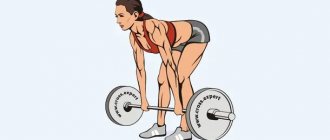
The Romanian single-leg deadlift is an exercise that has been popular since the days of the Soviet sports school, which very effectively works the gluteal and hamstrings. Unlike the classic version of the movement, the single-leg deadlift additionally engages a large number of stabilizer muscles, and also develops coordination and balance.
Similar exercises
The load is indicated on a 10-point scale (the total load is summed up)
| Small of the back | 9 (high) |
| Buttocks | 7 (high) |
| Posterior thigh | 7 (high) |
| Upper back | 4 (average) |
| Front thigh | 3 (average) |
| Inner thigh | 3 (average) |
| Forearms | 3 (average) |
| Outer thigh | 2 (weak) |
| Total load/exercise type | 38 (high) / basic global |
| Load on the spine | 8 (high) |
The load is indicated on a 10-point scale (the total load is summed up)
| Small of the back | 8 (high) |
| Buttocks | 7 (high) |
| Front thigh | 6 (average) |
| Posterior thigh | 5 (average) |
| Upper back | 4 (average) |
| Inner thigh | 3 (average) |
| Forearms | 3 (average) |
| Outer thigh | 2 (weak) |
| Total load/exercise type | 38 (high) / basic global |
| Load on the spine | 8 (high) |
The load is indicated on a 10-point scale (the total load is summed up)
| Small of the back | 9 (high) |
| Buttocks | 7 (high) |
| Posterior thigh | 7 (high) |
| Front thigh | 3 (average) |
| Inner thigh | 3 (average) |
| Outer thigh | 2 (weak) |
| Total load/exercise type | 31 (high) / basic global |
| Load on the spine | 10 (high) |
The load is indicated on a 10-point scale (the total load is summed up)
| Small of the back | 8 (high) |
| Buttocks | 7 (high) |
| Posterior thigh | 7 (high) |
| Front thigh | 3 (average) |
| Inner thigh | 2 (weak) |
| Total load/exercise type | 27 (high) / basic global |
| Load on the spine | 6 (average) |
Rate the material: rate
Found an error in the article? Select it with the mouse and press Ctrl + Enter. And we will fix it!
| SHARE | WE ARE IN SOCIAL NETWORKS |
- Individual selection of a set of exercises
- Training program for beginners - girls
- Workouts at home, or how to pump up at home
- Calorie consumption counter
- Training Plan for Beginners - Men
- Daily calorie consumption calculator
- A set of exercises for weight loss
- Women's diet for weight loss
- Weight loss exercise program for men
- Workouts for girls on relief with emphasis on the hips and buttocks
- Lat training - exercises and techniques
- How to pump up your back - exercises and techniques
- Deadlift - increasing results
- How often can you train one muscle group?
What muscles work when performing deadlifts with dumbbells?
Deadlift (any of its types) refers to basic exercises, that is, to perform it, a large number of muscles and joints of the whole body are involved in the work.
When deadlifting with dumbbells, the same muscles work as when deadlifting with a barbell:
- back muscles - greater emphasis is placed on the extensors in the lumbar region, while the trapezius and latissimus dorsi muscles are little involved;
- press;
- gluteus maximus muscles;
- hamstring biceps;
- quadriceps.
Muscles working during the deadlift exercise.
In addition, of course, there are stabilizers that help maintain balance, and several other muscle groups that are activated to a much lesser extent.
However, we draw your attention to the fact that depending on the choice of exercise technique, the load on the muscles can shift, for example, almost completely eliminating the load on the quadriceps, loading the gluteal and hamstrings, or vice versa. Next, we will look at what types of deadlifts with dumbbells there are, and which muscle groups they affect to a greater extent.
Nuances
In practice, there are about eight types of deadlifts. Not everyone understands the differences between them. It is worth remembering that the essence is to shift the loads, that is, for each variety the goal will be the development of certain muscles. Several features of the exercise in question should be noted:
- low weight of the projectile;
- short range of motion;
- maintaining the vertical position of the lower leg.
Before you start training, you should choose suitable shoes. It should be comfortable, without a heel or with a heel no thicker than 1 cm, with a flat and wide sole. Otherwise, the exercise may well end in a back injury.
If the weight is too heavy, a different grip is often used. However, this method can become traumatic, especially for the spine. Therefore, when using a different grip, it is advisable to reduce the number of repetitions or do the exercise using wrist straps.
A fairly common mistake when performing deadlifts is a rounded back. Such a mistake can be costly for the spine. You can insure yourself against unnecessary injuries if you carefully monitor the perfectly straight position of your back.
Often athletes neglect the correct approach to the barbell, as a result of which it moves at some distance from the legs
It is important to remember that the sports equipment should be located quite close to the legs or even touching them
Some athletes with powerful, well-developed hands mistakenly pull the barbell with them at the last stage of the exercise. This is strictly prohibited. The hands should only perform the function of holding the weight, and lifting the bar is carried out only through the work of the gluteal muscles and hamstrings.
