Leg raises are an abdominal exercise. It partially engages the front of the thigh. The movement itself came to us from gymnastics. There, this exercise is performed in full support - hands hold the handles, elbows are straightened and inserted, and the legs are fully raised with the toes above the midline, passing at waist level. In the fitness version, the movement is performed in a machine, with the athlete standing on his forearms.
Execution technique
- Initial position
- Stand facing the machine;
- Step onto the footrests;
- Grasp the handles with your hands;
- Turn your back to the stops;
- Take a standing position on your forearms.
Movement
- The exercise itself is simple:
- You need to shorten your abs and pull your stomach inward;
- Next, the straight legs are brought upward by contracting the abs and pulling the pelvic bones to the lower ribs;
- For maximum contraction, the hips must pass the midline of the abs;
- Once peak contraction is achieved, the legs should be released slowly and in a controlled manner.
It's the HANGING LEG RAISES, baby.
Attention
- It is necessary to completely eliminate attempts to cheat with your feet. The technique used in competitive CrossFit for the toes to bar exercise is not valid or acceptable here;
- The knees do not need to be pushed in tightly so that the legs are straight. With this position of the joint, it will not be possible to achieve a full contraction of the abs, and the legs will be partially driven by the quadriceps;
- The tension in the trapezoid needs to be removed. Shoulders raised to the ears are a bad help here. They will only contribute to an even greater buildup of the body and an active violation of technique, in addition, shoulders to ears greatly increase the risk of spasm of the trapezius itself and pain after training;
- Throwing your legs down is not recommended. For beginners, a barbell is often placed on the midline across the lower clamps of the machine so that they do not lower their legs below this bar and work in a balanced manner.
Important
- The legs need to be lifted using the press, and not by the force of swing, inertia and quadriceps. To achieve this, you need to imagine how the pelvic bones are drawn to the lower ribs, and not how the athlete actively throws his legs;
- After passing the midline with your hips, you need to bring your legs a little higher, and then not throw them down, but smoothly “unwind” your abs and lower yourself down;
- You can’t pull your socks back like a ballerina, then they will allow you to “insert” your knees as much as possible, and the quadriceps will engage in work, but on the contrary, you need to work with your abs;
- You can master this movement better if you learn how to do a pelvic lift while lying down with your legs straight and pulled up. You need to understand exactly how the rectus abdominis muscle contracts, and not how a person simply swings his legs above the waist.
On knees
The entire workout will take place on the mat and will take only 5 minutes. At the same time, you will well load the muscles of the hips and abs, tone the muscles of the arms and stretch the shoulders and back. Set a timer and do each exercise for 30 seconds. If the movement involves working with only one arm or leg - 30 seconds on each side.
“Cat-cow” with a turn
Photo: Alexander Starostin
The exercise warms up the back and shoulders, stretches the sides. Get on all fours with your wrists under your shoulders. As you inhale, arch your back and press your chin to your chest. As you exhale, bend into a reverse arc and squeeze your shoulder blades together. Then, inhaling, turn your body to the right, straighten your right leg and right arm, stretching your side.
advertising is not displayed
Return to all fours and repeat the same thing, only this time, after arching your back, turn to the left, stretching your left side.
Side leg raises
This exercise pumps up the gluteal medius muscles and strengthens the core muscles. Get down on your right knee and extend your left leg to the side. Place your right hand on the floor and place your left hand behind your head. Raise and lower your straight leg. Make sure that your body is in the same plane and that your chest does not lean forward.
Back leg raise
The exercise pumps up the buttocks. Get on all fours with your wrists under your shoulders. Raise your leg, bent at the knee, until your thigh is parallel to the floor or slightly higher. At the top point, tighten your buttocks.
Knee push-ups
Exercise for pumping the chest and back of the shoulder. Push up from your knees, lower yourself until your chest touches the floor and rise back up. Follow the technique: do not place your elbows to the sides, do not lift your shoulders towards your ears. Tighten your buttocks to avoid arching your lower back.
Raising legs and arms
The exercise will strengthen the muscles of the back, buttocks and shoulders. Get on all fours and raise your right arm and left leg as high as possible. Squeeze your buttocks, hold for a second and return to the starting position. Then raise your left arm and right leg. Alternate sides every other time, direct your gaze to the floor in front of you.
Child's pose
Photo: Alexander Starostin
This exercise stretches your shoulders. Sit on your heels, slightly spread your hips to the sides. Extend your arms forward and lie with your stomach on your thighs. Spend 30 seconds in this position, stretching your shoulders and back. Breathe evenly and deeply.
Maybe after a short workout you will want to move more. Then repeat it or try a longer and more intense version.
