Both professionals and amateurs sooner or later set themselves the goal of increasing strength indicators. If this is a team sport, then development primarily concerns jumping ability. The height and force with which a jump is made directly affects success in basketball, gymnastics, breakdancing, and volleyball.
To achieve the desired result and jump as high as possible, you can train explosive strength - the ability of muscles to push their own body weight to a certain height. Moreover, explosive power can be developed for both arms and legs. It all depends on which muscle groups are paramount in a particular sport.
What is a jump
Jumping involves lifting your body off the ground. The stronger the push, the better. Do not forget about the time frame within which the muscles should be activated - no more than 0.5 s. Otherwise, nothing will work. The jump itself belongs to the group of speed-strength exercises with an acyclic movement structure.
Jump technique
The jump mechanism consists of two phases:
- shock absorption or leg flexion phase. In this phase, inferior muscle work is observed, the knee bends at an angle of 90-1100, and the center of gravity moves to the fulcrum.
- active repulsion. In this phase, the muscles work to overcome the force, since during repulsion from the surface the center of gravity moves away from the support.
For an effective jump, it is necessary to apply maximum force during the transition from the leg flexion phase to active push-off. And the faster the repulsion occurs, the higher the initial take-off speed will be.
The jump consists of stages:
- Preparatory work for the push from the ground.
- The process of repulsion.
- Flight.
- Returning in the opposite direction.
To jump high, sets of jumping exercises are performed for the muscles involved in preparing for the jump and during the jump. These include:
- thigh muscles: quadriceps and vastus medialis;
- muscles of the back of the thigh: biceps, semitendinosus, semimembranosus muscles;
- calf muscles: soleus, gastrocnemius, tibialis, tibialis posterior.
Jumping characteristics
Basic terms
Jumping ability is the body’s ability to achieve maximum concentration of muscular and volitional efforts in a minimum period of time when covering vertical and horizontal distances.
Explosive strength is the ability to exert large amounts of force in the shortest amount of time.
In volleyball, basketball, and handball, explosive power is realized in jumps, fast breaks, and powerful long passes.
Types of jumping ability
- General jumping ability. Ability to jump high or long.
- Special jumping ability. The ability to develop high repulsion speed while jumping.
A quick take-off initially sets a high take-off speed. And the higher the speed, the higher the athlete can jump.
Factors influencing the development of jumping ability
Level of muscle coordination. It is characterized by coordinated work, sequential inclusion in the process, and the ratio of optimal tension values of groups or individual muscles involved in the jump.
High lability of nerve centers. Allows the athlete to concentrate efforts in a minimum amount of time to perform a high-quality jump.
Neuropsychic and emotional state. A stable psyche, the ability to concentrate on the task at hand and make volitional efforts in critical situations are the key to high results in sports.
Individual characteristics of the athlete’s joint-ligamentous and muscular systems. Extensibility, elasticity, elasticity of muscle fibers, rate of increase in tension, all these parameters will affect the athlete’s jumping ability.
The degree of manifestation of physical qualities. To increase explosive strength, develop and improve jumping ability, it is necessary to work on both general physical indicators and endurance.
Development of jumping ability in young athletes
As they grow older, the level of development of jumping ability in young athletes increases. Thus, the jump height increases by an average of 6 cm per year.
From 10 years to 18 years, the jump height increases by an average of 48 cm.
Experiment statistics
During the experiment, it was found that the jumping ability of a young volleyball player at a certain age increases on average by:
- 12.50 cm—11-12 years;
- 5 cm—12-13 years;
- 3.5 cm - 13-14 years;
- 2 cm - 14-15 years;
- 4 cm - 15-16 years;
- 5.5 cm - 17-18 years old.
Application of experimental results in practice
The most significant increase in jumping ability occurs at the age of 11-12 years. Conclusion: taking into account these data, it is necessary to build the training process of young athletes.
To develop explosive strength in children, plyometric exercises are introduced in classes:
- jumping up,
- jumping over a low barrier,
- jumping rope,
- exercises with rope, gymnastic or power balls.
When drawing up a plan for the training process, the number of hours and intensity of training, the age of the athlete is always taken into account.
Decrease in jumping performance
In 14-15 year old athletes, jumping performance drops significantly. This is due to functional and morphological changes in the body, which decrease at this age. The coach and athlete are faced with the task of supporting and preventing a decrease in the achieved indicators.
Number and scheme of approaches
Thanks to this simple training program, you can develop not only jumping ability, but also endurance. Improved performance will help you achieve optimal results in sports and defeat your opponents.
Learning to jump at a high pace:
| High jump | Calf raise | Step-up | Burnout | |
| 1 Week | 1 set of 50 reps | 2 sets of 10 reps | 2 sets of 10 reps | 1 set of 50 reps |
| 2 week | 1 set of 100 reps | 2 sets of 20 reps | 2 sets of 15 reps | 1 set of 100 reps |
| 3 week | 1 set of 125 reps | 2 sets of 25 reps | 2 sets of 15 reps | 1 set of 150 reps |
| 4 week | 1 set of 150 reps | 2 sets of 30 reps | 2 sets of 20 reps | 1 set of 200 reps |
| 5 week | 1 set of 100 reps | 2 sets of 35 reps | 2 sets of 20 reps | 1 set of 250 reps |
| week 6 | 1 set of 125 reps | 2 sets of 40 reps | 2 sets of 25 reps | 1 set of 300 reps |
| week 7 | 1 set of 150 reps | 2 sets of 45 reps | 2 sets of 25 reps | 1 set of 350 reps |
| 8 week | 1 set of 200 reps | 2 sets of 50 reps | 2 sets of 30 reps | 1 set of 400 reps |
The importance of jumping ability for athletes
In team sports, especially volleyball and basketball, an athlete with good jumping ability will bring significant benefits to the team.
Types of jumping exercises in volleyball
To develop special jumping ability in a volleyball player, when constructing the training process, it is necessary to take into account the individual mode of operation of the muscles of each player. To do this, the jumping training volume is compared with the competition volume.
