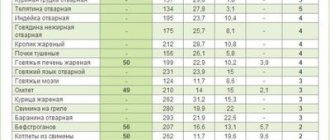
People suffering from diabetes and following the rules of a low-carbohydrate diet are accustomed to daily counting the glycemic index and calorie content of foods. This is necessary for complete and safe nutrition.
Cereals should be an important component of any person's diet. The value of cereals lies in the presence of a large amount of fiber, amino acids, antioxidants and minerals in their composition. The glycemic index of cereals, their nutritional properties, safety for diabetics - all these indicators are discussed in the article.
What is the glycemic index
GI is an indicator of the effect of various foods on blood glucose levels. The higher the index of a particular product, the faster the processes of carbohydrate breakdown in the body, and accordingly, the moment of increasing the amount of sugar accelerates. The calculation is based on GI glucose indicators (100). The ratio of other products and substances to it determines the number of points in their index.
GI is considered low, and therefore safe for a patient with diabetes, if its indicators range from 0 to 39. From 40 to 69 is average, and above 70 is a high index. Decoding and recalculation are used not only by those suffering from diabetes, but also by those who are trying to lead a healthy lifestyle and follow the principles of a healthy diet. GI indicators, calorie content, ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates of main cereals are indicated in the table.
Glycemic index is an important safety indicator for diabetics
Cereals, flour, pasta. Table of caloric content and chemical composition of food products.
This guide contains information about food products
and ready meals. You can also find out the full chemical composition: nutritional value, vitamins and minerals for each item.
(Content of proteins, fats and carbohydrates per 100 grams of product and calorie content.)
| Product | Calorie content | Squirrels | Fats | Carbohydrates |
| Amaranth, grains, uncooked | 371 kcal | 13.56 g | 7.02 g | 58.55 g |
| Amaranth, grains, cooked | 102 kcal | 3.8 g | 1.58 g | 16.59 g |
| Amaranth flakes | 353 kcal | 15.54 g | 7 g | 61.65 g |
| Arrowroot (arrowroot starch) | 357 kcal | 0.3 g | 0.1 g | 84.75 g |
| Pearl barley balls with cottage cheese, 1-294 each | 166 kcal | 7.9 g | 6.4 g | 18.9 g |
| Millet balls, 1-292 each | 170 kcal | 6.9 g | 5.9 g | 22.2 g |
| Bulgur, cereal | 342 kcal | 12.29 g | 1.33 g | 63.37 g |
| Bulgur, cooked | 83 kcal | 3.08 g | 0.24 g | 14.08 g |
| Ready-to-eat breakfast, puffed wheat, fortified | 364 kcal | 14.7 g | 1.2 g | 75.2 g |
| Breakfast Puffed Rice (Producer: The Quaker Oats, Co.) | 383 kcal | 7.01 g | 0.9 g | 86.38 g |
| Ready breakfast, puffed rice, enriched | 402 kcal | 6.3 g | 0.5 g | 88.1 g |
| Ready breakfast, wheat germ, toasted | 382 kcal | 29.1 g | 10.7 g | 34.5 g |
| Ready breakfast, oat rings with marshmallow pieces | 400 kcal | 7.1 g | 3.33 g | 80.4 g |
| Ready-to-eat breakfast, cinnamon oatmeal, QUAKER | 379 kcal | 11.23 g | 4.88 g | 69.39 g |
| Ready breakfast, oatmeal, QUAKER | 379 kcal | 11.38 g | 4.83 g | 69.47 g |
| Ready breakfast, wheat with bran, nuts and fruits, dry | 385 kcal | 7.1 g | 5.6 g | 66.5 g |
| Ready-to-eat breakfast, crispy rice (producer: Ralston Foods) | 383 kcal | 6.69 g | 1.26 g | 85.52 g |
| Ready breakfast, crispy rice, MALT-O-MEAL | 346 kcal | 6.07 g | 1.12 g | 86 g |
| Buckwheat, grain | 343 kcal | 13.25 g | 3.4 g | 61.5 g |
| Buckwheat, whole grain unprocessed | 296 kcal | 10.8 g | 3.2 g | 56 g |
| Buckwheat porridge from kernels 1-278 | 101 kcal | 3 g | 3.4 g | 14.6 g |
| Crumbled buckwheat porridge (boiled buckwheat without salt and oil) | 100.9 kcal | 4.182 g | 1.095 g | 18.567 g |
| Buckwheat | 300 kcal | 9.5 g | 2.3 g | 60.4 g |
| Buckwheat kernels | 308 kcal | 12.6 g | 3.3 g | 57.1 g |
| Buckwheat, fried, cooked | 92 kcal | 3.38 g | 0.62 g | 17.24 g |
| Buckwheat, roasted, dry | 346 kcal | 11.73 g | 2.71 g | 64.65 g |
| Buckwheat flour | 353 kcal | 13.6 g | 1.2 g | 71.9 g |
| Buckwheat flour, whole grain | 335 kcal | 12.62 g | 3.1 g | 60.59 g |
| Pressed yeast (*ergosterol) | 109 kcal | 12.7 g | 2.7 g | 8.5 g |
| Incaparina, a mixture of corn and soy flour, uncooked | 379 kcal | 21.75 g | 5.58 g | 50.63 g |
| Kamut (Khorasan wheat), uncooked | 337 kcal | 14.54 g | 2.13 g | 59.48 g |
| Kamut (Khorasan wheat), cooked | 132 kcal | 5.71 g | 0.83 g | 23.3 g |
| Potato starch | 357 kcal | 6.9 g | 0.34 g | 77.2 g |
| Farina porridge (starch, potato flour), enriched, cooked in water, with salt | 53 kcal | 1.82 g | 0.34 g | 10.12 g |
| Farina porridge (starch, potato flour), dry | 369 kcal | 10.6 g | 0.5 g | 76.1 g |
| Quinoa, uncooked | 368 kcal | 14.12 g | 6.07 g | 57.16 g |
| Quinoa, cooked | 120 kcal | 4.4 g | 1.92 g | 18.5 g |
| Dumplings, 2-196 | 131 kcal | 4.1 g | 4.1 g | 19.4 g |
| Semolina cutlets 1-294 each | 141 kcal | 3 g | 5.3 g | 20.2 g |
| Potato starch | 313 kcal | 0.1 g | 0 g | 78.2 g |
| Buckwheat krupenik, 1-288 each | 199 kcal | 8.8 g | 8.8 g | 21.1 g |
| White corn, dry grain | 365 kcal | 9.42 g | 4.74 g | 74.26 g |
| White Corn, Steamed (Navajo) | 386 kcal | 9.72 g | 5.18 g | 58.6 g |
| Yellow corn, frozen whole kernels, microwaved | 113 kcal | 3.62 g | 1.42 g | 23.27 g |
