The seated dumbbell press is an exercise for developing the deltoids. The predominant load falls on the anterior and middle deltas. Variations of the exercise vary depending on the inclination of the bench. The more vertical the angle of inclination is applied, the more the middle delta is loaded, and the less the anterior and chest muscles are loaded. An incline of 30 degrees or lower shifts the emphasis to the pectoral muscles. Part of the weight of the dumbbells falls on the pectoral muscles. Then the exercise is used as a special preparatory exercise for the bench press in order to develop synergy (simultaneous work) of the chest and shoulder muscles. In all other cases, the bench press serves to increase shoulder volume and muscle strength.
Strength or volume?
In fact, it all depends on the sport. In tennis, team sports, rowing and other sports where muscle endurance and joint health are required, strength is usually developed in the off-season, and a maintenance regime is used during the competitive period.
In bodybuilding, they either work in “mass and cut” cycles, or simply perform exercises in a maintenance mode for as many repetitions as are optimal for the recovery of a particular athlete.
For normal life, you need a moderate combination of joint mobility, muscle endurance and strength. The fact is that holding weights above your head, lifting objects, and even simply holding a handrail in transport requires a combination of strength and endurance.
Important: Shoulder muscle training should combine both strength and endurance elements. There is no universal set-repetition regime for everyone. Some athletes initially have more developed strength, while others have more endurance.
It is important
- Choose the appropriate weight.
- Do the exercise on a bench with a backrest, this will give maximum load to the target muscles. During the entire approach, maintain a slight arch in your lower back.
- Spread your legs wide, placing them firmly on the floor: this will provide you with reliable support and allow you to concentrate on working your shoulders.
- Monitor the correct trajectory of raising and lowering the dumbbells and the range of movement.
- Don't forget to breathe correctly: exhale powerfully while lifting the dumbbells and take a deep breath when lowering them.
- Pay special attention to the negative phase of the movement - then your shoulders will grow as quickly as possible.
- While performing the exercise, mentally concentrate on the work of the deltoid muscles - this will allow you to work them out really well.
How to develop endurance
Endurance for sporting purposes develops during the off-season. For “vital” ones, it’s enough to simply choose 1-2 months when you are not gaining weight and can afford to work in a high-repetition mode. You usually need to work out 2-3 times a week, but you can increase it to 5 workouts.
A regular seated press is performed with a weight that is 60% of the working weight or slightly higher. Let's say you do 12 repetitions with a weight of 25 kg, for endurance work with 12-15 kg. You should do about 25 reps per set, and work with 30-60 seconds of rest between sets. Number of approaches – at least 4.
During such training, the muscles feel a burning sensation, you must endure it. Endurance is not built by daily training when it comes to strength endurance. Still, this is not cycling; the shoulder can become inflamed from atypical load. You need to start with 3 workouts per week, and gradually increase to 5. Again, frequency indicators in training are individual and determined by the speed of recovery. According to the textbook, there should be 24 to 36 hours between endurance training sessions.
Developing the volume and strength of the deltoids
Many people think that this is not true, but training for strength and hypertrophy are fundamentally different. Strength training occurs in repetitions from 1 to 6, and is extremely rarely done with dumbbells, and even while sitting. This contradicts the main goal of the strength cycle - to develop overall strength, including the muscles of the stabilizers and core. Usually for strength training they choose something like a military press. Press dumbbells for 5-6 repetitions to work the muscles in isolation. But this is an extremely rare practice. A really strong athlete will require the help of two spotters, but a beginner runs the risk of injury when performing this exercise.
Hypertrophy mode: 8-12 repetitions. Do 3-4 working approaches. The fundamental difference between strength training and volume and mass training is that strength is developed only if the weights in the working sets do not cause significant fatigue. But for hypertrophy it makes sense to work to failure, whereas in strength training failure is not allowed at all.
Important: the strength cycle and the hypertrophy cycle are different periods of time. Usually, they first gain strength and endurance, and then “swing”, but this is true for sports. There are different options in fitness. Impressive strength is usually not needed, just tone and volume are enough.