If a volleyball player performs an average of 80 jumps per game at competitions, then this jumping volume must be maintained during the training process.
In the jumping training of volleyball players they use:
- exercises aimed at overcoming your own weight: squats, jumps, jumping over objects, multi-jumps on two legs, from one leg to another, on one leg;
- weight training;
- jumping with imitation blocks, attacks.
Jumping ability of basketball players
In basketball, the specific features of jumping ability are:
- speed and timeliness of the jump;
- performing a standing jump or a short run-up, mainly in the vertical direction;
- performing a jump with your arms raised high;
- jumping while fighting for control of the ball (serial jumping ability);
- control of your body in an unsupported position;
- landing accuracy and readiness for immediate subsequent technical and tactical actions.
To develop explosive power, basketball players perform jumping exercises during the training process:
- aimed at overcoming one's own weight: squats, jumps, jumping over objects, multi-leaps on two legs, from one leg to another, on one leg;
- with external weights - dumbbells, weights, discs and a barbell;
- using auxiliary equipment and sports equipment - gymnastic apparatus, athletics barriers, coordination ladder, medicine balls, jump ropes;
- in a playful way.
Process Features
Of course, learning to jump 2 meters in just 1 day is an absolutely unrealistic task, but you need to work hard to achieve it.
The best solution to this issue would be to conduct training sessions in a specially equipped jumping sector.
The main task for the athlete here will be to achieve the greatest horizontal length after a standing jump.
The technology for performing the jump begins with a set starting position, then pushing off from a special board at the edge of the pit with two feet and then jumping into a pit filled with sand.
In this case, the distance result will be considered the distance from the mark on the board to the beginning of the hole left by the athlete’s foot from the landing on the sand.
During the flight phase, the athlete can use techniques of varying complexity, such as:
- In step;
- Bend over;
- Scissors.
How to measure jump height
There are several ways to measure jump height. Each of them has its own characteristics and nuances.
Hand touching an object
- Take a small piece (4-6 cm) of adhesive tape (duct tape, duct tape, tape).
- Fold in half, sticky layer facing out.
- Secure the tape to the two highest fingers.
- Stand sideways against a straight wall.
- Press your shoulder against the wall.
- Stretch your hand as high as possible, without lifting your feet from the floor.
- Mark the maximum point of contact - attach a piece of tape to the wall (first mark).
- Take another piece of adhesive tape.
- Secure the tape to the two highest fingers.
- Stand sideways to the same wall.
- While jumping, fasten a piece of tape to the wall above the first mark. This will be the second mark.
- Measure the distance between the marks - the height of the vertical jump.
- Repeat the jump three times.
- Enter the best result in the table, indicating the date of measurement.
- The introduction of measurement accounting allows you to monitor the dynamics of the jump (growing or falling) and draw appropriate conclusions.
VERT sensor
In this case, a specialized VERT sensor is used. It is a special device that is used to measure jump performance. Must be worn at the athlete's waist - attached directly to clothing thanks to clips or inserted into any item of clothing.
Sensor Features:
- it is possible to view the obtained measurement results on the device or on a smartphone - the presence of a data transfer function;
- no additional stationary equipment is required.
The advantage is the ability to download a specially developed VERT application to a smartphone or tablet in order to further compare personal indicators with the data of other athletes. This allows you to achieve effective results and develop your jumping ability before all kinds of international competitions.
Phone application
If an athlete is fond of basketball and has expressed a desire to improve the quality of his shot, the optimal solution would be to use the developed HomeCourt iOS application. With its help, it becomes possible to analyze personal skills and abilities, while receiving high-quality advice on improving your jump in the shortest possible time.
When using the application, you just need to point your smartphone’s camera at the playing field, after which the mobile program will be able to find not only the players, but also the basket, as well as the three-point line. The software will understand whether the ball was thrown successfully and will measure the following indicators:
- player reaction speed;
- the current angle of the leg during the throw.
Using the free version of the software makes it possible to analyze about 10 thousand throws per month. For many athletes this is quite enough.
High jump ruler
This simulator is used in sports organizations to accurately measure an athlete's vertical jump. The cost is approximately 35 thousand rubles. Movable plates are fixed to the metal body at a distance of 2 cm from each other. The jump measurement range is from 2.0 m to 3.8 m.
Jump Height Determinator
A useful trainer for developing jumping ability. A rotating bracket with white PVC plates of 70x70x10 mm in size suspended on chains is installed on the metal frame. The plates are located at a distance of 120 mm from each other and in a height increment of 50 mm. During a jump, the athlete hits the plate with his hand, deflecting it to the side, and thus the result of the jump height is recorded.