| Yellow corn, dry grain | 365 kcal | 9.42 g | 4.74 g | 66.96 g |
| Yellow corn, dry grain (Northern Great Plains Indians) | 419 kcal | 14.48 g | 10.64 g | 45.77 g |
| Corn with red and green peppers, canned | 75 kcal | 2.33 g | 0.55 g | 18.17 g |
| Corn, high lysine | 314 kcal | 11.2 g | 4.8 g | 55.33 g |
| Corn, germ | 147 kcal | 16.3 g | 30.5 g | 0 g |
| Corn, grain | 325 kcal | 10.3 g | 4.9 g | 60 g |
| Corn, dent | 320 kcal | 8.3 g | 4 g | 61.4 g |
| Corn, canned food | 58 kcal | 2.2 g | 0.4 g | 11.2 g |
| Liquid corn porridge, white, cooked in water, without salt | 71 kcal | 1.71 g | 0.46 g | 13.96 g |
| Corn porridge liquid, white, cooked in water, with salt | 71 kcal | 1.71 g | 0.46 g | 13.96 g |
| Corn porridge is liquid, yellow, cooked in water, without salt | 65 kcal | 1.23 g | 0.39 g | 13.16 g |
| Corn porridge liquid, yellow, cooked in water, with salt | 65 kcal | 1.23 g | 0.39 g | 13.16 g |
| Corn grits | 328 kcal | 8.3 g | 1.2 g | 71 g |
| Corn grits, white, enriched | 370 kcal | 7.65 g | 1.75 g | 74.49 g |
| Corn grits, yellow | 371 kcal | 8.8 g | 1.2 g | 78 g |
| Corn flour | 331 kcal | 7.2 g | 1.5 g | 72.1 g |
| Coarse white corn flour | 362 kcal | 8.12 g | 3.59 g | 69.59 g |
| Corn flour, white, coarse, germless | 370 kcal | 7.11 g | 1.75 g | 75.55 g |
| White corn flour, coarse, germless, enriched | 370 kcal | 7.11 g | 1.75 g | 75.55 g |
| Corn flour, white, coarse, self-raising, enriched, germ-free | 355 kcal | 8.41 g | 1.72 g | 67.69 g |
| Cornmeal, white, coarse, self-raising, sifted, enriched | 334 kcal | 8.28 g | 3.4 g | 63.58 g |
| White cornmeal, coarse, self-raising, sifted, enriched, with added wheat flour | 348 kcal | 8.41 g | 2.85 g | 67.13 g |
| Fine white corn flour, whole grain | 361 kcal | 6.93 g | 3.86 g | 69.55 g |
| White corn flour, masa (from nixtamalized grain) | 363 kcal | 8.46 g | 3.69 g | 70.19 g |
| Corn flour, white, masa (from nixtamalized grain), enriched | 363 kcal | 8.46 g | 3.69 g | 70.19 g |
| Corn flour, yellow, coarse, germless | 370 kcal | 7.11 g | 1.75 g | 75.55 g |
| Yellow corn flour, coarse, germless, enriched | 370 kcal | 7.11 g | 1.75 g | 75.55 g |
| Corn flour, yellow, coarse, self-raising, germless, enriched | 355 kcal | 8.41 g | 1.72 g | 67.69 g |
| Cornmeal, yellow, coarse, self-raising, sieved, enriched | 334 kcal | 8.28 g | 3.4 g | 63.58 g |
| Yellow cornmeal, coarse, self-raising, sieved, with added wheat flour, enriched | 348 kcal | 8.41 g | 2.85 g | 67.13 g |
| Yellow corn flour, coarse, whole grain | 362 kcal | 8.12 g | 3.59 g | 69.59 g |
| Corn flour, yellow, finely ground, germless | 375 kcal | 5.59 g | 1.39 g | 80.85 g |
| Yellow corn flour, finely ground, whole grain | 361 kcal | 6.93 g | 3.86 g | 69.55 g |
| Yellow corn flour, masa (from nixtamalized grain), enriched | 363 kcal | 8.46 g | 3.69 g | 70.19 g |
| Purple finely ground corn flour, whole grain, (maiz morado) | 364 kcal | 8.75 g | 5.09 g | 65.49 g |
| Cornmeal, blue (Navajo) | 398 kcal | 10.4 g | 5.44 g | 68.23 g |
| Corn bran | 224 kcal | 8.36 g | 0.92 g | 6.64 g |
| Cornflakes | 360 kcal | 6.7 g | 0.1 g | 82.2 g |
| Corn flakes, Ralston Corn Flakes | 384 kcal | 5.9 g | 0.91 g | 85.31 g |
| Corn starch | 343 kcal | 1 g | 0.6 g | 83.5 g |
| Corn starch | 381 kcal | 0.26 g | 0.05 g | 90.37 g |
| Homemade corn pudding | 131 kcal | 4.42 g | 5.04 g | 15.77 g |
| Couscous (couscous), cooked | 112 kcal | 3.79 g | 0.16 g | 21.82 g |
| Couscous (couscous), dry | 376 kcal | 12.76 g | 0.64 g | 72.43 g |
| Homemade noodles, 2-198 each | 322 kcal | 12 g | 3.7 g | 60.1 g |
| Chinese noodles, flat, crispy | 521 kcal | 10.33 g | 31.72 g | 50 g |
| Chinese noodles, chow mein | 471 kcal | 10.88 g | 21.24 g | 56.94 g |
| Spinach egg noodles, enriched, cooked | 132 kcal | 5.04 g | 1.57 g | 21.95 g |
| Egg noodles with spinach, enriched, dry | 382 kcal | 14.61 g | 4.55 g | 63.52 g |
| Egg noodles, enriched, cooked | 138 kcal | 4.54 g | 2.07 g | 23.96 g |
| Egg noodles, enriched, cooked with salt | 138 kcal | 4.54 g | 2.07 g | 23.96 g |
| Egg noodles, enriched, dry | 384 kcal | 14.16 g | 4.44 g | 67.97 g |
| Egg noodles, cooked, no salt | 138 kcal | 4.54 g | 2.07 g | 23.96 g |
| Egg noodles, cooked, with salt | 138 kcal | 4.54 g | 2.07 g | 23.96 g |
| Egg noodles, dry | 384 kcal | 14.16 g | 4.44 g | 67.97 g |
| Japanese noodles, soba, cooked | 99 kcal | 5.06 g | 0.1 g | 21.44 g |
| Japanese noodles, soba, dry | 336 kcal | 14.38 g | 0.71 g | 74.62 g |
| Japanese noodles, somen, cooked | 131 kcal | 4 g | 0.18 g | 27.54 g |
| Japanese noodles, somen, dry | 356 kcal | 11.35 g | 0.81 g | 69.8 g |
| Lapshevnik with cottage cheese, 1-308 each | 180 kcal | 7.7 g | 7.4 g | 20.3 g |
| Pasta baked with egg, 1 -306 each | 152 kcal | 4.6 g | 8.3 g | 14.8 g |
| Pasta made from 1st grade flour | 333 kcal | 11.2 g | 1.6 g | 68.4 g |
| Pasta made from premium flour | 338 kcal | 11 g | 1.3 g | 70.5 g |
| Pasta made from premium flour, fortified | 337 kcal | 10.4 g | 1.1 g | 69.7 g |
| Pasta made from premium flour, dairy | 345 kcal | 11.5 g | 2.9 g | 67 g |
| Pasta made from premium flour, egg | 342 kcal | 11.3 g | 2.1 g | 69.6 g |
| Boiled pasta with fat, 1-304 each | 135 kcal | 3.4 g | 5 g | 19 g |
| Boiled pasta, 1-302 each | 98 kcal | 3.6 g | 0.4 g | 20 g |
