Back in 2008, when I first bought sports nutrition to prepare for future bodybuilding competitions, then I did not yet know that I would play American football and coach a team, I remembered one phrase that my bodybuilding coach told me: “ They haven’t come up with anything better for anabolism than a chicken egg, so leave your beautiful packaging and lean on normal foods.” At that time I just bought several packages of gainer, a package of protein, a jar of bcaa amino acids and creatine. Of course, then I did not take his words seriously, but as the years passed, I realized that my coach was right! Chicken eggs for gaining muscle mass are what those athletes need who train as amateurs and do not have ambitions to conquer Olympus by becoming professional bodybuilders. It’s a pity that my ambitions are somewhat high...
Eggs are the best food for weight gain
If you love them, that's great, keep it up, continue reading the article further and find out how many eggs you need to eat per day for muscle growth. It will be easiest for you to increase the number of eggs you consume and most quickly achieve the desired result. If you're one of those people who doesn't like eggs or is too lazy to cook them and instead prefers a delicious whey protein shake, no problem. After reading this article, I am sure that eggs will be the first thought in your mind when you wake up in the morning.
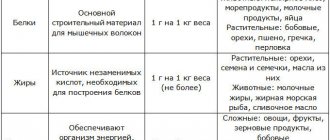
The egg is one of the most complete, versatile and affordable foods for gaining muscle mass. It plays an important role in ensuring a healthy diet for everyone and especially for bodybuilders. We all know the importance of protein in the muscle building process, without protein your muscles simply won't grow.
Protein is the next most abundant element after water and makes up the majority of our body. For bodybuilders, its importance is invaluable, since during heavy training, muscle fibers are severely damaged, and protein is needed to restore and strengthen them. A bodybuilder's diet should contain much more protein than the average person.
Before answering the question of how many eggs should you eat per day to gain muscle mass ?
you need to figure out the nutritional value of eggs
.
Because we need to understand how much protein we need per day for muscle growth, and how much we get from other foods.
To gain weight, you need 2-2.5 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight.
From this you can already calculate how many eggs you need to eat per day for muscle growth, but you need to know about their nutritional value.
How many eggs can you eat per day?
If a person is healthy, you can even eat eggs, but you need to do it correctly, focusing on the norms recommended by nutritionists for various categories of people. An adult can eat 1-2 eggs a day with breaks without harm to health (no more than 7-8 eggs per week). An athlete needs much more: great physical activity contributes to intensive digestion of food.
The rate of consumption of eggs by people involved in sports depends on the specifics of the diet, age, body weight, and type of activity. The average daily norm is 3-5 eggs. To build muscle mass, a bodybuilder needs to eat up to 10 pieces a day. During drying, you need to limit yourself to protein only - no more than 20 g (1 protein) daily.
Nutritional value of chicken white versus yolk: which to choose?
Which came first: the chicken or the egg? I think it's an egg, since this entire article is dedicated to them. Another controversial question on this topic is which is healthier, chicken white or yolk?
Eggs contain about 6 grams of high quality protein, so high that it is used as the standard by which other foods are measured. Eggs are a rich source of vitamins, including vitamins A, E and K, as well as a number of B vitamins such as B12 (energy), riboflavin and folic acid. Eggs also contain all eight essential amino acids needed for optimal muscle recovery and building valuable minerals such as calcium, zinc and iron.
Eggs are an excellent source of high quality, complete protein that contains few calories. One whole egg contains ~5.5 grams of protein and only ~68 calories. Eggs contain choline, which is very important for the human body as it is not produced in sufficient quantities. Without enough choline, there won't be another nutrient, folic acid.
Let's take a closer look at each of the components of the egg.
Protein
Egg whites are a low-calorie, low-fat food. They contain the bulk of protein at about 4 grams, 55 mg of sodium and only 17 calories. It also contains 1.3 micrograms of folic acid, 6.6 micrograms of selenium, 2.3 mg of calcium, 3.6 mg of magnesium, 4.9 mg of phosphorus and 53.8 mg of potassium.
Yolk
Why don't bodybuilders eat yolk? Egg yolks are the part of the egg that contains cholesterol, fat, and saturated fat. And it is believed that they are harmful and may not fit into the diet. However, many people forget that the yolk contains a ton of nutrients, fat-soluble vitamins, and essential fatty acids. One egg yolk contains about 55 calories, 4.5 grams of fat and 1.6 grams of saturated fat, 210 mg of cholesterol, 8 mg of sodium and 2.7 grams of protein.
The table below, compiled by the National Food Database, compares the nutritional content of egg whites and yolks and the percentage of total nutritional value of each.