Types of deadlifts
"Sumo"
This is a deadlift in which the legs are placed wide, like in sumo wrestling.
The technique is very similar to the classical one. The bar is over the middle of the foot, the shoulder blades are perpendicular to the bar, the back is in a neutral position. But the sumo stance rotates the torso more vertically than a traditional deadlift. This changes the muscles that participate in the movement. The lower back is less involved because the body is more upright. The groin area is worked on more - it is under tension. The quadriceps muscles are also involved because the hips are lower (knees bent more). It is worth noting that squats with a barbell work the quadriceps muscles and groin area better. Therefore, there is no reason to choose the sumo deadlift. Perhaps you have seen very strong people doing sumo and decided to follow their example. A very useful tip: do not switch to sumo deadlifts until you have completely mastered the classic ones. Wait until the results increase to 160-180 kg with proper form in the regular deadlift. There is only a very small group of people who, due to their anatomical structure, cannot do the traditional one. We are talking about people who have long hips and very short arms. In this case, it is impossible to do the exercise with conventional technique. Then they resort to sumo. Most likely you don't have such a problem.
Deadlift on straight legs
Performed with both a barbell and dumbbells. The quadriceps muscles do not help in this exercise because they are already straightened. Therefore, the gluteal and hamstring muscles do all the work. The load on the knees is minimal; they do not participate in the movement at all. This is a complement to the traditional deadlift, but in no way a replacement.
Romanian deadlift
Starting position - the barbell is in the middle of the thighs, the knees are slightly bent, the grip is slightly wider than shoulder width. Bend at the waist and lower the barbell to the middle of the shin. We return to the starting position. Very popular among girls when training their legs and buttocks.
Where does such a strange name come from?
I don’t know about you, but from the very first time I heard about the Romanian deadlift, I wondered where such a strange name came from. I remember when the coach asked what I would do today, I answered that I would hammer the Romanian deadlift. To which he asked the stupidest question by nature: “Are you Romanian?” I’m almost sure that the coach didn’t know why the Romanian deadlift is called that way (just like I did then)... oh, if only I caught him now
.
So, Romanian cravings were first mentioned in literature in the early 90s. But it was invented much earlier, somewhere in the early 80s. These years were truly the peak of Romanian weightlifting.
The most outstanding Romanian weightlifter was a certain Vlad Nicolae. The sports career (performances) of this outstanding athlete lasted from 1984 to 1996. And at the beginning of the 1990s, fellow lifters noticed a somewhat strange exercise in Vlad’s arsenal, which was similar to the deadlift, but at the same time noticeably different from it. Vlad used the Romanian deadlift solely for the purpose of developing lagging muscles in the deadlift, but our fellow bodybuilders soon adopted this exercise from him and took it to a new level.
What are the alternatives to this exercise?
Lunges with dumbbells are an effective exercise for the buttocks and thighs, and should not be ignored unless there is a compelling reason to do so. If axial load on the spine is contraindicated for you, try performing lunges in a hack machine or Smith machine. This way you will not only protect your spine, but also work on your target muscle groups in more isolation.
You can perform steps onto a box or other hill; the biomechanics of this movement and classic forward lunges are almost the same, and in terms of the effectiveness of steps, they are in no way inferior to lunges. Watch the position of your body and perform this exercise with a straight back, without leaning forward.
Pistol
Single-leg pistol squats can also replace cross lunges, but performing this exercise in a high rep range will be harder for most athletes since single-leg squats require more control and balance.
Sissy squats
Sissy squats are a technically difficult and traumatic, but at the same time incredibly effective exercise. We hold onto some support with our hands, direct our pelvis and knees forward, and ourselves lean back as far as possible. We perform the movement until the biceps of the thigh lies on the calf muscle, and the knees are extended as far as possible beyond the level of the toes. The unusual thing about this exercise is that here we rely not on the heel or the entire foot, but on the toe. Huge range of motion, isolated and targeted work of the quadriceps. If you don't want to do forward lunges or cross lunges, try doing sissy squats at the end of your leg workout, when all the ligaments and muscles are fairly tired. It’s hard, painful, difficult, but effective.
Jumping on a box
Box jumps or spring jumps are less effective for the glutes and thighs than classic lunges, but can be a great complement to forward lunges or cross lunges. Try doing several sets of lunges and jumping jacks in a row without stopping for a great, functional cardio workout.
What muscles does the Romanian deadlift work?
Let's consolidate all of the above. The main muscle group when performing the Romanian deadlift is:
Gluteus maximus muscle. It occupies the largest area of our pelvis. And it is the main muscle responsible for hip extension.
Gluteus medius. Also gets a load. Helps the gluteus maximus. And is a leg stabilizer.
It is to develop these muscle groups that we set ourselves the task when performing the Romanian deadlift
Therefore, try to focus all your attention on their work. . In addition to the main muscles, there are secondary ones:
In addition to the main muscles, there are secondary ones:
Back of the thigh. This includes the biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semitransversus muscles. In this exercise they receive very little load. Acting also as hip stabilizers.
Quadriceps. Also loaded to a minimum. And the hip stabilizes.
