13.10.2018
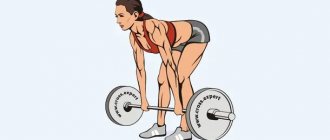
The deadlift is included in the basic powerlifting routine, along with the bench press and barbell squat. However, compared to other exercises, it is not as popular, especially among beginners. What is usually scary is a lack of understanding of the mechanics of the exercise, its purpose and potential injury.
Deadlifts can really be dangerous if the execution technique is not followed - like any other exercise, even pull-ups or push-ups. But with a reasonable approach, it allows you to develop and strengthen the muscles of the lower back, back and buttocks, increasing results in other exercises1.
What is a deadlift?
This is a basic exercise, or in other words, a multi-joint exercise. Basic exercises include all exercises that involve two or more joints. Deadlift specifically requires the work of almost all large joint groups - ankles, knees, hips, shoulders. In fact, only the wrists and elbows remain motionless, which is important from the technical side.
In powerlifting and extreme strength sports, the deadlift is a competitive exercise, performed in a complex (eventing and biathlon) or separately. It is also practiced in bodybuilding and martial arts, but for other purposes.
We will talk more about deadlifts in bodybuilding below. As for martial arts, during the strength training phase, professional athletes perform deadlifts in order to strengthen the muscles, joints and ligaments of the legs and back, as well as to develop the strength parameters of the lower extremities.
For example, the master of Brazilian jiu-jitsu, one of the top lightweight divisions of the UFC, Tony Ferguson, regularly does deadlifts with a trap bar2. This exercise is also practiced in an original interpretation by Alexander Emelianenko3 and other famous fighters.
The most dangerous exercises[edit | edit code]
The most dangerous exercises are those during which the direction of the applied force to the spinal column changes, which in turn can lead to a change in the line of the spine. At the same time, shifting under the influence of the weight of the barbell or other weighting materials, the vertebrae in the lumbar region become excessively mobile. By moving forward or backward (in a tilted position) relative to the axis of the spine, they are automatically maximally vulnerable. In this case, the tissues of the intervertebral discs can quickly wear out.
Dangerous exercises in bodybuilding and powerlifting include, first of all, squats, deadlifts and bent-over rows.
When squatting with a barbell, there is a high probability
- Compression fractures
- Dislocation of intervertebral discs
With deadlifts and bent-over rows, soft tissue sprains, vertebral displacement, and separation of the transverse process of the first lumbar vertebra most often occur.
Conclusion:
The cause of injuries to the lumbar spine is the use of excessive weight in the exercise, incorrect exercise technique, violation of the training process (violation of the principle of gradually increasing the load), lack of insurance and proper equipment.
What muscles work in the deadlift?
The functional advantage of the deadlift is that it engages 3/4 of the muscle frame, more than any other compound exercise4. In terms of the direction of work, it belongs to traction.
The deadlift works the following muscles:
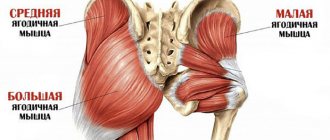
- – The erector spinae muscle (“popular name” is the back extensor).
- – Gluteal muscles, quadriceps, biceps and adductor muscles of the thigh.
- – Latissimus dorsi, trapezius muscles, posterior deltoid muscles.
- – Forearm muscles and biceps brachii (biceps).
- – With the “deadlift” – additional emphasis on the biceps muscles (biceps) of the thigh and the upper lobes of the gluteal muscles.
Deadlifts in powerlifting are performed only in the classic form and in the “sumo” version, since here the athlete is faced with the task of distributing the load as evenly as possible across all muscle groups to improve the overall result.
In bodybuilding, deadlifts are performed more variably, since here another goal is to “pump up” the muscles, develop them, increasing their volume. Variants of the classic deadlift (“dead”, “sumo”, with a trap bar) allow you to shift the emphasis of the load to one or another muscle group.