DIY height meter
Developing technical basketball skills at home
Once the strength training system has been established, you should move on to direct basketball training at home. For those living in the private sector, restrictions are kept to a minimum. Residents of apartment buildings will have a more difficult time, but there is also a way out. The main problem with home basketball training is the noise level that will certainly accompany almost any activity. The BallGames project team has selected optimal and silent exercises with a basketball ball
and without at home:
— Broadcast
. All you need to do is call your friends or parents and perfect the technique of passing with one hand, two hands, behind your back, behind your head. You should alternate between a basketball and a weighted ball (you can do it yourself). If you have several friends, then an exercise for 3 or 4 people called “machine gun fire” is perfect. We described it in our article about passing techniques in basketball;
— Throw
Sitting on a chair and taking the ball in one of your hands, you need to concentrate all your attention on the correct throwing technique. The hand movements will be exactly identical to a standard throw - from a triple threat position, the hand rises in one movement, releasing the ball at the highest point from the tip of the middle finger to the very ceiling
In this case, the ball should be directed forward, with the point of impact near the toe (it is worth catching it at chest level);
— Deceptive movements
. Who said basketball training at home can't be done in front of a mirror? There are a number of moves that will force your opponent to change their movement in the wrong direction, which will result in you being beaten and scoring points. These are the movements that should be practiced without the ball. From the outside, this will be very reminiscent of the work of a boxer and “shadow boxing,” but thanks to extreme concentration on the task at hand, it will create the basis for subsequent work with the ball. Suitable exercises include pointing with the body and head in one direction and moving to the other, moving the ball under the foot with a step forward and stopping with a readiness to throw, and much, much more. The most important thing is to train in gaming shoes with good grip;
— Footwork
. The success of advancing to the ring depends on the speed and sharpness of the first step. A two-legged stop, a pivot, a Eurostep, a step-up—this is the minimum set of movements in the arsenal of a modern basketball player. It is worth concentrating as much as possible on proper footwork;
— Reaction
. The simplest tennis ball provides a wide range of exercises for basketball without a ball. Unlike its older brother, a tennis ball can be thrown against a wall (preferably internal partitions) and hit on the floor without negative emotions from neighbors. By the way, if you don’t have a tennis ball, then for some of the exercises you can use an apple, an orange, and make a weighted ball from a grapefruit by stuffing it with cereal and wrapping it with tape;
— Feints
. After all, why not learn how to spin a basketball on your finger? Of course, this will not directly affect the development of basketball skills, but it will bring emotional pleasure and create a new challenge for your own capabilities. Other basketball exercises at home will require you to have a prepared podium that will act as a damper and prevent vibration and sound from reaching your neighbors. You can assemble one from four Euro pallets, laying sheet rubber under them with an additional layer between the floor and the pallets themselves (installation on a sheathing with rubber inserts).
Jumping ability assessment
There are basic rules for keeping records of changes in the dynamics of “jumping ability”.
Jump measurements must be carried out:
- at the same time - morning, afternoon or evening; before warm-up, after warm-up or training;
- in the same place - indoors or outdoors;
- with the same mentor;
- in athletes without health problems.
Tests for assessing jumping ability
| Jumping test | Result |
| Perform a running jump with a push of both legs. The task is to touch the marking line or higher | The best result out of three attempts is counted |
| Stand on your toes, extend your arm up. Fix the highest point of contact (1 point). Perform a running jump with a push of both legs. The task is to touch the marking line or higher (2nd point). Calculate the difference between 2 and 1 points | The best result out of three attempts is counted |
| "Uccelli Test". Perform a running jump with a push of both legs, touching the marking line. Fix height ( 1 result). Stand on your toes, extend your arm up. Record the highest point of contact ( 2nd result). Calculate score - result 1 divided by 2 |
|
| Perform a standing long jump. Record the result |
|
Tests to assess jumping endurance in volleyball players
| Jumping test | Result |
| Jumping to the “optimal” height (add 100 cm to height for men, 80 cm for women). Jump from a place with a push of two legs and reach the marked marks with both hands. End the attempt the first time the mark is missed | Record the number of jumps and compare with previous indicators |
| Perform running jumps, reach the “maximum” height with one hand (- 10 cm) The attempt ends when the mark is missed for the first time | Record the number of jumps and compare with previous indicators |
| Set the jumping bar at a height of 75% of the athlete’s maximum jump height. Perform a jump over the bar by pushing both legs sideways to the bar | Record the number of jumps and compare with previous indicators |
| Perform a running attack from zone 4 (2). The assistant throws the ball. Perform strikes with an intensity of 12 beats/min for a certain time (3 minutes for men and 2 minutes for women) alternately at two targets (3x3 m squares), marked along the side lines behind the attack line. Evaluate whether the ball hit two targets. Count the number of ball losses (shots into the net, out, off target) |
|
Schedule:
to complete the Air Alert 3 program three days a week, and it is very desirable at the same time. The entire program will take 15 weeks (just under 4 months).
Designations such as 2 x 25 in the table above mean that you need to do two sets of 25 repetitions each.
The third version of the Air Alert program suggests resting between sets, not exceeding 2 minutes, while there SHOULD BE NO breaks at all between exercises. When you pause between sets, massage the muscles that are currently under stress.
The best time of day to perform the exercises of the program will be 13-15 hours (peak time for muscle work).
Week 13 is for complete rest. You should not do any exercise this week.
14 * - this week specifically has reduced amounts of exercises, since it is preparatory to the last 15th week.
15 ** - exercises during the 15th week are performed 4 days - on Monday, Tuesday, Thursday and Friday. The last week is characterized by maximum load on the muscles before final recovery. Therefore, the number of repetitions here is increased, and classes are held for 4 days. Your jumping ability will reach its maximum 4-7 days after finishing the program.
Important! Air ALERT III has its own specific execution schedule!
On odd numbered weeks (1, 3, 5, ...) complete the program on Mondays, Wednesdays and Fridays.
On even weeks (2, 4, 6, ...) the program must be performed on Tuesdays, Thursdays and Saturdays.
On days when you are not performing the exercises of the program, it is ideal to still give the usual jumping load to the muscles, which would be best done in a game. Just go out on the court and play. At the same time, try to do all jumps “aggressively” enough to maintain and consolidate a certain muscle memory.
If you wish, you can also go through the presented program again, but the break after the previous time should be at least a month. In addition, you should understand that repeating it will not bring the same good results as the first one.
Well, friends, that’s basically all. Here she is. The famous program for developing jumping ability Air Alert 3, in all its glory is in front of you in this post. Then it's up to you, actually. Start training when you're ready.
I wish you all pleasant and productive activities, good results that please you, good health, muscles, joints, nerves. (: In general, all the best to each of us, and may our jumps continue higher and higher and higher...
General Tips
- Keep an athlete's diary to track changes in the dynamics of jumping ability.
- Schedule a personal training program day by day, taking into account the personal multifunctional characteristics of the athlete’s body.
- Keep records of indicators. Use a green marker to mark the best results.
- Build graphs based on the taken indicators for analysis and better perception of the results of the work done.
- Make adjustments to the training process when jumping results drop.
