The energy value of foods, or calorie content, refers to the amount of energy (kcal and kJ) that is produced by the human body when digesting foods eaten.
Nutritional value is measured in calories or joules. Ideal values are derived in the laboratory using a special device - a calorimeter. The measurement process is as follows: food is placed in the device and burned, measuring the amount of heat released. It has been scientifically established that one calorie is enough to raise the temperature of a gram of water by a degree. It has now become common practice to measure calories in kilocalories. That is, such a unit is spent on heating not a gram, but a kilogram of water.
Nature has it in such a way that the human body is not able to absorb all nutrients. Thus, proteins are absorbed only by 92%, carbohydrates by 98%, and fats by 95%.
Who needs to count calories and why?
The term “calories” was coined in 1918 by American nutritionist Lulu Hunt Peters. Since then, the developed system for calculating the nutritional properties of foods has not lost popularity.
From food a person receives the energy necessary for the functioning of the body. Each product consumed has its own calorie content. Counting is important for meeting your daily energy intake.
If the calorie content of the daily menu is too low, too little energy comes from food, loss of strength and apathy occur, dizziness and fainting are possible. The body experiences stress and often begins to store nutrients for future use, creating fat reserves. A clear excess of calories leads to the conversion of unspent energy into fats and contributes to the appearance of excess weight.
With the correct ratio of BJU and systematic training, body weight will increase due to muscle tissue. In this case, the extra calories will contribute to muscle gain.
It is recommended to count calories:
- Those who want to lose weight : a lack of calories leads to the fact that body weight decreases from the waste of fat reserves produced by the body to cover the energy deficit;
- Those seeking to build muscle : an excess of calories guarantees an increase in body weight; you can achieve growth not in the fat layer, but in muscles, by consuming a sufficient amount of protein and regularly training in the gym;
- For adherents of a healthy lifestyle , determined to maintain their existing physical shape: a balance of calories received and spent is necessary to maintain normal weight, and the optimal ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates will make nutrition complete, ensuring the healthy functioning of the body.
Properties of human fat
There is an opinion that the number of fat cells in the body is determined by a hereditary factor, such as eye or hair color. However, there is other information that refutes this opinion, and it lies in the fact that the number of fat cells in a child is determined by how the mother ate. It also became known that in obesity, fat cells can divide on their own, and then only surgical intervention can help overcome them.
Fat in the body is divided into several types: brown, subcutaneous and internal . The brown type of fat is needed so that the body can maintain the correct temperature. There is enough such fat in the body of infants - it protects them from hypothermia. Subcutaneous fat, as its name implies, is located directly under the skin and is the familiar cellulite. This is exactly the type of fat that we constantly struggle with. As for internal or visceral fat, it is deposited on the surface of human organs and inside them. Fat can grow into muscle tissue and even penetrate into the heart.
Together with the blood, excess fat circulates through the vessels, clogs them, and is deposited on the wall. It becomes difficult for blood to penetrate the body's cells, blood pressure rises, and possible malaise. Cholesterol plaques cause stroke and heart attack. Therefore, it is important to get rid of not only the fat that is visible to the naked eye, but also to free the internal organs from it. Despite the fact that the effects of different types of fat are different, their calorie content remains the same.
Algorithm for calculating KBJU for weight maintenance
To organize proper nutrition and maintain your existing weight, if you are completely satisfied with it, it is important to calculate the daily calorie intake and the percentage of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
Calorie content
will help determine your daily calorie intake .
Step 1. Calculate your basal metabolic rate.
Basic metabolism is the number of calories that ensures the normal functioning of the body in a state of absolute rest.
For men: Basal metabolic rate = 88.36 + (13.4 x weight, kg) + (4.8 x height, cm) - (5.7 x age, years).
For women: Basal metabolic rate = 447.6 + (9.2 x weight, kg) + (3.1 x height, cm) - (4.3 x age, years).
Step 2. Take into account the activity coefficient.
- 1.2 - minimal (no activity at all, sedentary work, sedentary lifestyle);
- 1.375 – low (light physical activity 1-3 times a week);
- 1.55 - average (workouts, active walks, physical work 4-5 times a week);
- 1.725 – high (training 6-7 days a week);
- 1.9 - very high (several training sessions a day, the usual regimen for athletes before competitions).
Step 3. Multiply the first digit by the desired coefficient.
Having carried out all the simple manipulations, we will get the result to maintain the existing weight.
