In this article we will tell you:
- Composition of milk
- Amino acids in milk
- Classification of proteins in milk
- Amino acid composition of milk proteins
- Factors influencing the composition of milk
Each of us knows what milk contains: proteins, fats and carbohydrates. But if you dig deeper, it turns out that this is a multi-component balanced system that is useful for children and adults. Cow's milk contains vitamins, micro- and macroelements.
What is included in milk, what exactly is hidden behind the words “proteins, fats and carbohydrates” on the packaging and why milk is so popular and should be included in the weekly menu, we will tell you in our article.
Composition of milk
All substances that make up cow's milk are divided into true and false. The former are formed as a result of natural processes during the secretion of milk, while the latter are introduced from feed, other sources and in production. These can be antibiotics, pesticides, heavy metals, radioactive substances, etc. For the latter, standards for permissible content have been established, since they are dangerous to human health.
From a technological point of view, the product of interest to us is divided into water and dry matter. The latter includes milk fat and dry fat-free residue.
- Macronutrient ratio.
Milk is rich in potassium and calcium: per 100 g of product there are 146 mg and 120 mg of these microelements, respectively. It is important that the calcium contained in this drink is absorbed by humans by more than 90%, and this is a very high figure.
This product also contains a lot of chlorine: in 100 g its share is at the level of 110 mg, phosphorus - 90 mg for the same weight. Also, 100 g of milk contains 50 mg of sodium, 29 mg of sulfur, 14 mg of magnesium.
- Micronutrient ratio.
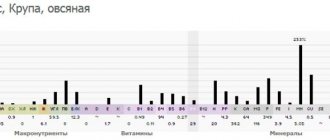
If we talk about what is included in milk, what microelements, then most of all this product contains zinc - 0.4 mg and iron - 0.1 mg. The manganese content is also noted - 0.006 mg.
Other microelements are calculated in micrograms: aluminum - 50 mcg, fluorine - 20 mcg, strontium - 17 mcg, tin - 13 mcg, copper - 12 mcg. The content of iodine is even lower - 9 mcg, molybdenum - 5 mcg, selenium and chromium - 2 mcg each. The analysis also shows a small proportion of cobalt - within 1 μg.
Lyubov Mikhailovna Guseva
Director and founder of Liton LLC
Package of documents for downloading from the founder
A dairy product labeling system will be launched in January 2022 and will become mandatory from May 1, 2022. Both manufacturers and those involved in the sale of this type of product will have to make some amendments to their work.
That is why we have made a selection of the most useful documents on dairy product labeling to help you. It's free. Download and use today!
- Requirements for the design of dairy product labeling Scheme of interaction with the printing house, recommendations for design layout, packaging example
- 11 important questions “About labeling” Parameters of the labeling code, how it can change, applying CM to packaging
- Labeling of dairy products step by step Structure of the marking code, identification code for group packaging of dairy products
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 15, 2022 No. 2099 On approval of the Rules for marking by means of identification and implementation features
1 ml of milk contains 100–10,000 bacteria. During the milking and primary processing process, from 100 thousand to 300 thousand microorganisms per milliliter enter the drink from the surface of the udder, milking equipment and other equipment. 1 liter of fresh milk contains 50–80 cm3 of gases, of which 60–70% is carbon dioxide, 25–30% is nitrogen and the remaining 5–10% is oxygen. During storage, they become smaller, and boiling allows you to completely get rid of gases in the product.
Only 11–14% is the share of dry substances from the total mass of milk, while the specific figure is related to the composition of the product. The mass fraction of dry fat-free residue is designated COMO and is in the range of 8-9%. The dry residue, namely the protein it contains, is valued most highly, so they try to preserve it as much as possible during cheese making.
Dairy products
Cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt, yogurt, fermented baked milk and any other milk-based products contain at least 8 g of protein. These foods are often enriched with many useful substances, so they should definitely be included in your diet.
Casein is a protein from low-fat cottage cheese that is 97% digestible and does not overload the body with extra calories.
Greek yogurt, which contains 10 g of protein, is especially beneficial. This low-fat product is rich in probiotics, B vitamins, magnesium and calcium. In addition to casein, yogurt contains whey protein. Their combination significantly reduces the amount of lactose. Therefore, yogurt is a great option for those who are lactose intolerant.
