Good day, friends, Yaroslav Brin is in touch.
Today the lesson will be in an unusual style for me, with elements of video inserts. Plus, this issue will be useful for those who are already doing something, and for those who just want to read, alas *PARDON* To begin with, I decided to revive my channel on Youtube , I was bored with the epistolary genre, but irritating the respectable public with my bald head is sacred case. I will upload my video lessons to the channel, which are asking from my cramped head into the outside world. Most lessons WILL NOT be sent out , so if you want to receive them in a timely manner, click on the link and subscribe to my channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/brinvideo
or by clicking on the picture:
In this issue we will analyze one of the most useful exercises, both for the hormonal system of a steadily aging body, and for its overall development. There are a lot of controversies and rumors surrounding this exercise, so for me, as a true proctologist, it’s time to delve deeper into this topic. Let's go deeper...
BASICS
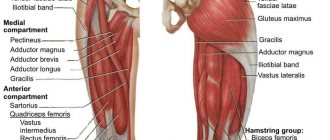
There are a wide variety of different squat techniques. All of them come from strength sports: Bodybuilding, Powerlifting, Weightlifting (Weightlifting), and various “other sports” add a little to the general treasury. Here, for example, is a crouching dragon =)
We will not divide them according to the above-mentioned criteria for preschoolers, but will divide them by style of execution and by goals, and then we will have JUST TWO GROUPS:
- Pelvic-dominant style
- Knee-dominant style
It’s too early to think about what these incomprehensible terms mean.
Mistake 4: Are you strengthening the arch of your foot enough?
The reason for the previous three errors is the lack of correct technique. Many athletes squatted with their knees spread in order to achieve their correct position in the future. Such training also has its place, but in the end it can lead to negative consequences and incorrect execution of the exercise.
The good news is that all 4 errors can be easily corrected using the tripod technique. When you correct any of the above mistakes, you will be able to achieve perfect squat technique.
Author: Sebastian Gonzalez
AMPLITUDE or DEPTH
The work of muscle groups depends on the depth of squats. The LOWER you squat, the MORE your gluteal muscles engage (but not only....)
Based on this postulate, boys are recommended to squat TO PARALLEL in order to maximally load the front surface of the thigh and minimize the load on the buttocks. A man with a big ass is not the most pleasant sight. And girls are recommended to squat BELOW PARALLEL in order to place emphasis on the rear, on the buttocks . In principle, the emphasis and priorities are set correctly, girls need to focus on working on the back of their legs, men on the top, but let’s look at how to squat correctly from an anatomical point of view.
First, let's figure out where it is, this PARALLEL?
I’ll take a picture from the textbook for clarity =)
This is considered a squat to parallel , i.e. the lower part of the thigh is parallel to the floor. AND THIS IS NOT CORRECT! should be parallel to the floor , and not the knees and bottom of the buttocks should be in a straight line, but the knees and the point (which I marked for clarity) where the elastic band of the panties is located. Then it will be a parallel.
When we squat partially, not to full amplitude, we cannot create full tension in the biceps muscles. These are:
The VECTOR OF FORCE is directed against the tibia, up and forward, from the quadriceps and their joints on the front of the tibia, below the knee.
This creates a forward shear, a forward shearing force in the knee that pulls the tibia forward from the patellar tendon. All this disgrace should be balanced by the biceps muscles, but in the half-squat we do not include them in the work, and create an imbalance of efforts. This shear force, due to the unbalanced load on the knee joint, leads to injury.
Our body is amazingly balanced and this force should be absorbed by the biceps femoris muscles , due to the adductors and buttocks, BUT any squat that is ABOVE PARALLEL loads the knee and quadriceps without loading the gluteal, adductor and biceps femoris muscles.
The biceps femoris and gluteal muscles perform their function in the squat when the pelvis is pulled as far back as possible , where they are tense.
The biceps and adductor muscles reach full stretch at the very bottom of the squat when the pelvis is pulled back, pulling back the ends of the muscles. Ugh tautology)
The tensile force pulls the tibia back toward the buttocks, canceling out the forward pulling force of the quadriceps.