Eg:
- A 30 year old man with a height of 172 cm and a weight of 80 kg, exercises 4 times a week, should consume daily (88.36 + (13.4 x 80) + (4.8 x 172) - (5.7 x 30)) x 1.55 = 2814 kcal.
- A 32-year-old woman with a height of 158 and a weight of 50 kg, attends 3 light workouts per week, should consume daily: (447.6 + (9.2 x 50) + (3.1 x 158) - (4.3 x 32) ) x 1.375 = 1732 kcal.
Find out how to reduce the caloric content of your usual diet here.
Calculation of BZHU
You can eat only sandwiches, stay within the calorie limit and lose excess weight. But you will have to forget about body quality and muscle tone. And health will deteriorate in the foreseeable future.
To get the figure of your dreams and avoid health problems, a person needs a balanced diet:
- Proteins act as building materials for all cells, and therefore for organs and muscles;
- Complex carbohydrates supply the body with energy and regulate the gastrointestinal tract;
- Fats regulate hormonal levels and promote the absorption of vitamins and microelements.
Standard BZHU ratio scheme for maintaining current weight (as a percentage): 30 / 20 / 50.
- 1 g protein = 4 kcal;
- 1 g fat = 9 kcal;
- 1 g carbohydrates = 4 kcal.
For example, with a norm of 2814 kcal per day:
- protein (30%) = 844 kcal / 4 = 211 g;
- fat (20%) = 563 kcal / 9 = 62.5 g;
- carbohydrates (50%) = 1407 kcal / 4 = 352 g.
At a norm of 1732 kcal:
- protein (30%) = 520 kcal / 4 = 130 g;
- fat (20%) = 346 kcal / 9 = 38 g;
- carbohydrates (50%) = 866 kcal / 4 = 216.5 g.
What are amino acids?
Proteins are made up of smaller molecules (amino acids) linked together. The structure of the protein resembles beads strung on a chain. The activated protein takes on a slightly different shape - a three-dimensional structure (the chain twists and wraps around itself, forming something like a ball). Like carbohydrates, amino acids are made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. But unlike them, they also contain nitrogen.
It is important that squirrels come in different sizes. Some amino acid chains are quite short and consist of 50 elements, but most contain 200-400. Individual proteins can combine to form so-called protein complexes.
The largest protein complexes are bones, skin, nails, hair, teeth. They are formed from collagen, elastin and keratin. Collagen, for example, consists of 3 thousand amino acids twisted into a long cylindrical chain. This chain bonds with other collagen chains and creates thicker and stronger cylinders called fibrils. Fibrils can combine from 6 to 20 collagen chains, which means they contain tens of thousands of amino acids. And this is the structure of only one individual protein.
A single amino acid resembles a simple carbohydrate - before absorption, the body breaks down the protein structure into an amino acid according to the principle of digesting carbohydrates. And only after that it digests one small block at a time.
Where to look for amino acids?
A healthy person needs approximately 40-65 grams of various amino acids per day. If the body does not receive the required amount of protein, it begins to draw reserves from its own muscles, destroying them. Insufficient intake of amino acids can cause growth retardation, poor muscle development, thin and brittle hair, skin diseases, a weakened immune system and other troubles.
The source of amino acids is proteins from food of plant and animal origin. The most protein-rich foods: nuts, legumes, fish, meat and dairy products. In processed foods, the substance is sometimes presented in the form of a peptide - a hydrolyzed protein (consists of amino chains formed from 2-200 amino acids). Such products are digested faster and easier to absorb.
Essential amino acids
There are 20 types of amino acids and the body needs all of them, since each is involved in the creation of protein at a certain level. The body can synthesize half of them on its own. However, 9 of them come from food alone. They are called basic, or essential, amino acids. These include leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, tryptophan and others.
The correct ratio of amino acids to each other is important for the body. Animal foods, for example, contain amino acids in proportions similar to those found in the human body. Proteins from plant foods have a slightly different structure.
Many nutritionists are concerned that vegetarians, by giving up meat, do not get all the necessary proteins in full measure. Other researchers reject this theory. They hypothesized that since different plant foods contain different essential amino acids, eating a variety of foods (whole grains, legumes, and other vegetables) can provide all the vital nutrients. In addition, some plant foods, such as soy, contain proteins similar in composition to those found in meat.
How to count KBJU for weight loss or weight gain
To lose weight, a calorie deficit is created: the daily norm of KBZHU is reduced by 10-20%, depending on the amount of extra pounds.