Amino acids in milk
Milk contains amino acids necessary for the human body. One of them is serine, which is necessary for the construction of brain proteins and myelin sheaths, designed to protect the nervous system from external negative influences.
Another amino acid contained in milk is considered the basis for the normal course of life processes on Earth. This is histidine, and it is a proteinogenic substance involved in the formation of protein, on which the body's metabolic reactions depend.
Tyrosine is another non-essential substance that is part of milk proteins.
Aminovaleric acid arginine is an essential acid and helps the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
Poline is a sheterocyclic non-essential amino acid and is essential for tissue regeneration.
While the sulfur-containing amino acid cysteine facilitates the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and neutralizes the effects of toxins in the body.
It should be noted that milk contains glycine, which is one of the simplest aminoacetic acids. It is no secret that glycine promotes more active mental activity, has a beneficial effect on performance, the formation of muscle tissue, and is necessary for the rapid restoration of muscle mass and healthy sleep. It plays an important role in the construction of DNA. This substance also softens the harmful effects of alcoholic beverages and medications on the body. In general, glycine is a probiotic that activates a person's internal defenses.
In addition, milk contains the amino acids tryptophan, lysine, and methionine.
Among all the products available to people, only milk can boast of the presence of milk fat, lactose, casein, albumin, and globulin, since all of these substances are synthesized in the mammary glands.
It is important that the drink we are interested in contains the enzymes dehydrogenase, catalase, plasmin, xanthine oxidase, lipase, amylase, peroxidase, phosphatase, lysozyme, etc. It contains many hormones: prolactin, oxytocin, somatotropin, corticosteroids, androgens, estrogens, progesterone, etc. And, as mentioned above, unfortunately, foreign chemicals can be found in this product: antibiotics, toxins, including bacterial ones, pesticides, radionuclides (90Sr, 137Cs, 131J), dioxins, detergents, etc., as well as gases CO2, O2, H2.
Prohibitions on protein nutrition for weight loss
The protein nutrition system for weight loss excludes some foods completely from the human diet. Such prohibitions include bakery products. Especially if they are made from wheat flour. If you want to eat a piece of bread, your choice should be rye. There is a taboo on buns and pies. Products with the highest protein content should prevail in the diet.
Sugar, sweets and carbonated drinks should be completely excluded from the menu. Milk is also prohibited. It can be added to the diet only in low-fat form and in small quantities. The adult body digests milk worse than the child’s body, which is why fermented milk products are considered recommended for consumption.
Knowing how much protein is in one egg, 100 grams of meat, cottage cheese, cheese, various cereals, you can easily create a balanced diet that will help the body effectively build muscle tissue, lose extra pounds and restore energy after physical activity.
Classification of proteins in milk
If you are interested in the nutrients that make up milk, then the most valuable among them are proteins that belong to high molecular weight compounds. The building blocks of proteins are amino acids held together by peptide bonds.
Milk contains 2.8–3.6% proteins. The latter have different structures, physicochemical properties, and biological functions. Initially, they were designed to ensure the normal development and growth of the calf, but today they have begun to play an important role in human nutrition.
Milk proteins are part of the group of caseins or whey proteins. The former make up 75–85% of the total protein content. While the remaining 15–22% are whey proteins, that is, globulins and albumins. Both types are not homogeneous; on the contrary, they contain a whole mixture of different proteins.
Table 1. Classification and main indicators of milk proteins.
| Protein | Content in skim milk, g/100 ml | Molecular mass | Isoelectric point, pH |
| Caseins: | |||
| αs1-casein | 1,2–1,5 | ~23 000 | 4,44–4,76 |
| αs2-casein | 0,3–0,4 | ~25 000 | — |
| χ-casein | 0,2–0,4 | ~19 000 | 5,45–5,77 |
| β-casein | 0,9–1,1 | ~24 000 | 4,83–5,07 |
| Whey proteins: | |||
| β-lactoglobulin | 0,2–0,4 | ~18 000 | 5,1 |
| α-lactalbumin | 0,06–0,17 | ~14 000 | 4,2–4,5 |
| Serum albumin | 0,04 | ~66 000 | 4,7–4,9 |
| Immunoglobulins | 0.04–0,09 | 150 000–1 000 000 | 5,5–8,3 |
| Lactoferrin | 2–35 or 10–30 | 76 500 | – |
This classification of substances that make up milk is based on a scheme created by the Committee on Dairy Protein Nomenclature and Methodology of the American Dairy Science Association.