The anterior cruciate ligament stabilizes the knee : it protects the tibia from moving forward relative to the femur. As we have discussed, this is also done by the biceps muscle group, which benefits from full amplitude. Disproportion in the development of these muscle groups leads to knee problems.
And this is how they teach you to move your buttocks back and feel the emphasis on your heels:
The full squat , done correctly, is the safest exercise for the knees and creates a more stable knee than any other leg exercise.
Correctly means deep, with the pelvis extending below the level of the top of the kneecap . THIS IS ACHIEVED NOT BY BENDING THE KNEES AT THE MOMENT OF SQUATTING, BUT BY ADVENDING THE PELVIS AS FAR BACK POSSIBLE. You seem to rotate the pelvis relative to the knee, this technique minimizes the extension of the lower leg, leaving it perpendicular to the floor and removes the load from the quadriceps femoris muscle, transferring it to the muscles of the back of the thigh and buttock.
This is the PELVIC DOMINANT STYLE of squats. If the load is shifted as much as possible to the quadriceps muscle, i.e. on the upper surface of the thigh, then the pelvis is not retracted back to its full amplitude, the lower leg does not maintain a vertical position, we get a rotational movement in the knee joint, this will be a KNEE DOMINANT style. Both styles are good, each for its own purposes.
ANGLES
Two parameters that need to be controlled:
- The knee should not extend beyond the toe.
- The angle at the knee should not be acute.
But not everything is so simple =)
The first recommendation for very low squats contradicts the second =)) i.e. If you try to sit “butt on the floor”, as is fashionable in narrow circles of fitness bikinis and is required in TA, then by keeping your knees and toes in the same plane, you will get the most acute angle in the knee.
BUT, at the same time, the biceps muscles are included in the work as much as possible, which compensates for the load from the quadriceps, so why do sharp angles injure the knees? The cause of damage to the ligaments in a low squat can only be lateral rotational movements, that is, the arch of the knees when trying to get up from a squat.
This occurs due to weakness of the adductor muscles (groin muscles) and poor conduction of signals from the brain, i.e. you cannot control your muscles under load, and they begin to perform their intended functions.
A sure sign of weak adductors is an inability to keep your knees apart during a squat.
The adductor muscles originate in the groin area and are attached to the medial part of the femur.
Thus, their function will be to reduce the distance between these two points. As you squat, the distance between these two points increases , and as you rise, the points will move closer together as these muscles contract during the squat. In real life, these muscles practically do not work, and when a beginner begins to put stress on them, they begin to contract and bring the knees inward. It is these lateral twists that injure the knee joint.
Another stone in the garden for not a full squat.
Why do they do it? Everything is very simple, the main goal is to satisfy your EGO , every unstable noob wants to seem stronger than he really is. If you don’t do the full amplitude under the guise of a “male” technique, then you can take twice as much weight as with the full amplitude, and then wonder why back injuries occur . Any weight that you can't squat deeply with will be too hard on your back , we need to develop body, strength and spirit, not play with numbers, right?
The Positive Effects of Squats
The main advantage of the exercise is its complex effect. An athlete who uses squats in training develops not only muscles, but also improves body function:
- Strengthening the heart . High-speed multi-repetition squats without additional weights are equivalent in effectiveness to full-fledged cardio exercises - the main training of the heart muscle and increasing endurance.
- Mass gain . We are talking about exercises with power equipment. Squats with a barbell on the shoulders provide a powerful boost to the production of growth hormones, which makes the element basic in the training program of bodybuilders and powerlifters.
- Strengthening the male reproductive system . Athletes who regularly squat with a barbell or other weights improve blood circulation in the pelvic organs, which helps to improve the genitourinary system and restore libido.
- Lower body workout for women . Most gym goers dream of having toned thighs and round buttocks. Squats help to specifically load these muscle groups and get rid of flabbiness.
- Losing weight . The reduction of subcutaneous fat depends on the energy intensity of the exercise. Squats force large muscles to consume a large number of calories, which means getting rid of extra pounds and cellulite.
