Share:
For a long time, an indicator of great physical strength was the ability to lift the weight of one’s own body above one’s head. However, how about doing push-ups while standing on your hands? Here you need not only physical strength - you will need perfect intermuscular coordination, an excellent sense of balance, and developed stabilizer muscles. All these qualities are possessed by athletes who practice handstand push-ups. Today we will talk about the benefits and harms of the exercise and the technique of doing it.
What muscles work in the exercise
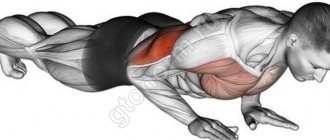
Handstand push-ups put maximum stress on the shoulders . However, as expected in a basic exercise, these are not the only muscles that are involved in the movement.
The deltoids are helped by the triceps, and the chest and trapezius are also included a little. But these are only the muscles that perform dynamic loads.
But hand push-ups involve muscles to stabilize the position in a static mode. First of all, these are the abs and lower back, buttocks, as well as the intercostal and serratus muscles.
Exercise technique
The handstand push-up exercise is difficult to coordinate and requires you to be in extraordinary physical shape. Therefore, if you tried to perform this movement and you couldn’t even get into a handstand, let’s learn a simple set of exercises necessary to get yourself into the right condition.
Before you start the exercise
- Push-ups from the floor for 3 counts, with a delay in the lower position: from the starting position at the support, lying down, by bending the arms at the elbow joints, we lower ourselves down: the chest does not reach the floor literally a few millimeters. The elbows are located along the body - thus, the load falls on the triceps and anterior delta - the main muscle groups for us. In the lower position, we perform a distinct pause of 2-3 seconds, rise in three counts, that is, quite slowly. We start with 10 repetitions in three approaches. The goal is to reach 20 or more repetitions without feeling too much muscle acidification.
- Push-ups in a closed horizon. Starting position: in a handstand, legs bent at the knees and hips, knees touching the chest. Hands touch hips. Bend the elbow joints, keeping the body horizontal. We start with 10 repetitions (or as many as you can). The goal is 20 or more confident repetitions.
- Raising the body from the horizontal position. The starting position is as described above. The arms are slightly bent at the elbows. Our task is to move the body from a horizontal position to a vertical position as much as you can. The task is to bring the body with bent legs to a completely vertical position.
When you succeed, begin to smoothly straighten your legs, first spreading them apart, then try to keep your body “in line.”
Near the wall
- Handstand push-ups against a wall. A movement that directly prepares you to perform a push-up upside down. Starting position: standing on your hands 20-50 cm from the wall. The body is stretched upward, the heels are “piled up” on the wall. Let’s make a reservation right away: you can swing the walls with your heels, you can swing with your toes, you can swing with your whole foot. The closer to the “socks”, the harder the option! Start with the simplest! Hands stand slightly wider than shoulders. Sliding the supporting part of the foot along the wall, we lower ourselves until the head swings to the floor, by bending our arms at the elbow joints. After this, resting our palms on the floor, we return the body to its original position due to the powerful combined effort from the triceps and deltoid muscles. The goal is to do 10 repetitions in at least one series.
© satyrenko — stock.adobe.com
- The last exercise is an attempt at a handstand. It is optimal to do this from a position of holding the “horizon”. It is fundamentally important to end this complex with this movement in order to consolidate the correct kinematics of movement against the background of muscle fatigue.
Systematic implementation of this complex at least three times a week will allow you to achieve a handstand in a fairly short time (1-2 months) and do your first push-ups from the floor upside down.
The exercise itself
Starting position : handstand, palms on the floor shoulder-width apart, or slightly wider. Body weight is evenly distributed across the entire surface of the palms and fingers. The spine is arched in the lumbar region, the pelvis is slightly in front of the head, the toes are directly above the head.
Let's go down...
We bend the elbows and shoulder joints, while the chest shifts slightly to a more horizontal position - this moment must be clearly grasped and the deflection in the lower back must be strengthened, thereby compensating for the shift in the center of gravity of the body.
...and we rise
As you lift your body, press your palms into the floor, returning your chest to its original position. Again, by shifting the pelvis, we compensate for the change in the position of the center of gravity.