| Pasta with vegetables, enriched, cooked | 128 kcal | 4.53 g | 0.11 g | 22.31 g |
| Pasta with vegetables, enriched, dry | 367 kcal | 13.14 g | 1.04 g | 70.58 g |
| Viscous semolina porridge, 1-276 each | 100 kcal | 2.2 g | 2.9 g | 16.4 g |
| Semolina | 333 kcal | 10.3 g | 1 g | 70.6 g |
| Semolina, unfortified | 360 kcal | 12.68 g | 1.05 g | 68.93 g |
| Semolina, enriched | 360 kcal | 12.68 g | 1.05 g | 68.93 g |
| Wheat germ flour | 335 kcal | 33.8 g | 7.7 g | 32.7 g |
| Sorghum flour | 357 kcal | 9.53 g | 1.24 g | 74.95 g |
| Sorghum flour, whole grain | 359 kcal | 8.43 g | 3.34 g | 70.04 g |
| Triticale flour | 338 kcal | 13.18 g | 1.81 g | 58.54 g |
| Oats, grain | 316 kcal | 10 g | 6.2 g | 55.1 g |
| Oats, dry grain | 389 kcal | 16.89 g | 6.9 g | 55.67 g |
| Instant oatmeal (instant) with raisins and spices, cooked in water | 88 kcal | 1.98 g | 0.95 g | 16.61 g |
| Instant oatmeal (instant) with cinnamon and spices, cooked in water | 96 kcal | 2.37 g | 1.21 g | 16.95 g |
| Instant oatmeal (instant) with cinnamon and spices, dry | 369 kcal | 9.53 g | 4.84 g | 68.08 g |
| Instant oatmeal (instant) cooked in water | 68 kcal | 2.37 g | 1.36 g | 9.97 g |
| Instant Oatmeal (Instant), Maple and Brown Sugar, Dry | 386 kcal | 9.25 g | 4.73 g | 69.47 g |
| Instant oatmeal (instant), dry | 362 kcal | 11.92 g | 6.9 g | 59.52 g |
| Liquid oatmeal, cooked in water, without salt | 71 kcal | 2.54 g | 1.52 g | 10.3 g |
| Liquid oatmeal, cooked in water, with salt | 71 kcal | 2.54 g | 1.52 g | 10.3 g |
| Oatmeal from Hercules flakes, 1-280 each | 105 kcal | 2.4 g | 4 g | 14.8 g |
| Oatmeal, 1-280 each | 109 kcal | 2.6 g | 4.1 g | 15.5 g |
| Oat groats | 379 kcal | 13.15 g | 6.52 g | 57.6 g |
| Oat groats | 342 kcal | 12.3 g | 6.1 g | 59.5 g |
| Oat flour | 369 kcal | 13 g | 6.8 g | 64.9 g |
| Oatmeal with bran | 404 kcal | 14.66 g | 9.12 g | 59.2 g |
| Instant Cinnamon Oatmeal, Dry (Producer: The Quaker Oats, Co.) | 369 kcal | 10.39 g | 5.1 g | 66.32 g |
| Oat bran | 246 kcal | 17.3 g | 7.03 g | 50.82 g |
| Oat bran, cooked | 40 kcal | 3.21 g | 0.86 g | 8.84 g |
| Oat flakes "Hercules" | 352 kcal | 12.3 g | 6.2 g | 61.8 g |
| Cornmeal pasta (pasta, spaghetti), gluten-free, cooked | 126 kcal | 2.63 g | 0.73 g | 23.11 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti) without eggs, homemade, cooked | 124 kcal | 4.37 g | 0.98 g | 25.12 g |
| Brown rice flour pasta (pasta, spaghetti), gluten-free, cooked | 138 kcal | 3.46 g | 1.67 g | 30.5 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti) made from corn and rice flour, gluten-free, cooked | 179 kcal | 3.2 g | 1 g | 36.65 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti) made from corn flour and quinoa flour, gluten-free, cooked | 152 kcal | 3.23 g | 2.07 g | 27.81 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti) made from corn flour, gluten-free | 357 kcal | 7.46 g | 2.08 g | 68.26 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti) from rice flour with rice bran extract, gluten-free, cooked | 200 kcal | 4.21 g | 1.7 g | 38.85 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti) made from whole wheat flour, cooked | 149 kcal | 5.99 g | 1.71 g | 26.17 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti) from whole grain flour, dry | 352 kcal | 13.87 g | 2.93 g | 64.17 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti) egg, homemade, cooked | 130 kcal | 5.28 g | 1.74 g | 23.54 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti), enriched, cooked without salt | 158 kcal | 5.8 g | 0.93 g | 29.06 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti), enriched, cooked with salt | 157 kcal | 5.8 g | 0.93 g | 28.79 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti), enriched, dry | 371 kcal | 13.04 g | 1.51 g | 71.47 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti) cooked without salt | 158 kcal | 5.8 g | 0.93 g | 29.06 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti) cooked with salt | 157 kcal | 5.8 g | 0.93 g | 28.79 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti), fresh frozen, uncooked | 288 kcal | 11.31 g | 2.3 g | 54.73 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti), fresh frozen, cooked | 131 kcal | 5.15 g | 1.05 g | 24.93 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti), fresh frozen, with spinach, uncooked | 289 kcal | 11.26 g | 2.1 g | 55.72 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti), fresh frozen, with spinach, cooked | 130 kcal | 5.06 g | 0.94 g | 25.04 g |
| Pasta (pasta, spaghetti), dry | 371 kcal | 13.04 g | 1.51 g | 71.47 g |
| Pearl barley porridge 1-270 | 135 kcal | 2.9 g | 3.5 g | 22.9 g |
| Pearl barley | 315 kcal | 9.3 g | 1.1 g | 66.9 g |
| Pearl barley | 352 kcal | 9.91 g | 1.16 g | 62.12 g |
| Pearl barley, cooked | 123 kcal | 2.26 g | 0.44 g | 24.42 g |
| Spelled, uncooked | 338 kcal | 14.57 g | 2.43 g | 59.49 g |
| Spelled (spelt), cooked | 127 kcal | 5.5 g | 0.85 g | 22.54 g |
| Millet, food grain | 298 kcal | 11.2 g | 3.9 g | 54.6 g |
| Rice pudding 1-292 | 202 kcal | 5.6 g | 5.7 g | 32 g |
| Soft white wheat | 340 kcal | 10.69 g | 1.99 g | 62.66 g |
| Soft red winter wheat | 331 kcal | 10.35 g | 1.56 g | 61.74 g |
| Soft wheat, grain | 305 kcal | 11.8 g | 2.2 g | 59.5 g |
| Sprouted wheat | 198 kcal | 7.49 g | 1.27 g | 41.43 g |