The exercise is used to recover from sprains and injuries. Light squats of half the amplitude without additional weight will help strengthen joint tissues and tendons and return mobility to the athlete.
ERRORS WITH ANGLE
Why do many trainers, including myself, recommend not bringing your knees past your toes? In order not to create sharp angles in the knee joints, because this may cause injury. This recommendation is only effective for squats to parallel and above, and since a beginner does not know how to squat deeply, hence the recommendation. Whether the coach is aware of this or just read it in a book, that’s another matter. If you sit down deeply, whether your knees extend beyond your toes or not depends on your anthropometry :
Example from Weightlifting:
If an athlete tries to align their knees with their toes without losing stability, this will increase the angle at the knee. What should he do to avoid increasing the angle and making his knees even? Pull our butts back, like the ladies do in fitness, BUT when we push our butts back, we have to bend forward.
Can he do all these manipulations with such a barbell? NO! Does he have knee problems? NO! (bar weight 160kg). Therefore, knees in the same projection as toes is not an axiom; this works for squats TO PARALLEL and for beginners.
Mistake 3: The arch of the legs is broken?
Incorrect foot position during a squat can cause your knees to roll inward. This knee position is a result of poor function or position of the joints above or below the knee. In this case, the legs and arched structure are to blame. There are several ways to identify these disorders:
- Look at the outside of the leg. Is she in the air?
- Look at the inside of your leg. Has the height changed in any way?
Try it right now: sit down and fix your feet. Bring your knees inward and notice if your sensations in your legs change. If yes, try one of the following options:
- Make sure your feet are flat on the floor;
- Spread your toes as wide as possible, squeezing the floor;
- Apply more pressure to your feet.
Once you correct this situation, you can also solve the following problems:
- Bringing the knees together;
- Internal rotation of the hips;
- Powerful dominance of the legs during the squat.
MEN VS WOMEN
Well, how can you squat anyway, if it’s good this way and that way, and it’s possible this way and that way.
FOR GIRLS:
- We sit down as deep as possible, by moving the pelvis back, and not by bending the knees.
- Your knees do not go beyond your toes))) and in order to squat as low as possible in this position, you need to tilt your body forward. BUT your back is always straight!!! It is allowed to tilt up to 45 degrees, but I wouldn’t go further than 30, try to keep your back as straight as possible, and bend only to pull your buttocks back if necessary. The more vertical your back is, the more your knees will move forward and vice versa , the stronger the back tilt, the closer your shins are to the vertical, i.e. less acute angle.
- Your main focus is on the glutes and lower thigh stretches. Only the pelvic-dominant style is suitable for you, when the knees are fixed and the pelvis rotates around them.
- Weight is practically irrelevant. Only the force of tension and stretching of the muscles.
WOMEN'S VERSION OF SQUATS: BOYS:
- We sit down to the CORRECT parallel. Knees and upper thighs in one line.
- We keep our back as vertical as possible, this creates maximum load on the front surface of the thigh. Which style you choose is your decision.
MEN'S VERSION OF SQUATS:
How do I do it? Like a damn half-girl))) I squat as low as the stretch allows, with the pelvis abducted, but I keep my body vertical, this is a lifter’s style.
Causes:
- I don't have time, like professionals, to divide workouts into different muscle groups, so I try to cover as much as possible. The lower the squat, the more muscles are worked, which allows me to avoid focusing on the hamstrings.
- Knees!!! I knocked out my wrists in boxing, injured my elbows in arm wrestling, my knees have been working in harsh conditions for 17 years now, and no problems, although for many they begin to “crunch” even without load. This is because in modern life there is no load on the biceps and adductors, this creates an imbalance and subsequent problems.
And not a big remark. What is the most UNSTABLE position of the knee joint? When the angle is 90 degrees . That's why honey. examinations, you are asked to sit in a chair before your knee is examined, i.e. he is diagnosed in his most vulnerable state.