We recommend
“Milk production in Russia: problems, prospects, statistics” Read more
Speaking of proteins, we need to mention enzymes, a number of hormones, for example, prolactin, and proteins of the membranes of fat globules.
Today, scientists know the biological functions of almost all proteins that the product of interest to us is rich in. Thus, caseins are directly edible proteins, because without additional processing they are perfectly broken down by digestive proteinases. Whereas ordinary globular proteins need to undergo a denaturation process for this.
Caseins coagulate in the newborn's stomach, forming highly dispersed clots. They play the role of important sources of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium, a large list of physiologically active peptides. Thus, due to the partial hydrolysis of χ-casein due to the reaction with chymosin in the stomach, glycomacropeptides are released. They are responsible for regulating the digestion process, namely maintaining the required level of gastric secretion. It is believed that physiological activity is also characteristic of soluble phosphopeptides resulting from the hydrolysis of β-casein.
When listing what is included in milk, one cannot fail to mention whey proteins, because they perform equally important biological functions. Immunoglobulins protect the body by being carriers of passive immunity. Lactoferrin and lysozyme, which are milk enzymes, have important antibacterial properties.
Also, lactoferrin and β-lactoglobulin perform a transport function, namely, they help iron, vitamins and other important elements enter the newborn’s intestines. Whey protein α-lactalbumin has a regulatory effect and provides lactose synthesis. B-lactoglobulin is considered an inhibitor of the enzyme plasmin.
Casein
The main protein of milk, casein (caseinogen), is a phosphoprotein, in the molecule of which phosphorus in the form of phosphoric acid is associated with hydroxy amino acids, forming an ester with serine and threonine. In addition, casein is associated with milk calcium and forms active casein - calcium phosphate complex. Casein, found in milk in the form of calcium salt, is called calcium caseinate.
During the process of curd formation when milk sours, calcium caseinate interacts with lactic acid and breaks down into calcium lactic acid and casein, which precipitates (a significant part of calcium lactic acid remains in the liquid part, in the whey). Casein is present in milk in several forms - α, β, γ.
The indicator that most distinguishes one form of casein from another is the phosphorus content. The largest amount of phosphorus is in a-casein (1%) and 10 times less in γ-casein (0.1%).
The main form of casein is α-casein, which makes up 85% casein. The most important property of α-casein is that when milk coagulates, only the α-form passes into a curd, while β-, γ-casein remains in solution. The amino acid composition of various forms of casein is given in the table.
Amino acid composition of milk proteins
Milk proteins contain almost all the amino acids found in any other type of protein.
Table 2. Amino acid composition of milk proteins
| Amino acids | Abbreviations | Milk protein content, % | ||||||||
| In casein | In β-lacto-globulin | In α-lactalbumin | In immunoglobulin G | In serum albumin | ||||||
| Generally | Including by faction | |||||||||
| α-casein | χ-casein | β-casein | ||||||||
| Indispensable: | ||||||||||
| Valin | Shaft | 7,2 | 5,6 | 5,1 | 10,2 | 5,8 | 4,7 | 9,6 | 12,3 | |
| Isoleucine | Ile | 6,1 | 6 | 6,14 | 5,5 | 6,1 | 6,8 | 3,1 | 2,6 | |
| Leucine | Lei | 9,2 | 9,4 | 6,08 | 11,6 | 15,6 | 11,5 | 9,1 | 12,3 | |
| Lysine | Liz | 8,2 | 8,7 | 5,76 | 6,5 | 11,4 | 11,5 | 9,1 | 12,3 | |
| Methionine | Meth | 2,8 | 3 | 1 | 3,4 | 3,2 | 1 | 1,1 | 0,8 | |
| Threonine | Tre | 4,9 | 2,5 | 6,64 | 5,1 | 5,8 | 5,5 | 10,1 | 5,8 | |
| Tryptophan | Three | 1,7 | 2 | 1,05 | 0,83 | 1,9 | 7 | 2,7 | 0,7 | |
| Femilalanine | Hairdryer | 5 | 5,6 | 4,07 | 5,8 | 3,5 | 4,5 | 3,8 | 6,6 | |
| Replaceable: | ||||||||||
| Alanin | Ala | 3 | 3,4 | 5,41 | 1,7 | 7,4 | 2,1 | — | 98 | |
