A gym, a fitness club, a school playground with horizontal bars, a school gym, these are places where every boy or girl, no matter what, started playing sports in childhood and youth, starting from the school family from 7 years old up to 16-18 years old inclusive.
Everyone went in for sports in order to improve their physical qualities and increase strength and improve endurance from an early age, doing sports, doing physical exercises, sports and physical education strengthened the muscular system of the whole body as a whole!
After years of training, everyone who continued their training in a fitness club, gym, or martial arts club improves their strength and endurance until they achieve their task and goal.
Bench press your own weight
Conquering a barbell of your own weight is the line that separates novice athletes from experienced athletes. You can’t imagine how many people there are in the gym who have been training for years but are unable to lift their own weight. If you don't take into account the six-foot guys with extremely poor leverage, anyone can reach their weight on the bench press.
What's stopping you? For some there is a lack of technicality, for others there is an excess of variability.
Technique problem : to be strong, you must not only be able to contract your muscles, but also use your joints correctly. Some people use a grip that would fit a fifth grader - it's so narrow. In the bench press, your elbows should be under your wrists. Have someone watch how your forearms move as you press: they should be vertical for the most part. It may take you a few workouts to learn how to bench press like this; but then you can press more.
Bench press with correct technique:
See also: all basic exercises with correct technique.
The Variety Problem : Remove all the unnecessary stuff from your workouts. The regular (standing) press translates positively to the bench press, but endless variations with different inclines, dumbbell lifts, and butterflies waste energy. There's no point doing them anyway unless you're pressing your own bodyweight. Throw it away without regret, then add it later.
If you already bench press your weight, can you take it to your chest and do a front squat? What about the jerk? You get the idea - conquer your own weight on the barbell in different movements, this lays a good strength base.
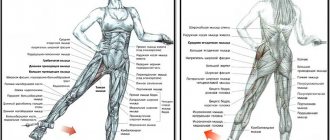
Anatomy
Hip Flexors
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint formed by the acetabulum of the pelvis and the head of the femur. It serves as the main connection between the lower limb and the torso and usually operates in a closed kinematic chain.
In addition to hip flexion, the above muscles are also involved in other movements, which are associated with variations in the positive Thomas test.
- Iliopsoas muscle - external rotation.
- Rectus femoris - knee extension.
- Tensor fascia lata - internal rotation, abduction.
- Sartorial muscle - knee flexion.
Deadlift with two body weights
It also seems like an easy exam, but some people can’t pass it for years. Lack of technique, weak grip, lack of muscles, back injuries - many different reasons.
An interesting observation: it is useful for many to give up the deadlift for a while in order to increase their record in it. Pull-ups will strengthen your grip, swings will teach the pelvic girdle to work, squats will add meat. By the way, I have not seen a single weightlifter who would not lift a lot in the classic deadlift, and they do not practice it at all. Get stronger in other exercises and your deadlift will increase too.
Not all powerlifters will agree with this, but the great champion Hugh Cassidy used to say that only a gorilla could lift more than once a week. So what to do in other workouts? Just “plow”: push and pull sleds, squat, do farmer’s walks, gain strength. Three-four-five-six months of hard training without deadlifting will only benefit her.
The role of manual muscle testing using the example of neurology
The Importance of Assessing Muscle Strength
Determination of muscle strength is an important component of the examination, especially in neurological patients. This method is used to assess muscle strength to differentiate true weakness from poor coordination or poor endurance. It may be called motor testing, muscle strength assessment, manual muscle testing, or other synonyms. Muscle strength assessments can be performed by nurses, doctors, physical therapists, osteopaths, chiropractors and other professionals.
Muscle strength testing function
Muscle strength is especially relevant in cases where the patient complains of weakness in the limbs, as well as when neurological pathology is suspected. It is an integral part of the neurological examination, especially for patients with stroke, traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury, neuropathy, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other diseases.