Execution technique
There are many technical nuances. This exercise is not performed correctly by the vast majority. People start to press with their shoulders raised, and all because they don’t know how to bring the dumbbells to their shoulders correctly
So, to press dumbbells while sitting, you need:
- Arrange them so that you can do sit-up hip raises from the floor, that is, place dumbbells on your hips, holding them with your hands;
- Use your feet to push the weights toward your shoulders;
- Spread your elbows so that the dumbbell bars are in a plane parallel to the floor;
- The press itself begins with lowering your elbows down and placing your forearms perpendicular to the floor;
- At the same time, it is recommended to bring the shoulder blades together and lower them down to the pelvis;
- A slight deflection in the lumbar spine is allowed, but there is no need to emphasize it;
- By engaging the shoulder and triceps muscles, the dumbbells are pulled up;
- The elbows are extended in a plane perpendicular to the floor; it is not recommended to “mow” them forward or backward;
- Lower the dumbbells to your shoulders and perform the required number of repetitions
This exercise is performed first with warm-up weights, then with working weights. There is no need to rush or try to push the weight away from you so that the dumbbells go forward. If heavy weights are used, you can use an athletic belt, just enough to remove excess mobility in the lumbar spine.
Exercises for shoulders. Seated dumbbell press.
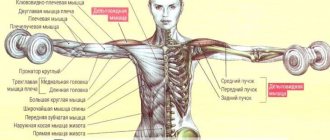
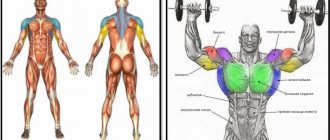
What muscle groups develop
Due to the high amplitude of execution, this exercise involves a large number of muscles.
Consider the list of these muscles:
- The main muscles that perform this exercise are the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor muscles.
- No less important are the triceps and deltoid muscles.
- The assistants are the biceps muscles, dorsal muscles, and in some cases the trapezius and serratus muscles.
- The legs perform the function of stabilizing the body.
You can see that this exercise is performed with the use of several muscle groups, which makes it possible to develop each of them.
Alternatives – standing dumbbell press
There are plenty of alternatives to the classic bench press. In women's training, they often use seated presses on a fitball to turn on the stabilizers, but it is better to choose a simpler option to load them - just press a barbell or dumbbells while standing.
The second “alternative press” option is the kneeling position. It is intended strictly for those people who do not know how to use their legs and are constantly trying to shunt, that is, push the working weight by sharply bending the knees. This does not give the feeling of isolated work, and develops completely different qualities - explosive strength and footwork.
The standing dumbbell press option allows you to:
- Take more weights, as the body position is more stable and more natural for lifting weights;
- Develop stabilizers from the foot muscles to the core muscles;
- Promote the development of strength in barbell presses, cleans and jerks;
- Work in a plane natural to the human anatomy and do not damage the joints
A technique to stabilize the center of the body is used. The athlete strains his quadriceps, buttocks, as if he were pressing his feet into the floor, pulls the abdominal wall towards the spine, draws in the stomach and brings the shoulder blades together, lowering them towards the spine. At the same time, the trapezius and shoulders remain relaxed.
Technique
- The dumbbells are brought to the shoulders by standing up, that is, the knees are slightly bent and the weight is brought to the shoulders in one powerful movement;
- The athlete stabilizes the core as above;
- Due to extension in the shoulder and elbow joint, it moves the dumbbells upward;
- Lowers them smoothly to the shoulders;
- The peculiarity is that dumbbells move along a “flat” trajectory than a barbell;
- There is no need to bring them behind the head, as is emphasized in the movement with a barbell.
Important: you need to avoid kicking your legs and rolling from heel to toe in order to perform the exercise technically correctly.
It's the STANDING DUMBELL PRESS, baby!
Recommendations
- For bodybuilding and fitness purposes, it is not recommended to completely “stick” your elbows at the top point;
- You need to avoid a flat trajectory, and try to move the dumbbells slightly to the top of your head, and not to your forehead;
- Complete relaxation of the arms, as well as “releasing tension” from the center of the body by relaxing the abdomen, is not allowed;
- The weight for strength training is lifted no more than 5-6 repetitions, there should be no more than 5 approaches.
Errors:
- Shvung weight, that is, acceleration and pushing with the legs;
- Rocking the body back and forth;
- “Strong’s” technique” in which the athlete seems to “roll” the dumbbells onto his shoulders in each repetition, and “push” the dumbbells with his stomach and chest at the start
Important: lifting dumbbells while standing is an exercise for experienced athletes; it is better not to do it if you are a beginner and your back is still weak.
Dumbbells can be replaced with weights. In this case, you need to start from shoulder level, but your palms should be directed towards each other. In the process of moving upward, the projectiles turn, as in the Arnold press. Some athletes initially press with their palms facing forward, but this position is quite traumatic for the wrists.
Variations
Often among beginning athletes the question arises as to what can replace the classical technique. The exercise has several variations; we suggest studying them in detail with photos. The most common and popular versions are:
Arnold press . This technique is more difficult than the classic bench press, so it is not recommended for beginners and people with a minimal level of physical fitness. To perform this, you need to sit down, take the dumbbells with an inward grip, and lower your arms along the body. You need to move in two stages, first raise the dumbbells to chest level, then squeeze them up, while turning your hands 180 degrees, so that at the top point your palms look outward.