| Vitreous white grain wheat | 342 kcal | 11.31 g | 1.71 g | 63.7 g |
| Glassy red winter wheat | 327 kcal | 12.61 g | 1.54 g | 58.98 g |
| Vitreous red grain spring wheat | 329 kcal | 15.4 g | 1.92 g | 55.83 g |
| Durum wheat, grain | 339 kcal | 13.68 g | 2.47 g | 71.13 g |
| Durum wheat, grain | 304 kcal | 13 g | 2.5 g | 57.5 g |
| Wheat porridge liquid, prepared in water, without salt | 62 kcal | 2 g | 0.4 g | 12.1 g |
| Wheat porridge liquid, prepared in water, with salt | 62 kcal | 2 g | 0.4 g | 12.1 g |
| Crumbled wheat porridge from Poltavskaya cereals, 1-272 each | 153 kcal | 4.4 g | 3.6 g | 25.7 g |
| Wheat gluten (gluten) | 370 kcal | 75.16 g | 1.85 g | 13.19 g |
| Wheat groats | 342 kcal | 11.2 g | 2 g | 65.7 g |
| Wheat groats "Artek" | 329 kcal | 11 g | 1.2 g | 68.5 g |
| Wheat cereal "Poltavskaya" | 329 kcal | 11.5 g | 1.3 g | 67.9 g |
| Premium quality wheat flour from soft wheat | 334 kcal | 10.3 g | 1.1 g | 70.6 g |
| Premium wheat flour, 10% protein, unbleached, enriched | 366 kcal | 9.71 g | 1.48 g | 73.82 g |
| Premium wheat flour, 10% protein, bleached, unfortified | 366 kcal | 9.71 g | 1.48 g | 73.82 g |
| Premium wheat flour, 10% protein, bleached, enriched | 366 kcal | 9.71 g | 1.48 g | 73.82 g |
| Premium wheat flour, 11.5% protein, unbleached, enriched | 363 kcal | 11.5 g | 1.45 g | 71.41 g |
| Premium wheat flour, 11.5% protein, bleached, unfortified | 363 kcal | 11.5 g | 1.45 g | 71.41 g |
| Premium wheat flour, 11.5% protein, bleached, enriched | 363 kcal | 11.5 g | 1.45 g | 71.41 g |
| Premium wheat flour, 13% protein, bleached, unfortified | 362 kcal | 13.07 g | 1.38 g | 69.8 g |
| Premium wheat flour, 13% protein, bleached, enriched | 362 kcal | 13.07 g | 1.38 g | 69.8 g |
| Premium wheat flour, 15% protein, bleached, unfortified | 362 kcal | 15.33 g | 1.41 g | 67.48 g |
| Premium wheat flour, 15% protein, bleached, enriched | 362 kcal | 15.33 g | 1.41 g | 67.48 g |
| Premium wheat flour, 9% protein, bleached, unfortified | 367 kcal | 8.89 g | 1.43 g | 74.92 g |
| Premium wheat flour, 9% protein, bleached, enriched | 367 kcal | 8.89 g | 1.43 g | 77.32 g |
| Premium quality wheat flour, confectionery, enriched | 362 kcal | 8.2 g | 0.86 g | 76.33 g |
| Premium wheat flour, tortilla mix, enriched | 405 kcal | 9.66 g | 10.63 g | 67.14 g |
| Premium wheat flour, all-purpose, unfortified | 364 kcal | 10.33 g | 0.98 g | 73.61 g |
| Premium quality wheat flour, all-purpose, enriched with calcium | 364 kcal | 10.33 g | 0.98 g | 73.61 g |
| Premium wheat flour, all-purpose, enriched, unbleached | 364 kcal | 10.33 g | 0.98 g | 73.61 g |
| Premium wheat flour, all-purpose, enriched, bleached | 364 kcal | 10.33 g | 0.98 g | 73.61 g |
| Premium wheat flour, all-purpose, enriched, self-raising | 354 kcal | 9.89 g | 0.97 g | 71.52 g |
| Premium quality wheat flour, baking, enriched | 361 kcal | 11.98 g | 1.66 g | 70.13 g |
| Whole grain wheat flour | 340 kcal | 13.21 g | 2.5 g | 61.27 g |
| Whole grain wheat flour from soft wheat | 332 kcal | 9.61 g | 1.95 g | 61.38 g |
| Wheat flour, second grade | 324 kcal | 11.7 g | 1.81 g | 63.7 g |
| Wheat flour, premium | 334 kcal | 10.8 g | 1.3 g | 69.9 g |
| Wheat flour, premium, fortified | 334 kcal | 10.3 g | 1.1 g | 68.9 g |
| Wheat flour, wallpaper | 312 kcal | 11.5 g | 2.2 g | 61.5 g |
| Wheat flour, first grade | 329 kcal | 11.1 g | 1.5 g | 67.8 g |
| Wheat flour, first grade, fortified | 331 kcal | 10.6 g | 1.3 g | 67.6 g |
| Wheat flour, baking, unfortified | 361 kcal | 11.98 g | 1.66 g | 70.13 g |
| Wheat germ, raw | 360 kcal | 23.15 g | 9.72 g | 38.6 g |
| Wheat bran | 165 kcal | 16 g | 3.8 g | 16.6 g |
| Wheat bran, raw | 216 kcal | 15.55 g | 4.25 g | 21.71 g |
| Millet porridge for 1-278 | 109 kcal | 2.8 g | 3.4 g | 16.8 g |
| Millet groats, polished millet | 342 kcal | 11.5 g | 3.3 g | 66.5 g |
| Millet flour | 382 kcal | 10.75 g | 4.25 g | 71.62 g |
| Millet (millet) puffed | 354 kcal | 13 g | 3.4 g | 77.3 g |
| Millet, cooked | 119 kcal | 3.51 g | 1 g | 22.37 g |
| Millet, raw | 378 kcal | 11.02 g | 4.22 g | 64.35 g |
| Rye flour, peeled | 298 kcal | 8.9 g | 1.7 g | 61.8 g |
| Rye flour, peeled | 349 kcal | 10.88 g | 1.52 g | 63.63 g |
| Rye flour, wallpaper | 294 kcal | 10.7 g | 1.9 g | 58.5 g |
| Rye flour, wallpaper | 325 kcal | 15.91 g | 2.22 g | 44.83 g |
| Rye flour, sifted | 305 kcal | 6.9 g | 1.4 g | 66.3 g |
| Rye flour, sifted | 357 kcal | 9.82 g | 1.33 g | 68.68 g |
| Rye bran | 114.2 kcal | 12.2 g | 3.4 g | 8.7 g |
| White rice, long grain, quick-cooking, enriched, cooked | 124 kcal | 2.18 g | 0.5 g | 26.16 g |
| White long-grain rice, fast-cooking, enriched, dry | 380 kcal | 7.82 g | 0.94 g | 80.42 g |
| Long grain white rice, enriched, cooked | 130 kcal | 2.69 g | 0.28 g | 27.77 g |
| Long grain white rice, enriched, cooked with salt | 130 kcal | 2.69 g | 0.28 g | 27.77 g |
| White long grain rice, enriched, dry | 365 kcal | 7.13 g | 0.66 g | 78.65 g |
| Long grain white rice, cooked without salt | 130 kcal | 2.69 g | 0.28 g | 27.77 g |
| Long grain white rice, cooked with salt | 130 kcal | 2.69 g | 0.28 g | 27.77 g |
| Long grain white rice, parboiled, enriched, cooked | 123 kcal | 2.91 g | 0.37 g | 25.15 g |
| Long grain white rice, steamed, enriched, dry | 374 kcal | 7.51 g | 1.03 g | 79.09 g |
