Running has been popular since ancient times; even the first Olympic Games, held BC in Greece, included competitions only in this sport. And now it remains the most accessible and favorite type of physical activity among fans of a healthy lifestyle. But there is a category of athletes who stubbornly deny the benefits of running for themselves - bodybuilders. Every second athlete is sure that running and bodybuilding cannot be combined, and simultaneous practice of these two sports will only reduce the results of each of them. Let's try to dispel this misconception.
What is strength training?
To avoid any misunderstanding, you need to immediately define what strength training is. Strength training is training that aims to increase your one-repetition performance with a maximum weight load. An increase in strength indicators is inherent in certain sports: weightlifting, bodybuilding, powerlifting, etc.
Strength training is designed to sculpt a strong, beautiful body, and the body will only benefit if cardio elements are added to anaerobic exercises
Cardio load
Cardio exercises are cyclic exercises, the purpose of which is to develop endurance and train the heart muscle. This includes: running, cycling, swimming, skating, dancing.
Execution Features
Cardio is an aerobic workout that is fueled by fats and carbohydrates.
What indicators does it develop?
The functioning of the cardiovascular system improves, the capillary network develops, and tidal volume increases. In addition, joints are strengthened, stabilizer muscles are trained, and stress tolerance increases.
These effects are why running after a workout can be beneficial.
Will running interfere with weight gain? Why is it better to run after strength training?
It is preferable to do cardio training after strength exercises, because otherwise the body will get tired, and strength training will be covered with a copper basin.
Argument 1. As a result of cardio load, the muscles will be forced to use up glycogen, and therefore energy, which will be catastrophically lacking during strength training. There will be a release of cortisol, a hormone that extracts energy directly from muscle tissue, destroying it. The result of such strength training is a decrease in muscle mass.
Argument 2. Here is another argument in favor of “after”: since the muscles after strength training exhaust their entire glycogen supply, the body begins to pump out fat reserves from the very beginning of the cardio session. That is, running after strength training also has a significant fat-burning effect. Also, the advantages of jogging “after” include the ability to consolidate the results of weight exercises.
For good health
Body-building
Competent work with weights in the gym has a beneficial effect on the human body. Especially men's. Strong muscles create excellent protection for internal organs. A trained back reduces the likelihood of tearing it.
There are a number of studies that claim that weight training improves heart function, normalizes blood pressure, helps cure diabetes and prevents brittle bones.
In addition, mental health also improves. This happens both due to chemical reactions in the body during training and due to improved attitude towards oneself. After all, a beautiful body gives confidence to any person
advertising is not displayed
And this is very important for mental health.
But bodybuilding also has its downsides.
Firstly, bodybuilding involves lifting heavy weights, which means that there is a huge load on the joints. If you approach training too fanatically and do not follow the tasks prescribed by the trainer, you can simply injure your joints. Therefore, you need to train with a working weight, and not try to beat your own records every time.
Injuries in bodybuilding are also not uncommon. Most often they are associated with improper execution technique, or mechanical injuries caused by carelessness.
Varicose veins are another side effect. Most often it occurs in athletes who lift too much weight.
In general, if you approach training wisely, then bodybuilding has much more advantages than disadvantages.
Run
The health benefits of running are legendary.
First of all, running trains the heart muscle. This is perhaps the best sport in the world for training the heart. Let's face it, bodybuilding is not even close in this regard.
Improving lung function is also one of the benefits of running.
Long-distance running increases your overall endurance, allowing you to have more energy for household chores and work.
During running, the so-called happiness hormone – dopamine – is released. Therefore, running also helps to get rid of depression.
Training your leg and core muscles while running has a positive effect on human health.
In addition, running strengthens the immune system. It has been proven that a person who regularly runs is much less likely to suffer from colds and viral diseases. Although this can be applied to any type of physical activity, including bodybuilding.
But there are also disadvantages
They are primarily associated with knee problems in avid runners. Unfortunately, it is this joint that suffers most often when running.
Runners usually don't train their upper body because they don't need it. And running itself mainly trains only the muscles of the legs, back and pelvis. Therefore, there is an imbalance in the figure.
But this only applies to long-distance runners. Sprinters, on the contrary, look more like bodybuilders. Since the work of the arms and shoulder girdle is no less important to them than the work of the legs.
There are fewer disadvantages to running, however, if you train properly, there will be none in either running or bodybuilding. This is proven by numerous examples of veterans of one sport or another, when at the age of 60, 70 and even 80 they show decent results in body beauty or running distances.
