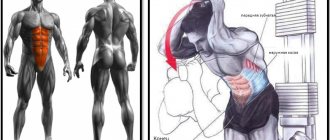
Shvungs are an exercise from weightlifting, which, in fact, is a power version of the military press . There are two types of pushups: classic and presses. The bench press version is more isolating, when the athlete helps himself with his legs or back, but still the shoulders take the main load. The classic shvung is performed with a jump; it is a purely strength exercise that fully develops the legs, back, shoulders, chest and joints. In general, before you start performing such heavy basic exercises, you should work on the strength of your ligaments and tendons, for example, you can use Zass exercises . It is also recommended to use a belt and elastic bandages while performing such exercises and, of course, warm up very well.
Shvungs are not recommended for beginner athletes or even athletes with an average level of fitness working on muscle mass. This exercise can be included in a strength training program , or in a training program for advanced athletes, which combines exercises of different classes. In any case, to perform such a technically complex exercise you will need good muscle sense, which must be specially developed. There are different methods for developing muscle sense , but, one way or another, before you start doing push-ups, you should feel the muscles in a classic army press. After you learn how to perform a simpler exercise technically correctly, you can move on to a more advanced one.
Benefits and features of the shvung exercise
Despite the fact that the main movement is performed by the muscles of the upper body, the lower part is also actively involved in shvungs. The fact is that when pushing the barbell over your head, your legs act as assistants during the push, due to which the projectile flies up using the force of inertia. Thus, during work, the hips, legs and buttocks also develop. The exercise develops explosive strength and increases endurance.
But there are also different types of shvungs, each of which has its own technical features and effect on the muscles. Let's take a closer look at each.
Jerk
The next exercise in classic kettlebell lifting is the kettlebell snatch.
The snatch can, as described above, be included in the classical combined event program along with the clean and jerk - for men - or be represented as a separate competitive exercise for women.
The snatch, unlike the clean and jerk, is performed with one kettlebell for 10 minutes with each hand alternately. When performing a snatch, only one change of hands is allowed.
So, jerk.
When performing a snatch, the athlete begins the movement from the initial “kettlebell down” position. In the trajectory of movement of the weight in a snatch, we can conditionally distinguish 4 points: the point of swing, the point of detonation of the weight, the point of inserting the hand into the arch of the weight, and the end point - the point of fixation of the hand with the weight.
Let's take a closer look at the entire trajectory of the weight's movement. The swing point is the extreme point from which the forward and upward movement of the weight begins. To perform the exercise most effectively, this point should be located as far back as possible between the athlete’s legs.
This is necessary for maximum inertial force when moving the weight, in order to reduce the load on the arm muscles. So, from the point of the swing, the weight begins an inertial movement forward and upward.
However, the force of inertia is not infinite and the weight sooner or later slows down and stops its inertial movement.
The point at which the inertial force stops moving the weight is the point at which the weight explodes. At this point, the athlete begins to apply his own effort to further lift the projectile. So, what are the actions of the athlete when the trajectory of the weight reaches the detonation point?
When the trajectory of the weight reaches the detonation point, the athlete must make certain efforts to ensure its further movement. At the point of detonation, the athlete makes a sharp reverse movement of the shoulder joint of the arm with the weight back and up, which creates additional force for further movement of the weight.
The next point of movement of the weight is the point where the hand is inserted into the arch. This happens when the projectile is at the level of the athlete's head.
Shvung press with barbell
This type of exercise is performed through the movement of the arms and a slight squat, in which the legs, when straightening the knee joint, help push the barbell above the head.
What muscles work
- Anterior and middle bundles of deltoid muscles.
- Pectoralis major muscle.
- Triceps brachii muscles.
- Trapezius muscles.
Accessory muscles:
- Quadriceps femoris muscles.
- Biceps femoris muscles.
- Large gluteal muscles.
- Lumbar extensors.
- Calf muscles.
Barbell press technique
The barbell must be removed from the racks or lifted from the floor and taken onto the chest.
Initial position:
- The barbell is located on the front deltas, holding it with your palms with an underhand grip slightly wider than your shoulders.
- The elbows extend slightly forward and upward; the shoulder and forearms should not be strictly vertical.
- The hands with the barbell are in the kink of the joint.
- The feet are located slightly wider than the shoulders - neither narrow nor wide.
Performance:
- You need to sit down slightly, but do not squat until your thighs are parallel to the floor.
- Exhaling, straightening your knees from the squat with the strength of your legs, simultaneously push the barbell up, lifting it above your head with your elbows straight. The body and the bar above your head should be in the same plane.
- With this option, the feet should not leave the floor.
- As you inhale, you need to gently take the barbell onto your shoulders and at the same time sit down to avoid shock loads on your joints with your knees bent.
Common mistakes
- Let's look at the starting position in more detail. Most beginners perceive this exercise as a military press; accordingly, they keep their forearms perpendicular to the floor, which is strictly prohibited when doing pushups. The elbows should rise upward, throwing the barbell over the shoulders, which is also fixed with a kink of the hand. That is, the palms hold the barbell from below, arching the wrist.
- Podsed. You can often see too deep a dip or lack thereof, as when taking a barbell, which can easily injure the knee joints. Therefore, make sure that there is a slight dip both when pushing the barbell and when taking it onto your shoulders.
- Top position of the bar. When pushing out, you can also see a deflection in the lower back or thoracic region, in which the spine suffers and the center of gravity changes. In this case, you may not be able to resist and lose your balance. For some reason, many people place the barbell too far behind their head, which is absolutely not allowed. For the correct position, tense your abs and push the barbell strictly vertically, keeping your back straight.
