Total or partial rupture of the tendon of the long head of the biceps is not uncommon. This is a severe disorder that leads to limited movement of the upper limb. Only qualified treatment will allow you to regain full use of your arm in the future.
Some patients are inattentive to their health and do not rush to see a traumatologist. If the tendon is completely damaged, the function of the limb will not be fully restored if the disease is not treated, and pain will become a constant companion.
Our clinic has accumulated extensive clinical experience in treating such patients, which allows us to restore the function of the shoulder joint even in the most difficult cases.
Anatomy of the biceps brachii tendon
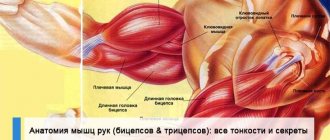
The biceps, or biceps muscle, is a flexor muscle. It consists of muscle fibers and tendon parts. When it contracts, the upper limb moves in the elbow joint.
The long head of the biceps is attached to the tubercle of the scapula, and the short head is attached to its coracoid process. Both heads fuse to form a single tendon and attach to the tuberosity at the proximal end of the radius of the forearm. The biceps can not only bend the arm at the elbow joint, but also participate in rotational movements.
Fig. 1 a, b Structure of the shoulder joint (schematic representation)
The long head tendon of the biceps brachii runs through the shoulder joint and is longer than the short head tendon, so it is more susceptible to injury.
Place among other muscle groups
All muscles that are located on the upper limb are divided according to the principle of anatomical localization (places of attachment and location) and function. There are muscles of the shoulder, forearm and hand. And according to their functions they are divided into flexors and extensors. The biceps belongs to the muscles of the shoulder: it is located in the anatomical region of the shoulder - the humerus.
This area is also divided into anterior and posterior groups. They are separated from each other by connective tissue plates. The anterior group performs the function of flexion, and the posterior group performs extension. The biceps belongs to the anterior group of shoulder flexors. And from these facts alone, its structure and field of activity become clear.
Causes and mechanism of rupture
A rupture of the distal biceps tendon is usually traumatic in nature. This injury occurs predominantly in men, as they are more likely to lift heavy objects and undergo intense physical activity.
In older people, a rupture of the head of the biceps tendon can occur for no apparent reason. This is due to age-related changes in the tendons and the consequences of microtraumas that have occurred throughout life. But the pathology often occurs in young, active men 35-40 years old. Predisposing factors are tendinitis resulting from constant microtrauma.
Professional sports and some activities that place constant stress on the biceps muscle over time make the anatomical structures vulnerable, and they rupture even with moderate force.
The injury usually occurs during sudden lifting of weight, as well as during sudden forced extension of the elbow joint. The tendon most often ruptures in the area of attachment to the scapula, the glenohumeral joint, or near the intertubercular groove.
Symptoms of a biceps tendon rupture
In clinical practice, complete ruptures of the biceps head are more common. In this case, the tendon is completely torn and separated from the bone, contracts and is pulled towards the elbow joint.
Upon examination, a pronounced tubercle is visualized on the inner surface of the lower third of the shoulder. Immediately after the injury, swelling occurs that quickly spreads throughout the shoulder.
Fig. 2 Appearance of the shoulder with a rupture of the long head of the biceps.
The rupture may be isolated or accompanied by damage to other structures, such as the rotator cuff. With concomitant disorders, the clinical picture is atypical.
At the time of injury, acute pain is felt, attempts to bend the elbow are painful or impossible. When a tendon is torn or injured in older people, the clinical picture is blurred. The pain syndrome is moderate, flexion strength is reduced.
To determine muscle tone on the injured side, you need to compare it with a healthy arm, since in some patients the tone may be initially reduced.
Why pump your arms at all?
First, let's figure out why you should pay attention to your hands and train these muscle groups. There are several points here:
- women love guys with strong arms. This creates the image of a reliable protector who can protect you from adversity;
- beautiful biceps and well-pumped triceps look great in the summer, for example, in a T-shirt or short-sleeve T-shirt. It is from the muscles of the arm that one can see that their owner is in excellent physical shape;
- if you are asked to demonstrate the result of work in the gym, then the biceps are shown first;
- by the appearance of the hands, as a rule, a conclusion is drawn whether a person is “hilyak” or not;
- worked triceps and biceps - an opportunity to achieve better results in working out other muscle groups. Strong arms allow you to work with heavy weights and, accordingly, results in the form of muscle growth are achieved faster;
- strong hands are a big plus for the weaker sex, because you can easily carry bags and other heavy objects (when there are no men nearby);
- beautiful and toned triceps - an opportunity to forget about the ugly appearance of your arms and the presence of “sagging”.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of a rupture of the long head of the biceps is carried out in several stages. At the beginning, the doctor finds out the mechanism and circumstances of the injury, clarifies whether there were injuries before, whether the patient was involved in sports, whether his work involves constant physical activity.