- Perform intense exercises to improve jumping endurance in 2-7 sets of 10-20 jumps or 1-4 minutes. The interval between approaches is 2-4 minutes or rest until the heart rate is restored (120-130 beats/min).
- Do not exceed the number of repetitions in one approach: 20-25 - in jumping exercises with overcoming your own body weight, 10-15 - in exercises using small weights.
- Switch to a moderate load to speed up recovery after intense exercise. Jogging is suitable for this.
- Strengthen the extensor muscles of the knee and hip joints, and the flexor muscles of the foot using special jumping exercises.
- Select the weight of the weight individually. It should not cause significant disruption to the technique of movements and lead to a slowdown in the speed of the jump.
- Pay attention to the amplitude and angular values of leg bending when performing jumping exercises.
- Record the time of occurrence of maximum muscle effort.
- You should not start practicing jumping exercises in a state of fatigue or poor health. The results of such training will be zero.
- To increase the effectiveness of your training, alternate jumping exercises with strength training, easy running and relaxation exercises.
- To develop jumping ability in your practice, use the main methods - repeated, “impact”, variable, circuit training, dynamic efforts, game, competition.
How to learn to jump high
Using basic methods for developing jumping ability, you can increase your jumping ability and explosive power.
Repeat method
- The idea of the method: physical activity alternates with intervals to restore performance.
- Objective: to increase the level of functional capabilities of the athlete’s body.
- Rules for execution: complete the repetition of the exercise at the moment of a noticeable decrease in the efficiency of the movement, as fatigue begins to develop. The rest pause between repetitions should be sufficient to restore the body’s performance and the athlete understands that he can perform the exercises efficiently.
Dynamic force method
- The idea of the method: exercises are performed with light weights (up to 30% of the maximum) at a fast pace.
- Task: to increase the indicators of “explosive” strength.
- Rules of execution: the exercise in one series is repeated 15-25 times. The number of episodes is 3-6, the break between them is 5-8 minutes.
"Shock" method
- The idea of the method: to use your own body weight for a sharp transition of the muscles into an active state, which creates an additional tension potential in it, which provides significant power and speed of the subsequent pushing movement, a rapid transition from inferior to overcoming work occurs. Example of exercises: jumping from a height in depth and instantly jumping up or long jump.
- Task: to increase the indicators of “explosive” strength.
- Rules for execution: jumps are performed by well-trained athletes - 4 series of 10 times, beginner athletes - 2-3 series of 6-8 times. The rest interval between series is 6-8 minutes, filled with light running and relaxation exercises.
- Features of the method: the musculoskeletal system is fully formed and the athlete has an integrated approach to physical activity.
Variable method
- The idea of the method: while performing jumping exercises, consistently change the weight of the burden, the speed of movement, and the amount of effort.
Complex workouts:
- Perform jumping exercises with different barbell weights of 50 (100, 150)% of your own weight in the following sequence: 50% - 10-12 times, 100% - 8-10 times, 150% - 5-7 times, 100% - 8-10 times, 50% - 10-12 times.
- Perform jumps on one leg in the following sequence: triple, fivefold, tenfold, fivefold, triple.
- Perform, with a rest break (10-15 seconds), 3-4 series of jumps in the following sequence: 10 jumps with alternating legs (2 on the left, 2 on the right), 8 jumps from foot to foot, 6 jumps on one leg (left, right).
Circuit training method
- The idea of the method: a special complex is performed sequentially. The athlete moves from performing one exercise to another, from one place of execution to another. After completing the last exercise in this series, he returns to the first.
- An example of circuit training. The athlete consistently performs: jumping with a barbell on his shoulders - 8 times; jump from foot to foot - 10 times; jumping with a weight in your hands - 8 times; jumping with two legs from a half-squat - 10-12 times; jumping onto a height (40-50 cm) with a push of two legs - 8 times; two-legged jumping over hurdles - 8-10 hurdles.
- Rules of execution: rest between exercises - 15-20 seconds, series - 2-3 circles, rest between series - 6-8 minutes.
- Features of the method: the number of laps, duration and content of exercises are selected taking into account the physical fitness of the athlete.
Game method
- The idea of the method: during a game situation, the athlete switches between the work of different muscle groups.
Competitive method
- The idea of the method: jump higher than your opponent, improve the result of your jump.
Exercises to develop jumping ability
To increase jumping ability, the training process uses exercises aimed at developing:
- maximum jump force;
- speed of motor reaction;
- movement speed.
To develop jumping ability, a set of exercises is compiled for each muscle group involved in the jump.
The lesson plan for developing strength and jumping ability includes the following exercises:
- General impact exercises with heavy weights.
- General strength exercises performed with light weights and at the highest possible speed.
- Jumping exercises are similar in structure to a competitive jump, for example, a volleyball player’s attacking jump or a basketball player’s jump when throwing a ball around the hoop.
Using exercises with additional objects during the training process, an athlete can increase the height of a standing jump by 6-8 cm in 12 weeks.
Experts advise an athlete to develop jumping ability:
- perform repeated jumps aimed at developing the speed of contraction of the extensor muscles of the knee and hip joints;
- use additional objects, since jumping with light weights preserves the structure of the movement;
- between series of jumping exercises, do a rest interval of 2-3 minutes to restore jumping ability.
To prevent injuries to the knee and ankle joints, when increasing the jump height in jumping exercises, do not forget to reduce the weight of aggravating objects.
Types of jumps
Knowing the types of jumps, it will be easy to diversify individual complexes to improve the athlete’s jumping ability.
Jumping:
- on the right (left) leg: in place, moving forward, across the line;
- on two legs: in place, with advancement, across the line;
- from foot to foot;
- legs apart - together;
- side steps;
- with different jump heights and waving your arms in place;
- with rotation 90, 180, 360°.
Jumps:
- walking with a heel-to-toe roll followed by a jump;
- with a swing of the leg and arms;
- with the removal of a suspended object.
