All the nuances of taking creatine. Options with and without loading. What is the best thing to mix it with? Drink the supplement before or after training. Scientists know this substance as a nitrogen-containing carboxylic acid, and we (ordinary people and athletes) know it as creatine. The purpose of the component is to ensure energy metabolism in cells, increase strength and endurance. In general, without it it is impossible to imagine the normal functioning of our muscles and the body as a whole.
Description of the drug
Creatine has the following effects on the body:
- Nitrogen-containing acid serves as an additional source of energy, so when taken it increases performance.
- It neutralizes lactic acid, which accumulates in the muscles after exercise and causes pain in them.
- Increases testosterone levels in the body, which leads to rapid growth of muscle tissue and improved muscle definition.
HOW TO TAKE CREATINE MONOHYDRATE
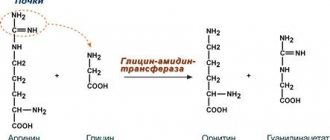
Creatine is a substance produced by the body in the kidneys, liver and pancreas. You also get it from food. Creatine is found, among other things, in red meat and various types of fish. A popular means of enhancing athletic performance is creatine supplementation. Using creatine certainly gives athletes something for the body. Here we will also look at the other side and look at the side effects of creatine. Creatine has a number of effects on your body and performance, such as:
- increase muscle mass;
- more noticeable muscle size;
- increased endurance;
- less acidification;
- more strength and energy.
Let's first figure out why you should drink creatine? to better understand what results to expect and how to influence the effectiveness of the supplement. Creatine is synthesized by the body independently; this substance is necessary for the body for energy potential. It is when performing physical activity that muscles consume creatine, and therefore it is very important to replenish the balance of this substance. Additional intake of creatine accelerates muscle mass gain and strength gains. It also speeds up the recovery process because it neutralizes lactic acid, which increases muscle fatigue and causes pain.
Instructions for use
If the manufacturer does not offer a different dosage regimen, then the creatine dosage regimen depends on the intensity of physical activity:
- ordinary people and amateur athletes are recommended to drink it in a daily dosage of 2 to 3 g;
- People who exercise regularly and expend a lot of energy can take up to 5 g of creatine per day.
If the body is susceptible to nitrogen-containing acid, then you can drink with so-called “loading” periods, when during the first 5-7 days its daily dosage varies from 15 to 20 g, and then they switch to a maintenance daily dose of 5 g.
You can take the tablets at any time of the day: in the morning, an hour after physical activity or before bed, between meals. But the effect will be better when the body produces more insulin: in the morning immediately after waking up and after playing sports. It is not advisable to drink it before training as it can cause nausea and poor health.
Pancreatin
Pancreatin can be prescribed to patients of any age, including infants and the elderly, due to the possibility of individual dose selection by combining drugs with different dosages, as well as due to the ability to use the contents of gelatin capsules (pellets) directly for administration.
Capsules are taken orally, during or after meals, without chewing, with a sufficient amount of liquid (water, juices). If a single dose of the drug is more than 1 capsule, you should take half of the total number of capsules immediately before meals, and the other half during meals. If the single dose is 1 capsule, it should be taken with meals.
If swallowing is difficult (for example, in small children or elderly people), the capsule is opened and the drug is taken directly in pellets, having previously mixed them with a slightly acidic (pH <5.0) liquid or liquid food that does not require chewing (pH <5.0). ). Any mixture of pellets with food or liquid should be consumed immediately after preparation.
When treating with Pancreatin, to prevent increased constipation, it is important to ensure a normal level of water intake, especially with increased fluid loss.
The dose of the drug is selected individually depending on age and severity of symptoms. To achieve an adequate individual dose, in addition to Pancreatin 40,000 IU capsules, it is possible to use the drug Pancreatin with dosages of 10,000 IU or 25,000 IU.
Cystic fibrosis.
For children over 4 years of age, the average dose is 500 IU of lipase per kilogram of body weight at each meal. For children under 4 years of age, the initial calculated dose is 1000 IU of lipase per kilogram of body weight at each feeding (it is recommended to use the drug Micrasim® capsules 10,000 IU or 25,000 IU).
The dose should be selected individually, depending on the severity of the disease, the severity of steatorrhea and nutritional status. The maintenance dose for most patients should not exceed 10,000 units of lipase per kilogram of body weight per day.
For other conditions accompanied by exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, the dose is set individually, taking into account the degree of digestive insufficiency and fat content in food, individual dietary habits and the age of the patient. The dose of lipase required by the patient during the main meal (with breakfast, lunch or dinner) varies from 20,000 IU to 75,000 IU.
