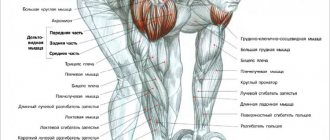
The half-squat, or half-amplitude squat, is an exercise that falls into the category of auxiliary. What is noteworthy is that many athletes categorically do not perceive it, calling it the offensive word “under-squats.” And completely in vain.
Despite its dubious reputation, the partial squat is actively used in weightlifting and powerlifting as an additional targeted exercise. It allows the athlete to target the upper phase of squats. Promotes better preparation of muscle tissue and ligaments for high loads, trains the quadriceps. Which in turn makes it possible to work with much larger weights in the future.
General recommendations for implementation
The workout works the lower body: legs and buttocks. But also pay close attention to the top one:
- tighten your stomach;
- straighten your back;
- look straight ahead.
Perform each exercise 10 times with minimal rest breaks.
No additional equipment needed. In fact, you don't even need a form. If your clothing does not restrict movement, you can perform this complex anywhere: at home, at work or on vacation.
Features of half squats
The half-amplitude squat is not used as a permanent training element. Since the technique of its implementation is not the safest and is inferior to other options in terms of effectiveness.
However, weightlifters often use this special exercise as a preparatory exercise. For them, this is a kind of method that allows them to accelerate in the moving phase of the push, accelerate and move the weight from a dead point.
Powerlifters also include half squats in their training programs. With their help, they manage to overcome the barrier (more psychological) to the increased load.
But in ordinary fitness or bodybuilding, a half-amplitude squat is quite a rare occurrence. As a rule, it is used only when an athlete faces problems with increasing strength indicators (progress stops, a stagnation phase begins). By the way, the ability of this exercise to quickly bring the athlete out of this state is its main advantage.
If the training program involves regularly lifting heavy weights aimed at building muscle mass, at a certain period the athlete will inevitably face a pressing problem - stagnation. The muscles get used to the given load (lifted weight) and stop growing. At this point, it would be appropriate to supplement your exercises with a half squat. This will not only diversify your training, but will also force sleeping muscles to awaken (start to grow again).
It works roughly like this. A half-amplitude squat sharply loads the muscles (more than usual), as it allows the athlete to lift more weight. His body, being in a state of stress because of this, receives a signal that next time it may not be able to cope with the increasing load. As a result, an intensive increase in muscle mass in the legs, back, and torso begins. Thus, the half squat is rightfully considered an effective way to get out of stagnation.
Please note that the full-range squat is not a simplified variation of the classic squat. Weightlifters perform it at an explosive, very intense pace. For powerlifters, this is a more dynamic version of the full squat, the technique of which does not allow for pauses at the top and bottom of the movement.
This exercise is performed with serious weights. Pulling light weights in a half squat is simply not practical. With a moderate load, it is much more practical and effective to do full squats. Accordingly, the risk of injury increases significantly. In addition, if we look at the anatomy, it is easy to understand that our knee joints, in principle, are not designed to work in such an amplitude, which is why the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee receives an excessively large load.
Since we touched on anatomy, it is worth noting one more nuance. Bodybuilders incorporate the half squat into their training regimens to target the quadriceps. But at the same time, they perform this exercise with their feet toes forward. Which, again, is not very consistent with the structural features of the human body.
Common mistakes
If doing squats doesn't give you the results you want, you're doing something wrong. Below is a short list of the most common mistakes that are common to most novice athletes:
Incorrect range of motion
Only deep squats give a truly serious effect. If you don't even go down to parallel level with the floor, then don't expect results. At the lowest point, the back of the thigh should touch the calf muscles
Not all athletes can do this right away due to weak stretching, so do not forget to stretch after training, special attention should be paid to the quadriceps and hip adductors
Rounding the back while lifting
This can be seen in every gym when an athlete squats with maximum weight. If your back is not strong enough to stay straight during heavy squats, then you should lower the weight a little and start training your spinal extensors. Hyperextensions with additional weights are best suited for this. Using an athletic belt also partially solves this problem.
Movement in the lumbosacral spine
You may have seen more than once how some athletes “peck” their tailbone at the lowest point of the amplitude. This makes lifting a little easier, but under no circumstances should you do this - this is a direct path to injury.
Movement in the knee joint
Throughout the entire exercise, your knees should be in the same plane as your feet. Movement of the knees inward relative to the proper trajectory is unacceptable. A meniscus injury can put an end to your sports career.
Incorrect foot position
The feet should be slightly turned out and slightly wider than shoulder level. This is the only way you can sit deep enough without creating a strong load on the knee joint.
Incorrect breathing technique
Remember one simple rule: exhalation is always done with effort. Therefore, you need to inhale while going down, exhale while going up. If you do not follow this technique, your muscles will not receive enough oxygen and the effectiveness of the exercise will be greatly reduced. Deterioration in health, headache, nausea and fainting are also possible as a result of insufficient cerebral blood supply and increased intracranial pressure.