It is dangerous to create a deficit above 20% even with a lot of excess weight; this is fraught with serious health problems.
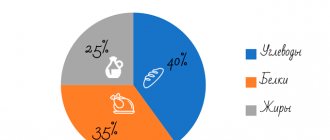
One of the BJU percentage schemes recommended by experts for weight loss is: 40 / 35 / 25.
- Let's consider the norm of KBZHU using the example of a woman who wants to lose weight, who is still 32 years old, height 158 cm, but her weight is already 65 kg, she trains 3 times a week:
Using the above formula, we calculate the daily calorie intake: 1922 kcal.
Subtract 10-20%.
To lose weight without harm to health, our heroine should maintain calorie content in the range of 1538-1730 kcal.
Of them:
- protein (40%) = 615-692 kcal = 154-173 g;
- fat (35%) = 538-605 kcal = 59-67 g;
- carbohydrates (25%) = 385-433 kcal = 96-108 g.
To gain muscle mass, the daily calorie intake needs to be increased by 10-20%.
The percentage of BJU recommended by experts for weight loss: 30 / 25 / 45.
- The KBZH norm for a 30-year-old man with a height of 172 cm and a weight of 60 kg, who goes to the gym 4 times a week in order to build muscle:
Daily calorie intake: 2398 kcal.
Add 10-20%.
To achieve the goal, a man must consume from 2638 to 2878 kcal every day.
Of them:
- protein (30%) = 791-863 kcal = 198-215 g;
- fat (25%) = 660-720 kcal = 73-80 g;
- carbohydrates (45%) = 1187-1295 kcal = 297-324 g.
Don’t forget, recalculation of the KBZHU norm must be done every ±5 kg. Then the transition to a new nutritional system will be as smooth and painless as possible for the body.
How to count KBJU dishes
Calculating the calorie content of a finished dish at a certain level of dexterity is easy and accessible to everyone.
Let's look at the calculation of KBZHU using a simple example: let's cook dietary crumbly buckwheat porridge.
The calorie content of 100 g of buckwheat is 340 kcal, BZHU: 13 / 3.5 / 64.
From 200 g of cereal (calorie content 680 kcal) you get 400 g of ready-made porridge (same calorie content 680 kcal), BZHU: 26 / 7 / 128.
Formula for calculating calories in one serving of a prepared dish:
BZHU is considered similarly.
For example: By eating a 150-gram portion of delicious buckwheat at a time without oil and other additives, you will get
680 kcal / 400 g x 150 g = 250 kcal, BZHU 9.75 / 2.63 / 48.
- To calculate the calorie content of a complex dish made from a large number of ingredients, you need to weigh all the ingredients before cooking, determine their energy capacity and add up the results.
The calorie content of a vegetable salad is calculated as follows:
tomatoes 300 g, 54 kcal, BJU: 2.64 / 0.6 / 8.07;
cucumbers 300 g, 45 kcal, BJU: 2.4 / 0.3 / 8.4;
lettuce 100 g, 15 kcal, BJU: 1.36 / 0.15 / 2.79;
radish 50 g, 10 kcal, BJU: 0.6 / 0.05 / 1.7;
olive oil 15 g, 135 kcal, BJU: 0 / 14.97 / 0.
Total weight 765 g, total calorie content 259 kcal, BJU: 7 / 16.07 / 20.96.
The calorie content of a 200-gram serving will be: 259 kcal / 765 g x 200 g = 68 kcal
Proteins: 7 g / 765 g x 200 g = 1.83 g,
Fat: 16.07 g / 765 g x 200 g = 4.2 g,
Carbohydrates: 20.96 g / 765 g x 200 g = 5.5 g.
It is important to note that when calculating, only the weight of the finished product is used, and not the total weight of all components.
As you can see, counting calories is not that difficult. The main thing is to start. Over time, you'll get used to weighing ingredients before cooking and portions before eating, and always keeping a calculator handy.
What is the glycemic index
How quickly each type of sugar increases blood glucose is indicated by the glycemic index.