An important technical point regarding the position of the legs: if the legs are spread apart, the center of gravity is closer to the hands; accordingly, maintaining balance becomes much more difficult. It is recommended to start mastering push-ups from the floor upside down with this option.
Recipes for healthy eating
Liver paste
- 18.1 g Protein
- 11.1 g Fat
- 7.0 g Carbohydrates
- 177.5 kcal
30-40 min.
- #breakfast
- #snack
- #carrot
- #low calorie
- #dinner
- #roasting
- #pate
- #liver
- #vegetable oil
- #onion
- #dinner
Other recipes
Advantages and disadvantages of movement
Shoulder push-ups have their pros and cons.
The main advantages include the following characteristics:
- No special equipment required
The exercise is performed anywhere, in any conditions - in the gym, at home or on the street.
- Increased load on deltoids
Unlike classic push-ups, where the main load is directed to the chest and only additional load to the shoulders and triceps, here the shoulders work to the maximum. The chest and triceps come in second.
- Development of coordination and balance
- Unusual biomechanics of movement forces the main muscle groups of the upper body to work to the limit
- Increased blood flow to internal organs and head due to upside down position
However, delt push-ups also have disadvantages:
- Not suitable for beginners
Even people with an average level of physical fitness have difficulty performing this exercise.
- Difficult to coordinate movement
In addition to a high level of strength training, good coordination is also required.
- Increased risk of injury to joints and ligaments – hands, elbows and shoulders
Benefits and harms
- Push-ups with a wide support allow you to increase the strength of your arms, back and abs;
- This is a great way to challenge your muscles without using extra weight;
- You can do push-ups in this way at home, on the street, and in the gym;
- The exercise helps women improve their breast shape, pump up their arms, and tighten their stomach;
- This is a great way to build muscle definition and improve muscle elasticity.
The exercise cannot cause harm, the exception being situations when a person begins to do push-ups if there are contraindications:
- Injuries to joints, ligaments, tendons;
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- Inflammatory processes occurring against the background of elevated body temperature;
- High blood pressure;
- Excessive excess weight;
- Condition after abdominal surgery;
- Special situations incompatible with sports physical activity.
Ways to do handstand push-ups
There are two options for the exercise:
- With feet resting on a vertical surface (wall)
Usually, shoulder push-ups start with this option, as it is easier.
- The emphasis is only on the arms, and the legs are held in weight
This is already a rather complex technique to perform, which only advanced athletes with gymnastics training can do.
There are also lighter versions of the movement that are used when learning the handstand push-up technique. For example, at half the amplitude.
Common Mistakes
Beginning athletes often make mistakes when performing a training routine. In order to properly fixate during exercises, you should study a number of common mistakes:
- Many people, feeling pain or discomfort, do not stop training. But in vain, since cartilage tissue and tendons take a long time to recover, so there will be pain and the person will not be able to exercise. Consult your instructor and choose the best option for yourself.
- Lack of control of hand position. Control the position of your hands, namely the elbow joint. During training, the percentage of injuries is very high.
- Full straightening of the upper limbs. When lifting, do not straighten your arms completely. They must be in constant tension. Do not stop at the starting point, this puts a lot of force on the elbow joints.
- Exercises after injuries. If you have suffered a shoulder or elbow joint injury, you should consult a doctor. It is possible that this sport is prohibited for you. If approved, wear elastic bandages. Perform the exercises smoothly, without sudden movements, observing the correct technique.
- It happens that a person who has just started doing push-ups puts unbearable stress on the body. Use weights initially with minimal weight. Increase the loads gradually.
- Using the wrong surfaces. Do not do push-ups on a soft or unstable surface. In this case, you may not maintain your body balance and get injured.
- Many beginners do push-ups with their fists. In this case, the entire load goes exclusively to the hands and when lifting and lowering, the arms go to the side. Therefore, do not experiment during the training process.
Bench push-ups can be performed in different variations, but beginner athletes need to initially master the basic technique. It is advisable to practice with an instructor, which will protect the person from injury. These push-ups make it possible to feel each muscle group and their stretching.