Back muscles. These include the lats, trapezius and spinal extensors. The complex focuses on maintaining weight and extending the back. The spine is stabilized in an even position.
Four important rules for any method of traction
- The bar is kept level, parallel to the floor throughout the entire training. The barbell is moved strictly vertically; it should not “walk” in the horizontal plane.
- The exercise is performed while holding your breath. This allows the lungs to fill and the diaphragm to hold. In the lower phase, the athlete inhales. Holds his breath on the way up. When the top point is passed, the downward movement is performed, the lifter exhales powerfully.
- Use wrist straps if there is not enough wrist strength.
- The back is kept straight, only a slight natural bend is possible in the lumbar region.
What muscles are involved in the training?
The deadlift works more than 75% of all muscles, so even a weak person can quickly build up the volume of the hips and back muscles. At the same time, completing the task does not seem difficult. Even a beginner in bodybuilding and powerlifting can do it.
The main muscles involved are the lower legs, thighs, buttocks, back, and shoulder girdle. The muscles of the wrist, flexors of the fingers and toes, the abdominal press and small muscles work as auxiliary muscles. So, they “work”:
- triceps surae (gastrocnemius and soleus);
- quadriceps femoris (fascia lata, sartorius, rectus femoris and vastus lateralis);
- vastus lateralis, biceps femoris, semitendinosus and adductor magnus muscles;
- buttocks (large and medium);
- back muscles (trapezius, latissimus, rhomboid and iliac crest);
- in the structure of the shoulder and forearm (infraspinatus, teres major and minor, deltoid), serratus anterior, triceps brachii;
- Deadlift techniques of any kind use the erector spinae muscle as a stabilizer.
Technique for performing on one leg
The purpose of this exercise is mainly to concentrate the load on the back of the thigh. This option also loads the quadriceps on the leading leg no less strongly, which turns the deadlift with a kettlebell on one leg into an excellent profiling exercise not only for the back, but also for the legs.
- A weight of suitable weight is taken with both hands.
- One leg is moved back slightly.
- A slow lifting of the projectile begins while maintaining the arch of the back.
- When the body rises evenly, the secondary leg should also be measured back to maintain a right angle between it and the body.
The general rules of execution are similar to the classic deadlift technique with a kettlebell.
It is always important to remember to breathe correctly. When moving up, exhale, and at the top point take one or more breaths
A set of exercises for a beautiful butt with a barbell
When performing each movement, take your time and pay attention to your technique.
Deadlift
Stand up straight, grab the barbell in your hands with an overhand grip shoulder-width apart. Bend your knees slightly. Move your pelvis back, lean your body forward, slide your hands with the barbell down over your thighs, lowering the barbell to knee level. Then smoothly, working the muscles of your legs, thighs, buttocks and core, return to a vertical position. This will amount to one repetition. Execute 30
such, then rest for 40 seconds.
Increase the weight of the barbell and perform another 20 repetitions
of the exercise.
After a short rest, take your maximum weight and perform 10 more repetitions
of the exercise. After this, rest for a minute and move on to the next exercise.
Lunges with a barbell
Take the barbell with an overhand grip, bend your elbows and place the barbell at the level of your collarbones. Stand straight, feet shoulder-width apart. Step your left foot back and lower into a lunge, bending your knees to a right angle. Work the muscles of the buttocks, thighs, abs and back. Then smoothly return to the starting position. This will amount to one repetition. Perform the required number on each leg.
Plie with barbell
Stand up straight, grab the barbell with an overhand grip and place it on your shoulders. Place your feet wider than your shoulders, pointing your toes slightly to the sides. Bending your knees, work the muscles of your legs, back, buttocks and abs, and lower yourself into a plie. Smoothly return to the starting position. This will amount to one repetition. Complete them as required.
"Sumo wrestler" with a barbell
Stand up straight, grab the barbell with an overhand grip and place it on your shoulders. Place your feet parallel, slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Bend your knees and work the muscles of your legs, back, buttocks and abs, lower yourself into a squat, and lean your body slightly forward. Then smoothly straighten up. This will amount to one repetition. Complete the required number of them.
Squats
Stand up straight, grab the barbell with an overhand grip and place it on your shoulders. Place your feet parallel, shoulder-width apart. Bend your knees, move your pelvis back and lower into a squat. Do not increase the arch in the lower back, work the muscles of the abs, buttocks, back and legs. Then smoothly straighten up. This will amount to one repetition. Complete the required number of them.
Bent over with barbell
Stand up straight, grab the barbell with an overhand grip and place it on your shoulders. Step your right foot forward (the heel of your right foot is slightly forward relative to your left toe). Gently lean your body forward, slightly bending your left leg. Work the muscles of the abs, back, buttocks. Do not increase the arch in your lower back. Then return to the starting position. This will amount to one repetition. Do the required amount in each direction.
One leg squat
Stand with your back to the fitball, grab the barbell with an overhand grip and place it on your shoulders. Shift your body weight to your right foot, bend your left leg slightly and place the instep of your left foot on the exercise ball. Working the muscles of the abs, back, buttocks and legs, bend your right leg, lowering into a squat, and slightly roll the exercise ball back with your left foot. Smoothly return to the starting position. This will amount to one repetition. Perform the required number of repetitions in each direction.