When treating with Pancreatin, the average initial dose of lipase is 10,000 - 25,000 units during the main meal (provided by using Pancreatin enteric capsules 10,000 units or Micrasim® capsules 25,000 units), however, higher doses may be required to achieve a therapeutic effect.
Typically, the patient should receive at least 20,000 units to 50,000 units of lipase with food. In case of severe steatorrhea (more than 15 g of fat in feces per day), in the presence of diarrhea, loss of body weight and no effect of diet therapy, treatment begins with a dosage of 25,000 IU of lipase at each meal, but if necessary and well tolerated, the dose is increased to 35,000 IU — 40,000 units of lipase per dose. Further increase in dose, in most cases, does not improve treatment results and requires a revision of the diagnosis, reduction of fat in the diet and/or additional prescription of proton pump inhibitors. The average dose of pancreatin for adults is 150,000 units/day; with complete blockade of the exocrine function of the pancreas - 400,000 units/day, which corresponds to the daily requirement of an adult for lipase. The maximum daily dose is 15,000 units - 20,000 units/kg. The permissible dose for children under 1.5 years of age is 50,000 units/day; over 1.5 years - 100,000 units/day. The duration of taking pancreatin can vary from several days (digestive disorders) to several months or years (long-term replacement therapy).
Side effects
Creatine is considered one of the safest supplements, but still, taking it can provoke a number of negative phenomena:
- Fluid retention in the body, which is manifested by a weight gain of 0.5-2 kg.
- If you are intolerant to the composition of the sports nutrition, it can cause allergies.
- Dehydration, which can disrupt metabolism, heat regulation and water-salt balance.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea.
- Spasms and convulsions.
- Acne is associated with increased testosterone levels in the body.
- If you overdose on creatine, there is a risk of weakening bone tissue and impaired kidney function.
While taking creatine, you should not limit your fluid intake or take diuretics, as this will cause even more severe dehydration of the body. On the contrary, when taking sports nutrition, you need to consume up to 3 liters of liquid per day. This will normalize metabolism, restore acid-base balance, and reduce the likelihood of seizures and muscle spasms.
Although Creatine tablets are considered safe, you should consult your doctor and carefully read the instructions before taking them.
Reception features
The main problem is that not everyone knows how to take creatine correctly. There are many assumptions and theories that confuse the athlete more than simplify his task. Let's look at the main subtleties of the technique:
- Dosage is one of the most important points when it comes to taking sports nutrition. There are two main approaches here:
- with loading. In this case, the daily dosage is 20-30 grams of the substance, which are taken in 4-6 approaches. The duration of this course is 5-6 days. This is followed by a maintenance period, when the dosage is reduced to 3-5 grams per day. Number of doses: once a day. The course of support is another 24-26 days.
without downloading. Here the daily dosage is 5-7 grams. Take creatine once a day. Course – 60 days.
- What to drink with it? There is a lot of discussion about this. Creatine is a very useful substance, but it still needs to be delivered to its destination. And this requires a special “transport” - insulin. This hormone has a powerful anabolic effect - it promotes maximum absorption of creatine by muscle fibers. Therefore, to improve effectiveness, it is better to take creatine with sweet juice or warm water with sugar. A sweet drink can speed up the production of insulin and improve the absorption of this much-needed substance. From juices it is better to take orange, apple or grape. In addition, experts recommend combining the supplement with fast protein or amino acids. Naturally, it is inconvenient to drink creatine with special mixtures. But this is not necessary. It is enough to drink them at approximately the same time. Many athletes are interested in whether it is possible to take this supplement with milk. But here you should not be confused. Protein is usually taken with milk. In this case, you can really achieve better digestibility of proteins and get maximum results from your workouts. As for creatine, taking it with milk can complicate the process. We must not forget that this product contains lactose, which not every stomach can digest. It also contains a slow protein – casein, which interferes with the normal absorption of the supplement. Therefore, there is no need to take creatine with milk. And why, if today there are no problems with choosing and purchasing juice.
- When should I take it? So, we solved the issue with milk and juice. Let's discuss when is the best time to take creatine - before you start exercising or after you finish it. Here the opinions of athletes differ, but we will proceed from research results and real facts. It has already been proven that the greatest effect can be achieved if you drink the substance after exercise - after 50-60 minutes. Why is that? There are several reasons. For example, taking a supplement before starting exercise can cause dehydration, which can be very dangerous during exercise. We must not forget that before training the body is not yet “warmed up”, and metabolic processes proceed too slowly. In such a situation, creatine may not get to its destination - muscle cells. But that's not all. As a rule, before and during exercise, the body has enough existing reserves of the substance. A deficiency may occur after the training process is completed. Experiments have shown that you should not drink nitrogen-containing acid during training. This can only cause harm and complicate the performance of a number of exercises. Let's also not forget about the dangers of dehydration. What's the point of taking the risk and translating the product? Drink creatine after exercise, about 50-60 minutes later, and get maximum results.