Jumping on one and two legs on:
- line;
- item.
The starting positions for performing jumps are various types of stance and squat.
The necessary conditions
More often, manuals recommend developing the abdominal muscles. But even if you train daily, you may not see any results, because at high intensity the muscles do not have time to recover. To give them this opportunity and get the effect, classes are held 3-4 times a week. This way the athlete does not experience overtraining, muscle tension and wear and tear.
To improve your jumping, you need to pay enough attention to it, i.e. perform exercises that develop jumping ability, without making concessions to yourself or skipping classes. Jumps in athletics are distinguished by technique, but they are all the same in terms of the final result. If the question of how to increase the jump is faced by a basketball or volleyball player, athletics terms should be left aside, as discussed below.
Jumping exercises
Multi-jump mechanism:
- When pushing off, the pushing leg is completely straightened in all joints.
- The swing leg, bent at the knee joint, is energetically sent forward and slightly upward with the knee.
- The torso is tilted forward.
- The arms, bent at the elbow joints, move vigorously back and forth.
Keep your body position strictly vertical. Actively help with your hands. Steps spring.
Exercise - simple multi-jumps
Starting position: stand straight (right side, left side). Perform jumps:
- on two legs. Taking off and landing is performed with both legs;
- on two legs up stairs;
- from foot to foot;
- on one leg;
- on one leg up the stairs.
Perform the same jumps on your toes.
Starting position - half squat. Jump up.
Starting position - squat. Jump up.
Exercises - complex multi-jumps
- Starting position: stand straight. Take the right ankle from behind. Perform jumping jacks on your left leg. Repeat the jumps, changing legs.
- Starting position: stand straight. Take the ankle of your right foot in front. Perform jumping jacks on your left leg. Repeat the jumps, changing legs.
- Starting position: stand straight. legs together. Perform jumping jacks on one leg, pulling your knees to your chest. Same thing on two legs.
- Starting position: stand straight, legs apart. Perform jumps on one leg, touching your toes with your toes.
- Starting position: stand straight, legs apart. Perform triple, quadruple jumps with a push with one or two legs.
Multi-jumps can be performed on soft ground, mat paths, and sand.
Standing long jump
Starting position: stand straight, place your feet shoulder-width apart, parallel to each other. Perform a jump, pushing off with both legs, swinging your arms forward and up.
Options - perform a jump:
- standing sideways, in the direction of the jump;
- with rotation 90°, 180°;
- in length from foot to foot, having previously agreed on the number of jumps or distance;
- two on the left, two on the right;
- from a deep squat to maximum length;
- from a half squat on one leg, my legs.
When jumping, stretch out as much as possible, applying force in two directions (horizontal and vertical). When landing, push your shoulders forward and try to keep your legs high. Strive for a wide range of motion and land on both legs at the same time.
A set of exercises for learning to pass the ball
What's Elton's point: race report and analysis of typical mistakes of an ultramarathon runner
Basketball is a team game. One player will not do the work that is assigned to the partners. Passing and the speed at which it occurs directly affects the tactical mobility of the entire team.
Two-hand pass to the wall
Starting position: legs bent, feet shoulder-width apart. The back is straight, the torso leans forward.
The pass is made with a push movement from oneself to the level of the player’s head.
In the second approach, the level of delivery changes to the chest area. The exercise is performed the number of times in one minute.
One hand against the wall
The starting position is similar to a two-handed pass. The transmission starts from the right shoulder behind the right ear. The pushing right hand is positioned behind the ball, fingers pointing upward. The guiding left hand is in front.
At the beginning of the transfer, the body weight shifts to the back leg, “charging” it. The ball comes off the hand, the body weight shifts to the front leg, and the arm completes the movement by rotating the forearm and hand inward and downward.
Reference! The thumb of the working hand should be located below.
Lying with one hand
The athlete lies on his back. At the moment of passing, the torso lifts and pushes the hand, which launches the ball. The position of the hands is the same as when passing with one hand into the wall.
Jump legs apart - legs together
Execution technique
- Starting position: stand straight, heels together, toes apart (foot width apart).
- Push off with both feet and jump up low.
- Lower your entire foot and assume a half-squat position. Feet are shoulder-width apart, slightly turned outward or parallel to each other.
- Important: distribute the weight of the body on both legs, point your knees and feet in the same direction, the angle at the knee joints is more than 90°.
- Bring your legs together with a small jump and return to the starting position. Important: do not allow the body to bend or turn.
Footwork technique
Simultaneously with the development of basic techniques, tactical game elements are introduced into the training.
Stops are elements in attack technique. Their task is to help the athlete get rid of the opponent and gain an advantage in attack.
Mastery begins simultaneously with the study of two-step throws, since this rhythm is the main one for attack techniques in motion.
Jump stop
The player takes a running start, pushes off the floor with his foot and makes a long jump as he moves. Landing is practiced in two ways:
- Landing on both feet at the same time.
- Landing on the supporting leg and then placing the second leg.
To consolidate the skill, practice it in motion:
- Stopping with a jump while walking or running.
- Jump stop after the signal.
- Jump stop after dribbling and catching.
Photo 2. The correct technique for performing a stop with a jump on both legs at the same time is shown.
Stopping with steps
Applies when the ball is in the player's hands. The athlete leads with a long step of his right (for a left-hander, left) leg, rolling from heel to toe, pulling the projectile to his chest. The second step is short with a turn of the body. Stopping occurs due to the distribution of body weight on both legs. The skill is reinforced as follows:
- Walking and running. The first step is short, the second is long.
- Starting position: the player stands, holds the ball in his hands. Then he throws it forward and up, tries to catch the projectile with a stopping step: the first long, the second short, stopping step.
Zigzag without the ball with a jump stop
To practice this technique, landmarks are used - cones or chips.
The track is set in such a way that the line from cone to cone gives a diagonal.
The player moves in dashes and stops in front of each cone with a two-legged jump and fixes the position.