Gluteal bridge (with progression)
Lie on your back, bend your legs and place your feet on the exercise ball. Take the barbell in your hands with an overhand grip and place it at the level of the iliac bones, holding the barbell with your palms. Using your shoulder blades, back of your head and shoulders, lift your pelvis off the floor. Then smoothly straighten your legs, rolling the fitball further away from your body. Without lowering your lower back and buttocks to the floor, bend your knees again and roll the exercise ball towards you. This will amount to one repetition. Complete the required number of them.
Squat with fitball
Stand with your back to the fitball, grab the barbell with an overhand grip and place it on your shoulders. Bend your knees and move your pelvis back, sit on the fitball. Then, working the muscles of the thighs and buttocks, smoothly return to the starting position. This will amount to one repetition. Perform the required number of repetitions.
One-legged squat with a chair
Stand with your back to a chair, grab a barbell with an overhand grip and place it on your shoulders. Shift your body weight to your right leg and lift your left leg off the floor. Bend your right knee and move your pelvis back, sit on a chair. Without lowering your left leg to the floor, smoothly return to the starting position. This will amount to one repetition. Perform the required number of repetitions on each side.
Close-grip barbell row to the chin
Squats on one leg: benefits, technique, mistakes
This exercise is more traditional and anatomically correct, however, not everyone can perform it technically correctly due to the presence of spinal curvature or injuries to the upper and middle sections.
What muscles work
This option includes the middle and anterior deltoid muscles, as well as the upper part of the trapezius muscles.
In addition to the target muscles, the rhomboids and biceps are also used.
Execution technique
- The barbell must be taken with an overhand grip. It is very easy to position your hands correctly on the bar; to do this, you need to place your thumbs on top of the bar so that they touch each other - this will be the correct placement of your hands.
- After this, you need to straighten up, slightly arching your back at the lower back. Shoulders should be straightened and arms straight at the elbow joints.
- In the starting position, the barbell should be on your hips.
- While pulling the barbell to the chin, the athlete exhales, concentrates lifting the barbell to the chin, tensing the deltoid muscles.
- Elbows should extend vertically upward.
- The movement is carried out by contracting (tensing) the deltoid muscles and moving the elbows upward.
- Throughout the entire amplitude, whether up or down, the bar slides strictly in a vertical plane along the body.
- No need to hang over the bar. Hanging over can cause excessive arching in the back.
- The chin should be in a horizontal plane throughout the entire movement.
- There is no need to tilt your head or lift your head up.
- At the top point of the amplitude, the elbow joint should form a thirty-degree angle.
- Pause briefly at the peak of the upward movement, then slowly lower the barbell down along the same path.
Errors
Everyone has heard about rounding the back and walking knees more than once and there is no discovery in these errors
Bone Wide brings to your attention mistakes that you most likely never paid attention to!
- Converting Deadlifts to Squats
Deadlifts are not squats with a barbell in your hands, no matter what indoor bodybuilders say. If we compare the deadlift with squats, then it is more like half squats rather than full-amplitude squats.
You need to start the deadlift in a half-squat position - yes, individual characteristics leave an imprint, but you should not lift the barbell from a very deep squat.
When you start too low, the bar is too far away from your torso, which is not good for your lower back and puts your leverage in a weaker position.
- Lean back
Those who are overly agile often lean back during deadlifts to demonstrate complete control over the working weight. Some do this completely unconsciously, but this fact does not change the matter. There is no need for this.
Even the rules for powerlifting competitions require you to lock your knees and hips while standing absolutely upright. When a person leans back, guess what happens to their knees?
They bend slightly, which weakens your stability, and arching in the lower back during deadlifts opens the door to spinal diseases, such as a herniated disc. For safety and effectiveness, deadlift until your joints are locked and your torso is upright—buttocks contracted, hips straight—without leaning too far back.
- Inappropriate shoes
Leave your Airmaxes in the locker room, just like your running shoes! As a rule, such shoes have shock-absorbing soles. This can lead to increased instability during heavy deadlifts. If you currently use thick-soled running shoes, changing your shoes—or simply taking them off for a deadlift—will instantly increase the amount of weight you can lift.
It is best to perform deadlifts in sneakers with flat, hard soles. This will add stability and evenly distribute the load on the foot. Read more about choosing sneakers in this article.
No need to go barefoot either!
- Excessive leaning over the barbell
Instead of squatting too deeply, which was our first point, here we are dealing with leaning over the bar and barely perceptible bending of the knees.
This technique is similar to the Romanian deadlift, which is an exercise for the buttocks and upper hamstrings.
This is a single-joint movement in the hip joints and should not be confused with a deadlift. You need to lean into a half squat, not just bend over.
About the harm
Romanian barbell deadlift
Deadlifts, like other strength techniques, have many contraindications. If you ignore medical prohibitions, the harm to your health can be irreparable.
