastics. The first tournaments in gymnastic disciplines took place at the beginning of the 19th century in Europe, and artistic gymnastics received the status of an Olympic discipline only in 1896. After 32 years, women's all-around competitions were held for the first time at the Olympic Games. Good results were shown mainly by athletes from France, Germany, Finland, the USA, and Italy.
World championships in this sport have been organized since 1903. Despite the fact that gymnastics is now associated with the public primarily as a women's sport, girls received the right to compete at championships only in 1934.
In our country, the history of artistic gymnastics began under Peter I. Commander Suvorov also trained his soldiers using gymnastic exercises. In the 19th century, the first courses in this discipline were opened in the capital, where those interested were trained for two years. Later, the Russian Gymnastics Society was formed, led by Vladimir Gilyarovsky. With money from community sponsors, the first gym was opened, which was located in Redlich’s house on Strastnoy Boulevard. This sports facility was equipped with all the equipment necessary and modern for that period.
The peak of popularity of artistic gymnastics occurred during the era of the Soviet Union. Sections and sports clubs opened throughout the country. Since 1933, various competitions began to be held regularly, at which both men and women showed their skills. Since the middle of the 20th century, the USSR Gymnastics Federation entered the international community, and in 1952 our compatriots took part in the Olympics for the first time.
Main exercises
Beginners often think that there is only one exercise on the parallel bars - push-ups. But in fact, this projectile is multifunctional, that is, a lot of other movements are performed on it.
Let's take, for example, performances in artistic gymnastics, where uneven bars exercises are one of the competitive disciplines. Or such a popular direction in sports as workout.
The elements performed on this apparatus amaze the imagination with their variety and complexity.
With the help of parallel bars in these disciplines, all motor qualities are developed - strength, strength endurance, flexibility, coordination and agility. As for the growth of muscle mass, here it is rather a pleasant “side effect”, and not the main goal of the exercise.
Bars are also widely used in the training process of bodybuilders. However, the main task here is to pump up the muscles.
A set of exercises on parallel bars in bodybuilding is characterized by relative ease and accessibility in technical execution.
Below is a list of exercises that are most applicable when training to develop muscle mass.
Push-ups for training the pectoral muscles
There are two main types of dips – pectoral and triceps.
Let’s immediately make a reservation that both techniques are aimed at developing the same muscles - chest, triceps and shoulders. The only difference is the emphasis of the load.
When doing push-ups for the pectoral muscles, wide bars (wider than the shoulders) and a large amplitude are used.
As the movement progresses, the elbows are spread to the sides to achieve better stretching of the chest muscles.
You can also tilt your body slightly forward. But this is more a matter of personal preference.
True, some bodybuilders claim that they know exactly how to pump up their pectoral muscles on the uneven bars as quickly as possible. To do this, they do not straighten their arms to the end at the top phase of the movement.
That is, the work occurs in two thirds of the trajectory - the lower and middle sections of the amplitude. This trick helps to engage the pectoral muscles to the maximum and minimize the load on the triceps.
Pumping up your chest on parallel bars using wide-grip push-ups is a must for men of entry-level and intermediate training. After all, this is one of the main basic exercises for the development of this muscle group. The main emphasis here is on working out its lower and middle parts.
The lower part of the pecs is quite easy to hypertrophy. That's why men love to use parallel bars in their workouts on a regular basis. But this exercise has one significant disadvantage:
If you do only dips for the pectoral muscles, then over time this will lead to the undesirable visual effect of sagging breasts, when the pumped lower part creates an imbalance in muscle development.
Therefore, over time, it is recommended to reduce the frequency of parallel bars training and devote more time and effort to developing the upper chest, which often lags behind.
In this way, balanced and harmonious proportions are achieved.
Push-ups with emphasis on triceps
Push-ups on narrow parallel bars will help you effectively work out your triceps on parallel bars.
This is one of the main basic movements for the triceps brachii muscle, which stimulates the growth of its muscle mass and strength.
To do this, use a grip approximately shoulder width apart. As the movement progresses, the elbows are pressed to the body , and the amplitude itself is limited to half the upper trajectory. That is, they lower down from straight arms to a right angle at the elbow joints.