| Long grain white rice, steamed, cooked | 123 kcal | 2.91 g | 0.37 g | 25.15 g |
| White long grain rice, dry | 365 kcal | 7.13 g | 0.66 g | 78.65 g |
| White long grain rice, dry | 374 kcal | 7.51 g | 1.03 g | 79.09 g |
| White glutinous rice (Asian), cooked | 97 kcal | 2.02 g | 0.19 g | 20.09 g |
| White glutinous rice (Asian), dry | 370 kcal | 6.81 g | 0.55 g | 78.88 g |
| White short grain rice, enriched, cooked | 130 kcal | 2.36 g | 0.19 g | 28.73 g |
| White short grain rice, enriched, dry | 358 kcal | 6.5 g | 0.52 g | 76.35 g |
| White short grain rice, cooked | 130 kcal | 2.36 g | 0.19 g | 28.73 g |
| White short grain rice, dry | 358 kcal | 6.5 g | 0.52 g | 79.15 g |
| Steamed white rice (Chinese cuisine) | 151 kcal | 3.2 g | 0.27 g | 32.98 g |
| White medium grain rice, enriched, cooked | 130 kcal | 2.38 g | 0.21 g | 28.29 g |
| White medium grain rice, enriched, dry | 360 kcal | 6.61 g | 0.58 g | 77.94 g |
| White medium grain rice, cooked | 130 kcal | 2.38 g | 0.21 g | 28.59 g |
| White medium grain rice, dry | 360 kcal | 6.61 g | 0.58 g | 79.34 g |
| White rice, rice cereal | 333 kcal | 7 g | 1 g | 74 g |
| Wild rice (black, Indian rice, cicinia), cooked | 101 kcal | 3.99 g | 0.34 g | 19.54 g |
| Wild rice (black, Indian rice, cicinia), dry | 357 kcal | 14.73 g | 1.08 g | 68.7 g |
| Yellow rice with spices, dry mix | 343 kcal | 7.02 g | 1.75 g | 72.88 g |
| Brown (unpolished) long grain rice, cooked | 123 kcal | 2.74 g | 0.97 g | 23.98 g |
| Brown rice (unpolished), long grain, dry | 367 kcal | 7.54 g | 3.2 g | 72.65 g |
| Brown rice (unpolished) medium grain, cooked | 112 kcal | 2.32 g | 0.83 g | 21.71 g |
| Brown rice (unpolished), medium grain, dry | 362 kcal | 7.5 g | 2.68 g | 72.77 g |
| Brown rice (unpolished), parboiled, cooked, UNCLE BENS | 147 kcal | 3.09 g | 0.85 g | 29.63 g |
| Brown rice (unpolished), steamed. dry, UNCLE BEN'S | 370 kcal | 7.6 g | 2.75 g | 75.18 g |
| Cream rice, instant crushed rice, cooked in water with salt | 52 kcal | 0.9 g | 0.1 g | 11.4 g |
| Cream rice, instant broken rice, dry | 370 kcal | 6.3 g | 0.5 g | 81.7 g |
| Rice, whole grain unprocessed | 303 kcal | 7.5 g | 2.6 g | 62.3 g |
| Rice casserole 1-288 | 144 kcal | 4 g | 5.6 g | 19.4 g |
| Rice casserole with cottage cheese 1-288 each | 189 kcal | 5.1 g | 7.1 g | 26.1 g |
| Rice porridge for 1-268 | 144 kcal | 2.4 g | 3.5 g | 25.8 g |
| Rice noodles, cooked | 108 kcal | 1.79 g | 0.2 g | 23.01 g |
| Rice noodles, dry | 364 kcal | 5.95 g | 0.56 g | 78.58 g |
| Dietary rice flour | 356 kcal | 7.4 g | 0.6 g | 80.2 g |
| Rice flour, white | 366 kcal | 5.95 g | 1.42 g | 77.73 g |
| Rice flour, brown | 363 kcal | 7.23 g | 2.78 g | 71.88 g |
| Rice bran, raw | 316 kcal | 13.35 g | 20.85 g | 28.69 g |
| Ground fried rye | 322 kcal | 7.9 g | 1.7 g | 68.7 g |
| Rye, grain | 338 kcal | 10.34 g | 1.63 g | 60.76 g |
| Rye, unprocessed whole grain | 283 kcal | 9.9 g | 2.2 g | 55.8 g |
| Sorghum | 323 kcal | 10.6 g | 4.12 g | 59.6 g |
| Sorghum | 329 kcal | 10.62 g | 3.46 g | 65.39 g |
| Spaghetti with spinach, cooked | 130 kcal | 4.58 g | 0.63 g | 26.15 g |
| Spaghetti with spinach, dry | 372 kcal | 13.35 g | 1.57 g | 64.21 g |
| Protein-enriched spaghetti, cooked | 164 kcal | 8.86 g | 0.21 g | 28.88 g |
| Protein enriched spaghetti, dry | 374 kcal | 21.78 g | 2.23 g | 63.25 g |
| Breakfast cereal, MALT-O-MEAL, regular, dry | 361 kcal | 11.8 g | 1.27 g | 75.6 g |
| Breakfast cereal, CREAM OF WHEAT, regular, prepared with water, no salt | 50 kcal | 1.44 g | 0.21 g | 10.52 g |
| Breakfast cereal, CREAM OF WHEAT, regular, dry | 370 kcal | 10.5 g | 1.5 g | 76.5 g |
| Breakfast cereal, ready to eat, GENERAL MILLS TOTAL, Cranberry Crunch | 328 kcal | 6.9 g | 1.72 g | 78 g |
| Breakfast cereal, ready to eat, GENERAL MILLS, Curves Fruit & Nut Crunch cereal | 347 kcal | 6.12 g | 3.06 g | 85.44 g |
| Breakfast cereal, ready to eat, GENERAL MILLS, DORA THE EXPLORER | 366 kcal | 5.6 g | 5.7 g | 82.8 g |
| Breakfast cereal, ready to eat, GENERAL MILLS, Fruity CHEERIOS | 383 kcal | 5.2 g | 5.2 g | 84.2 g |
| Breakfast cereal, ready to eat, GENERAL MILLS, OATMEAL CRISP with Almonds | 393 kcal | 9.8 g | 6.7 g | 78.9 g |
| KELLOGG'S SPECIAL K Chocolatey Delight Ready-to-Eat Breakfast Cereal | 381 kcal | 6.5 g | 7.3 g | 81.2 g |
| Breakfast cereal, ready to eat, QUAKER, QUAKER OAT CINNAMON LIFE | 373 kcal | 9.01 g | 4.05 g | 79.16 g |
| Breakfast cereal, ready to eat, WEETABIX WHOLE WHEAT CEREAL | 373 kcal | 11.5 g | 2.8 g | 77.4 g |
| Breakfast cereal, ready-to-eat, sweetened puffed wheat, any brand | 390 kcal | 5.8 g | 1.3 g | 90.7 g |
| Breakfast cereal, ready to eat, chocolate flavored rings, sweetened, any brand | 415 kcal | 4.8 g | 8.8 g | 81.9 g |
| Breakfast cereal, ready to eat, oats and corn and wheat, squares, sweetened, maple flavored | 430 kcal | 6 g | 9.8 g | 79.9 g |
| Breakfast cereal, ready-to-eat, wheat, crushed, regular, no sugar or salt | 337 kcal | 11.37 g | 2.21 g | 78.76 g |
| Breakfast cereal, farina, starch, potato flour, enriched, cooked with water, no salt | 53 kcal | 1.82 g | 0.34 g | 10.92 g |
| Tapioca (cassava sago), dry | 358 kcal | 0.19 g | 0.02 g | 87.79 g |
| Teff, uncooked | 367 kcal | 13.3 g | 2.38 g | 65.13 g |
| Teff, cooked | 101 kcal | 3.87 g | 0.65 g | 17.06 g |