Specific contraindications:
- imbalance of the muscle corset. Common among those who are keen on different grips and have developed one side better than the other;
- any problems with the spine and lumbar back;
- rehabilitation period after operations and injuries;
- gastrointestinal ulcers;
- hypertension.
If you have problems with blood pressure, you should not use scales. If the necessary breathing technique is observed, hypertensive patients experience an exacerbation of the disease. Any deadlift should not be done after pull-ups. The fact is that when pulling up, the spinal discs relax and stretch; if you then begin to pull the weight, pinching will occur.
The exercise will not bring benefit, but harm if you do it incorrectly or exceed your normal load. If you neglect the technique, a microdislocation of the lumbar region may occur, and the formation of a vertebral hernia is possible.
The barbell is too heavy
The first rule in bodybuilding, and indeed in any sport. Excessive loads only lead to injuries! Indeed, there has never been a single person who could grab any weight without thinking and became an outstanding champion. But there are more than enough athletes who have suffered injuries like this. When you take on a weight you can't control, your technique automatically becomes incorrect. Starting from rounding the lower back, and ending with bringing the knees beyond the toes. Therefore, if you want to get results from your workouts over a long period of time. So increase the working weight gradually. Especially in such a traumatic exercise as the Romanian deadlift!
Lumbar rounding
As I said earlier, rounding of the lower back can occur due to too much weight on the barbell. Which pulls us down. To avoid this, simply lose weight. But this is not the only reason. Each person has their own limit to the depth of descent in the Romanian deadlift. It depends on the elasticity of your muscles. Basically, the barbell is lowered to the middle of the shin. But there are also more flexible athletes. Although there are not so many of them, about 10-20% of the total mass. If an athlete who is not one of these people begins to continue moving downwards. That is, instead of stretching the gluteal muscles further. He will begin to round his back. This will create a greater load on the spine. Further consequences, as you understand, will be disastrous.
Pulling weights by curling your arms
In the Romanian deadlift, all movements occur due to the work of the gluteal muscles. If you start to bend your arms while lifting. The exercise will turn into a BELOW ROW. And most of the load will begin to go to the latissimus dorsi muscles. But we don't need this.
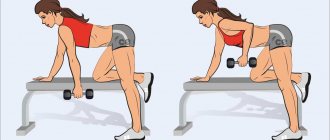
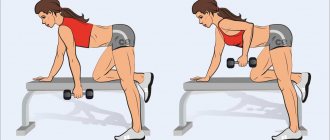
Bent-over dumbbell row
Working muscles
The muscles of the upper back occupy a fairly large area. If they are qualitatively developed, then the rear view of the body turns out to be very impressive and powerful. It is for this reason that dumbbell rows are such a popular exercise - because this exercise allows you to perfectly work this area.
As a variation of the bent-over barbell row, the same muscles receive the load:
- "Wings".
- Big round.
- Posterior deltoids.
Partially the trapezius and rhomboid muscles have to work.
Unlike using a barbell, dumbbells allow you to move through the maximum possible amplitude, moving your elbows much further than the bar allows you to do. Naturally, this significantly increases the efficiency of its implementation. In particular, the load on the posterior deltoids increases significantly (although other muscles also receive additional tension).
To whom, when and why
Since the exercise belongs to the “base”, it can be seen both in the programs of beginner athletes and in the complexes of major professional athletes. If we consider all the existing exercises in terms of effectiveness, the bent-over dumbbell row certainly deserves the highest rating.
To whom?
Despite the fact that this is a basic exercise, it is better for beginners to start with bent-over barbell rows - this option has a simplified technique, since you should pull one barbell, and not two dumbbells separately.
Most often, dumbbell rows are used by experienced athletes who want to diversify their bodybuilding program.
When?
Naturally - on the day of training the back muscles. If you are doing more serious compound exercises (for example, deadlifts), then dumbbell rows should be performed after.
Dumbbells can be pulled at almost any time during training. During bulking, you can use them to “finish off” the muscles after bent-over barbell rows (or even do the exercise with dumbbells as the main one), during “drying” - this method is generally irreplaceable.
For what?
In addition to the fact that this option loads the upper body much better than working with a barbell, it “outlines” the shape of the middle of the back quite effectively. If you want your backside to look powerful and sculpted, doing dumbbell rows is a must.
Execution technique
- We take dumbbells in our hands. Maintaining the natural curve of the spine, we lean forward (the angle of the body relative to the floor is no more than 45 degrees). Bend your knees slightly. We lower our hands freely down. Head – looks straight ahead.
- Keeping the body, legs and head in a stationary position, we begin to pull the dumbbells towards the lower abdomen. In this case, the elbows are pressed against the body, moving along it as long as possible.
- At the top point, we make a short pause and smoothly lower the dumbbells down.
- Repeat the required number of times.
Important nuances and tips
- Working weight. Typically, this exercise does not use large weights; a barbell is most often used for this. The best option is dumbbells of medium or minimal weights, allowing you to do at least 10 repetitions efficiently.
- Number of repetitions. Optimally – from 8 to 20.
- Movement speed. You should move smoothly, you can pull a little faster than lower. In any case, be sure to ensure that inertia does not arise, which will reduce the load. In this case, reduce your driving speed.