Important! Legs bent at the knees
Zigzag without the ball with stopping steps
It is performed in the same way as a zigzag with a jump stop, only at the end of the diagonal the athlete stops in two steps and fixes the position.
Power jumping exercises
Weighting is external resistance to movement (barbell, weights, vests), complicating the exercise, helping to increase muscle effort.
Exercises with a barbell on the shoulders
Starting position - squat (half squat). Jump with your arms up.
Starting position - stand. Perform a slow squat with a sharp rise to your feet and jump up.
Starting position - stand. Perform hops on one or two legs:
- on the spot;
- with moving forward;
- with changing legs in a lunge position.
Set of exercises: squats with a barbell weighing 70-80% of the maximum (2 sets of 5-6 times), rest (4-6 minutes), standing triple jumps (2-3 sets of 6-8 times).
Set of exercises: squats with a barbell weighing 80-85% of the maximum (2 sets of 2-3 times), rest (3-4 minutes), jumping with a weight (2 sets of 4-6 times).
The optimal weight of the weight is: for beginners - 3-4% of their own weight, for athletes with advanced categories - 4-5%. Special belts, vests, barbells, and dumbbells are used as weighting materials. Exercises are performed in 2-3 sets of 5-20 jumps.
Exercises with an object
Pick up an object (medicine ball, dumbbells, barbell)
- Perform a squat with a sharp rise to your feet with a wave of your arms up.
- Perform a squat with a sharp rise to your feet and jump up.
- Perform serial jumps with dumbbells in your hands in a half-squat (squat) position without pausing with an active swing forward and up.
- With dumbbells in your hands (arms pointing down), perform jumping jacks on one leg, on the forefoot, in place.
- With dumbbells in your hands (arms pointing down), perform jumps on one leg, on the front of the foot, moving forward 20-30 cm.
- Take a rack position, a gymnastics bench between your legs, dumbbells or barbell discs in your hands. Perform jumps on the bench - feet together, from the bench - feet apart: in place; with moving forward.
- Repeat the complex 2-3 times: jumping with a weight or a disc from a barbell (2 sets of 8-10 times), rest (3-4 minutes), jumping from foot to foot (2 sets of 10 times).
Exercises with medicine balls
- Starting position - squat (half squat), medicine ball in hands. Perform serial jumps up, extending your arms with the ball and legs at the same time.
- Starting position - squat (half squat), medicine ball on shoulders. Perform serial jumps up, the pushing leg is in front.
- Starting position: stand with your legs apart and place a medicine ball between your legs. Jump up with your feet touching the ball and land in the starting position.
- Starting position: stand with your feet together. Jump forward and backward over a medicine ball; forward and backward with a 180° rotation.
- Starting position: - one foot on the ball, bend the other. Jump on one leg around a medicine ball, leaning on it with the other leg; - stand-up, hold the ball (3 kg) in straight hands above your head. Perform jumps on the coordination ladder; - stand up, hold the ball (3 kg) in straight hands above your head. Perform tempo jumps in place (moving forward); - squat, hands behind head with ball (3 kg). Perform upward jumps on one leg, the other one behind in place (moving forward).
- Perform jumps on two legs (one leg, from foot to foot) through 10-15 medicine balls located on the same line at a distance of 80-100 cm from one another. Perform jumps on two legs (one leg, from foot to foot) through 10-15 medicine balls located on the same line at a distance of 80-100 cm from one another, with dumbbells in your hands.
Air Alert 3 program
Why Air Alert 3? It's quite simple. Because the person who recommended this program to me said that the third one was the most sensible in his opinion. And I am inclined to trust his opinion, as I wrote above, in this matter, since he, along the way, went through all the Air Alert programs, in addition to a lot of other training, because he himself is a basketball player... so. Here it is - the Air Alert 3 program - a set of exercises for training jumping ability that will help me and you learn to jump high. And why exactly does anyone need this? Learning how to do dunks or, for example, ideally playing the role of a kangaroo in a musical about Australia is everyone’s business.
The Air Alert 3 program was developed by TMT sports specialists, essentially refining some aspects and improving the very popular previous Air Alert 2. The new program, however, has been changed quite noticeably. The total course time was increased to 15 weeks, while the frequency of exercises was reduced to 3 days a week (with the exception of the last 15th week). Air Alert 3 also involves doing exercises on strictly defined days of certain weeks! The creators of the program assure that after completing a full course of 15 weeks, you can increase your jump height by 20-35 centimeters. At the same time, it is very important to ensure good nutrition and sleep throughout the 4 months of the program.
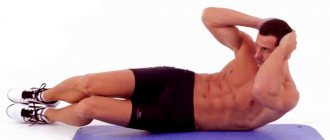
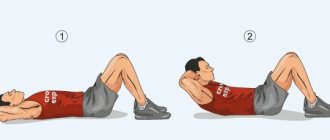
High jump
Execution: Place your feet shoulder-width apart. Jump vertically upward as hard as you can. As you lower yourself to the ground, squat down about a quarter—this will be one jump.
Note: In this exercise, the most important key factor is the speed of the jump. The point is to jump up as quickly as possible, while the time you spend on the ground between jumps should be literally fractions of a second.
Calf raises
Execution: To begin the exercise, stand on your toes so that your heels do not touch the ground. For example, it could be a small step, a threshold, a thick book, some kind of board. Rise as high as you can on one leg. Then do the same on the other leg.
Rest 25-30 seconds between sets.
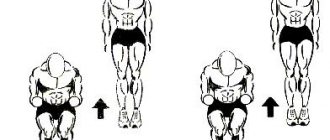
Step-ups
Execution: Place one foot on some strong elevation, for example a bench, chair, parapet on the street or something else, preferably quite hard. Next, we push up with our supporting leg, and already in the air we switch our legs. After this, we repeat the same thing with the other leg.
Jumping on straight legs
Execution: Place your feet shoulder-width apart. We do high jumps without bending our knees. Try to jump as high as you can.