| Oatmeal | 363 kcal | 12.5 g | 6 g | 64.9 g |
| Triticale | 336 kcal | 13.05 g | 2.09 g | 72.13 g |
| Triticale | 293 kcal | 12.8 g | 2.08 g | 54.5 g |
| Hominy corn (nixtamalized) white, canned | 72 kcal | 1.48 g | 0.88 g | 11.76 g |
| Hominy Corn (Nixtamalized), Yellow, Canned | 72 kcal | 1.48 g | 0.88 g | 11.76 g |
| Barley flour | 284 kcal | 10 g | 1.6 g | 56.1 g |
| Barley flour or semolina | 345 kcal | 10.5 g | 1.6 g | 64.42 g |
| Barley malt | 361 kcal | 10.28 g | 1.84 g | 71.2 g |
| Husked barley | 354 kcal | 12.48 g | 2.3 g | 56.18 g |
| Barley, whole grain, unprocessed | 288 kcal | 10.3 g | 2.4 g | 56.4 g |
| Barley porridge for 1-278 | 96 kcal | 2.1 g | 2.9 g | 15.3 g |
| Barley grits | 313 kcal | 10 g | 1.3 g | 65.4 g |
Buckwheat
Cereals are quite popular among those who decide to eat healthy. There are even a number of specially designed diets based on porridge in combination with vegetables and lean meats.
An interesting point is that the GIs of raw and cooked cereals are in different categories:
- raw buckwheat – 55,
- boiled cereal – 40.
The composition and content of nutrients does not change, but the index values vary due to the presence of water in the boiled dish.
Water during the cooking process reduces the GI values of any cereal. This condition only applies if there are no other additives, not even oil.
The product belongs to the middle group. Adding milk or sugar already shows completely different results, transferring the cereal to the category of cereals with a high glycemic index. A quarter of 100 g of buckwheat consists of carbohydrates, which means you should refrain from eating it for dinner and combining it with other carbohydrate foods. It is better to combine with vegetables and add proteins in the form of fish and chicken.
What role do carbohydrates play in the human body?
Once we have determined what carbohydrates are and what major foods they are found in, we need to understand the process that occurs in the human body after these components enter the digestive tract. This way we will be able to assess the value of oligo- and polysaccharides for the functioning and maintenance of optimal human life in different age groups. This will also allow you to see the difference in their quantity required for people engaged in mental or physical labor.
So, carbohydrates act as the main fuel for humans, providing all energy-consuming processes that occur not only at the level of the whole body or an individual organ, but also at the cellular level. The body of living beings is capable of storing this component internally in the form of glycogen. Most of all it is concentrated in muscle structures and in the liver.
Carbohydrates are necessary to ensure the following life processes and reactions:
- For nutrition and brain growth.
- For the synthesis of amino acids essential for many systems, including muscles and brain structures.
It should be noted that without sufficient carbohydrate intake, the body will not be able to cope with everyday stress. It is this component that provides vigor to all living beings, because from carbohydrates, in the process of certain chemical reactions, glucose is produced, which enters the bloodstream and provides the cells of the whole body with the necessary amount of energy.
Rice
The performance of rice depends on its variety. White rice, a grain that has undergone the process of cleaning and polishing, has a score of 65, which puts it in the middle group of products. The brown variety of rice (not peeled, not polished) is characterized by an indicator of 20 units less, which makes it safer for diabetics.
Rice is a world-famous cereal that saturates the body with essential substances.
Rice is a storehouse of vitamins B, E, macro- and microelements, as well as essential amino acids. Patients need all this to prevent complications of diabetes (polyneuropathy, retinopathy, kidney pathology).
The brown variety is more beneficial both in terms of the amount of substances needed by the body and in terms of individual GI and calorie indicators. The only negative is its short shelf life.
Milk reduces the GI values of rice compared to water (70 and 80, respectively).
You may be interested in these products:
Cashew nuts
Nutritional information per ¼ cup:
• 314 calories
• 17.1 g carbohydrates
• 25 g fat
• 10.3 g protein
If you're tired of almonds, cashews are a great alternative! They contain healthy calories, but don't need to be overindulged.
Avocado
Nutritional value of 3/4 avocado:
• 241 calories
• 12.9 g carbohydrates
• 22.1 g fat
• 3 g protein
Avocado is the king of healthy fats! This is a delicious product that contains many beneficial nutrients and goes with almost everything! You can eat it raw with a spoon, cut it into slices and add it to a healthy breakfast or make a spread. Try starting your day with an avocado and see how your body uses energy throughout the day .
Peanut paste
Nutritional value in two spoons:
• 180.6 calories
• 3.66 g carbohydrates
• 14.58 g fat
• 8.7 g protein
We love peanut butter! It can be consumed in many ways, either by spooning it or adding it to various dishes and recipes, sweet and savory. 100% peanut butter that does not contain unnecessary ingredients such as sugar, salt or palm oil.