Execution options
Raising the knees while resting on the elbows
This version of the exercise is suitable for beginners and those who find it difficult to lift their straight legs up. It is anatomically simpler, as it is easier to understand how to bring the hips to the ribs if the legs are bent. The athlete takes the starting position similar to the previous option, and then carefully pulls the pelvic bones to the lower ribs. Lowering is also smooth. There is no need to straighten your knees with each repetition.
Side leg raises
This is the same gymnastic exercise that imitates a fitness option. For fitness purposes, you do not need to learn to throw your legs with your toes pointed up due to inertia and rotation in the shoulder joints. Here you need to carefully pull up your straightened legs with your toes pulled slightly above the midline of the body, and just as carefully lower the entire “structure” back.
Leg raises supported by parallel bars
This option is intended for those who want to pump up their oblique muscles. Here you need to pull your knees to your waist, but “obliquely”, aiming your knees first to one or the other shoulder.
Leg raises: 3 difficulty options
Complex training on simulators and multi-span gymnastic equipment
Complex training is carried out with the aim of increasing the density of the lesson, improving the physical qualities and military-applied motor skills of the trainees. Its content includes previously studied program exercises, techniques and actions, as well as exercises on simulators and multi-span gymnastic apparatus.
The training is organized in a group or frontal manner.
In the group method, the unit is lined up in a column of three (four, etc.). The commander, having indicated the training places, gives the command: “MARCH to the training places by walking (running).” At this command, the squads move forward along the shortest route to the training areas, position themselves so that the indicated places are to the left of the formation, and indicate a step in place. Then, on a general command, they stop and turn left. The commander gives the command: “GET TO THE EXERCISES.” The squad leaders go to the middle of the formation, turn to face the unit, name the exercise being performed and give the command “FREE” (“Gymnastic stance - ACCEPT”) and supervise the training of their subordinates. To change training locations, the leader gives a command, for example, “Platoon, exercise - FINISH.” At this command, the students stop doing the exercises and line up in one line. Changing places of training is carried out using the commands: “Headward-VO”, “To change places of training by walking (running) - MARCH.” At the first shift, the transition order is indicated.
With the frontal method, the commander determines the first training place and gives the command: “To the place of training, step (run) - MARCH.” the unit moves forward along the shortest route to the specified location, stops at the commands of the leader and turns left. After completing the exercises, the unit moves to the second training location, then to the third, etc.
| Exercises on a gymnastic bench | |
| Perform on a gymnastic bench simultaneously with the entire unit for the maximum number of times |
| Exercises on a multi-span bar | |
| Perform on a multi-span bar in pairs with assistance, for the maximum number of times |
| Exercises on multi-span bars | |
| Perform on multi-span bars simultaneously with the entire unit, for the maximum number of times. Walk on the uneven bars on your hands to the distance specified by the leader. |
| Exercises with weights | |
| Perform using multi-span cargo simultaneously by the entire unit or based on the number of cargo for the maximum number of times |
It is advisable to carry out training in performing strength exercises on simulators and multi-span apparatus using the repeated method or the method of maximum effort. The number of repetitions of the exercise in one approach depends on the level of the current individual indicators of the student, which must be recorded by the commander.
Repetitive training consists of repeating an exercise many times with the same power (the amount of effort should be no more than 60 percent of the maximum).
Training using the maximum effort method is carried out after 3-4 training sessions using the repeated method. In training, when the practitioner performs an exercise with maximum effort, it is sometimes advisable to provide assistance in the final stage of the approach in order to overcome the psychological barrier of a certain number of repetitions. You should not stop at the achieved results. It is always necessary to create a reserve of motor abilities, guaranteeing the necessary level of preparedness.
The maximum effort method is characterized by performing exercises in which the soldier exhibits the maximum strength of which he is currently capable. Maximum effort refers to the maximum resistance training weight that a student can lift (perform) without significant emotional arousal.
Analysis of the exercise
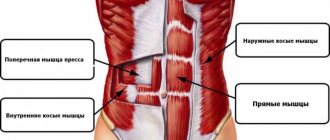
Anatomy of exercise - which muscles work
This exercise uses the rectus abdominis muscle as the main engine. If an athlete bends his knees, then the hip flexors are also involved; if done carelessly, the load often goes into the quadriceps. The back muscles work as stabilizers and are activated when the athlete brings his shoulder blades together and lowers them towards the pelvis.
pros
- This movement allows you to build a strong core, especially for those who have problems pumping the rectus abdominis muscle due to significant lumbar lordosis;
- The exercise uses the abs in isolation, but provides a significant load;
- One of the movements that relieves tension from the iliacus muscle. Those who like to work their back and buttocks with hyperextensions and any kind of bending with a barbell need to do one of the hanging leg raises. This option is suitable even for those who have already done a fair amount of work on their grip and have done a bunch of deadlifts;
- The exercise is well suited for those who have problems with fixing the upper back and hanging coverage. It allows you to relieve the compression load from the spine, but does not additionally involve the muscles of the forearm and palm. Thus, the movement allows those who perform a lot of deadlifts to get their share of the load;
- This exercise will help relieve tension in your lower back. The athlete must press his back well against the back of the machine and work by twisting upward.