Rest for a minute between sets.
In this exercise, the most important factor is the speed of execution. Try to jump out as quickly as possible, spending only a split second on the ground between jumps.
Burnout
It is no coincidence that this exercise is called “burning out”, since if performed correctly, you should feel a burning sensation in the muscles of your legs.
Execution: Take a half-squat position, raising yourself on your toes, lifting your heels from the floor. Jump in this pose, never resting on your heels. At the same time, also try to focus on the speed of execution, making sure not to drop your heels, jumping only on your toes.
Jumping in full squat
Full squat jumps are a new exercise in the program. It is designed to put stress on the entire hips, helping to increase the so-called “explosive force” of the jump. In addition, this exercise is good for improving cardiovascular endurance, lateral speed, and speed over short distances.
- You can pick up a ball for more balance, but this is not necessary.
- Squat down completely. You need to sit on your toes with your heels raised, while your hips should be parallel to the floor line and your back straight and perpendicular to the floor.
- Jump 10-15 centimeters in this position, while trying to completely keep the floor parallel to your hips.
- As soon as you land on the ground, push off again.
- When performing the last jump in a set (for example, the 20th of 20 jumps), jump as high as possible from a full squat up.
This exercise, due to its very heavy load on the muscles, must be performed only once a week, on Wednesday. If you increase the frequency of this exercise, you risk overloading the muscles, thereby significantly increasing recovery time, reducing the overall jumping tone of the legs for a long period.
The end of each set should end with the most “explosive” jump to the highest possible height for you. At the same time, it is extremely important to jump with maximum sharpness, which will make the thigh muscles work well, strengthen them well and generally add 3-5 cm to the jump during the entire course.
Exercises using sports equipment
Exercises using a gymnastic bench
Jumps are performed:
- from the starting position relative to the bench - face, side, back;
- in place, with advancement in any direction;
- from the bench, to the bench, jumping over the bench.
The location of the bench in the gym is two rows of 2-3 benches in a row, parallel to one another, in a cross, a star, a rectangle, a triangle, a square.
- Starting position: stand with your legs apart, a bench between your legs. Perform tempo jumps for a while (20, 30, 45 seconds) on the bench - feet together and from the bench - feet apart: in place; with moving forward.
- Starting position: stand with your legs apart, a bench between your legs. Jump up with your feet touching the bench (legs together) and land in the starting position: on the spot; with moving forward.
- Starting position: stand with your legs apart, a bench between your legs. Perform upward jumps with your feet touching the bench (legs together) and turning 180°.
- Starting position: stand facing (sideways) to the bench. Perform tempo jumps on and off the bench in place and with advancement.
- Starting position: stand facing (sideways) to the bench. Perform a jump over the bench in place and with advancement.
- Starting position: stand with your legs apart on two gymnastic benches. Perform deep jumps between the benches for a while (20, 30, 45 seconds), followed by jumping into a legs apart position on the benches.
- Starting position: stand on one leg. Perform jumps on one leg moving forward by jumping and jumping off benches.
- Starting position - stand. Perform forward jumps over benches on two legs (on one leg).
Exercises with a stand
To perform the exercises, use a specialized simulator - a stand for practicing jumping ability.
Execution technique
- Stand on the stand.
- Take a step forward and, as you begin to fall, attach your other leg to it.
- Land on both feet. Important . The landing should be elastic and shock-absorbing.
- Use a shock-absorbing mat to prevent ankle injury.
Stands for practicing jumping ability. There is an anti-slip coating. Height - 0.1; 0.2; 0.3; 0.4; 0.5; 0.6; 0.8; 1.0 m.
Starting position: stand on a stand. Jump off the pedestal and make a jump:
Options:
- jump up;
- long jump;
- 3 long jumps.
Starting position: stand on a stand. Jump from the pedestal, jump onto another pedestal.
Options:
- jump and jump onto another pedestal, jump and jump onto another (up to 10 jumps). After the last stand - jump up or long jump;
- jump off the pedestal, jump over the athletics barrier, jump onto the next pedestal;
- jump onto a hill, jump with a 180° turn.
Variant of exercises with a pedestal - serial jumping over benches:
- sideways;
- sideways from foot to foot;
- with a rotation of 90°,180°.
Jumping on the steps of a ladder is performed on one or two legs, up, down.
Variant of the complex with steps: jump on both legs over the step, jump one step back, jump up again over the step, down one step, etc.
Exercises using track and field hurdles
To perform exercises, up to 10 barriers with a height of 40-90 cm are placed in the hall at a distance of 1-1.5 m from one another. The height and distance between barriers must correspond to the age, gender, and preparedness of the athlete.
Jumping over hurdles can be performed with dumbbells in your hands, as well as with weights on your legs.
The optimal height of the barrier is 70-80% of the maximum standing jump for men, and 60-70% for women.
Perform two-legged jumps through:
- four barriers arranged in a “cross”. Execution time - 10-15 seconds;
- one barrier with a 180° rotation. Execution time - 10-15 seconds;
- barrier. After landing, perform a starting dash of 7-10 m;
- three barriers of different heights. After landing, perform a starting dash of 7-10 m;
- one barrier. After landing, perform a starting dash of 5-7 m and jump with your hand reaching for a suspended object;
- a barrier followed by acceleration, catching and passing the ball to a running partner;
- a hurdle followed by a fast long jump;
Perform jumps with a short run (pushing off with one leg):
- Having overcome a barrier with a height of 76-91 cm, land on the swing leg (push leg);
- take out the suspended object and jump over the barrier;
- through 5-7 hurdles, land on the swing leg, perform an intermediate step between the hurdles from the swing leg to the push leg;
- through 5-7 hurdles, land on your swing leg, perform two intermediate jumps between the hurdles on one (two) legs.
Perform jumps on one leg over 7-10 low barriers, cover a distance of 10-20 m by jumping on one leg.
Method "Stepping over"
It is also called “scissors” and is one of the simplest techniques to perform a running high jump.