Execution technique
Initial position
- The barbell is installed on racks at a level just below the athlete's collarbones. It is important. The implement must not be placed too high so that the athlete has the opportunity to remove it correctly;
- The athlete takes a grip 10 cm wider than the edges of the bar, or 10 cm wider than his shoulders, if they are wide. The palms are placed symmetrically on the bar;
- Then you need to step under the bar strictly in the center and place it on the clavicle bones, grabbing it from below with your hands;
- The knees are bent; due to extension at the knee joint, the bar is removed from the racks;
- The athlete moves away from the racks, that’s it, he is ready to move as soon as he aligns his position and stabilizes his body
Movement
- The legs are slightly bent at the knees and sharply straightened;
- In proportion, the palms begin to move upward;
- The projectile overcomes the dead center by inertia;
- Elbows straighten;
- Hands press the projectile up and behind the head;
- The athlete fixes the barbell above his head;
- Then he bends his knees and returns the barbell to his chest.
Attention
- It is not allowed to throw the projectile behind the back as in a jerk;
- There is no need to stop at eye level and so that the bar is projected onto the top of the head;
- You should not knock the projectile away from your chest and drop it sharply on your collarbones;
- If possible, you should use a soft technique and do not insert your knees until they click;
- You should avoid sudden movements of your wrists and do not twist them at the top point of the trajectory;
- The hip joints extend in the same direction as the movement;
Shvung push with a barbell
The name itself refers to the presence of a push, in which the feet lift off the floor and the bar flies up thanks to the explosive force and momentum created by the strength of the legs.
What muscles work
This technique works the same muscles as the push press. The only difference is that when pushing, the muscles of the legs work harder, or rather the shins, biceps and quadriceps of the thigh and buttocks.
Push push technique with a barbell
- Take the starting position described above ↑.
- Next, do a shallow squat and push up with your feet, lifting your heel off the floor while simultaneously pushing the barbell up above the top of your head.
- At the top point, the athlete’s position remains the same - strictly vertical.
- As you inhale, gently lower the barbell onto your deltoids, while sitting down so that your knees do not experience shock load. There is no need to tear off your feet here.
Creating a program
Depending on the time allocation and goals of the athlete, sets of 1-6 repetitions can be performed.
4-6 reps will help with hypertrophy and help develop some strength.
Sets of 3-5 reps will most effectively develop strength and will help a little with hypertrophy.
1-2 repetitions per set are generally used to understand the athlete's maximum capabilities, but also develop strength characteristics.
Alternative Exercises
Overhead barbell push
This exercise is performed with a barbell positioned behind your head on the top of your trapezius muscle. The difference from the previous options is that the load and center of gravity shifts back, while the rear and middle bundles of the deltoid muscles, back and lower back muscles are activated, and the load on the triceps increases.
The overhead swing can also be a push and a press, the difference, respectively, is the lift-off of the feet with the push version, and the absence of lift-off with the press.
Overhead press press
Technique:
- Step up to the racks and place the barbell on the top of your trapezius muscle. Place your palms slightly wider than your shoulders, but not too far or too close to your shoulders.
- Remove the barbell from the racks and step back one step. Place your feet slightly wider than your hips for stability, but not too wide.
- Squat down slightly, not like in squats, and exhale while straightening your knees and push the barbell over your head, placing it strictly above the top of your head with straight elbows.
- As you inhale, gently accept the barbell onto your upper trapezius while sitting under the barbell again to protect your knees from shock and injury.
Common mistakes
Shvungs are by no means the most technically simple exercise. Mastering, especially the push version, sometimes requires months of training and, preferably, the participation of a competent trainer.
Those who decide to study on their own usually make the following mistakes:
- They perform military presses instead of push-ups, completely forgetting about footwork.
- When performing the bench press version, they sit under the barbell, relieving the load from the shoulders.
- Slowly lower the weight down and do not absorb its landing with a small half-squat.
- Do not straighten your arms at the elbows, keeping them slightly bent.
- Bend your back to make it easier to press the bar by connecting your chest to the work.
- They neglect warm-up or spend insufficient time on it.
All of these mistakes can ultimately lead to injury and a long absence from your training schedule. So be careful, friends!
Recommendations for training
- For beginners, it is important to perform shvung with minimal weight, or better yet, with an empty bar. A specialist must monitor the technique, otherwise you can make basic mistakes and learn the technique incorrectly.
- More advanced athletes should increase the working weight gradually, performing approximately 10 repetitions of 5-10 cycles. It is worth choosing a working weight within 60-70% of the maximum. Only after honing the technique can you increase the working weight.
- Girls should select a working weight for 10-20 repetitions and perform 5-10 cycles. The working weight should not be heavy. You should think of the exercise as a method of increasing endurance, not strength. In combination with other cardio and plyometric exercises, shvungs will help improve body contour and reduce adipose tissue.
Why is the overhead kettlebell press dangerous?
Like any other exercise, there are a number of contraindications. First of all, the kettlebell press is dangerous for unprepared beginners, who will definitely violate the execution technique.
It is not recommended to perform the exercise for those who have spinal pathologies, sore elbow and shoulder joints, or wrist injuries.
What to replace the exercise with? If there are pathologies, it is better not to do anything, but to recover and give rest.
If there were pathologies in the past, then pressing movements must be started deliberately and gradually. Starting with exercise machines, then with dumbbells and gradually moving on to minimum weight kettlebells. Learn to perform movements under control without pushing the body, etc.