Disadvantages of the exercise
- The movement will be technically difficult for those athletes who have not learned to work with the press and are trying to throw their legs by inertia, or lift them by swinging and using the body. Such athletes may not be able to perform the exercise correctly the first time;
- Spasms of the trapezius muscle with weak or, conversely, overloaded trapezius is a typical disadvantage of this movement.
How to avoid getting injured
Each exercise is traumatic in its own way. In some cases, you can learn from mistakes, and in others, mistakes can result in serious damage. To avoid having to treat sprains and dislocations, we will describe possible injuries and ways to avoid them.
- The most basic thing to remember is don’t overdo it . If you want to get better results, then just do the exercise better. There is no need to do 10-15 approaches 30-50 times.
- For many people, the wrist is a weak point that is constantly injured. When performing the exercise, use an elastic bandage that will strengthen the tendons.
- If you have problems with your lower back, then under no circumstances straighten your legs while lifting. You won't feel pain right away, but after a few hours the problem will make itself felt.
- When performing exercises on the horizontal bar, make sure that your hands are dry and will not slip when you lift your legs.
Preparing for the exercise
Preparation can be considered normal and joint warm-up, as well as warm-up of the hip joint. But in ordinary life, this movement is performed as the last exercise of the workout, therefore the entire workout serves as a kind of warm-up; there is no need to perform additional warm-ups. Sometimes it is recommended to do one set of pelvic lifts from a supine position before lifting your legs in a hanging position in order to engage the abs in the work.
Notes[edit | edit code]
The prone leg raise poses a completely different challenge in terms of pelvic stability compared to the previous one, since you are facing down instead of up. Adopting a neutral position requires active work of the abdominal muscles, preventing the force of gravity, which tries to bend the spine in the lower back and tilt the pelvis forward. Too much effort from the abdominal muscles can lead to the opposite effect - flexion of the spine. Raising the leg allows you to work the muscles that extend the leg at the hip joint, but at the same time complicates maintaining stability. If you can maintain a neutral pelvic position, the exercise will provide a good stretch to the hip flexors, as already described in the scissors exercise. In addition, you have the opportunity to develop scapular stabilization skills, which will be useful for all pushing exercises and will help eliminate the common postural problem of protruding shoulder blades.
Stabilization with the abductor muscles. In the prone position (1st phase), the force of gravity forces the shoulder blades to converge in the direction of the spine (scapula adduction). This is counteracted by the muscles that dilute the shoulder blades, in particular the serratus anterior muscle, which makes it possible to maintain a neutral position of the shoulder girdle. Retracting your shoulder blades significantly reduces the potential benefits of this exercise.
Proper execution
- Your back must be firmly pressed against the back of the machine and during the exercise, do not tear it off;
- The shoulder blades must be brought together to the spine and lowered to the pelvis, and the abs must be tightened, only then will it be possible to pull the lower ribs to the pelvic bones;
- Swinging of the legs is not allowed, there is no need to bring them behind the line of the back after lowering, and “throw them off” from top to bottom with sudden movements;
- The exercise is performed according to the general rules of synergy between muscle contraction and breathing, that is, exhalation occurs with effort;
- The movement should not be too active, that is, fast. You need to try to work more smoothly, and avoid sudden jerks and throwing your legs
Errors
- You cannot swing your legs sharply, change the position of your forearms on the supports and push your toes towards the bar too quickly;
- It is better to do the exercise synchronously with breathing, and not change the position of the body at random and hold your breath while making an effort;
- You should not place your hips behind the line of your back, so as not to gain excess inertia and train efficiently.
Raising the legs while resting on the elbows
Safety
Before you start lifting, you need to make sure that the machine itself is stable. If the position of the bar is too shaky, it can cause it to constantly wobble, preventing the athlete from completing the exercise.
Leg raises are a difficult exercise for beginners, so they should be careful to keep their elbows and forearms in place. Constantly forcing this part of the body can lead to painful elbow injuries. That’s why it’s better to prepare in advance for working out your abs by improving your arm strength.
