Anatomy of arm muscles - Scientific approach to arm training
06/17/2016 Training
Pumped up, sculpted arms will complement any body type. Let's explore the anatomy of the biceps and triceps and see which exercises are most effective for building muscle in your arms.
Most likely, when you first stepped into the gym, you immediately started training your arms. Both girls and guys want to have slender and beautiful hands, because they are the most noticeable part of our body. It's impossible to go to the gym without seeing at least one person doing bicep curls.
Perhaps you have already trained your arm muscles and did not get the desired results. It's time to learn how to competently and effectively pump up your biceps and triceps. I'll teach you about muscle structure, different grip types, and specific exercises that will make a noticeable difference in your results.
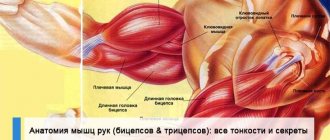
Anatomy of arm muscles
To pump up your arm muscles more effectively, you need to understand how they work. Here are the muscles you should know about.
Muscles of the front of the arm
To build impressive biceps, you must focus on the following 3 muscles: the biceps brachii (biceps), the brachialis (brachialis), and the brachioradialis. It is very important to understand how they differ from each other.
Biceps brachii
It has two heads: short and long. The short head originates on the front of the scapula and attaches to the radius (the bone in the forearm that ends near the thumb). The long head also originates from the scapula and attaches to the radius, but runs a longer route.
Brachialis muscle
It starts at the middle of the humerus and attaches to the ulna (the bone in the forearm that ends next to the little finger). It is not involved in rotational movements of the arm (pronation and supination) due to the fact that it is not attached to the radius. The main function of the humerus is to flex the arm at the elbow.
Brachioradialis muscle
A muscle of the forearm that is long. It originates at the humerus and attaches to the edge of the radius.
“To build impressive biceps, you must focus on the following 3 muscles: the biceps brachii (biceps), the brachialis (brachialis), and the brachioradialis.”
Muscles of the back of the arm
Most people focus on training their biceps because they look great in the mirror. However, the triceps brachii (triceps) muscle takes up almost 75% of the upper arm, so it also needs a lot of attention. It consists of 3 heads. To pump up the famous horseshoe, you must work on all heads.
Lateral head of triceps
It originates from the outer surface of the humerus and is attached to the olecranon process of the ulna.
Medial head of triceps
It originates at the back of the humerus and attaches to the ulna.
Long head
Slightly different from other triceps heads. It starts at the scapula and attaches to the ulna. Because it is attached to the shoulder blade, you can isolate it by moving your arms and shoulders. But I'll tell you about this later.
Pain in the arms from the shoulders to the elbow - causes
Pain in the shoulder muscles occurs due to inflammation of the bone tissue and joints, pathology of the periarticular structures - muscles, ligaments, tendons. Pain syndrome may be a concomitant background symptom of an underlying disease that is not directly related to the musculoskeletal system. That is why doctors at the Yusupov Hospital determine the cause of the pain before starting treatment.
Periarticular pain in the shoulder is most often provoked by instability of the joint, which can be caused by the following factors:
- overexertion, sprain of the shoulder girdle during intense strength training;
- damage, inflammation of the joint capsule;
- stretching of the muscles located near the joint capsule;
- damage to the cartilage of the glenoid cavity, lack of support for the biceps muscle.
Tendonitis is inflammation of the tendons that surround the shoulder joint. Damage to the tendon inevitably leads to pain in the shoulder muscles. The rotator cuff, biceps, infraspinatus, and subscapularis muscles are affected. Pain may occur in the infraspinatus shoulder muscle. The cause of pain is often calcific tendonitis, in which calcifications accumulate in the tendon tissue. Pain in the muscles of the arm on the inside may occur due to inflammation of the tendon of the inner shoulder.
Bursitis is an inflammation of the joint, closely associated with overexertion and sports injuries. In addition to pain in the shoulder, swelling occurs in the area of the joint capsule. Often the pain radiates to the arm, limiting range of motion.
Frozen shoulder syndrome or retractile capsulitis is a sign of reflex dystrophic damage to the shoulder joint capsule with parallel damage to bone structures in the form of osteoporosis. A symptom of the disease is pain in the shoulder muscles.
With glenohumeral periarthrosis, the nature of the pain syndrome can vary from acute, intensifying pain to aching, constant pain. It does not subside with rest, may be accompanied by insomnia, and noticeably limits movements of the upper limb.
Myofascial pain syndrome is a typical disease of muscle tissue in various areas of the body, but its favorite location is the shoulder girdle and lower back. Muscle pain that accompanies tense muscles develops in clearly defined places - trigger points. The cause of pain in the shoulder muscles can be osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, when a secondary complication develops - radiculopathy.