Its range is a scale from 1 (the slowest effect on the body) to 100 (the fastest saturation, this indicator is equivalent to the speed of action of pure glucose). Glycemic index table for some foods
| Category | Product | GI |
| Legumes | Red lentils | 33 |
| Soybeans | 14 | |
| Bread | Made from coarse rye flour | 49 |
| White | 69 | |
| Wholegrain | 72 | |
| Flakes | All bran | 54 |
| Corn | 83 | |
| Oatmeal | 53 | |
| Rice | 90 | |
| Wheat | 70 | |
| Dairy | Milk, yogurt, ice cream | 34-38 |
| Fruits | Apple | 38 |
| Banana | 61 | |
| Orange | 49 | |
| Strawberry | 32 | |
| Cereals | Barley | 22 |
| Brown rice | 66 | |
| White rice | 72 | |
| Pasta | 38 | |
| Potato | 86 | |
| Corn chips | 72 | |
| Oat cookies | 57 | |
| Potato chips | 56 | |
| Sugar | Fructose | 22 |
| Glucose | 100 | |
| Honey | 91 | |
| Refined sugar | 64 |
Carbohydrates with a high glycemic index raise blood glucose quite quickly. As a result, the amount of insulin in the blood increases, causing hypoglycemia and hunger. All this leads to the consumption of excess calories, which means excess weight.
Carbohydrates with a low glycemic index help to slowly increase plasma glucose, which eliminates sudden spikes in insulin production. Eating foods with a lower GI reduces the risk of developing obesity, diabetes or its complications.
Tips for those who want to calculate the daily calorie content of their diet as accurately as possible
- Keep a food diary where you write down all your meals, including snacks. Don't rely on your excellent memory, it often fails. All calories consumed must be recorded and accounted for. Only then will you get the most accurate result at the end of the day.
- Buy a kitchen scale; do not determine the weight of food by eye. Small errors result in a noticeable difference in the final calorie content of the daily diet.
- Weigh food before cooking.
- Consider the calorie content of butter, sauce, sugar and other auxiliary products in the dish.
- Place on the scale only that part of the product that will be directly consumed as food (boneless meat, pulp of fruits and vegetables without peels and seeds, eggs without shells).
- Don’t look for the calorie content of a multi-ingredient dish on the Internet and mobile apps, calculate it yourself. Before cooking, weigh the ingredients, calculate their energy value and add up the results. The final data will be more accurate.
- Try to avoid eating at food establishments. The calorie content of the dishes on the menu is very approximate. Only you can calculate the KBZHU for yourself as accurately as possible.
Energy sources
Sources of simple carbohydrates:
- fruits and berries;
- vegetables;
- milk products;
- sweeteners (sugar, honey, syrup);
- candies;
- soft drinks.
Source of complex carbohydrates:
- bakery products;
- cereals;
- pasta;
- rice;
- beans;
- peas;
- starchy vegetables;
- green pea;
- corn.
Many of the foods mentioned are also sources of fiber. Complex carbohydrates are found in most vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains.
Where to look for KBJU products
In order to correctly calculate the calorie content of your diet, it is important to know where you can find information about the calories and nutritional value of the foods you consume.
- Please read the product packaging carefully. The manufacturer always indicates accurate information on it.
- If the product does not have packaging, data on calorie content and nutrient content can be easily found on the Internet: there are a great many tables. By entering a query about the product you are interested in in the search bar, you will receive comprehensive information. For maximum reliability, compare results from several sources.
- Numerous mobile applications used for calorie counting already contain a wide list of products with calculated calorie values. Enjoy it for your health!
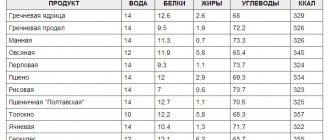
Example of a calorie table
Counting calories is a matter of habit. The troublesome and tedious process becomes easy and understandable over time. Start counting with simple products, gradually add complex recipes with many ingredients. One day you will bring your actions to automaticity. You no longer have to go on diets, giving up delicious food. You will receive aesthetic pleasure when looking at yourself in the mirror. And the body will thank you for your care with the smooth functioning of all vital organs.
Lowest calorie vegetables
The minimum amount of calories is contained in Chinese cabbage - 12 calories / 100 g. In addition, all vitamins are perfectly preserved in this vegetable throughout the winter. Lysine – perfectly cleanses the blood and removes cholesterol. In general, losing weight will benefit your health.
In second place are cucumbers, 100 g of whose fruit contains 14 kcal. This vegetable is 95% water, rich in folic acid, potassium, iodine and various vitamins. Eating cucumbers has a positive effect on the functioning of the nervous system, thyroid gland and gastrointestinal tract.
The following vegetables also contain minimal calories:
- radishes – 19 kcal;
- tomatoes – 23 kcal;
- zucchini – 27 kcal;
- broccoli – 33 kcal;
- carrots – 35.
The calorie table contains a complete list of all the vegetables that you can include in your diet menu.