Alternating press . You need to sit on a bench, take dumbbells and lift them to the sides and up so that they are at head level. This creates a right angle at the elbows. It is necessary to alternately press the dumbbell up with one hand, the second hand remains in its original position, i.e. motionless at this moment, we do the same for the other.
Press in the simulator . This version will be the best solution for those who are just mastering the technique. The load is correctly distributed in the simulator, and the athlete moves along the correct trajectory.
Standing _ This is a complicated version of the exercise, which is characterized by high productivity. Suitable for those who do not have back problems and can withstand such a load.
See also video:
Basic mistakes in dumbbell presses
Work without warming up
Even if your shoulders are positioned after your legs, you still need to bench press the warm-up weight. Or rather, start with the minimum weight and approach the worker in increments of 3-5 kg. This will not only help you prepare well for training weights, fill your muscles with blood, and warm up your ligaments, but will also allow you to gain an additional amount of work to practice your technique.
You should always do a joint warm-up before the main workout. And if the athlete has been injured before, then work with rubber. The rubber should be pulled towards your face, as in the rear delt exercise, and not stretched in front of you, as many people mistakenly do.
One arm press
This variation of the press creates increased stress on the pelvis and spine unless the athlete is standing on one knee of the opposite leg, in a position resembling a deep lunge. Beginners should not perform this movement while sitting, as this may lead to poor posture.
The one-arm press is performed when necessary due to muscle imbalances, but most people do not need it at all and should not replace the regular press.
Important: the one-arm version of the Arnold press involves holding a dumbbell in the non-working hand to stabilize the body, this is important to maintain balance and not load non-target muscles.
Breath
Usually athletes tend to hold it when it's hard. This is not correct and can even cause you to lose consciousness when lifting dumbbells overhead. The seated dumbbell press obeys the usual rule - exhale when making an effort, inhale when lowering the implements.
By the way, you shouldn’t drop the dumbbells on yourself and inhale quickly and shallowly. You need to carefully lower the dumbbells to your shoulders and inhale quite loudly.
Snatching, pushing and cheating
Snatches and other ways to push more weight up without stressing the muscles should not affect the quality of the lifts. Avoiding them is quite simple - learn to center your body and don't let your ego lift the weight for you. Yes, you need to choose adequate weights, and strive to load only the target muscles. Snatches and jerks can be performed as independent techniques in the speed-strength training of a weightlifter or strongman, but in bodybuilding they are not always needed.
Important: the elbows should bend and extend at the same speed in the same amplitude. There is no need to let them “walk” back and forth. This will help make the movement technically correct and safe.
Types of grips
A variety of grips allows you to pump muscle tissue from different angles, which improves not only the technique of execution, but also works out a larger volume of muscles. When changing the grip, the loaded group changes.
In sports practice, there is no exact answer to the question of which grip is best to use in training. Depending on the individual characteristics of the athlete, a certain hand position is selected.
Correct technique for performing seated dumbbell presses.
There are 3 main types of grip:
- Straight. Palms face up with elbow joints down. Used to pump the front part of the muscle corset, as well as to strengthen the wrist joint. Recommended for beginners.
- Parallel or neutral. Places a large load on all muscle fibers due to the presence of a high range of motion. In addition to the dumbbell press from a sitting position, it is used on the horizontal bar.
- Back. Palms face forward with arms down. Allows you to work the external muscles of the corset and train your biceps to a greater extent.
Depending on the width of the hands, 3 additional types of grip are used:
| Grip | Description |
| Narrow | Hands are placed slightly closer to shoulder width. With this grip, the amplitude is maximum, which has a positive effect on the final result. A narrow arrangement can reduce the effectiveness of a particular exercise due to the fact that the triceps takes the bulk of the load. |
| Average | Hands are positioned shoulder-width apart. This grip is the most common among athletes due to the comprehensive development of the muscular corset. Great for those just starting to exercise. |
| Wide | Hands are placed slightly wider than shoulders. Allows you to develop the target muscle, despite the fact that the grip can reduce the effectiveness of the exercise due to the small range of motion. |
Training with dumbbells is performed only with a closed grip, in which the athlete holds the bar or bar with 4 fingers, and the thumb closes the palm on the other side. This allows you to hold the sports equipment more safely.
The forward or reverse grip varies depending on the workout used, which is especially effective for lateral lifts. Dynamic load and changing grips allow you to develop your muscle corset much faster.