| Arginine | Arg | 4,1 | 4,4 | 4 | 3,4 | 2,9 | 1,2 | 3,5 | 122 | |
| Aspartic acid | Asp | 7,1 | 8,45 | 7,3 | 4,9 | 11,4 | 18,7 | 9,4 | 218 | |
| Histidine | Gies | 3,1 | 3,3 | 1,67 | 3,1 | 1,6 | 2,9 | 2,1 | 90 | |
| Glycine | Gli | 2,7 | 3 | 1,31 | 2,40 | 1,4 | 3,2 | — | 47 | |
| Glutamic acid | Glu | 22,4 | 23,6 | 17,35 | 23,2 | 19,5 | 12,9 | 12,3 | 717 | |
| Proline | About | 22,3 | 8,2 | 8,78 | 16 | 4,1 | 1,5 | — | 302 | |
| Serin | Ser | 6,3 | 7,4 | 7,4 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 5,4 | — | 186 | |
| Tyrosine | Shooting Range | 6,3 | 7,4 | 7,4 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 5,4 | — | 184 | |
| Cysteine + cystine | Cis | 0,34 | – | 1,4 | — | 3,4 | 6,4 | 3 | 6 | |
You need to understand that milk proteins include both cyclic and acyclic amino acids, that is, neutral, acidic and basic, with the largest share of the latter being acidic. The physicochemical properties of proteins depend on the number of individual groups of amino acids. And this indicator is largely related to the breed, individual characteristics of the animals, stage of lactation, time of year and other characteristics.
If we compare milk proteins with globular proteins of other foods, the former include more leucine, isoleucine, lysine, glutamic acid, also serine and proline, while they contain less cysteine. While whey proteins are distinguished by a large proportion of sulfur-containing amino acids.
We recommend
“Rules for milk acceptance: criteria for evaluating raw materials” Read more
In terms of the quantity and ratio of essential amino acids, milk proteins are considered biologically complete. This is especially evident in whey proteins.
Pros and cons of a protein diet
Despite the possibility of losing weight with protein foods, such a nutritional system has its positive and negative sides. The advantages of this method include the following points:
- Fast and effective results.
- If all the rules are followed, the feeling of hunger should not torment a person losing weight.
- The consumption of almost all products is allowed, but in small quantities.
On the other hand, the disadvantages of this method include:
- Good results can be obtained by doing physical exercises.
- Not suitable for people who do not consume meat or other animal products.
- It is well known which foods contain a lot of proteins, but often they are low in other important elements, so you need to take multivitamin complexes separately.
Cereals
It was not for nothing that Hercules received its name in honor of the ancient Greek hero. Oatmeal (rolled oats) contains 10–12 g of protein, as well as all minerals and vitamins. Oatmeal is easily digestible, so this porridge will give you strength for the whole day. There is an exotic type of cereal - quinoa, which contains 14 g of protein. This is one of the most useful products, which, unfortunately, is not always easy to find in stores. On average, grains contain 6 g of protein and many other healing substances.
Female zebu milk
The milk of female zebu is consumed by the peoples of Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan and Armenia.
In its composition, it is close to cow's milk, but contains slightly more fat, protein, minerals and less sugar.
It is used in its natural form and for the preparation of dairy products.
It should be noted that in places where zebu livestock are bred, people often suffer from piroplasmosis, which is transmitted through tick bites. However, zebu have developed immunity (immunity) to this disease.
Therefore, people who constantly drink zebu milk usually do not get sick with piroplasmosis.
Buffalo milk
Buffalo milk is consumed in Georgia, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Dagestan, Kuban and the Black Sea coast of the Caucasus.
Buffalo milk is a viscous white liquid with a pleasant taste and odorless.
Its biological and nutritional value is very high. It contains more fat, protein, calcium, phosphorus, vitamins A, C and B than cow's milk. This milk is used for food in its whole form, as well as with coffee and cocoa.