After collecting anamnesis, the orthopedist-traumatologist proceeds to the examination. The doctor visually assesses the condition of the upper limb, determines whether there is a hematoma or tubercle in the distal part of the shoulder. An important factor is the presence, localization and persistence of pain. The volume of active and passive movements of the upper limb is also determined. If the case is serious and the gap is complete, active movements are limited.
To clarify the diagnosis and determine the extent of damage, additional examination methods are used. Ultrasound is widely used; the method allows you to accurately determine complete ruptures. MRI is used to obtain more accurate information about the location of the injury, as well as to visualize small tears and intra-articular injuries.
Fig. 3 MRI picture of a tendon rupture of the long head of the biceps
Treatment
Treatment for a rupture of the head of the biceps can be conservative or surgical.
Tactics are determined depending on the degree of damage and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Conservative therapy
Conservative treatment is indicated in the following cases:
- middle and old age;
- contraindications to surgery;
- activities not related to the use of physical force;
- minor tendon damage.
After conservative therapy, the strength of supination is reduced by 20%, if the patient does not engage in activities associated with heavy load on the upper limbs, this factor does not affect the quality of life and allows one to fully take care of oneself.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is indicated for young people, patients who play sports or do physical work. The operation completely restores range of motion and muscle strength. The most progressive treatment method for biceps tendon rupture is such a modern surgical treatment method as arthroscopy.
The technique is based on the use of an arthroscope, which is inserted through small punctures, allowing you to examine the area of damage in detail using optics, as well as carry out the necessary manipulations to restore the tendon.
The effectiveness of the procedure is high, and the recovery period is minimal. In some cases, a technique with traditional surgical access through an incision is also used.
Rice. 4 Schematic representation of tenodesis (fixation to the head of the humerus) of the tendon of the long head of the biceps muscle with a screw (a) and an anchor fixation (b).
Base for developing DMB
To develop a certain foundation, an athlete needs to start small. Of course, this will not bring really tangible results. He won’t do all the work, but he will be able to prepare the body so that in the future there will be no problems when switching to strength options.
The base is also aimed at training without any equipment.
Example training plan
Let's take a look at what a basic complex for development might look like.
Bend the knee and return to the starting position. To do this, you will need a straight surface on which you can lie on your stomach, leaving your legs in the air. For example, a bench, or even an ironing board. Often women choose this option. By the way, they often use this exercise. After all, the place where the hamstring biceps is located in girls is no different from men. And they have the same problems when training.
The second stage is working with resistance. This could be an elastic band fixed to each leg, or an assistant who will help hold the limb by creating pressure. Naturally, not strong, remember to be careful.
The third stage is deep squats. At the beginning of classes we do not use weights. But remember that the back leg needs to be extended to the maximum possible extent.
Squat with weight
Let us warn you right away that this exercise is suitable for professionals. For those who have been involved in sports for a long time, have well-developed muscles, and know the basic safety rules. You should always start working from this angle under the watchful supervision of a trainer. Otherwise, you can damage not only the biceps on the leg, but also a lot of other parts of the body.
Performed using a barbell. Choose your weight carefully and calculate your strength.
Key aspects:
- Always have a straight back, as well as full tension of the muscles involved throughout the entire movement.
- The basis for forward movement is push. Which comes from the hip part, and not from the knees and lower legs.
- Bend your knees up to an angle of 90 degrees.
- Lifting is a uniform and forceful movement that should not have visible stops. But remember that the weight should always be parallel when lifting, do not allow it to wobble or transfer to the toe or side of the foot. We rest strictly on the heel, if it staggers, stop.
Squat with dumbbells
For those who are not yet ready to work with a barbell, this option is recommended. This is a lighter and simpler version. And it can be done even without serious supervision from a trainer. Although, it all again depends on choosing the right weight. It should come from the parameters of weight, athletic training, and development at the current stage. At first, limit the number of repetitions to the minimum parameters - 10-15, no more.