- Can it be combined with food? Again, opinions differ here. Some believe that it is better to drink creatine on an empty stomach, while others are confident that the presence of food and an acidic environment in the gastrointestinal tract does not affect the absorption of the substance. What to believe? Studies have shown that the presence of food in the stomach does not in any way affect the quality and completeness of absorption of the supplement. So there are no special recommendations in this regard.
Rules of use
As a rule, most athletes do not know whether to take creatine before or after training, what the dosage should be, whether to take creatine at night, and so on. In general, there are many more questions than answers. But we'll fix it. So, let's look at the main nuances of creatine and its intake:
- What are the schemes? This is where many people fall asleep, because there are two main approaches:
- in the first case, creatine is taken taking into account the so-called loading phase, that is, saturation of the body. This is done as follows. In the first week, you should take five grams of the supplement daily, four times a day. The total daily portion is 20 grams. Time of administration: between meals. If we are talking about days with training, then one serving should be taken immediately after leaving the gym. Further - less. Starting from day 6-7, reduce the portion to 2 grams. In this case, the frequency of administration should be 1 time per day. When should I take it? — In the morning (if it’s a rest day) or after class (if there’s a workout). The duration of the course should not exceed one month, after which a break of several weeks is necessary (usually 3-4 is enough);
in the second case, no loading is expected. It is believed that this option is better and safer for the body. The dosage is 5-6 grams daily. On workout days, creatine should be in your stomach immediately after leaving the gym, and on rest days, before meals. The optimal time of admission is 60 days. After this, it is worth giving the body a short rest - three, or better yet, four weeks.
- When should I take it? Another important question that many athletes cannot decide on is the optimal time to take the supplement. There are opinions floating around online that it is better to take the supplement before working out in the gym. But that's not true. Studies have shown that this approach is the least effective. There are several reasons:
- water metabolism is disrupted, which can lead to significant dehydration of the body. It is absolutely not advisable to allow this to happen;
Before training, the body is configured in such a way that the delivery of nutrients to muscle cells is inhibited. As a result, taking creatine may not bring the expected effect;
- The body expects the arrival of slow carbohydrates before training. Fast carbohydrates are quickly absorbed and can contribute to an increase in body fat. Naturally, there is no need for this;
- muscle fibers do not need creatine during training. They need it after completion, when there is a clear lack of energy.
- What should I take it with? So, with the questions “when?” And How?" we figured it out, and now we can consider the intricacies of combination. Everything is simple here. To improve the absorption of the supplement and speed up insulin secretion, it is advisable to drink creatine along with:
- with fast carbohydrates (you can wash the supplement down with sweet juice or water with sugar);
- with fast protein (helps improve absorption);
- with amino acids.
In both the first and second regimens, it is allowed to take creatine along with other sports nutrition, for example, amino acids, protein or a carbohydrate-protein mixture (gainer).
By the way, using the supplement during exercise is also useless, because it can only complicate the work and slow down the growth of muscle fibers.
Now we can answer the question of when to drink creatine. The answer is exclusively after going to the gym. Moreover, it is advisable to do this within 40-60 minutes. As a rule, this time is most favorable for the body to absorb all the beneficial components of the complex - amino acids, carbohydrates, protein and others.
As for rest days, on these days the supplement can be taken at any time (even at night). By the way, during the loading period it is recommended to drink the last portion before bed. It is believed that taking such a useful component at night allows the supplement to be better absorbed and prepare the body for the training day.
Iron Health
Despite the vast amount of information about creatine on the Internet and in the literature, we hear many of the same questions from beginners regarding the uses and methods of taking creatine. To close this topic once and for all, I decided to write this article, presenting it in a “question-and-answer” style.
#1 – Can I mix/drink creatine with protein, gainer and BCAA?
Creatine can be easily added to protein, gainer, or taken together with BCAA. Creatine goes well with all types of sports nutrition and does not cause side effects. In addition, this intake can contribute to better absorption of creatine by muscles.
See article - Benefits of Taking Creatine with Protein.
#2 – Can I take creatine with milk, tea, honey or water?
In principle, it makes absolutely no difference what you take with creatine - it does not affect its effectiveness. However, the degree of its absorption can be significantly increased by adding sugar or any other fast carbohydrates. This is due to the fact that creatine is absorbed in the presence of the hormone insulin, which, in addition to its main function (removing excess sugar from the blood), is also involved in the transport of nutrients to muscle tissue.
#3 – Can I take creatine at night?
Taking creatine is most effective during the periods before and after exercise. Taking the supplement at night does not provide any benefits and is therefore not advisable.