Almond
Nutritional information per ½ cup:
• 275 calories
• 9.4 g carbohydrates
• 24.1 g fat
• 10.1 g protein
Almonds are the perfect snack that you can take with you anywhere. It's high in healthy fats and provides a healthy dose of protein . They are also a great product because they can be easily counted and can be stored for a long time.
Olive oil
Nutritional information per 1-1/2 teaspoon
• 180 calories
• 0 g carbohydrates
• 21 g fat
• 0 g protein
Olive oil is the easiest way to add fats to your diet . You can cook almost any dish with it, add it to salads or add a little to a protein drink or smoothie.
Pshenka
Millet porridge is considered a product with high index values. It can reach 70, which depends on the degree of density. The thicker the porridge, the higher its sugar content. However, individual beneficial properties make it no less popular:
- prevention of cardiovascular diseases;
- acceleration of the removal of toxic substances from the body;
- positive effect on digestive processes;
- reduction of cholesterol levels in the blood;
- acceleration of lipid metabolism, thereby reducing fat deposition;
- normalization of blood pressure;
- restoration of liver functions.
Wheat cereals
Wheat cereals have indicators ranging from 40 to 65 points. There are several varieties of wheat-based cereals that are popular among patients with diabetes and are famous for their valuable ingredients:
- Arnautka,
- bulgur,
- spelt,
- couscous.
Wheat porridge is considered a high-calorie product, but it has the properties to help reduce glucose levels, stimulate the gastrointestinal tract, and also activate regenerative processes on the mucous membranes.
Arnautka
This is a cereal made from ground spring wheat. Its composition is rich in vitamins, amino acids, and microelements, which help strengthen the immune system, restore the health of the heart and blood vessels, and improve the activity of the central nervous system. In addition, cereals have the properties of accelerating the regeneration processes of the skin and its derivatives, which is important for complications of diabetes.
Bulgur
A type of cereal obtained by steaming wheat grains. Next, they are dried in the sun, peeled and crushed. This processing gives the future dish a unique taste. Its index is 45.
Bulgur can also be used whole. These are brown grains with an outer shell. It is this porridge that has the greatest amount of nutrients and beneficial substances. Bulgur is rich:
- tocopherol;
- B vitamins;
- vitamin K;
- microelements;
- carotene;
- unsaturated fatty acids;
- ash substances;
- fiber.
Dishes based on bulgur - table decoration
Regular consumption of cereals restores the condition of the nervous system, regulates metabolic processes, and has a positive effect on intestinal function.
Spelled
It is a special type of wheat with a GI of 40, which differs in both shape and size from all known varieties. The spelled grain is quite large and is protected on the outside by a hard film that is not eaten. Thanks to this, the cereal is protected from all kinds of negative influences, including radioactive radiation.
Spelled grains are superior to wheat in terms of the value of their chemical composition. They help strengthen the body, normalize blood glucose levels, improve the functioning of the endocrine system, heart, blood vessels, and central nervous system.
Couscous
One of the types of wheat cereal with a GI of 65. Its composition is valuable with a large amount of copper, necessary for the normal functioning of the musculoskeletal system, the prevention of osteoporosis, as well as a significant amount of vitamin B5, which normalizes the functioning of the nervous system.
The need for an individual approach to calculations
Although the exact ranges for carbohydrate norms are given above, it is necessary to understand that the optimal amount of carbohydrates for each individual person is individual and is determined at a minimum by: age, gender, body composition, level of physical activity, internal metabolic rate and, obviously, may vary significantly from person to person.
If you think what we do is important, support our project!
YES!
Athletes, especially those with high muscle mass, need more carbohydrates even at rest.
In sports, carbohydrates are the main source of energy. If they are not consumed enough, it is impossible to gain muscle mass in bodybuilding or ensure speed in running.
Moreover, muscles can even begin to break down if there is a lack of carbohydrates (=energy) in order to provide energy needs through the amino acids that make up the muscle fibers. This is the so-called “muscle catabolism”.
Taking into account the above, athletes should “limit” the amount of carbohydrates very carefully. This is why the standard ketogenic diet is NOT recommended for athletes to cut their bodies.
Internal metabolic rate is another important parameter. It is individual and is the main consumer of calories in our body: about 70% (!) of daily calories are used to ensure the functioning of internal organs and systems only.
This is a lot and explains why exercise is NOT very effective in losing weight.
The indicated value is an average and can vary quite widely from person to person.
People with fast metabolisms are called ectomorphs in body type parlance. Everyone, without exception, has met them in life: they eat a lot, but remain thin. For them, the issue of losing weight is most often irrelevant, as is the question of the need to limit carbohydrates.
The opposite body type to this is called an endomorph: the metabolic rate is low, and fat mass is gained very easily. Endomorphs need to be very careful with carbohydrates .
What's all this for?
Moreover, for people with a high metabolic rate or a high level of physical activity, more calories are required during the day, and they are provided primarily by carbohydrates.
And vice versa: for physically inactive people and those who have a low metabolic rate, carbohydrate standards for weight loss can be further reduced.
The amount of carbohydrates for weight loss is individual and determined by numerous factors, among which the level of physical activity and the rate of internal metabolism are of paramount importance.
We recommend : Cholesterol in chicken eggs: how many eggs can an adult eat per day?
Corn porridge
This type of cereal is also a storehouse of vitamins, amino acids and minerals, but it must be handled with extreme caution, since the GI of the product can reach up to 70. It is advisable not to use milk and sugar when preparing corn porridge. It is enough to boil the cereal in water and add a small amount of fructose, stevia or maple syrup as a sweetener.
Corn grits are famous for their high content of the following substances:
- magnesium – in combination with B-series vitamins, improves cell sensitivity to insulin, has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the heart and blood vessels;
- iron – prevents the development of anemia, improves the process of saturating cells with oxygen;
- zinc – promotes normal functioning of the pancreas, strengthens immune processes;
- B vitamins – restore the functioning of the nervous system, their use is a preventive measure in the development of diabetes complications;
- beta-carotene – normalizes the functioning of the visual analyzer, prevents the appearance of retinopathy.
Corn grits should be used exclusively in boiled form. Corn flakes, popcorn or sticks have much higher GI values.
Pearl barley
Barley porridge is a leader in the ranking of healthy and safe products. The index is 22-30 if it is cooked in water without adding oil. The porridge contains a large amount of protein and fiber, iron, calcium, and phosphorus. These elements should be present in the daily diet of both healthy and sick people.
Barley also contains substances that are involved in the processes of lowering blood glucose levels. It is used for preparing crumbly and viscous second courses, soups.
Pearl barley is the “queen” of cereals
Other visual keto guides
To learn more about specific topics—like what fruits or nuts you can eat on a ketogenic diet—check out our handy visual guides.