It is important to properly protect your back. It should press well against the back of the machine, since any deflection in the lower back can stretch it
If you can’t keep your back straight, you can ask your partner to help - hold your legs or reduce the sway of the machine.
Tips for increasing the effectiveness of the exercise
- Experienced athletes can do this exercise with weights. It is convenient to hold the medicine ball between your shins and lift your legs up. If there is no ball in the gym, you can try hanging weights on your feet, or lifting a dumbbell by holding it between your legs. At a slow pace of exercise, this is more than realistic;
- The start always occurs through the muscles of the legs, but if you move your hips forward a little and start by twisting your abdominal muscles, you can make the exercise more effective;
- The slower the pace, the better it will be to pump up your abdominal muscles;
- If you use the option for pumping obliques, it is important to press the upper back to the back. The hips must be carefully brought to one and the other shoulder;
- It is more effective to do the exercise with straight legs, but in this case you need to maintain a slight angle in the knee joint and not straighten your knees completely;
- Bent legs are suitable for beginners and those who find it difficult to do twisting.
Inclusion in the program
It is worth including this movement in the training program at the stage when you already have the physical ability to perform the exercise and there are no problems with mobility in the hip joints. Beginner women often simply cannot hold onto the forearm stand. They fall down due to the fact that a weak back and trapezius do not allow them to stabilize their own weight. Girls should first strengthen their backs with pull-downs and standing (plank) exercises, and then do this movement. You can replace the exercise with hanging leg raises.
Typically, the movement is included on the day when the athlete squats rather than pulls, but with the parallel bars this rule does not work; you can do any option, even if it is not possible to space the deadlift and abdominal exercise on different days.
Working muscles
First, let's talk about the group of muscles that are used during training.
Basic
During the exercise, the rectus and oblique abdominal muscles are activated.
It is worth understanding that these muscles bear the main load, so we classify them as the main ones.
Additional
Additional ones include those that are indirectly involved in one way or another when performing the exercise and to which the largest part of the load is distributed. That is, they will also swing, but less intensely.
Additional muscles include the rectus femoris and iliopsoas muscles.
The muscles described above are used when performing the exercise on a special simulator. If you do not use such equipment, then the arm muscles may be involved in the training process.
Contraindications
- Intervertebral hernias and protrusions are considered a contraindication for this exercise, but this is not recognized by all trainers. A number of experts believe that you can perform exercises in this style without any problems, even if there is a hernia, but then you will have to twist quite smoothly and train slowly, under control;
- Diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscle is a contraindication for all crunches, including this exercise too;
- The movement is not suitable for training pregnant women, although it does not involve direct pressure on the abdominal area;
- This option cannot be performed with injuries to the hip joints;
- If a person cannot move his head away from his shoulders and stand firmly throughout the entire approach, he should strengthen the trapezius muscles;
- You should not do the exercise when the trapezius is overtrained and the inflammatory process has already begun;
- Usually the movement is not placed on a heavy bench day if the lifter prefers a medium grip and triceps press;
- The exercise is contraindicated for radicular syndrome, that is, pinched nerves in the lumbar spine;
- Forearm stand is not recommended for injuries and inflammation of the elbows, shoulders, and other joints. It should not be done for cervical osteochondrosis if pinched nerves occur.
The main mistakes that beginners often make when performing leg raises hanging on their elbows
- Swinging your legs too much (this is not recommended, since the effect of this exercise will be almost zero, so swinging should be avoided).
- The following error is the most common of all listed. Many people assume that the faster they do this exercise, the faster they will achieve their results. But in this type of activity this is far from the case. Here it’s the other way around: the slower and better you approach each execution, the better the result will be.
- There is also such a defect as incompleteness of the exercise, that is, the lower part of the body (in this case, the knees) does not come into contact with the upper part of the body (chest), thereby a certain fold is not formed, the abdominal muscles are not twisted enough, and the effectiveness of the exercise is noticeably reduced. Therefore, absolutely all approaches need to be completed to the end.
- The second most important mistake is completely straightening the legs and failing the body. By allowing this violation in the exercise, you risk damaging or tearing your back muscles, especially in the lumbar region. Therefore, first you need to familiarize yourself with all the rules.
Interesting fact
This is a favorite exercise of past champion Mike Francois. He believed that only hanging leg raises help build a strong and sculpted abs, and no twisting can compare with lifting in this great matter. Mike recommended alternating regular hanging leg raises with weights, and a fast tempo with a slow tempo to get better abs. He did the movement three sets to failure, but fitness enthusiasts can limit themselves to 3 sets of 12-15 repetitions. Only experienced athletes should do more.