Nutrients: Egg Yolk vs. Egg White
| Nutrient | Protein | Yolk | % total in protein | % total in yolk |
| Protein | 3.6 g | 2.7 g | 57% | 43% |
| Fat | 0.05 g | 4.5 g | 1% | 99% |
| Calcium | 2.3 mg | 21.9 mg | 9.5% | 90.5% |
| Magnesium | 3.6 mg | 0.85 mg | 80.8% | 19.2% |
| Iron | 0.03 mg | 0.4 mg | 6.2% | 93.8% |
| Phosphorus | 5 mg | 66.3 mg | 7% | 93% |
| Potassium | 53.8 mg | 18.5 mg | 74.4% | 25.6% |
| Sodium | 54.8 mg | 8.2 mg | 87% | 13% |
| Zinc | 0.01 mg | 0.4 mg | 0.2% | 99.8% |
| Copper | 0.008 mg | 0.013 mg | 38% | 62% |
| Manganese | 0.004 mg | 0.009 mg | 30.8% | 69.2% |
| Selenium | 6.6 mcg | 9.5 mcg | 41% | 59% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.01 mg | 0.03 mg | 3.2% | 96.8% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.145 mg | 0.09 mg | 61.7% | 48.3% |
| Vitamin PP | 0.035 mg | 0.004 mg | 89.7% | 9.3% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.63 mg | 0.51 mg | 11% | 89% |
| B6 | 0.002 mg | 0.059 mg | 3.3% | 96.7% |
| Folic acid | 1.3 mcg | 24.8 mcg | 5% | 95% |
| B12 | 0.03 mcg | 0.331 mcg | 8.3% | 91.7% |
| Vitamin A | 0 IU | 245 IU | 0% | 100% |
| Vitamin E | 0 mg | 0.684 mg | 0% | 100% |
| Vitamin D | 0 IU | 18.3 IU | 0% | 100% |
| Vitamin K | 0 IU | 0.119 IU | 0% | 100% |
| Dehydroepiandrosterone and AA | 0 | 94 mg | 0% | 100% |
| Carotenoid | 0 mcg | 21 mcg | 0% | 100% |
As you can see from the table, the egg yolk contains more nutrients, but in my opinion, a whole egg provides a more complete set of nutrients.
At different times, there were different recommendations from nutritionists regarding which part of the egg was best. A new study has found that moderate egg consumption does not have a negative impact on cholesterol levels. Regular consumption of two eggs per day does not affect a person's lipid metabolism and may even improve it.
Research shows that saturated fats raise cholesterol levels, and eggs contain dietary cholesterol. However, if you have coronary artery disease or other heart problems due to high cholesterol, the recommendations for you remain the same - limit your cholesterol intake.
What about the fat contained in eggs, you ask. I hasten to reassure you, the white does not contain fat, but the yolk of a chicken egg contains about 5 grams of fat, but only a small part of it is saturated (bad fat) - about 1.6 grams. Bodybuilders seeking to pump up their muscles should include fats in their diet, since energy costs during training are colossal, and these costs need to be replaced somehow.
Eggs contain cholesterol, but it is classified as dietary because it does not increase blood cholesterol levels. Eggs are easy to digest and digest, extremely healthy, and an integral part of a balanced diet for bodybuilders.
What foods contain glucosamine and chondroitin?
Before talking about what products to use to compensate for the deficiency of glucosamine and chondroitin, you need to have an idea of what joints are made of.
Any joint in the body is formed by at least two bones. The contact points are covered with articular cartilage, which, like a sponge, has a cellular structure. The space between the cartilages is filled with synovial fluid. It consists of a liquid part - blood plasma, and a protein part - chondroitin, glucosamine, hyaluronan.
When a person moves, cartilage acts like a sponge: fluid from the deep layers of cartilage penetrates between the fibers and lubricates the articular surface. When the load decreases, the fluid flows back into the cartilage. With this mechanism, friction between bones is reduced and their strength is maintained.
In order to restore the osteoarticular system, special preparations have been developed - chondroprotectors, which include glucosamine and chondroitin. In addition to medications, for proper joint function, you need to take vitamins and microelements and eat the “right” foods. Chondroitin and glucosamine are found in small quantities in almost all products, but they are bound in the structure of polymers, so their digestibility is low.
The main substances from which these substances are well absorbed are:
- cartilage;
- white meat;
- hard cheeses;
- beef;
- fish of the sturgeon and salmon families;
- dairy products;
- butter;
- vegetables;
- fruits;
- gelatin dishes: jellied meat, jelly;
- legumes;
- nuts and dried fruits;
- eggs;
- linseed oil.
How to eat eggs for muscle growth
Now let's return to the main topic - how much is needed
eating eggs a day
to gain muscle mass?
6 whites and 2 yolks in the morning will provide your body with
- 26.5 grams protein
- Not a single gram of carbohydrate
- 5.23 grams fat, 2.7 grams of which unsaturated fat (healthy fat)
- 153 calories
And if you correctly calculate how many calories (that is, proteins, carbohydrates and fats) you need, then you can determine how many eggs an athlete, that is, you, can eat per day. There is no magic number or way to cook eggs that will help you build muscle faster. The main thing is to maintain an energy balance, that is, consume more calories than you expend and maintain the proportion of macronutrients in the diet: 50% - carbohydrates, 40% - proteins, 10% - healthy fats.