Manufacturing materials
Today, weightlifting belts are made from genuine leather and leatherette, fabric and synthetic bases. Each option has its advantages and disadvantages depending on how the equipment is used. Leather athletic belts have a long service life and therefore are the most expensive option. The bulk of products in this category are equipped with reliable metal fasteners with two pins.
Faux leather belts belong to the budget category. At the same time, such belts are characterized by a variety of fixing components.
Synthetic devices are suitable for working with medium weights. Most often they have a Velcro fastener.
What problems does deadlift solve?
In powerlifting and extreme strength sports, deadlifts are performed for the result, that is, for the maximum one-time effort - the weight of the barbell the athlete is able to lift and lower, technically correctly completing all phases of the exercise. Here it is a competitive discipline.
In bodybuilding, deadlifts are not performed with maximum weight; priority is given to lighter weights and more sets and repetitions (individual and depending on the training program). The same strategy is valid for those who go to the gym “for themselves,” that is, they strive to generally improve their physical condition and “pump up muscles”5.
Deadlift allows you to:
- – work several muscle groups at once in a short time;
- – increase strength indicators and results in isolated exercises;
- – increase the volume of muscles involved in the work;
- – strengthen the ligaments and muscles of the back and legs.
The deadlift is important for wrestlers and mixed martial arts athletes, as it allows you to more effectively lift your opponent off the ground for a throw and take him to the ground6. Since the exercise involves 3/4 of all muscles, it comprehensively stimulates muscle protein synthesis.
Beginner athletes often don't pay attention to the fact that deadlifting also increases grip strength. However, this is only relevant if the training is performed without athletic belts, the use of which removes some of the load from the forearm muscles. Grip strength is an important parameter for wrestlers and arm-lifters.
Try a different stance
Incorporate both versions of the competitive deadlift into your training: classic and sumo. In classic, the back and thigh biceps work more, in sumo - quadriceps and other pelvic muscles. By increasing the strength of all these muscle groups, you will lift more.
If you only lift conventionally, switching temporarily to sumo will relieve the load on your lower back and may even improve your squat performance.
If you have always been a “sumo wrestler,” then the classics will strengthen the lower back and other important back muscles.
Don’t try to reach the same weights in an unusual variation, just add loads to groups that were not previously included in the deadlift. Then, returning to your favorite option, you will reach new records.
Types of deadlifts, exercise mechanics, basic principles
There are four types of deadlifts - classic, deadlift (aka Romanian), sumo-style deadlift and trap barbell deadlift. Competitive technique involves performing classic deadlifts or sumo-style deadlifts; deadlifts and trap bar work are not practiced by powerlifters.
Regardless of the type of exercise, the deadlift from a mechanical point of view includes three phases
:
- – Lifting the barbell off the floor (in powerlifting the concept of “breakdown” is used).
- – Raising the barbell to the middle of the thighs with fully straightened legs.
- – Fixing the barbell in the middle of the thighs and returning to the starting position.
Fixing the bar (on average 1-2 seconds) at the top point is the first conceptually important point. The second is that when returning the barbell to the floor, the hands do not come off it - that is, the athlete does not drop the barbell, but leads it to the starting position.
If an athlete misses one of these nuances, his result will not be counted at the competition. As part of training work in the gym, these points must also be observed, otherwise the exercise is performed incorrectly and its effectiveness decreases. Fixing the bar in the upper position is necessary to ensure static load, and full support to the floor is necessary for better muscle development and strengthening of ligaments7.
Deadlift problems in bodybuilding:
- – Deadlift is a highly traumatic exercise.
- – The muscles of the back, buttocks and legs can be worked more effectively with targeted isolated exercises.
- – Deadlift requires high energy expenditure, after which it is more difficult to perform other exercises.
However, deadlifting produces a complex response that is important for those looking to build muscle mass quickly. Traction also helps improve results in other exercises (squats, leg presses, all exercises with a barbell and dumbbells on hands - due to strengthening the grip).