The jumper runs at an angle of about 30-40 degrees and consists of only eight running steps. In this case, the athlete pushes off with the far leg from a distance of 80 centimeters. The pushing leg in this case is absolutely straight, just like the swing leg. The latter bends only at the highest point. The body in a jump is vertical, and the bent arms rush upward. While the athlete reaches the bar with his swing leg, the pushing limb is also pulled towards it. When she crosses the bar, the athlete turns his shoulders towards her. The body is pulled back due to the fact that the athlete moves the pushing arm back. He lands sideways on his fly leg and turns his chest toward the crossbar. The “Stepping Over” method is good because it doesn’t require a special place to land correctly. As a result, the athlete can easily land on ordinary mats in the gym.
Exercises in pairs
- “Cockfight” Starting position: bend your left leg and hold your foot with your left hand, bend your right hand at the elbow and place it behind your back. The task is to jump on one leg and push your partner’s shoulders.
- "Salki." Starting position: bend your left leg and hold your foot with your left hand, bend your right arm at the elbow and place it behind your back. The task is to jump on one leg to catch up with your partner.
- The starting position is to stand facing each other, holding outstretched hands. Perform jumping squats on one leg: in place; in different directions.
- Starting position: - stand facing each other on one leg, put your hand on each other’s shoulder, and grab the shin of your leg with your free hand. Perform jumping movements on one leg; - face each other. Move by jumping in a squat to the sides, throwing a medicine ball with both hands from the chest to a partner.
- Starting position: - stand facing each other. The first one stands on the right leg, the left leg is forward and upward to waist level, the partner holds the left leg with both hands by the ankle joint. Perform jumps on one leg (on the front of the foot) moving forward 20-30 m. The partner pulls the straight leg. Repeat the exercises on the left leg; - face each other. Hold the ankle joint of your partner’s opposite leg with your hand, the other hand on your partner’s shoulder. Perform jumping jacks on one leg in place; forward and backward; moving left and right.
- Starting position: - the first partner is in a supported position, crouching on one leg, the other leg, laid back, is held by the partner's ankle joint. Jump up while moving forward; — stand in a column (from 3 to 6 people). Take your partner's opposite leg with your hand by the ankle joint, and place the other hand on your partner's shoulder. Jump on one leg simultaneously forward and to the sides.
- Starting position - stand on opposite sides of the bench, hold hands. At the signal, without separating your arms in motion, perform a synchronized jump to the left, to the right, in place.
Training program
You don't need any special equipment to start high jump training. They are quite doable at home. The program for increasing the jump includes moving 15 times with a pause of 15 seconds, in total you need to do 3 approaches for each exercise.
Description:
- Exercise 1. Take a lying position. You need to bend your left knee and place the foot of the same leg between your hands. Next, you will need to lean on your left leg and completely straighten your body, then jump, while raising your right knee and left arm up. After returning to the starting position, change legs.
- Exercise 2. Take a straight position, and your arms should be extended at your sides. In this position, the performer will be required to jump as high as possible, while pulling his arms towards the floor, and leaving his legs straight without moving to the side. Upon landing, you will need to squat and spread your knees to the sides at a right angle. After this, jump up and return to the starting stance.
- Exercise 3. You need to sit down completely and then jump. Your arms should be raised up as you jump and then rotated 90 degrees to land on the ground. Next you will need to jump again, but this time turn to the right.
- Exercise 4. Take a push-up position and bring your legs together. After this, you need to jump, while your hands should not be torn off the ground, and your knees should be bent. The movement will need to be repeated in reverse order.
Special jumping exercises
- Starting position - pushing leg in front, swing leg behind, arms in a swing position before taking off in a high jump. Perform a swing movement and push-off, “hit” with your swing leg the ball suspended at a height of 130-160 cm.
- Starting position - stand. Jump from a step up with one leg, reach objects located at a height with your head, chest or swing leg.
- Starting position - stand. Jump up with a running start and land with your pushing foot on a stack of mats with a height of 40 to 80 cm.
- Starting position - stand. Perform a take-off jump with one, three and five take-off steps. Land on your push foot.
- Starting position - stand on soft ground (sand, mat path). Jump up from one to three take-off steps.
- Starting position - stand. Perform a straight take-off run, jump over the bar, and land on your push leg.
- Starting position: place your swing leg on a raised platform and put weights on your shoulders. Perform jumps on the pushing leg.
- Starting position - stand. Take a running start with one step, throw medicine balls, catching them with the toe of your swing leg.
- Starting position - stand, put cuffs weighing 1-3 kg on your forearms. Perform serial take-off jumps with one and three take-off steps, using your arms.
My background
First, a little background. I really liked basketball back in the 5th grade, and ever since then I LOVE THIS GAME. For some time in my teens I played basketball professionally. But not for very long. (: Then breakdancing appeared in my life, so basketball took a bit of a back seat, but at the same time I often played on the street, in school gyms, and generally everywhere whenever possible.
It is worth noting that in my life up to this point I had already done slam dunks several times, only with a couple of concessions.
- First, there was the hoop in my school yard, which, according to the guys who used to play there regularly with a tape measure, is located at a height of 3 m 2 cm from the surface of the court, while the standard height of a basketball hoop is 3 m 5 cm (or 10 feet ).
- Secondly, I dunked not with a basketball, but first with a tennis ball, and then with a small Coca-Cola ball, slightly smaller in size than a handball.
That's all. Several years have passed since then, during which I, one might say, did not play basketball at all, and I also did not do anything else where you can learn to jump well. Only breakdancing and riding all sorts of extreme mechanisms. (:
Nevertheless, the desire to learn how to jump high and still make slam dunks on a standard hoop with a standard basketball ball has not disappeared anywhere, and even vice versa - it has become even more ingrained in my mind as a powerful challenge, a challenge, as I already said, for myself, with a very, essentially, specific goal - to develop jumping ability and learn how to do slam dunks.