How to quickly pump up your buttocks
You can quickly pump up juicy buttocks only if you give the load necessary for growth, load the buttocks, and not the legs or back, and also recover well (eat 3-5 times a day + sleep 8-10 hours).
We need the shortest + most effective path, so the training will be aimed specifically at the gym, because... it's logical.
You can endlessly kick your legs in aerobics, or go to the pool, but you will get the most beautiful and juicy buttocks only from bodybuilding and fitness classes. Because this sport is aimed at changing the shape of muscles!
It's logical. After all, if a person wants to learn how to run fast, then he goes to athletics, because... it is aimed at this, and not at throwing the shot. So I don’t understand why people want to make themselves beautiful buttocks, but go to aerobics, which does not provide the load necessary for growth? Rave.
Now let's look at the most effective exercises for developing your buttocks.
Exercise deep squats with a barbell on the shoulders
Deep squats with a barbell on your shoulders are the best exercise in bodybuilding and the number one exercise for developing sexy buttocks.
What is needed is deep squats, i.e. so that your calves press into your hamstrings. You need to squat not to parallel with the floor, but lower!
Technique:
First, it’s better to squat with an empty bar in front of the mirror. Evaluate the depth of the squat with different leg positions and choose the most optimal option for yourself.
Exercise deadlift with a barbell
Deadlift – This is a great exercise for developing your hamstrings and glutes. One of the best.
There is a type of deadlift, when we do not lower the barbell to the floor, but lower it to the middle of the shins, it is called the Romanian deadlift. Essentially, this is the same exercise, but the Romanian deadlift, in my opinion, more concentratedly loads the buttocks and the back surface (biceps) of the thigh.
I won’t write additionally about the Romanian deadlift, you’ll forgive me (by the way, it’s exactly what’s shown in the picture above), because... The technique differs only in that the bar does not fall to the floor, but stops in the area of the middle of the shins.
The main thing is to first establish the correct technique for performing this exercise, and then increase the working weights.
Try to do this exercise very slowly! Stop at the bottom point for a couple of seconds, thus prolonging the negative phase.
Technique:
Split squat (alternating lunges)
This is an exercise that concentrates on this muscle group! It grows your gluteal muscles in a very intense way! Don’t overdo it, develop your buttocks evenly with other muscles so that there is no disproportion.
There are three types of lunges:
- Step your feet forward.
- Step your feet back.
- Step your feet to the side.
Stepping your feet forward is the most classic option. We will carry it out.
Technique:
Swing your legs
Leg swings are a great isolation exercise and an effective way to tone your butt. You can perform them from a standing position, holding a support with your hand, or lying on the floor. Swing forward, backward, and to the side, straining your gluteal muscles.
To increase the load, you need to tie a weight to your ankle, or perform swings in a crossover, as in the picture below.
If you want to pump up your butt at home, then lifting your legs back can be done not in a crossover, but while standing on all fours.
Swings are performed with the leg bent at the knee. You need to lift it by tensing your gluteal muscles. In the lower position, do not place your knee on the floor until the required number of repetitions has been completed.
You can use special devices like these (sold in any sports store) as weighting agents, or simply wrap water bottles around them.
What are the benefits of barbell squats?
Deep squats with a barbell are suitable for girls.
They help them solve a number of problems:
- Eliminate slouching. To perform the exercise correctly, you will have to “pull yourself together.” connect and lower the shoulder blades, pull in the stomach, fix the lumbar region;
- Strengthen the abs. The benefit of women's squats is that they pump up the abs in a static manner much more effectively than many other exercises for girls;
- Reduces cardio load and helps burn a large number of calories.
But if you practice without proper concentration on the technique, you may get injured.
A barbell on your shoulders is a fairly heavy load, so you can only lift it this way after preliminary preparation and under the supervision of a trainer.
How to do exercises correctly?
The technique is slightly different in bodybuilding and powerlifting. The latter option is anatomically determined, therefore it is more in demand. You need to approach the barbell with your shoulder blades pulled toward your spine and your stomach pulled in. The bar should be set very low, slightly below the line that runs through the rear delts.
You need to check your posture, gather yourself, remove the equipment, take two steps back, and sit comfortably. The feet should be at a width that is comfortable for the hips. In this case, the kneecaps should not move inward.
Due to the fact that the bar lies low, the position of the back is fixed and injuries are excluded. If there is not enough stability, the socks can be moved slightly to the sides.
You need to start the exercise by moving your pelvis down and back, bending your knees accordingly.
During the entire process, the stomach should be pulled in, the back should be in a natural deflection. Bend forward moderately so that your body does not rest on your hips.