- Frame. A mandatory aspect is a stationary and straight body. Make sure your spine remains straight until the end of the exercise.
- Holding your breath. If you can’t keep your body still, hold your breath while pulling.
- Delay at the top. Holding when your elbows are at the top is effective and relevant. This allows for maximum load on the teres major muscles. When doing this, be sure to bring your shoulder blades together.
- Amplitude. To increase the effectiveness of the exercise, work not only with your hands - at the top point, try to bring your shoulder blades as close as possible. This will increase the load on the teres major muscles. At the lowest point, lower the shoulder joint down, thereby stretching the back muscles. Also try to move your elbows as far as possible.
- Elbow joint. Elbows should move as close to the body as possible. Their deviation to the sides reduces the load on the “wings”, shifting it to the large round muscles and deltoids.
- Direction of palms. The best option is if your palms are directed towards each other. However, you can experiment with their position.
Now you know how to pump up your back with dumbbell rows.
Anatomy
All types of muscles that form the silhouette of our legs can be divided into the following groups:
- gluteal;
- quadriceps or front of the thigh;
- muscles of the back of the thigh;
- calf muscles.
The first group includes:
- gluteus maximus (the largest and thickest, responsible for the “fleshyness” of the butt, with its help the hip moves);
- middle (external pelvic muscles, helps the leg move back and fixes the body during extension);
- small (located next to the middle one and has the same functions).
- rectus femoris (located in the front of the thigh, responsible for its flexion);
- vastus lateralis muscle (occupies the anterior outer part of the thigh);
- intermediate wide (does not allow the knee joint to bend when the heel touches the ground when walking);
- medial wide (located on the inner side of the thigh).
All muscles in this group provide hip flexion/extension.
Find out what to do if your muscles hurt after a workout.
The third contains:
- biceps (together with the gluteus maximus it participates in extension of the torso);
- semitendinosus (borders on the biceps, flexes/extenses the lower leg, thigh at the knee joint);
- semimembranosus (rotates the lower leg inward and extends the thigh in the pelvic area if the knee is extended).
The muscles of the lower leg include:
- gastrocnemius (occupies the back of the lower leg, ensures movement of the foot and stabilization of the torso while walking);
- soleus (flexes the foot at the ankle joint);
- plantar (rudimentary, works together with the previous two);
- anterior tibial (performs the function of extending the foot).
CrossFit complexes containing lunges with dumbbells
The functional complexes given below contain lunges with dumbbells and will not only contribute to the complex development of the athlete (strength, endurance, coordination, muscle mass gain, etc.), but will also significantly increase your energy expenditure during training.
Don’t forget to eat right and recover, since this is what determines whether you can show a truly champion result today. If you feel unwell of any kind, lack sleep, or simply feel not at your best, we recommend holding off on these complexes until you have fully recovered your strength and replace them with something easier.
| Chicken Legs | Perform 30 dumbbell forward lunges, 10 classic barbell squats, 10 front squats, 10 overhead squats. Only 3 rounds. |
| Heavy Metal Maniac | Perform 6 deadlifts, 10 pull-ups, 20 side lunges, 20 forward lunges, 20 burpees. Only 5 rounds. |
| Hamstrings Boom! | Perform 20 forward lunges, 5 stiff-legged deadlifts, 20 Bulgarian lunges, 5 straight-legged deadlifts, 20 box step-ups, 5 straight-legged deadlifts. |
| Exactly | Perform 6 barbell thrusters, 8 deadlifts, 30 dumbbell forward lunges. Only 5 rounds. |
| Quadzilla | Perform 10 front squats, 20 forward lunges, 10 spring jumps, 20 forward lunges, 10 classic squats, 20 forward lunges, 10 box steps, 20 forward lunges. Only 3 rounds. |
| Carina | Complete a 400m sprint, 15 overhead squats, 15 box jumps, 50 forward lunges. Only 5 rounds. |
Exercises on the topic
Bulgarian lunges
Lunges with a barbell to the sides
Lunges with a barbell on the shoulders
Author Yaroslav Khvatov
Training experience - more than 8 years. Winner and medalist of All-Russian powerlifting and deadlift tournaments. Candidate for Master of Sports in deadlift.
When is it okay to bend over?
So, we have already established that for an amateur bodybuilder the exercise is useless - the oblique abdominal muscles are worked in the main basic movements.
For girls, bending over, which is most often done just to narrow the waist, only harms them. They lead to the opposite of the desired result.
But is it really impossible for anyone to do side bends with dumbbells?
No, there are exceptions:
- You are a professional bodybuilder who knows his body and his business. And you need perfect proportions. Such a person can balance between a wide waist and developed oblique abdominal muscles;
- You are a man, and you are friends with your head. Friendship is found precisely in the field of bodybuilding. 1 to 3 sets of obliques once a week will not widen your waist much;
- You are a woman who wants to become a professional bodybuilder. That is, you don’t really care about waist width. The main thing is that the muscle grows.
There is nothing uniquely useful. As well as definitely useless.