If you squat TO PARALLEL, then the knee angle will be 90 degrees, you take more weight than for a deep squat, which means the load on the knee is greater and the biceps muscles of the back surface do not balance the squat. We get the fastest way to twist our knees like a grasshopper =)
3. Back injuries - the smaller the amplitude, the more weight we can lift, and I have already grown beyond the age at which I want to measure my pussy, I am interested in the maximum development of the body, and not in records, so my modest 150 kg will always be for me top bar.
4. There is no problem getting a fat ass from deep squats, because... it depends on the amount of fat in the body, so whether men should be afraid of this or not, everyone decides individually:
I won’t show my ass for clarity, we are family. They will leave you without borscht.
Comparison of squats with other exercises
In fitness, one of the most popular exercises for the lower body is lunges. Using various options for performing the element, you can specifically load individual muscles: quadriceps, calves, buttocks. Lunges without additional weights, performed at a fast pace, are suitable for fat-burning workouts.
The main disadvantage of the exercise is the inability to build large muscle volumes due to the use of relatively small weights. During a lunge, the athlete needs to have good control of his body balance, which is not easy with a heavy implement on his shoulders. Therefore, classic barbell squats are much more effective for building muscle mass and increasing leg strength.
Another exercise for training the lower extremities is leg presses. The element is performed in a special simulator and involves pushing a carriage with a load upward at an angle of 45°.
Presses are a strength, basic exercise, so they can be used as a replacement for classic squats. The main advantage is the elimination of the back from the work. Thanks to this, even athletes with spinal injuries can safely train for strength and mass.
The bench press machine allows you to shift the emphasis of the load to different parts of the legs. This is achieved by changing the placement of the feet on the platform. But the main advantage of the exercise is the ability to exercise with much more weight than with classic squats with a barbell.
BASIC RULES:
Rules that, as they say, are “no brainer”, but to me, let’s say, a lot of what is “no brainer” is not clear to me! I hate hedgehogs! Assholes are too smart. Therefore, let us repeat:
— The height of the racks should be in the middle of your chest.
— Setting the feet. Turned outward from 30 to 45 degrees. The knees point towards the socks.
— The width of the legs is slightly wider than the shoulders. If it’s too wide, it overstrains the pelvis at the bottom, which in principle is not bad for girls; if it’s too narrow, it interferes with the stretching of the adductor muscles of the thigh.
— We go down as far as stretching allows, but at the top we don’t fully straighten our legs. We do not insert the knees so as not to miss the load and injure the menisci.
— We rise upward by lifting the pelvis upward, and not forward!
— If you have positioned the bar correctly, pulled your buttocks back and squatted, the bar will be in the middle of your foot:
- No matter how much experience you have in this exercise, the first approach is ALWAYS performed with an empty bar. ALWAYS, or even with your own weight.
- Grip width. The wider the grip, the less static load on the shoulders and back; the narrower the grip, the greater the load. The choice is yours. In the first case, only the legs work, and this is correct; in the second, the bar does not cut into the back.
- The back should ALWAYS be straight. No arching in the lower back. The lower you go, the stronger the twisting force on your lower back. This needs to be controlled
— The hands should not take the load, they are only used to stabilize the barbell on the back.
— We always step back from the counter. To put the barbell in place, we step forward. And not vice versa, i.e. We stand facing the counter and our backs to our friend
— There is no need to return the barbell to the racks by bending forward. You need to approach the racks until you touch the bar and lower it down. It's like an extra repetition.
-Do not lift your heels off the floor.
— When lowering, INHALE, when RISING, exhale. We NEVER hold our breath.
— A proper squat does not cause tension or pain in the lower back and knees.
- You can't do anything through pain.
— The bar moves strictly up and down, without any side deviations. This means that when squatting, the bar should “draw” a straight line, perpendicular to the floor, and the back tilt is carried out only to the extent that it is necessary to balance the abducted pelvis, no more.
HERE'S A VIDEO OF HOW TO LEARN TO SQUAT
Deep squat self-test
Starting position: feet shoulder-width apart, slightly turn your hips outward.
Test: Squat down so that your thighs are parallel to the floor, keeping your back straight. Stop and then return to the starting position.