And below you will find an example of increasing your caloric intake.
+ A bowl of oatmeal, 1 banana and 2 tablespoons of flaxseed oil
- 39 grams protein
- 78 grams carbohydrates
- 48 grams of fat, only 4 grams of which is saturated fat (bad fat)
- A total of 900 calories
= The above recipe three times a day is equal to
- 117 grams of protein
- 234 grams carbohydrates
- 144 grams fat, only 12 grams saturated
- Only 2700 calories
+ Protein bar between one of the three meals above
- 24 grams of protein
- 38 grams carbohydrates
- 5 grams fat, 3.5 grams saturated
- Total calories - 295
= Total:
- 141 grams protein
- 272 grams carbohydrates
- 149 grams fat, 15.5 of which saturated
- Total calories - 2995
+ Post-workout cocktail and you'll get
- 50 grams of protein
- 80 grams carbohydrates
- Total calories -520
+ Add 2 liters of milk per day here
- 66 grams of protein
- 94 grams carbohydrates
- 72 grams fat, 46 grams of which saturated
- 1280 calories
+ 300 gram of tuna with a glass of broccoli
- 64 grams protein
- 10 grams carbohydrates
- 6 grams fat, 1 gram saturated fat
- 350 calories
= At the end of the day you will receive
- 321 grams protein
- 431 grams carbohydrates
- 227 grams fat, saturated fat 62.2 grams
- Total calories per day 5051
- Who said building muscle mass is difficult?
Is it possible to drink raw eggs?
Many athletes prefer to include raw eggs in their meals. On the one hand, this is reasonable: thermally untreated eggs are digested more slowly, which means more calories are burned, and moreover, raw eggs retain all the nutrients in their entirety. However, it is recommended to drink raw eggs only if you are confident in their quality and manufacturer. Otherwise, this may result in salmonellosis. In addition, boiled protein is completely absorbed, while raw protein is only half absorbed.
Healthy foods
It is better to prevent a disease than to treat it. By consuming healthy foods, we give the body all the necessary vitamins and microelements, thanks to which the body is restored at the cellular level. To prevent diseases of the musculoskeletal system, you first need to adjust your diet by consuming foods for joints.
What products are needed for joints and cartilage?
- red fish;
- greenery;
- animal cartilage;
- white meat;
- milk;
- hard cheeses;
- yogurt;
- low-fat kefir;
- gelatin;
- dried fruits: prunes, dried apricots, dates, raisins;
- eggs;
- cereals;
- mushrooms;
- corn.
Red fish contains a lot of phosphorus, calcium, and healthy fats, which improve the composition of synovial fluid and strengthen cartilage. Greens are rich in magnesium, which strengthens nerves in joints. Animal fats are well absorbed because... they are similar to human cartilage.
White meat contains iron to nourish joints. Dairy products supply calcium for arthrosis of the joints. Gelatin contains a lot of chondroitin and glucosamine. Foods rich in selenium and sulfur are involved in protein synthesis, so selenium-containing foods should be on the table every day - legumes, eggs, cabbage, apples, onions, radishes.
Chondroitin and gelatin are destroyed during heat treatment, so it is recommended to cook at low temperatures, preferring boiling or stewing.
Let us note which products contain glucosamine and chondroitin:
- Plant glucosamine is obtained from corn.
- Animal glucosamine is produced from the shell of crustaceans.
- Chondroitin of animal origin is extracted from the trachea of cattle and the cartilage of red fish: salmon, sturgeon.
Chondroitin and glucosamine obtained by such methods have high bioavailability and are used in the manufacture of chondroprotectors.
Why do the body need chondroitin and glucosamine?
Glucosamine is part of chondroitin, synovium, and is a building material for cartilage, as well as tendons, ligaments and muscles, providing strength and resistance to stretching.
Chondroitin is produced by cartilage tissue and is also a component of intra-articular fluid. Due to the fact that it retains water and stimulates the production of hyaluronic acid, the strength and elasticity of the joints is maintained.
Thus, chondroitin with glucosamine for joints is necessary for the normal functioning of the osteochondral system.
With a deficiency of glucosamine and chondroitin, the quality of the synovial fluid changes, which leads to a change in the function of the joint - friction occurs between the bones and subsequent wear.
Glucosamine and chondroitin are synthesized in small quantities in the body independently, but with age, as well as during heavy physical activity, injury and inflammation, their quantity decreases and the deficiency must be replenished from the outside. If treatment is started at the wrong time, irreversible consequences begin in the joints, which can lead to osteoarthritis.