Vegetables
Nuts
Alcohol
Beverages
Fruits and berries
Snacks and appetizers
Oils and sauces
Barley grits
The product belongs to the group of substances with average index values. Raw cereal – 35, barley porridge – 50. Grains that have not been subjected to grinding and crushing retain the largest amount of vitamins and minerals, and the human body needs them daily. The cell contains:
- calcium;
- phosphorus;
- manganese;
- copper;
- iodine;
- unsaturated fatty acids;
- tocopherol;
- beta-carotene;
- B vitamins.
Thanks to its rich composition, cereal helps eliminate excess cholesterol, lowers blood sugar levels, strengthens the immune system, and normalizes the functioning of the central nervous system. Cereals contain a large amount of fiber, which ensures saturation of the body for a long time.
Vitamins and minerals contained in cereals
Cereals
- An excellent source of antioxidants, vitamins and minerals. Thus, we have already written that in most countries, pediatricians prefer cereals as the first complementary food product - and all due to the iron content in many of them. However, unfortunately, the digestibility of the latter will be significantly less compared to the form that is concentrated in food of animal origin. However, given the increasing needs of the growing body for this element, which breast milk is not able to cover (starting from 4-6 months of life), the addition of cereals makes a certain contribution in the context of preventing anemia in children.
Let us emphasize right away
: When we talk about vitamins, antioxidants and minerals, we primarily mean their content in unprocessed cereals.
While refined cereals contain only the core (endosperm), whole grain products are a whole mixture of biologically active compounds: micronutrients, dietary fiber, starch and lipids.
Compare for yourself - as an example, we gave the nutritional composition of whole and refined wheat flour (per 100g of product):
| Nutritional composition | Whole wheat flour | Purified |
| Carbohydrates, g | 62 | 71 |
| Protein, g | 10 | 12.6 |
| Fats, g | 2 | 1.1 |
| Dietary fiber, g | 11 | 4 |
| Vitamin B1, mg | 0.4 | 0.07 |
| Vitamin B2, mg | 0.15 | 0.04 |
| Vitamin B3, mg | 5.7 | 1 |
| Vitamin E, mg | 1.4 | 0.4 |
| Iron, mg | 4 | 0.8 |
| Zinc, mg | 2.9 | 0.64 |
| Magnesium, mg | 124 | 20 |
| Potassium, mg | 250 | 156 |
| Phosphorus, mg | 370 | 103 |
So, it is obvious that whole grains are much more nutritious compared to refined grains. In addition, they contain dietary fiber - indigestible carbohydrates that are fermented in the lumen of the large intestine by resident microflora.
| Cereal name | Calcium per 100 g of product | Iron per 100 g of product | Phosphorus per 100 g of product | Magnesium per 100 g of product |
| Wheat groats | 40 mg | 3.4 mg | 379 mg | 122 mg |
| Couscous | 24 mg | 1.1 mg | 170 mg | 44 mg |
| Sorghum | 13 mg | 3.4 mg | 289 mg | 165 mg |
| Green buckwheat | 18 mg | 2.2 mg | 347 mg | 231 mg |
| Quinoa | 47 mg | 4.6 mg | 457 mg | 197 mg |
| Cereal name | Beta carotenoids | Vitamin B1 | Vitamin B3 | Vitamin B9 |
| Corn | 74 mcg | 0.7 mg | 4.3 mg | 149 mcg |
| Spelled | 5.0 mcg | 0.4 mcg | 6.8 mcg | 45 mcg |
| Pearl barley | 13 mcg | 0.2 mcg | 4.6 mcg | 23 mcg |
| Rye | 7.0 mcg | 0.3 mcg | 4.3 mcg | 38 mcg |
| Amaranth | 1.0 mcg | 0.1 mg | 0.9 mg | 82 mcg |
Oatmeal and muesli
Oat porridge is considered an indispensable product on the table. Its GI is in the average range, which makes oatmeal not only healthy, but also safe:
- raw flakes – 40;
- on the water – 40;
- with milk – 60;
- with milk and a spoonful of sugar – 65.
Oatmeal is a dish allowed for the daily diet of both sick and healthy people.
You should not give preference to instant porridge, just like muesli (GI is 80). Because, in addition to flakes, the composition may include sugar, seeds, and dried fruits. There is also a glazed product that you should avoid.
Why does the body need carbohydrates and the consequences of their lack?
Even when managing weight, carbohydrates are not the enemy.
They are an integral part of the diet and the main source of energy. 1 g of carbohydrates, like 1 g of proteins, contains 4 kcal, but the thermal effect is much lower - within 5-15% of the kcal is spent by the body on their processing.
Thus, the main function of carbohydrates
- providing the body with energy. But she is not the only one: they are also necessary for the normal functioning of the heart, liver, muscles and central nervous system. They are an important component in the regulation of protein and fat metabolism.
Although carbohydrates as sources of energy can be replaced by proteins and fats, the absence of carbohydrates in food can adversely affect health.
Except for states where it is necessary. For example, diabetes, insulin resistance, polycystic disease. Then a low-carb eating plan can make you feel better, but most women need at least 70-90 grams of carbohydrates per day, especially during times of increased stress.
And sometimes a little higher if you are breastfeeding, pregnant, or actively exercising.
Body "signals"
, which may mean you should reconsider the amount of carbohydrates in your diet:
- regular feeling of fatigue;
- irregular cycle;
- sleep poorly, often wake up at night;
- symptoms of hypothyroidism;
- do not recover well after training;
- weak immunity;
- low body temperature.
A low-carb diet carries risks for women's health, fertility, adrenal and thyroid health.
On the one hand, a low-carb diet (less than 20%) can boost energy, help with weight loss, support immunity and hormonal adjustments during menopause, but for a young, active woman, especially during times of high emotional or physical stress, a meal plan is usually appropriate with a medium amount of carbohydrates with a low glycemic index.
Therefore our task
— add a safe amount of carbohydrates and at the same time support the body’s hormonal system.
Expert advice
Cereals contain more than 70% carbohydrates, which tend to break down into glucose. The faster the breakdown process occurs, the higher the blood sugar level rises. There are ways to lower the GI of the prepared product so that the breakdown process slows down, and also make it safe for diabetics:
- adding a spoon of vegetable fat;
- use coarse grains or those that cannot be ground;
- do not use products with an index above average in the daily diet;
- use a double boiler for cooking;
- refuse added sugar, use substitutes and natural sweeteners;
- Combine porridge with proteins and a small amount of fat.
Following the advice of experts will allow you to eat not only healthy foods, receiving all the necessary substances, but also make this process safe for health.
List of foods with complex carbohydrates
Complex saccharides are more beneficial. On the contrary, their quantity should be increased in your diet. But to do this, you need to know exactly which foods contain such carbohydrates.
| Name | Glycemic index |
| Corn | 35 |
| Unprocessed rice | 35 |
| Milk products | 30 |
| Lentils, beans | 30 |
| Fresh fruits | 30 |
| Fresh green beans | 30 |
| Chocolate black | 25 |
| Berries | 20 |
More: List of foods that contain healthy carbohydrates