Pain in the shoulder muscles can be caused by the following diseases:
- impingement syndrome;
- polymyalgia rheumatica;
- neuralgic amyotrophy, myelopathy;
- herniated disc of the cervical or thoracic spine.
Pain in the shoulder muscles can be a reflected symptom of diseases of the respiratory system, diaphragm, heart, and liver.
How to relieve shoulder muscle pain? After identifying the cause of pain in the shoulder muscles, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital neutralize all factors that provoke pain - they immobilize the arm and shoulder, and often recommend complete rest. Complex therapy is prescribed, which includes:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in tablets, injections and in the form of ointments, gels;
- compresses with a 30% dimexide solution, local anesthetics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Doctors give corticosteroid injections for arm muscle pain. Homeopathic medicines – traumeel, zell – are injected around the joint. With the help of physiotherapeutic procedures, nutrition of the periarticular zone is improved and metabolic processes are activated. A complex containing B vitamins and microelements is prescribed.
At the rehabilitation clinic, specialists perform muscle massage, including joint development. Therapy for mild muscle pain that develops as a result of muscle strain lasts no more than 3-5 days. Adjusting training exercises, rest and a gentle, warming massage helps relieve pain in the arm muscles.
In other cases, contact the Yusupov Hospital. Doctors will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis, dynamic examination (monitoring the condition of the shoulder girdle in motion) and prescribe a course of medications that reduce the perception of pain, improve the trophism of muscle fibers, and neutralize inflammation.
Bone anatomy
Bones and joints play a critical role in arm movement. A clear understanding of how they work will help you choose the right exercises and pump up your target muscles.
Front of the hand
Biceps training is influenced by 2 main joints. Their position determines which muscles will be involved in the exercise.
Shoulder joint
Plays an important role in arm training because the long head of the biceps passes through it.
Elbow joint
It also plays an important role, because the rotation of the hand determines which muscle will be involved in the work. Plus, you can't build biceps without bending your elbows.
Back of the hand
In training the triceps, the same bones and joints play an important role, but for different reasons.
Shoulder joint
The main importance here is the long head of the triceps. To isolate it, you need to raise your arms above your head.
Elbow joint
Elbow extension is present in almost every triceps exercise. Crossover arm extensions, bent over arm extensions, and basic exercises such as the bench press require elbow extension.
Shoulder structure
The main movements of the arms are performed by the shoulder joint.
It contains two main bones:
- The humerus, a long tubular bone, serves as the basis for the entire human shoulder.
- The scapula bone provides the connection between the clavicle and the shoulder, while it is connected to the shoulder by the glenoid cavity. It is quite easy to detect under the skin.
Bones of the shoulder girdle
From the back of the scapula you can see the spine, which divides the bone in half. The so-called infraspinatus and supraspinatus muscle clusters are located on it. Also on the scapula you can find the coracoid process . With its help, various ligaments and muscles are attached.
The next arm bone to the scapula is a tubular, curved bone called the clavicle. Flexion and extension of the arm, as well as other movements, are performed by a muscle called the rotator cuff.
Functions of the arm muscles
We looked at those muscles, joints and bones that are involved in arm training. Let's go further and see how they work together to produce movement. Once you understand the difference between shoulder and elbow positions, you will be able to train your arms much more effectively.
| Glossary of terms Pronation – turn the hand so that the palm is facing down Supination - turning the hand so that the palm faces up |
Front of hands
Supinated grip (reverse)
The biceps plays an important role in flexion and external rotation of the arm. Therefore, to work it more effectively, use a supinated grip.
Parallel grip
When using a parallel grip (as in the "Hammers" exercise), the shoulder muscles are maximally activated.
Pronated grip (overhand)
If you use a pronated grip, you reduce the load on the biceps and move it to the brachioradialis muscles. That is why, to isolate them, it is recommended to lift dumbbells with an overhand grip.
“Supinated, parallel and pronated grips.”
Back of hands
Extension of the arms at the elbows
When you extend your arms, you evenly engage all 3 heads of the triceps.
Extension of arms at the elbows above the head
When you press a weight overhead, you engage the long head of the triceps more.
Structure of the hand
Wrist
This part includes 8 bones.
All of them are small in size and arranged in two rows:
- Proximal row. It consists of 4.
- Distal row. Also includes 4 dice.
In total, all the bones form a groove-like groove of the wrist, in which lie the tendons of the muscles that allow you to bend and straighten your fist.
Wrist
Metacarpus
The metacarpus, or, more simply, part of the palm, includes 5 bones that are tubular in nature and have a description:
- One of the largest bones is the bone of the first finger. It connects to the wrist using the saddle joint.
- It is followed by the longest bone - the index finger bone, which also articulates with the bones of the wrist using the saddle joint.
- Then everything goes like this: each subsequent bone is shorter than the previous one . In this case, all remaining bones are attached to the wrist.