What are the disadvantages of running after strength training?
The disadvantages include the fact that jogging can significantly slow down the growth of muscle mass if you are an ectomorph or a transitional type between ectomorph and mesomorph (that is, thin build with a relatively small percentage of subcutaneous fat).
In addition, there is still a possibility of a negative impact on the recovery process if the intensity is incorrectly selected.
Incorrectly selected load during the jogging phase can slow down the process of restoring the body's resources due to exaggerated running intensity
Here we naturally move on to the next question.
When using the “strength training - jogging” combination, you need to be extremely careful. An incorrectly selected load during the jogging phase can significantly slow down the body’s recovery resources due to the exaggerated intensity of running, or may not give the desired result due to insufficient load.
Afterword
So, today we looked at the rather interesting topic of running and bodybuilding. In conclusion, I would like to say that running or fiddling is a personal matter for everyone, there is no categorical “obligation” here, so if you like it, go for it, if not, it’s okay, it’s just not your thing. The main thing here is to start and take the first step, then, once you gain acceleration, you will no longer be stopped, believe me.
That's all for now, all the best and have great runs!
PS. As always, don’t forget about the form below, it’s also comments, write down questions, thoughts and other miscellaneous things.
The article was taken from the site bodymaster.ru.
Women's fitness
Interval running for fat burning
You can try to realize the opportunity to spur fat-burning processes in the body, and through this speed up metabolism, with the help of interval running. Interval running is an alternation of intense and calm jogging paces. This method is definitely a shake-up for the body, which will result in even greater weight loss. But the risk of overtraining with this approach increases significantly, since the body may not recover until the next workout if the load is calculated incorrectly and turns out to be excessive.
Read on: Interval training on the treadmill
Where to begin?
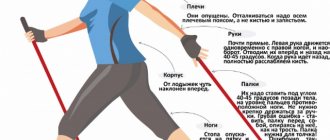
- Before the race, it is better to warm up - run for 5-10 minutes at a moderate pace, stretch and warm up your joints.
- It is better to start training with ultra-short distances of 20-30 meters. Only as the body adapts can this distance be increased up to 100 meters.
- For jogging, choose a perfectly smooth surface . Any unevenness on the path can result in a fall and serious injury.
- Running shoes and loose clothing are the key to a successful sprint. Sprint shoes should have spikes in the front, as sprinters run exclusively on their toes without their heels touching the ground. An important point is comfortable and strong lacing that will not let you down at a crucial moment.
Hormonal sphere
What happens to a person’s hormonal sphere during heavy (training) physical activity? Catabolic hormones are released into the blood. These are primarily thyroid hormones, adrenal hormones, glucagon (pancreatic hormone). All these hormones cause the breakdown of glycogen into glucose, proteins into amino acids, fats into fatty acids and glycerol. This “working” catabolism is designed to provide the body with as many energy substrates as possible to compensate for the energy deficit that occurs during the training process.
In addition to the above hormones, there is also a “release” of sex hormones and somatotropin (growth hormone) into the blood. They do not cause the breakdown of protein structures; on the contrary, the release of these hormones prevents excessive protein breakdown. However, the decomposition of glycogen to glucose increases, and, to an even greater extent, neutral fat from subcutaneous fat depots to fatty acids and glycerol. Fatty acids and glycerol, in turn, are included in energy metabolism.
After finishing the training, the picture is somewhat different. The content of thyroid hormones, adrenal glands, and glycogen in the blood decreases. The content of sex hormones and somatotropin remains almost unchanged, but the content of insulin in the blood increases sharply. Insulin, in combination with somatotropin and sex hormones, causes a significant increase in anabolism and inhibition of catabolism. Muscle tissue, liver, and heart muscle begin to accumulate protein structures, carbohydrates (glycogen) and, to some extent, fats. If the amount of growth hormone is large enough, then the release of insulin contributes mainly to protein synthesis. If the amount of somatotropin is not enough, then insulin enters the “fat pathway” and can lead to increased synthesis of fat molecules.
The greatest changes in hormonal levels are observed precisely during running loads, because It is in this case that the energy deficit is most pronounced. (Let's not forget that all hormonal changes are subordinated to one big goal - compensation for energy deficiency).