A commonly accepted method for assessing muscle strength is the Manual Muscle Strength Diagnosis Scale. This method involves testing the major muscle groups of the upper and lower extremities against the examiner's forces and rating the patient's strength on a scale of 0 to 5, respectively:
- 0 - no movement or muscle contractions;
- 1 - weak muscle contraction;
- 2 - movements only in the horizontal plane;
- 3 - ability to lift a limb, but not against resistance;
- 4 - ability to lift a limb against slight resistance, full range of motion;
- 5 - normal strength, full range of motion.
A standard determination of muscle strength is carried out to identify pathology of the nervous system, neuromuscular junctions, or the muscles themselves. Muscle testing in the upper extremities includes the study of the following movements - flexion of the supinated arm at the elbow joint, extension of the arm at the elbow joint, extension at the wrist joint, opposition of the thumb to the hand, abduction of the little finger, extension of the main phalanges of the II-V fingers. Muscle testing in the lower extremities includes hip flexion, knee extension, knee flexion, ankle extension (dorsiflexion), and ankle plantar flexion.
What to consider when performing manual muscle testing (MMT)
Invitation of Sergei Gritsenko to seminars on applied kinesiology
During testing, a special examination technique must be used to ensure reliable results. The patient should be asked to remove tight or restrictive clothing so that the examiner can see the muscles and observe muscle contraction. The examiner should also stabilize the joint and ensure that other muscles are not working during the examination. First, the specialist examines the range of passive movements in the joints to exclude local lesions of the musculoskeletal system (muscle and joint contractures). Then the patient's range of active movements is examined. The ability to lift the limb without resistance is determined; if the patient is unable to engage the muscle with the force of gravity removed, the examiner should place a hand on the muscle and ask the patient to try moving it again, which allows the examiner to feel the tension in the muscle even if the twitch is not visible. This will differentiate a score of 0 from a score of 1. When the patient demonstrates full range of motion, the test should be repeated with resistive motion for the full range of motion. If these actions are successful, the patient must overcome some resistance, and then the maximum resistance of the examiner. The unaffected or less affected side for comparison should be tested first to measure contralateral strength; all four limbs should be checked for full range of motion.
This method is very common, easy to use and does not require special equipment. Despite these advantages, it also has its limitations. The assessment depends on the subjective perception of the doctor. Depending on their own physical strength, examiners may provide different resistance. The test does not take into account musculoskeletal conditions that may make testing painful or difficult to tolerate, such as tendinopathy or arthritis. The test depends on the efforts of patients who may have poor resistance due to pain, misunderstanding of instructions, psychological or other characteristics. Finally, this system detects the level of resistance, but does not directly measure force.
Alternative muscle testing methods
Muscle strength can be measured in weights, strength units, or other units.
This requires specialized equipment; dynamometers are most often used. Dynamometry provides a more precise measurement of the force a muscle can exert and allows one to monitor changes in muscle strength over time. Hand grip dynamometry is a popular example where the patient squeezes a handle which records the force applied. The disadvantages of dynamometry are the need for expensive or specialized equipment, the study is limited to a certain muscle group, and this method is available to doctors only in certain specialties. Another option for testing muscle strength is to measure functional movements rather than quantitative strength. An example of a functional muscle test would be squatting or standing up from a chair. This testing provides information about how well the patient’s daily activities are maintained. However, functional activity tests do not provide a quantitative or qualitative assessment of muscle strength, as is the case with dynamometry. Accordingly, changes in this indicator cannot be tracked over time.
Clinical significance of manual muscle testing
Muscle testing can help identify neurological problems in which muscle weakness is an important symptom of the disease.
Specific muscle groups should be examined, depending on the suspected diagnosis. Careful examination technique is important to ensure reliable results. This method is used by therapists of various specialties; it does not require special equipment and has good reliability. While more precise measurement methods, such as hand-grip dynamometry, are less subjective and provide a quantitative measurement that can be tracked over time. Functional strength assessment is used in cases where it is necessary to assess the quality of life of patients and their daily activities. Schedule of seminars on applied kinesiology »
Two minutes plank
Personally, I prefer the traditional plank position, but you can choose any variation. The main thing is to hold it for 120 seconds. Dr. Stu McGill said that if you can't do a couple of minutes of planking, you either have too much fat or no abs. I’ll add: either you don’t know how to tense your muscles and hold tension. This is exactly what the plank teaches, and this is exactly the skill that beginners lack: they simply cannot bring the whole body together to lift a large weight.