Correct squat
Criteria for verification:
- the squat should be performed smoothly, without jerking;
- keep your back straight throughout the entire exercise;
- the knees are directly above the feet;
- don't lose your balance;
- the feet are completely pressed to the floor throughout the entire exercise;
- maintain a neutral head position.
To evaluate your performance according to all criteria, squat in front of the mirror: first facing it, and then sideways.
You can also ask a friend to follow your movements. It can be difficult to assess the position of the body ourselves, and in addition, we often lack self-criticism.
A good option is to ask to be filmed. You will be able to watch the video several times, evaluate your technique and notice any mistakes.
So, if you managed to perform the test perfectly, following all the criteria for correct technique, congratulations! You can perform squats with free weights without fear of injury.
If your technique does not correspond to the correct one according to any of the criteria, it means that weak or, conversely, tight muscles do not allow you to perform the exercise correctly. In this case, before picking up dumbbells or a barbell, you need to correct your mistakes.
Box squat
This option, in my opinion, has a serious drawback (see cons), but sometimes I use it for certain purposes.
The thing to understand is that you don't just sit on the box. You sit back and on the box: at the lowest point, the lower leg is vertical (or even tilted back). That is, this is a more hip-dominant version of the squat with a low bar position on the back.
pros
More includes the gluteal and thigh biceps, teaches you to lower to the desired depth (by adjusting the height of the box), and also rise after a pause from the lowest point. An excellent utility room for a deadlift.
Minuses
Potentially more dangerous than regular squats - there is a higher compression load on the spine, which is pressed against the box by the barbell.
Of course, if you try to do everything correctly, then the risk of injury is minimal, but it is too easy to make a mistake, for example, relax too much at the bottom point, quickly fall onto the box, or miss before reaching it.
For whom is it more effective?
For powerlifters who perform in special equipment (a squat suit helps to rise from the lowest point). If you only belt squat, practicing this variation won't really improve your performance in competition.
Features of the projectile
Many athletes needlessly ignore the sandbag, because at first glance, the bag is not as convenient as a barbell or dumbbells, and sand probably spills out of it?
In fact, training bags are made from a special dense fabric. In most cases, each bag is equipped with several handles on different sides. This allows you to add significant variety to your workout by performing a range of exercises.
The bag has several significant differences from metal projectiles. One of them is a constantly shifting center of gravity. Due to its loose texture, sand moves from place to place with every movement. For this reason, you will have to apply a completely different force each time to perform the exercise. The sand will flow forward or backward, as well as sideways - you will need to adapt to this.
In addition, sandbag training has the following advantages:
- Active development of core muscles. Small stabilizer muscles play a special role in bag exercises, helping the body adapt to constantly changing loads.
- Variety of exercises. In addition to the fact that with a bag you can do many exercises that are already familiar to you for different muscle groups, there are also a number of specific movements adapted specifically to the characteristics of this apparatus.
- If you want and have some skill, you can sew a training bag yourself and collect sand on the street. You can even use an old backpack. The price of a factory-made equipment varies depending on its technical characteristics, but on average, purchasing it will cost you no more than one month of training in the gym.
Belt and intra-abdominal pressure
Typically, intra-abdominal pressure is not noticeable among gym goers, because... a protruding belly is a standard condition of a modern person.
Here is a picture, it clearly shows what intra-abdominal pressure is:
There is a constant argument over the belt. Not wearing a belt will strengthen your core muscles, which is good, but wearing one will take some of the load off, which is bad, although it will prevent your core from stretching and your waist from expanding. So when should you wear it?
Subscribe to our Yandex Zen channel!
During the exercise, your back should be straight and your stomach should be pulled in! Very often, people hold their breath while performing an exercise - this helps them overcome the weight, but increases the pressure. At that moment, or rather with that weight, when you cannot keep your stomach pulled in, then put on a belt. It will keep your belly and waist from expanding.
Squats are a very difficult exercise, so if you don’t succeed the first time, that’s NORMAL. Approximately 80% of people over 30 years of age cannot sit down even once! You can progress very quickly in this exercise, and after hard days you will feel unprecedented lightness, both due to the strength of your body and due to the hormonal surge.