This technique focuses on the triceps, with minimal involvement of the pecs.
Horizontal push-ups
Here classic push-ups are performed while lying down, only the emphasis is placed on the bars with hands and feet.
The movement is popular for representatives of workout, since it requires full-length long poles to perform it. Most gyms are equipped with gymnastic corners with short supports.
Horizontal push-ups work the same muscle groups as classic push-ups - chest, shoulders and triceps.
An unstable starting position further develops stabilizer muscles, as well as coordination and dexterity.
If you exercise outdoors, then this option will fit perfectly into your training program.
Walking with your hands
This parallel bars exercise is suitable for beginners who are not yet able to do full push-ups.
From the starting position in support on straight arms, they are moved forward and backward. You will see the equipment here.
Despite the ease of movement and simplicity in technical execution, this exercise quickly strengthens the arms and shoulders , gradually preparing the muscles for the classic push-ups.
Horizontal pull-ups
This exercise is also known as Australian Pull-Ups.
When performing it, the hands are placed on one pole, and the legs straight or bent at the knees are on the floor. Next, the torso is pulled up.
If the projectile is too high, stand in the same position between two crossbars, holding on to their bases. Then only a parallel grip is possible.
Australian pull-ups are available even to those who cannot perform classic pull-ups on the bar (both men and women). We can say that this is their simplified version.
As with regular pull-ups, it works the latissimus dorsi, dorsal trapezius, rear deltoid, biceps, and forearms. Indirect load falls on the abs and lower back.
Depending on the position of the hands and the type of grip, the emphasis shifts to different muscles :
- with a reverse grip shoulder-width apart (palms turned toward you), the biceps are activated more
- a direct grip (palms facing away from you) shoulder-width apart or wider more specifically loads the latissimus dorsi muscles
Exercises for the abs
Also on the apparatus they do various variations of leg or knee lifts to train the abdominal muscles.
There are two main methods of emphasis when pumping the press:
- On straight arms
- On the forearms
The emphasis on straight arms additionally involves the muscles of the shoulder girdle in a static mode.
This option is more common in artistic gymnastics. However, given the design of classic bars, there are no other methods available here.
Another thing is bodybuilding. In gyms there are horizontal bars with special soft supports for the forearms.
This position helps to pump up the abs more fully. Since very often fatigue of the arms, which are noticeably tense in static conditions, occurs much earlier than fatigue in the abdominal muscles.
In any case, when focusing on straight arms or bent at the elbows, the same movement is performed - raising the knees or straight legs up. The second option is suitable for more prepared athletes. In such movements, the rectus abdominis muscle is pumped.
Less popular is lifting straight legs up with extensions to the sides (legs are raised above the bars). Here, in addition to the straight line, the oblique abdominal muscles also actively work.
Books
There are few books about artistic gymnastics, but enough to highlight interesting publications worthy of attention.
- Author: Gaverdovsky Yu. “Gymnastic all-around.” This 1987 textbook remains one of the best today. It contains up-to-date information about exercises from both men's and women's disciplines. The publication is suitable not only for beginner gymnasts, but also for accomplished athletes. The training manual describes in detail the technique of performing the most complex gymnastic elements and their combinations. For clarity, the book contains diagrams and pictures.
- Author: Menkhin Yu. “Physical training in gymnastics.” Before competing at international competitions, an athlete goes through a long journey: he engages in grueling training and hones his skills in gymnastic elements. In this publication, the author describes in detail what you need to pay attention to when physically training gymnasts of one discipline or another. Menkhin examines in detail the issues of organizing training at home and in the gym.
- Author: Douglas G. "Raising the Bar." The two-time Olympic champion published a series of books in which she shared her own experience of participating in artistic gymnastics competitions. This is not a textbook, but a story about the behind-the-scenes life of an athlete, everyday training. The author not only talks about personal things, shares photographs, but also gives a lot of valuable advice on how to achieve your goals.
Bars are a spectacular, but at the same time difficult sport. The discipline requires the athlete to have excellent physical fitness and the ability to feel his body. As you know, to achieve good results in any sport, persistent regular training is necessary.