Contraindications
Head-down handstand push-ups are an exercise for physically fit and absolutely healthy people. Or rather, athletes. This is why you rarely see this movement in the gym.
The limiting factors for performing hand push-ups will be the following:
- Injuries and diseases of the spine, as well as joints, ligaments and muscles involved in movement
- Heart and blood pressure problems (due to upside down position)
- Weak vestibular system and poor coordination
Simplified push-ups
The exercise cannot be called basic, suitable for a beginner; the vestibular apparatus must be well developed.
Modified exercises are performed to improve muscle mass, but the simple version does not reduce the benefits. Upside down push-ups are difficult to perform when compared to the standard type.
Performing the exercise requires additional equipment. At home, you can use a chair or a cabinet where you need to put your feet. Thanks to the support, it will be easier to rest your arms on the floor, and your hands should be placed further than the shoulder line, which helps to better maintain balance.
Alexander Shestov
TRX Certified Trainer
Ask a Question
Standing push-ups in a lighter version will prepare the muscles for a more tense state, but the first results of the training will appear quite quickly.
Inclusion in the training program
It is advisable to perform such push-ups at the beginning of the complex on the deltoid muscles , with the first movement. In this case, preliminary warm-up on the shoulders is mandatory.
Be aware of the risk of injury when doing hand push-ups. Thoroughly warm up and lightly stretch all working muscles, joints and ligaments.
After warming up, perform 3-4 sets of push-ups upside down, 8-12 times each. Next, move on to the following shoulder exercises (standard presses and swings).
If, as your training progresses, you can do 15 or more repetitions, move the movement to the end of the complex. Doing push-ups against the backdrop of accumulated fatigue will be much more difficult.
Recommendations
- Provide yourself with the widest possible support area. Try to place your fingers as wide as possible, so that you can stand firmly at emphasis;
- Work on the width of your palms. Fix your body position so that it is comfortable to do push-ups, moving your elbows slightly to the side or forward;
- Bend your arms at the same speed, do not fall on one side;
- Place a special stand or a regular mat under your head;
- Don't be ridiculous, this can lead to injury;
- Place your palms at the same distance from the shoulder joint; if on one side the distance is a little further, you can “fall” on this side or just simply fall;
- Tighten your body so that the stabilizer muscles are activated and the body does not tilt in one direction or another;
- Do not use a headrest that is too high, so as not to artificially reduce the amplitude of work.
Is it possible to pump up your shoulders with push-ups alone?
In CrossFit, head-down push-ups are one of the basic exercises in training athletes. And walking on hands at speed is completely included in the competition plan.
Bodybuilders do not do this exercise, but often their deltoids are more developed.
It will not be possible to pump up your shoulders using only push-ups on your hands, or indeed using just one exercise per muscle group. Their volume will, of course, increase, but their development will not be impressive.
To make your deltoids really big and give them a spherical shape, you will need a whole set of exercises for this muscle group.
It should include basic and isolating movements aimed at working out different muscle bundles of the deltoid.
Hand position
Youdas et al. (21) found that a pronated grip (Fig. 1) during pull-ups (56 ± 21%) of maximum voluntary isometric contraction (MVIC) was more effective in activating the lower trapezius muscle compared to a supinated grip (45% ± 22% MVIC). The pronated grip (Fig. 2) also resulted in greater activation of the infraspinatus muscle (79 ± 56% MPIS) compared to “perfect” pull-ups (71 ± 52% MPIS), which uses 2 handles with the ability to rotate through 3600 (subjects began the execution at pronated position and ended in a supinated position). At the same time, perfect pull-ups showed the ability to increase activation of the latissimus dorsi muscles (130 ± 53% MPIS) compared to the supinated grip (117 ± 46% MPIS). A supinated grip, compared to a pronated grip, resulted in greater activity in the pectoralis major (57 ± 36% MPIS vs. 44 ± 27% MPIS) and biceps brachii muscles (96 ± 34% MPIS vs. 78 ± 32% MPIS). It should be noted that the % MPIS of the latissimus muscles when performing any of the exercise variants was higher than that of all other muscles assessed.