There is a myth that deadlifting causes a disproportionate increase in waist size. This has not been confirmed by either research or training practice. As a result, how much deadlift is needed in bodybuilding is something everyone decides for themselves.
On one leg
Performing deadlifts on one leg has a lot of advantages: it allows you to specifically work the back of the thigh and gluteus maximus muscles, prevents buttock asymmetry, develops coordination and flexibility, and stabilizes the knee joint. In addition, this exercise is a solution for those who want to train their legs, including their buttocks, but for some reason cannot do squats and leg presses, and also have back problems.
The deadlift is not considered very difficult, so even beginners can try it.
- You need to pick up dumbbells (you should start with small weights) and extend your arms so that the dumbbells are at hip level. One leg is slightly laid back.
- As you exhale, you need to move your body forward, while the front leg bends slightly at the knee, and the back leg lifts off the floor and rises higher, the lower the body goes.
- When the body is parallel to the floor, you need to stay in this position for a few seconds, and then, at the entrance, take the starting position again.
The exercise is performed both with weights and dumbbells, and with a barbell. If you want to use weights for only one arm, you can use the lower block of the simulator.
There are several recommendations for performing deadlifts correctly and effectively:
the back should be perfectly straight throughout the entire exercise; you need to look in front of you; lingering at the lowest point, you should forcefully squeeze your buttocks; you need to lower yourself at least to parallel with the floor, and if possible, a little lower; the heel of the leg being pulled back should stretch upward; beginners should try to perform deadlifts without weight, improving coordination, and only after the technique has been worked out, move on to working with weight; it is important to monitor your breathing: exhale when the body lowers, inhale when rising; 4-5 approaches are enough, but they will bring results if there are at least 15 repetitions in each (their number is gradually increased to 20).
Classic (weightlifting) deadlift
The classic deadlift is the original and most versatile version of this exercise. It is in the classical deadlift, and not in the sumo deadlift, that the vast majority of world records are set (for example, this is exactly how the legendary Lamar Grant “pulled”8).
Technique for performing classic deadlifts:
- - Initial position.
Place your feet at shoulder width or narrower. Hand position is shoulder-width apart or wider. The shins almost touch the bar. The pelvis is set back, the back is arched at the lower back, the legs are bent at the knees. - – Failure and rise.
The lifting of the barbell from the floor is performed by pushing with the legs, and not by straightening the back (otherwise the spine can be damaged). Extension is the second phase of lifting, performed after a fall, simultaneously with straightening the legs at the knees and shifting the pelvis forward to a natural position. The bar moves straight up along the legs until they are completely straightened. - – Fixation.
Phase of maximum static voltage. Arms and legs are fully straightened, the bar is located in the middle of the thighs. As part of the training process, a fixation lasting up to 1 second is sufficient; on the platform, depending on the federation holding the competition, the fixation can be up to 3 seconds. - - Return.
All stalling and lifting movements are performed in reverse order. The legs are bent at the knees while the pelvis is pushed back (to prevent a critical load on the spine). The return is much faster than the stall and recovery. - - Nuances.
Throughout the exercise, look straight ahead, shoulders are pulled down and back, shoulder blades are brought together, arms are fully straightened. Any movement of the head or arms can cause injury.
As part of powerlifting, the classic deadlift is recommended for athletes with a short torso and long arms, which will minimize the range of motion of the bar. However, in this case, short fingers may be the limiting factor. To solve this problem, a special “lock” grip is used.
Types of injuries and mechanism of injury
When pain occurs as a result of deadlift exercises, it can be caused by a number of traumatic changes in the body. Let's look at the easiest ones.
- A stretch, and doctors insist on the term rupture, of muscle fibers, provoking a muscle spasm that prevents the muscle from working normally.
- Ligament rupture, separation of some of the fibers, or complete rupture of the tissue connecting muscles and bones. The latter, more severe option, may be accompanied by the formation of hematomas.