It is necessary to ensure that the lumbar region does not “unwind” at the point of maximum depth. and the pelvis did not “fall” down. You need to lift the weight smoothly, straightening the knee and hip joints.
To determine your individual squat depth, go to the mirror, stand in profile and squat. As soon as you notice that the pelvis makes a characteristic “peck”. then there is no point in continuing further.
Do you need a coach?
Ideally, it is better to practice the squat technique for girls with a barbell with a trainer. Self-training can be done after you learn to automatically lift the weight by collecting yourself correctly. Often, a few training sessions are enough to consolidate skills.
The coach will be able to observe you from the side and determine what “bad habits” you have in the squat. He will tell you how to get rid of them and perform the exercise correctly.
Training should be progressive.
You can't always squat with an empty bar or a stable weight. It is necessary to gradually increase the load so that the body adapts to new conditions.
Types of squats with a barbell
Squats for girls with a barbell on their shoulders can be different. The weightlifting version involves a high position of the bar and great flexion in the hip joints. But it is rarely used in health and fitness practice.
Barbell squats for girls for the buttocks will be effective if you do wide and deep squats, while spreading your toes to the sides. If you place your feet close to each other and move your pelvis back, then the front surface of the thigh will “work.” Basically, men like this technique.
Depending on how the bar is positioned, squats can be divided into types:
- frontal;
- with a barbell overhead.
When performing front squats, the barbell should be placed on the chest, held with a hook grip (forearms parallel to each other) or with arms crossed. In the second option, the bar is located behind the head.
The barbell must be grabbed with a jerk, turning your shoulders and pointing the projectile behind your head. The squat should be done in this position, controlling your posture and keeping your back correct.
What muscles are involved?
First of all, the gluteal muscles are worked. Also involved are the quadriceps, adductors, quadriceps, and hamstrings. During the exercises, there is a load on the rectus and oblique abdominal muscles, the long back muscle, which fixes the spine in the desired position.
Many girls are afraid of barbells and dumbbells, afraid to pump up their body. This will not happen if you approach the matter without fanaticism. It is enough to train three times a week, gradually increasing the weight of the barbell for girls, which is used for squats.
Some women complain that they feel uncomfortable lifting the barbell.
To reduce discomfort, it is recommended to open your shoulders and chest wider. This will relax the trapezius muscle bundles and create a cushion effect for the barbell.
Types of squats
On the Smith machine you can experiment with different variations of squats, which may, although not significantly, differ from the basic movements. Depending on how the legs are placed, the level of load on specific leg muscles depends. For example:
- Feet are placed together. In this position, the maximum share of the load falls on the front parts of the quadriceps of the thighs. Slightly less load is distributed across the knees. This option is suitable for those with healthy knees.
- Feet are placed shoulder-width apart. As a result of squats, the main load is distributed along the lateral parts of the thighs and their inner surfaces. This option is more suitable for girls.
- Squats with legs wide apart are also practiced more by girls. Here the main load acts on the inner thighs.
To develop the buttocks, you can put your legs slightly forward and rest your back on the bar. At the same time, you should be afraid of losing your balance. The design features of the Smith simulator do not allow this.
It should be noted that there are other squat options used by athletes. For example:
- Squats from your knees. It is considered a fairly heavy exercise, which is used in powerlifting and weightlifting. It is intended for better development of the lower phase of squats with a barbell. Such movements allow you to develop large muscles, as well as some smaller muscle groups that are inactive under classical loads. Squatting on your knees does not allow you to build muscle mass, but it does have a complex effect on the muscles. This exercise is characterized by maximum load on the knees. Therefore, this exercise is not suitable for beginners. For less stress on your knees, it is better to use soft knee pads.
- Front squat with barbell. Its difference is that the barbell is not located on the back muscles, but on the chest muscles and deltoid muscles. As a result, the back will take a purely vertical position, which radically changes the load on all muscle groups. Although the exercise is rare, it is effective and allows you to work out not only your legs, but also your upper body. In addition, strong abs are formed.
- Pique or sumo squat with wide legs. In this position, the load on the quadriceps is minimal, but the load on the inner thighs is maximum. Your legs should be spread as wide as possible, with your toes pointing to the sides at an angle of 45 degrees. At the same time, you need to make sure that your knees do not bend inward, and that your abdominal and buttock muscles are tense.
Squats with lunges. This is a classic version of squats, but with one difference: one of the legs moves forward. You should squat until your thigh and shin form a right angle. After this you need to raise your torso. In such conditions, the maximum load falls on the front leg. After each squat, the leg must be changed.
Advantages and disadvantages of the half squat
pros
First of all, let's look at the benefits of this exercise:
- Performing a half-amplitude squat helps prepare the muscles, ligaments and even the endocrine system for increasing working weights. This also includes the ability to more easily and quickly overcome the psychological barrier to increased stress.