- With the help of hemisphere-shaped heads, the metacarpal bones of the human hands are attached to the proximal phalanges.
Metacarpus
Finger bones
All fingers of the hand are formed from phalanges. Moreover, all of them, with one exception, have a proximal (longest), middle, and distal (shortest) phalanges.
The exception is the first finger of the hand, which lacks the middle phalanx. The phalanges are attached to human bones using articular surfaces.
Finger bones
Key exercises for arm training
Let's start practicing. The following exercises will help you build strong and beautiful arms. After watching the video, you may get the impression that these exercises are easy, but remember the intensity of the training. You have to challenge your muscles to make them grow.
Exercises for the front of the arms
Incorporate these exercises into your biceps training program.
Exercise 1 Barbell curl with EZ bar
I like the curved bar better because it makes the exercise easier. Many people have imbalances in the elbows and shoulders, and such a bar allows you to evenly distribute the load on your arms. The EZ bar also reduces stress on the shoulder and elbow joints.
To get the most benefit from barbell curls, keep your abs and glutes tight. This will help you lift more weight and protect your lower back. In the lower phase of the exercise, fully extend your arms, and in the upper phase, bend them completely. Use a supinated grip to better target your biceps.
Exercise 2 Lifting the barbell with an EZ bar on a Scott bench
For this exercise, use a pronated grip to target the brachioradialis muscles. Keep your elbows firmly pressed to the platform of the machine. Take a short pause in the upper phase of the exercise, and fully extend your arms in the lower phase. The range of motion must be full.
A curved bar provides more isolation, so you won't be able to lift as much weight as you could with a straight bar. Do this exercise at the end of your workout.
Among other things, this exercise is great for developing the muscles of the forearm. This way you simultaneously develop the muscles of the upper and lower arms.
Exercise 3 Lifting dumbbells with a hammer grip in a seated position
This exercise will help work your shoulder muscles. Use a parallel grip (palms facing each other). If you want to make the exercise more challenging, rotate the dumbbells slightly (supination) at the top to engage your biceps. Keep your abdominal muscles tense. This will help you maintain the technique and take the pressure off your lower back.
Exercises for the back of the arms
Perform these exercises to hit all 3 heads of your triceps at maximum intensity.
Exercise 1 Close grip bench press
In my opinion, this is the best exercise for triceps. Many of you know that the bench press is an exercise for the chest muscles. This is true, but in it you extend your arms, which means you force your triceps to work.
Grab the bar shoulder-width apart. If you use a grip that is too narrow, then too much stress will be placed on your wrists in the lower phase of the exercise. When your wrists are positioned correctly, your knuckles should be facing upward. Lower the bar toward your chest, keeping your elbows close to your body.
Many people believe that all arm exercises are isolation (single-joint) exercises. But this basic exercise can give the muscles a lot of stress. Here the chest muscles come into play, which allows you to lift heavy weights, which means making your muscles stronger and larger.
Exercise 2 Extension of arms from behind the head with a dumbbell
Raising your arms overhead isolates the long heads of the triceps. This is a simple exercise, but remember to keep your abdominal muscles tight and have a full range of motion. Elbows should remain motionless.
The structure of the joints of the hand
The human hand has three main articular sections, which have names:
- The shoulder joint is shaped like a ball, so it can move widely and with a large amplitude.
- The ulna connects three bones at once, has the ability to move in a small range, bend and straighten the arm.
- The wrist joint is the most mobile and is located at the end of the radius bone.
Articulations of the hand
The hand contains many small joints called:
- The midcarpal joint combines all the rows of bones in the wrist.
- Carpometacarpal joint.
- Metacarpophalangeal joints – attach the bones of the fingers to the hand.
- Interphalangeal connection . There are two of them on any finger. And the bones of the thumb contain a single interphalangeal joint.
Joints of the hand
Best results with a scientific approach to arm training
Arm training is more than just a set of isolation exercises at the end of your workout. If you want to build up your arm muscles, then do basic exercises more often.
Don't forget that you are working on your arm muscles in almost every workout. The biceps and triceps are used in exercises such as pull-ups and bench presses. Exercises for the back, chest and shoulders also indirectly contribute to the development of arm muscles. And if you add the above isolation exercises for the arm muscles, you will only improve your results.
Structure of the human thumb: bones and muscles with names
The structure of the human thumb
The structure of the human thumb: bones and muscles with names.
The structure of the thumb consists of two phalanges:
- Proximal
- Distal
At the end of the phalanx there is a bony plane that connects the phalanges to the joints. The thumb has a wide variety of muscles compared to other fingers:
Structure of the human thumb
- Abductor pollicis brevis muscle
- Opponus pollicis muscle
- Flexor pollicis brevis
- Adductor pollicis muscle
There are no muscles in the fingers themselves at all. Flexion and extension movements are carried out by the muscles of the palm and forearm.