- Displacement of the vertebrae - in the mild stage, is not accompanied by tissue damage and can be easily corrected if quickly detected. in severe cases, it can lead to pinched nerve processes and paralysis of the limbs. Frequent displacements lead to a high probability of their recurrence after the vertebrae (and discs) are put in place.
- Intervertebral hernia. At the beginning of its formation, a so-called protrusion (protrusion of the disc) occurs, in which destruction of the fibrous ring does not occur, but irritation occurs due to compression of the nerve roots. The second stage, prolapse, prolapse of the disc, with rupture of the outer shell, is the hernia itself.
- Vertebral fracture. More often this is a compression fracture caused by pressure and “sagging” of the intervertebral cartilage, which a person may not notice. But an untreated compression fracture can cause very serious complications in the future.
Sprains are usually caused by “incorrect” muscle work and insufficient recovery after training, which also causes wear and tear on the soft tissues of the spine. Depletion of spinal tissue and chronic overload are serious aggravating factors. Repeated overload makes the spinal tissue so vulnerable that even habitual stress can cause injury.
"Dead" or Romanian deadlift
It is not used in powerlifting due to increased trauma and the inability to lift maximum weight. It differs from the classic deadlift in that the legs are straightened completely or almost completely throughout the exercise (determined by individual anatomical features). Width – shoulder level or narrower.
The technique of performing a “dead” deadlift is completely similar to the classic version. The specificity of the exercise is that the load is accentuated on the back and buttocks, the legs are involved to a lesser extent than in the classic version.
“Dead” deadlifts are practiced mainly by bodybuilders, in particular – Arnold Schwarzenegger used only “dead” (Romanian) deadlifts9, not classical ones, in his training.
Features of the deadlift:
- – The work is performed with light weight (individually up to 50-70% of the maximum).
- – The exercise is performed with a large number of approaches (from 3 workers) and repetitions (from 10).
- – It is permissible to lower the bar not all the way to the floor, but to the middle of the shin.
This variation is called a deadlift because ideally the legs should be completely straight and motionless. However, due to the lack of flexibility in the legs, athletes often allow a slight bend in the knees.
Working on weak points
To avoid flaws in technique that arise due to problems in a certain part of the amplitude, you need to separately work on weak points. To work out the upper part of the amplitude, many people use traction from plinths (small elevation). However, Yuri Belkin states that problems with the upper part of the amplitude are most likely caused by gaps in technique, so it is better to simply reduce the weight and more closely monitor the correct execution of the movement.
If you have problems with the bar falling off, you can use the so-called pit row.
In fact, you don’t need any pit here, you just stand on an elevation of 5-10 centimeters and perform an extended version of the deadlift. Nastin Sergey
Sumo style deadlift
The execution technique is completely identical to the classic version. The specificity of the execution is in the positioning of the legs, they are placed as wide as possible, so that the socks almost touch the pancakes or stands.
The sumo deadlift shifts the load from the back to the legs, since the amplitude of movement of the barbell is significantly reduced - this shortens the lifting phase, the athlete focuses on the fall. This deadlift variation is recommended for powerlifters with short arms and long torsos. A weak back is offset by strong legs (in the classic version, it’s the other way around).
Sumo-style deadlifts reduce back injuries. Practiced by many professional powerlifters, but inferior in popularity to the “classics”. For example, the Russian athlete, world record holder Dmitry Nasonov10, pulls in the sumo style.
Trap bar row (trap bar)
The peculiarity of this traction is in the projectile used - it uses not an ordinary bar, but the trap bar itself. This barbell was invented and patented by Al Gerard in 1985. It was originally conceived as a multi-purpose sports equipment with which you can perform:
- – deadlift;
- – squat;
- – shrugs;
- - military press.
When performing deadlifts with a trap bar, the load on the spine is reduced. The trap bar is also convenient for beginners, since it makes it easier to maintain a strictly vertical body position and allows you to “miss” some technical points11.
There are no studies or expert opinions that can say for sure how effective or ineffective a trap bar is. However, many athletes train with it, for example, Tony Ferguson as part of the CrossFit program.