- Work in the upper phase of the squat. Often it is she who lags behind in athletes. This is especially true for those who use inertia when lowering the barbell down.
- The half squat is often used to place more emphasis on the quadriceps muscle. It is not performed constantly, but only in combination with extension of the knee joints in the simulator.
- It allows you to thoroughly strengthen the back muscles in static conditions. By holding a lot of weight on the shoulders.
- Helps to practice core stabilization.
- Great for training the “knee insertion” skill of the deadlift.
In addition, it is the half squat that helps many athletes cope with the state of stagnation (plateau effect). When muscle tissue stops growing, progress from training is no longer observed.
And yet, it is very important to understand that not all people, due to their own individual physique, are able to do regular squats. For some, performing a full squat is beyond their ability. They simply cannot drop below hip parallel to the floor without putting compression stress on the lower back. The only possible option for them is a half squat.
Minuses
While listing the benefits of the exercise, one cannot help but talk about its disadvantages. These include the following points:
- Half squats place excessive stress on the cruciate ligament of the knee, which causes pain and can cause inflammation.
- Doing this exercise can cause a lower back injury. When an athlete has problems with the spine (hyperlordosis or protrusion), but he ignores the need to abandon training with heavy weights.
- Not everyone manages to develop sufficient coordination through half-amplitude squats. Many people end up having to master the full squat technique.
Squats at home
The fastest ways to pump up your buttocks at home are the following types of squats:
- classic squats;
- plie squats;
- jump squats;
- lunges.
Classic squats
Beginners are recommended to start training their buttocks with classic squats. They will help you quickly master the technique, learn to breathe correctly, and prepare your body for more complex exercises.
Execution algorithm:
- Place your feet at shoulder level.
- Straighten your arms in front of you.
- Tighten your abdominal muscles and straighten your back.
- While inhaling, do a squat until it is parallel to the floor.
- As you exhale, return to the starting position.
- Perform 12-15 repetitions using a similar scheme.
- After a two-minute pause, to restore breathing and strength, do another 4-6 approaches.
Plie squats
The main advantage of this type of squats over classic ones is that the wide stance of the legs and the spread of the toes to the sides makes it possible to emphasize the load on the buttocks and the back of the thigh. It is advisable to make this exercise the main one for those girls who want to pump up their butt without increasing the volume of the quadriceps (front of the thigh).
Technique:
- Spread your legs wide (70-80 cm).
- Point your toes outwards.
- Place your palms in front of you at chest level.
- While inhaling, smoothly lower yourself into the squat position.
- As you exhale, rise sharply upward.
- Do 12-15 repetitions.
- Rest for 2 minutes and perform another 4-6 similar series.
Jump Squats
The peculiarity of the exercise is that during the jump there is a powerful functional load on the buttocks, which helps to use the small and deep muscles of the butt, which are not included in the work during other types of squats.
Correctly perform a complicated exercise like this:
- Take the starting position: standing, feet shoulder-width apart, arms down along the body.
- Tighten your abdominal muscles and straighten your back.
- As you inhale, lower your body into the “squat” position, simultaneously raising and folding your palms in front of you at chest level (there should be a right angle between the shin and thigh).
- As you exhale, make a powerful jump up.
- Return to original position.
- Perform about 15 jumps.
- After a two-minute rest, do another 4-6 approaches.
Lunges
A more complex type of squats is performed with alternate lunges on each leg. This allows you to provide a more powerful load on the gluteal muscles and thereby stimulate their growth. You can complicate the exercise, making it even more effective, using dumbbells (if you don’t have them at home, you can use any other weight: water bottles, sandbags, etc.).
Algorithm for performing lunges:
- In a standing position, take dumbbells in your hands and place them on the sides of your body on straight, lowered arms.
- Bring your feet together.
- While inhaling, take a long step forward with your right leg, while bending your back leg at the knee.
- As you exhale, rise to a standing position, bringing your back leg to your front.
- Lunge on your left leg in the same way.
Number of repetitions - 12-14, approaches - 4-5. Rest time between approaches is 1.5-2 minutes.
Program for studying at home
The basic volume and intensity of the exercises described above may vary throughout the training program. How many approaches are needed to pump up your butt depends on the training day.
Table: example of a 30-day squat program at home
| Period | Number of repetitions | Number of approaches | Pause between sets | Types of squats |
| 1st week | 14-16 | 6 | 2 minutes | classic squats |
| 2nd week | 12-14 | 5 | 1.5 minutes |
|
| 3rd week | 10-12 | 4 | 70-80 seconds |
|
| 4th week | 8-10 | 3 | 60 seconds |
|
It is recommended to exercise according to this scheme twice a week, for example, on Monday and Thursday. At the end of the month-long program at home, it is advisable to move on to training in a fitness club. Using a barbell, heavy dumbbells, as well as training on exercise machines will speed up the process of pumping up the gluteal muscles.