Interestingly, pronounced hormonal changes in response to significant physical activity occur only in the initial stages of training. Subsequently, as training develops, the body adapts to stress in such a way that it increases not the release of hormones, but the release of intracellular hormonal signal intermediaries, which increase the sensitivity of cells to hormones. In this way, great savings in energy resources are achieved. Instead of causing a “hormonal storm,” the body simply increases the sensitivity of cells to hormones already present in the blood. The training effect is the same, but energy consumption is significantly reduced. This allows the body to adapt to more and more physical activity even when hormonal changes have already exhausted all their possibilities.
The adrenal gland's response to repeated exercise is the most studied. The adrenal medulla (the adrenal medulla is the central part of the adrenal gland) produces adrenaline. In the adrenal cortex (peripheral part) there are glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid hormones. In response to physical activity, large amounts of adrenaline and glucocorticoid hormones are released into the blood. Adrenaline selectively increases the permeability of cell membranes to glucose as a fast fuel for cells, which dramatically increases endurance [A frightened person whose heart rate increases to two hundred beats per minute as a result of a sharp release of adrenaline and is more able to run significant distances at high speed. Some runners deliberately, using self-hypnosis techniques, induce a feeling of fear in themselves in order to show the best results at a distance during competitions.]. Glucocorticoid hormones cause the breakdown of glycogen into glucose, the breakdown of muscle tissue into amino acids, and the breakdown of adipose tissue into fatty acids and glycerol. In addition, glucocorticoids promote the conversion of fatty acids, amino acids and lactic acid into glucose in the liver.
In the post-exertion period, the recovery period, the release of adrenaline and glucocorticoids decreases significantly, but the release of mineralocorticoid hormones into the blood increases significantly. Mineralocorticoids do not have any anabolic effect, but they exhibit a significant anti-catabolic effect, being to some extent antagonists of adrenaline and glucocorticoids. Under their influence, the breakdown of protein structures slows down and this indirectly enhances the anabolic effect of somatotropin, sex hormones and insulin, which provide post-training recovery and supercompensation (the predominance of anabolism over catabolism).
Any regular training load leads to gradual hypertrophy of the adrenal glands. The adrenal glands increase in size and become more “productive”. No other endocrine glands undergo such hypertrophy as the adrenal glands, which indicates their special role in adaptation to repeated physical activity.
In runners, the adrenal glands do not hypertrophy to the greatest extent compared to representatives of other sports; the cells of their body acquire increased sensitivity to adrenaline and glucocorticoids. In highly skilled runners, their content in the blood at rest is lower than normal due to the high sensitivity of cells to them, which leads to a decrease in the activity of catabolic processes. The breakdown of tissue proteins slows down.
This is a very serious prerequisite for muscle growth, because it has been proven that muscle mass grows not so much by increasing its synthesis, but by slowing down its breakdown. Slowing down the rate of breakdown of tissue proteins is one of the main reasons why muscle mass in runners (with appropriate training, of course) grows very quickly.
Adrenaline is a strong physiological stimulator of the release of somatotropic hormone into the blood. During intense running, the content of somatotropin in the blood can increase 3-7 times. No pharmacological means (with the possible exception of very large doses of insulin) can achieve such results. Even after the release of adrenaline has ceased, the concentration of growth hormone in the blood remains elevated for several hours, ensuring the predominance of anabolic processes over catabolic ones.
Organize a corporate running club or join an existing one
Leaders of many large companies have long known that there is no better way to get closer to colleagues than joint events, especially those held for recreational purposes. Running helps employees go beyond formal interaction - when people see each other in an informal setting, overcome difficulties together, they begin to communicate on a new level.
If your company does not already have such team building, think about how to organize it. Talk to your colleagues and bosses, discuss joint jogging routes and benefits that the company can provide to sports employees.
Facts speak louder than rumors
It's no secret that running is very important for human health. It has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular, digestive, respiratory systems, etc. But can we consider that running is a panacea for all diseases or their prevention? Let's figure it out.
Scientists from the University of Iowa have proven that running at least 7 minutes a day reduces the risk of premature death from any disease by 30%, and from cardiovascular disease by 45%.
By the way, 50,000 Americans took part in the study, which indicates the scale of the study. Additionally, scientists from the Institute of Orthopedics in Milan found that running also has a beneficial effect on strengthening human bones.
But there is no doubt that in cases where there are medical contraindications, it is better not to get carried away with jogging. Otherwise, they can not only worsen a person’s well-being, but also aggravate the existing disease process.