High-quality yoghurt (Bulgarian curdled milk with a high content of dry substances), cream, matsun, sour cream, curd cheese, ice cream are prepared from it, you can also make butter, and local cheeses are made from a mixture with cow’s milk.
Reindeer's milk
deer milk in their diet.
It differs from cow's milk in that it contains 3 times more protein and 5 times more fat.
The calorie content of 1 liter of deer milk is equal to 4 liters of cow's milk.
Reindeer milk is used to make butter, cheese and cottage cheese.
When used whole, it is better to dilute it with water, since it has a high fat content and therefore not every person’s stomach is able to digest it normally.
Goat milk
Goat milk is consumed in large quantities by residents of Transcaucasia and Central Asia.
In terms of its chemical composition, it is not inferior to cow milk, and in some respects even surpasses it.
Therefore, it is recommended to give goat's milk to infants along with cow's milk. Many people use it as a substitute for human breast milk.
The quality of goat's milk and its taste largely depend on how carefully hygiene rules are observed during milking.
Before milking, the goat's udder must be thoroughly washed, since its sebaceous glands secrete a large amount of volatile fatty acids. When they get into milk, they give it a specific smell.
Goat milk mixed with sheep is processed into feta cheese and local pickled cheeses.
Sheep milk
Sheep milk is used for food purposes in the Crimea, Transcaucasia, Central Asia and the North Caucasus.
The color of sheep's milk is white with a faint grayish tint.
It is 1.5 times richer in protein and fat and contains 2-3 times more vitamins A, B1, B2 compared to cow's milk.
However, sheep's milk fat contains a lot of capric and caprylic fatty acids. They give milk a specific smell. This limits its consumption in food in its whole form.
Cheese (chanakh, Tushino, Ossetian) and feta cheese, as well as fermented milk products, especially yogurt, are often prepared from it. You can make butter from sheep's milk, but it will have a greasy taste.
Sheep often suffer from brucellosis, so it is better to boil their milk.
Cheese and feta cheese can be consumed only after storage for a month, since during this time the brucella (causative agents of the disease) die.
Coprecipitate
Milk protein concentrate is actively used by athletes to build muscle mass. In terms of its amino acid value, casein is comparable to whey substances. The main difference is only in the content of methionine and lysine. Manufacturers of effective proteins prefer to use a universal combination of casein and whey proteins. Multifunctional coprecipitates are obtained from skim milk by co-precipitation of milk components. The desired effect is achieved by simultaneous exposure to temperature and calcium chloride. An integrated approach makes it possible to increase the degree of use of protein elements several times.
Low fat
It is obtained by separating milk from cream. Then they add a little fat and sell it. Of course, this is beneficial to manufacturers. This milk drink can be increasingly seen in our stores. But there is a controversial opinion regarding its use. Previously, such liquid (common name: skim milk) was used only as feed for livestock.
The fact is that to digest this type of dairy product, our digestive system uses reserve reserves of vitamins D and E. Some nutritionists believe, on the contrary, that this type of drink is the most useful, since it has a minimal amount of fat, and there is enough protein for normal nutrition .
Low-fat contains the following indicators of the main components per 100 ml:
Powdered milk
This type was invented in the last century. The easy-to-use milk powder is a dry concentrate made from whole milk. It takes up less space and lasts longer. For one hundred milliliters of such diluted milk with a fat content of 2.5%, there is 2.42 grams of protein. Just like a natural product, it gives our body energy.
It is used for the production of instant infant formula. Each person’s body is individual, so listen to it and use the product that is right for you. Some skeptics believe that this drink is generally harmful to the body, but if it is not absorbed, then it cannot be used as food.
Source
Mares' milk
Mares' milk is white with a bluish tint, sweet and slightly tart in taste.
It is inferior in nutritional value to cow's milk, since it contains almost half as much fat.
However, the high content of milk sugar, albumin, globulin, vitamin C (6 times more than in cow's milk), and the fine fragmentation of fat globules give it, after fermentation into kumiss, a special medicinal and dietary value.
In terms of the ratio of protein fractions and the amount of lactose, mare's milk resembles that of women, so it is very useful when feeding infants.
In the diet of adults, it is better to use mares' milk in the form of kumys.