Rice. 1
In an experiment by Lusk et al. (12), which assessed the effect of grip width (narrow and wide) and forearm position (supinated and pronated for both grip options), did not reveal any effect on muscle activity when performing lat pull-downs. Using 70% RM, they found 9% greater activation of the latissimus dorsi muscles with a pronated grip. There were no differences in the activity of the biceps brachii or the middle portions of the trapezius muscles. In a similar study, Signorile et al. (19) assessed differences in muscle activity between wide grip (chest and overhead rows) and close grip (supinated and pronated) lat pulldowns; greater activation of the latissimus dorsi has been shown with a pronated grip. The pectoralis major muscles showed greater activity with a neutral grip compared to a pronated grip; although this exercise is not a chest exercise, according to Youdas et al. (21), due to low muscle activity of 44 - 57% MPIS with various variants of upper pulley rows. The posterior deltoids showed no differences in activity between different arm positions. At the same time, Lehman (11), examining the levels of muscle activation during lat pulldowns using a load of 10 RM, found small differences in muscle activity between the pronated and supinated grips in the latissimus dorsi and biceps brachii muscles.
Rice. 2
Example of a push-up program for beginners
You need to train according to this table every other day. The numbers indicate the number of repetitions in the approach, the sign > rest between approaches. The rest time is arbitrary, but try not to rest longer than necessary to regain your breathing.
- You can start the approach with classic push-ups, and continue from your knees or from the wall. When the circuit ends, repeat the last day, performing more and more repetitions from the floor.
- You can go through the entire circuit against the wall, then the entire circuit from your knees, then the entire circuit from the floor.
| Day | Women's program |
| 1 | 2—2—2—2—3 |
| 2 | Rest |
| 3 | 4—3—2—2—4 |
| 4 | Rest |
| 5 | 5—4—4—3—5 |
| 6 | Rest |
| 7 | 4—5—4—4—5 |
| 8 | Rest |
| 9 | 6—5—3—4—6 |
| 10 | Rest |
| 11 | 5—6—4—5—6 |
| 12 | Rest |
| 13 | 9—8—10—8—10 |
| 14 | Rest |
| 15 | 13—10—11—11—10 |
| 16 | Rest |
| 17 | 15—11—14—10—11 |
| 18 | Rest |
| 19 | 20—14—14—12—15 |
| 20 | Rest |
| 21 | 14—12—12—10—13 |
| 22 | Rest |
| 23 | 18—11—13—12—13 |
| 24 | Rest |
| 25 | 21—18—14—13—19 |
| 26 | Rest |
| 27 | 18—11—13—12—13 |
| 28 | Rest |
| 29 | 14—11—11—9—13 |
Below we present a push-up program for men, it is also designed for a month.
| Day | Program for men |
| 1 | 6—6—5—4—5 |
| 2 | Rest |
| 3 | 8—8—6—5—7 |
| 4 | Rest |
| 5 | 9—8—8—5—9 |
| 6 | Rest |
| 7 | 8—7—5—4—6 |
| 8 | Rest |
| 9 | 10—8—6—7—9 |
| 10 | Rest |
| 11 | 9—9—7—7—9 |
| 12 | Rest |
| 13 | 13—10—9—12—10 |
| 14 | Rest |
| 15 | 15—15—13—13—10 |
| 16 | Rest |
| 17 | 20—14—14—12—15 |
| 18 | Rest |
| 19 | 14—12—14—12—15 |
| 20 | Rest |
| 21 | 20—12—14—13—16 |
| 22 | Rest |
| 23 | 20—17—14—15—18 |
| 24 | Rest |
| 25 | 22—21—16—20—22 |
| 26 | Rest |
| 27 | 13—12—10—8—25 |
| 28 | Rest |
| 29 | 10—10—8—7—28 |
Train regularly - and in a month you will be able to do 30-40 push-ups!
Breathing rules for push-ups
Inhale as you move down. Move up while exhaling. If you're having trouble maintaining a normal breathing rhythm, you're probably doing push-ups too fast. Reduce the speed of the exercise, move more smoothly, stopping at the top point of the amplitude.
The second reason for shortness of breath during push-ups is smoking. After getting rid of a bad habit, breathing during training returns to normal.
Incorrect breathing technique during push-ups often contributes to increased blood and intracranial pressure.