See the article - The correct course of taking creatine.
#4 – Can girls take creatine?
Women's workouts in the gym, as a rule, involve high-repetition loads - minimal working weight, simpler and easier exercises, a large number of repetitions (15-20). Such training is not intense strength training and does not lead to muscle growth, so in this case, taking creatine for girls is not advisable.
See the article - The effect of creatine on endurance.
Girls can take creatine only if they are involved in heavy strength sports - for example, bench press, powerlifting or weightlifting. In this case, creatine will help increase strength and increase the overall intensity of the workout. #5 – Can I take creatine with L-carnitine and other fat burners?
Taking creatine with L-carnitine or other fat burners has no advantages or contraindications. Creatine goes well with any sports nutrition product and does not cause any side effects.
#6 – Can you take creatine on a regular basis?
The recommended duration of a creatine course is 2 months, after which it is recommended to take a break for 2 weeks. However, keep in mind that the use of creatine is mandatory during periods of high-intensity strength training programs, so build your training plans so that the rest period from taking it coincides with the start of a high-repetition endurance or fat-burning program, where taking creatine is inappropriate.
#7 – Can you gain weight from creatine?
One of the properties of creatine is muscle hydration, that is, the process of fluid accumulation in them. However, it does not manifest itself so strongly as to have a noticeable effect on the appearance of the athlete. As for gaining excess weight (fat mass), creatine has absolutely no effect on this process.
WHEN IS THE BEST TIME TO TAKE CREATINE?
- home
- Sports Nutrition Blog
Taking creatine on training days
On days when you exercise, there are three main options for when to take creatine. You can take it shortly before your workout, shortly after your workout, or some time before or after your workout. Another option is to divide your daily dose of creatine into equal portions and take them throughout the day.
Illustration
Should you take creatine after a workout?
Several research labs have tried to find the best time to take creatine supplements. One study looked at whether it was more effective for adult men to consume five grams of creatine before or after exercise. During the four-week study, participants did weight training five days a week and took creatine before or after the workout. At the end of the study, the group taking creatine after exercise had a greater increase in muscle mass and a greater decrease in fat mass. However, other studies have found no difference between taking it before or after a workout. Overall, based on the limited number of publicly available studies, it is not clear that there are any significant differences between taking creatine before or after exercise.
It's best to take creatine shortly before or after your workout.
It seems logical that taking creatine immediately before or after a workout should have better effects than taking it long before or after a workout. In one 10-week study, adults doing strength training took a supplement containing creatine, carbohydrates and protein. The participants were divided into two groups. One group took the supplement shortly before and after exercise, while the other group took the supplement morning and evening well before exercise. At the end of the study, the group that took the supplement immediately before or after exercise gained more muscle mass than the group that took the supplement in the morning and evening. Based on this study, it appears that taking creatine immediately before or after exercise has the best effect on exercise performance. Alternatively, you can take the entire dose after your workout, or split the dose and take half before your workout and the other half after.
Taking creatine on rest days
Meal timing on weekends is probably much less important than on training days. The purpose of eating on weekends is to maintain increased levels of creatine in the muscles. When starting creatine supplementation, a “loading phase” is usually recommended. This phase involves taking relatively large doses of creatine (about 20 grams) for about five days. This method increases muscle creatine content fairly quickly within a few days. After this, it is recommended to reduce the daily dose to 3-5 g to simply maintain the achieved creatine level. According to research results, it may be more appropriate to take creatine with meals on days off from training.
Illustration
Should I take something along with creatine?
Although the benefits of taking creatine are widely known, many people wonder how they can improve the benefits. Various studies have attempted to add other ingredients to creatine, including protein, carbohydrates, amino acids, cinnamon, and various plant compounds, to increase its effectiveness. Several studies have reported that consuming carbohydrates with creatine increases the rate of its absorption into muscles. However, other studies have shown that adding carbohydrates does not provide additional benefits in increasing efficiency. Moreover, some studies used doses of almost 100 grams of carbohydrates, or about 400 calories. If you don't need these extra calories according to your meal plan, excess calories can lead to weight gain. In practice, the logic may be to take creatine when you eat your regular carbohydrate-containing meals, rather than adding carbohydrates beyond your daily value. It may also be beneficial to add protein to these creatine meals, as protein can help increase your body's retention of creatine.
Illustration
conclusions
Creatine is a safe and effective supplement, but the best time to take it is still up for debate. Research shows that on workout days it is better to take creatine shortly before or after exercise than long before or after. On weekends it may be helpful to take it with food, but timing is obviously not as important as on training days. Additionally, taking creatine with foods that contain carbohydrates and protein can help you get the most benefit from this supplement.
This is an adapted translation of the article; you can read the original text here.
To the list of news