This exercise should be placed at the beginning of the workout, but after the warm-up. After all, if the body is not warmed up enough, you can get injured.
Key recommendations:
- The tools must be held in straight hands, strictly parallel to the body itself. Keep them in this position throughout the entire movement. No displacement is allowed.
- The legs are straight, but not shoulder-width apart. You should take a slightly wider range, about 20-30%.
- We do not move from our axis. Avoid any sideways bending or loss of balance. If you feel that you simply cannot physically control the movement, displacement still occurs, then you should take a break or stop doing it until next time.
Deadlift
This is the most difficult option of all that we have described. Start it only if you have already managed to adapt well, and under the supervision of an instructor. Remember to perform correctly. After all, a huge number of injuries occur when working with deadlifts. It is also sometimes called “dead”.
So, be sure to remember:
- Let's keep our back straight. We do not allow any loss of balance or jerks. Otherwise, you can not only disrupt the correct technique, but also damage the spine. Which threatens very serious injuries and long-term health problems.
- The biceps muscle of the leg is well worked out if we place our legs not shoulder-width apart, but a little narrower.
- First of all, we need to tilt our pelvis. Don't try to lift the weight without this small movement.
- We hold the bar parallel to our legs and do not move away from them. The distance is literally 2-5 centimeters. At first, beginners often touch their own limbs, but this is acceptable.
Isolating complex
As we remember, for the most effective impact on DMB, it is not enough to use the usual technique. You will have to resort to specific work that is aimed at one point. A kind of exclusive approach.
These activities should complement the main ones; you cannot focus only on them, forgetting about the rest. By themselves, they are not very effective for development, but only make up for lost time. But if you remember them, you will be able to develop your body truly harmoniously.
Hyperextension
Looking at the photo of the anatomy of the femoral biceps, it can be noted that this exercise affects these groups. True, if the footrest is shifted lower than usual, opposite the front of the quadriceps.
It is worth noting that despite its exclusivity, this particular type is excellent for developing the back. Which is very convenient, because you can combine several techniques at the same time.
Rules:
- We keep the body level and do not deviate from the axis.
- It is also important to place your hands correctly. You can put them behind your head or connect them on your chest, press your palms to your chest, or whatever is comfortable. But don't straighten it.
- The legs should be tense throughout the entire execution.
- We are not in a hurry, we move without jerks. It is especially important if there is little physical strength left. At such moments, it is sometimes difficult to refrain from unevenness.
Lower limb flexion
For this type of training you will need a machine. You can't replace it with anything. Although this technique itself is quite simple, it is highly effective for the development of DMB. Therefore, it is not recommended to exclude it.
Peculiarities:
- We lie down on the machine with our stomach down. The legs are pressed from the back with a special roller. Which will serve as the main force of resistance during execution.
- We hold the simulator itself and any of its components with our hands.
- Grab where it's convenient. And fixation will definitely be needed. Otherwise, when the roller rises, the body will also begin to rise. And then the work will largely be transferred to other departments. Avoid this by pressing firmly to the surface.
- Again, we are afraid of twitching. If you lift the roller with one jerk, the efficiency will be greatly reduced. Only uniform and continuous movement. Don't try to force it or increase the pace. Calmly and deliberately, work through each point. Otherwise, there will be practically no benefit for the hamstring muscle.
- Even when we stretch our legs, we cannot fully extend the knee joint. Otherwise, we will give the body a moment of rest, which reduces the load. And accordingly, there will be a gentle effect that is unnecessary for us.
Rehabilitation after surgical treatment
After restoration of the anatomical integrity of the ligaments and tendons, the limb is immobilized for a period of 3-6 weeks. For quick recovery, physiotherapy and physical therapy are widely used, which is a set of exercises to improve muscle tone and increase range of motion in the joint.
Therapeutic massage is used to activate metabolic processes and improve muscle tone. Restoration of performance occurs within 6-10 weeks from the moment of injury.
Biceps brachii tendon rupture is a serious injury that can lead to dysfunction of the upper extremity if not treated properly.
If trouble occurs, seek medical help from an orthopedic traumatologist as soon as possible. High professionalism, individual approach, mastery of modern technologies, rich practical experience and good material resources allow the specialist to return patients to a full, active life.