Problems begin where people think they are doing themselves good, when reality shows undeniable harm.
Side bends with dumbbells are just such an exercise.
It must be treated with extreme caution
Do you use tilts in your practice?
What's your reason?
Will you use them now?
Deadlift while standing on a stand
It's a pull from the pit. It is performed in the same way as the classic version, but the legs are placed on a stand. Thus, the barbell must be pulled and lowered to a lower position. The amplitude increases - the efficiency increases. The height of the stand is 5 – 10 cm. Discs, boards and anything that you can confidently stand on are suitable.
The exercises are difficult to perform and are only suitable for experienced athletes. But it is extremely effective for the buttocks. I would put it in first place in terms of effectiveness for the butt among all pull-downs. But there is one caveat. You need to bend your legs and lower your pelvis quite low (much like in the video). And then you will feel your butt right to the bones.
By the way (applies mainly to girls), if you do deadlifts with small-diameter discs, then you don’t have to stand on a stand, but simply lower the barbell all the way to the floor. The effect is the same. This refers to discs whose diameter is smaller than the standard diameter of 15, 20 and 25 kg discs.
Order an individual set of exercises from the author of this project - Timko Ilya
Features of deadlift
This technique is rarely used under normal conditions and is more relevant for girls. Professional bodybuilders also use it, because it has a great effect on the back of the thigh. In addition to the biceps, the exercise has a positive effect on the buttocks and lower back muscles.
The peculiarity of the technique is the prohibition of excessive weight. The pursuit of significant indicators in this regard inevitably leads to injury. We can’t set records here; we leave them for other modifications of the deadlift.
The deadlift technique is different; the main difference is straight legs. Yes, there is no need to bend your knees here, if only a little due to the anatomical features of the body. It is also advisable that the bar be on racks and not on the floor.
The stance is similar to the classic one (legs are shoulder-width apart and feet are parallel). The grip is similar to the classic one (from above, shoulder width apart). Bend your elbows (a little) and keep your back straight, as if it were fixed at the back by planks. The shoulder blades must be brought together throughout the entire process of lifting weights. Already moving down, we arch our backs and bend over, moving our pelvis back (synchronously). Be sure to keep your shoulder blades brought together, and your back always remains arched. You cannot round your back at the very bottom; you should feel the maximum stretch in the muscles located on the back of the thigh. There is no need to straighten your arms, your knees are slightly bent. Lower the bar to the middle of the shin. Climb. The barbell rises only due to the tension of the hamstrings. You need to lift the projectile no higher than the middle of the thigh, and the bar moves upward along the shins
It is important to start lifting without jerking, and the secret lies in lifting correctly. It needs to be implemented not with the back muscles, but with the legs
Your feet should be firmly planted on the floor and your legs should be pushing the weight upward. Then your back will not get tired, and the effect will be maximum. The gaze is always directed forward during the exercise. The bar moves exclusively vertically along the legs; there should be no deviations.
Deadlifts are often performed not with a barbell, but with dumbbells.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Xs0lJRk3Csw
Types of deadlift: what are they?
There are the following variations of this exercise:
- Classic.
- Romanian.
- Dead.
- Sumo.
These are the most basic variations that we will look at today. In fact, the biomechanics of the exercise differs in different performances in that different muscles are involved in the work. All these variations were invented in order to emphasize the load on certain muscles.
The deadlift should be a primary exercise, not an additional exercise.
It is worth noting that types of deadlifts with a barbell can be performed using other equipment. For example, dumbbells, kettlebells and other weights. Their use is justified by a slightly changing load vector, thanks to which the muscle can be worked from a different angle and given an impetus to growth.
Any of the presented variations is best performed from a power rack, starting the movement with an existing projectile in hand. After all, the correct technique for performing deadlifts is from the floor. But at the same time, the lower back is very heavily loaded.
In view of the mistakes that beginners make, it is better not to resort to the method of lifting from the floor, but to use exclusively a power frame. Of course, this will reduce the range of motion, but it will help preserve the lower back.
Be sure to warm up before deadlifting.
As for the technique of execution, the differences between the types of deadlifts are minimal. These include the width of the legs and grip. And the movements themselves are almost identical.
The essence of the exercise is that you need to lower yourself down with weight in your hands by bending the hip and knee joints and then return back to the starting position. Depending on the grip, position of the foot and trajectory of movement, the load on different muscle groups will change.
In some variations you can lift quite a lot of weight, but in others, for example, in the deadlift, this should not be done to avoid injury.
Regardless of the variation, it is very important to maintain the correct body position. The back is straight, without increased arching in the lower back
It is very important not to violate this position during the exercise. As this may reduce efficiency and also cause injury.
Classic deadlift
During the exercise, the main load falls on the back and lower back. The legs work only during the initial movement, when the projectile is being lifted.
- The stance of the legs is medium or narrow, depending on how comfortable it is for the athlete.
- Hands are positioned shoulder-width apart.
- The amplitude of movement of this variation is one of the largest.
- Recommended for general body strengthening.
Romanian deadlift
A popular variation among both boys and girls.
- The main load falls on the back of the leg - the biceps of the thigh, as well as the lower back.