Plank.
There is another way, for example, a farmer's walk with a weight in one hand. This “suitcase” version is a bar in dynamics. Just don’t chase weight, try 20 kg, not all 50 at once. You need to walk gracefully, and not sway like a blade of grass in the wind.
These walks are easy to add at the end of any workout: pick up the apparatus with one hand, carry it as far as possible, and bring it back with the other. You will immediately know how strong your grip is. And tomorrow you will discover the existence of some muscles on the sides of the body.
Sources[edit | edit code]
- ↑ 1,01,11,21,31,41,51,6 Essentials of strength training and conditioning. National Strength and Conditioning Association / Editors TR Baechle, RW Earle. — 3rd ed. - Hong Kong: Human Kinetics, 2008. - 642 p.
- ↑ 2,02,12,2 Fry, A. Measurement and Evaluation / A. Fry // Presentation 5: Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning Multimedia Symposium / NSCA Certification Commission. - Lincoln, 2006. - 36 p.
- ↑ 3,03,13,2 Strength training. National Strength and Conditioning Association / Editor L. E. Brown. - IL: Human Kinetics, 2006. - 368 p.
- Earle, R. W. Weight training exercise prescription. In: Essentials of Personal Training Symposium Workbook / R. W. Earle. - Lincoln, NE: NSCA Certification Commission, 2006.
- ↑ 5,05,15,2 Evans, N. Anatomy of bodybuilding / N. Evans; lane from English S.E. Borich. — 2nd ed. - Minsk: Potpourri, 2012. - 192 p.: ill.
“One-pillow” sleep
If you need two pillows (or more) to sleep well, it's time to work on your stretching, flexibility, and mobility, and it might be a good idea to check with your doctor. When you need to raise your head high (when sleeping on your back), this may be a sign of excessive kyphosis, in other words, you are too slouched.
Vladimir Yanda revealed to us half a century ago that the tonic muscles (especially the pectoralis, biceps, hamstrings and hip flexors) tighten with age, due to injury or weakness. So start stretching them.
When the problem is more serious, for example in the joints, then do not self-medicate, but consult a specialist. Noticeable asymmetry and various posture disorders affect both sleep and everything else in life. The sooner you fix them, the better for you. Sleep better and you'll lift more.
Read also[edit | edit code]
- Functional movement abilities: mobility and stability
- Strength abilities
- Dynamometry (method of measuring muscle strength)
- Tests to assess speed-strength abilities and power
- Medball
- Bicycle ergometry
- Tests to evaluate the special strength abilities of field players
- Speed abilities
- Tests to evaluate reaction speed
- Tests to evaluate the special speed abilities of field players
- Endurance tests
- Flexibility
- Physical abilities of hockey players
- Coordination abilities
Sit-to-stand test
Try sitting on the floor without supporting anything with your hands, knees, or shins. Happened? Then try to stand up - also without touching anything, just your feet on the floor.
This ability is vital for you and I am not exaggerating - that's what scientists say. Using this test, researchers can predict life expectancy. And we will learn something more about our flexibility, strength and coordination.
If you are under fifty and cannot cope with this test, you should think about your physical fitness and health in general. Believe me, it’s better to fix this now; it may not be possible in retirement.
Here's how to do this test correctly:
Strength and endurance of a teenager at 12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20 years
Also, to test your strength and endurance, if you don’t go to the gym, but go to the horizontal bars and work out in a workout environment, then you can test your strength on the horizontal bars on the street!
Strength test on horizontal bars exercises
- Maximum dips
- Wide grip pull-ups max.
- Lifting the legs on the hanging horizontal bar a maximum of times
- Classic plank on elbows for maximum time
- Classic squats maximum times
- Close-grip bicep pull-ups max.
Between exercises, rest for at least 10 minutes until breathing is completely restored and it is recommended to eat well.