- The exercise can be called a gentle version of the deadlift on straight legs, since during its execution the knees are slightly bent, and the pelvis can be pulled back.
Deadlift
One of the best solutions for the fair sex.
- Target muscles: hamstrings and glutes.
- The biomechanics of the exercise stretches the back of the thigh very well due to the fact that it is performed on straightened legs. If you bend your knees slightly and move your pelvis back, you get a Romanian deadlift.
- It is worth considering that for this exercise it is recommended to use minimal weight.
Sumo deadlift
This variation is called a lifter variation. It is characterized by:
- Wide stance of the legs and a relatively narrow grip, slightly narrower than shoulder width.
- In this case, the socks are turned slightly to the sides for better stability.
- This technique allows you to lift a little more weight.
The subtleties of this type of physical activity
It is important to perform basic effective exercises such as deadlifts, Romanian rows and squats, strictly adhering to the technique, because the work uses serious weight, involves a large number of muscles and places a lot of stress on the spine. All these factors indicate that this exercise is dangerous, so athletes often wear a special reinforcing belt that fixes the position of the spine.
Any exercise that is performed in a standing position and involves the use of weights puts a compression load on the spine, which in the future is fraught with pain or, at a minimum, osteochondrosis
Therefore, before starting training, be sure to consult with your doctor about the health of your back and the ability to carry out such physical activity on it.
Any exercise that is performed in a standing position and involves the use of weights puts a compressive load on the spine, which in the future is fraught with pain or, at a minimum, osteochondrosis. Therefore, before starting training, be sure to consult with your doctor about the health of your back and the ability to carry out such physical activity on it.
In addition to the scheme for performing the Romanian deadlift, you need to know some important nuances that will allow you to get a greater effect from the exercise and reduce the risk of injury to a minimum:
- Your comfort and safety depend on the right choice of shoes. It should have a heel no higher than 1 cm or without it at all, the sole should be wide, flat and rubberized.
- Often, when the weight of the barbell is very heavy, a different grip is used, i.e. one hand holds the projectile with a direct grip, and the other with a reverse grip, which is quite dangerous. If you decide to use this method, perform fewer repetitions and use special wrist straps.
- Very often, when performing Romanian deadlifts, athletes make the same mistake - they round their back. This not only shifts the load from the hips to the back muscles, but also threatens spinal injury, so before using heavy weights, you need to carefully work out the technique, and when performing deadlifts, watch yourself in the mirror to avoid serious mistakes.
- During bending and lifting, the barbell should be kept as close to the legs as possible, literally sliding the projectile along them, which will help increase the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Some athletes with developed arm muscles at the final stage of the exercise pull the barbell towards themselves, which is undesirable, because the main physical load on the muscles of the buttocks and thighs is carried out precisely due to their efforts to lift the apparatus.
The Romanian deadlift is a very effective exercise that allows you to engage almost all the muscles of the body and especially load the hips and buttocks, which often need development.
Effective exercises with dumbbells for slender legs, firm buttocks and beautiful thighs
The muscles of the legs and buttocks work every day. They are accustomed to constant load, so additional loads must be used to pump them. Habitual weight-bearing exercises can speed up the process of volume reduction. For exercise, you should choose dumbbells weighing more than 3 kg. After the muscles get used to the load, the weight needs to be increased.
Before picking up weights, it is important to warm up your muscles and joints. This will prevent injuries from occurring
With limited time, you can perform only 5 exercises:
- Squats with dumbbells. They differ from performing regular squats only by the presence of weights in their hands.
- Plie squat with dumbbells. To perform these squats, keep your legs wider than your shoulders and point your toes out to the sides. The dumbbell is held with both hands in front of you. When performing any squats, your knees should not extend beyond your toes. You should lower yourself into a squat until your thighs are parallel to the floor.
- Lunges with dumbbells. Hold dumbbells in each hand. Perform a lunge from a standing position, straighten up. You can do it on one leg first or alternate them.
- Weighted gluteal bridge. A dumbbell or a barbell plate is placed on the stomach below the waist and a regular bridge is performed.
- Bend forward with weights. Take a barbell or dumbbells in your hands. Without rounding your back, lean forward and hold for 2-3 seconds. and straighten up.
In addition to these exercises, you can also do the complexes given later in the article with additional load.
Additional recommendations
As a rule, this exercise is included in the program as the first strength exercise. It is basic, but can also be auxiliary. In this case, it is performed second. The weight chosen is medium, but the first workouts are carried out with dumbbells of minimal weight. Too heavy shells are not needed. It is very difficult to perform the necessary actions with them.
Repetitions, as a rule, are sufficient in the range of 8–12. If the training is aimed at reducing body weight, their number can be increased to 15. The intensity of the load directly depends on the purpose of the training.
To increase efficiency, you can additionally use any strength training device. True, in this case it is not worth developing a training scheme yourself. It is better to entrust this task to a specialist. Thus, it will be possible to achieve the desired result in the shortest possible time and avoid injuries that are possible when performing various strength exercises.
Choosing the right weight for dumbbells
Do enough repetitions