From this article you will learn:
- What are the benefits of exercise therapy for the lumbar region?
- The effectiveness of exercise therapy for the lumbar region and the main contraindications
- 10 principles of exercise therapy for the lumbar region
- Features of exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
- What you need to know about exercise therapy for the lumbar region
- How to prepare for lumbar exercise therapy
- Effective exercise therapy for the lumbar region depending on the stage of the disease
- Gentle physical therapy exercises for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
- Exercise therapy training exercises for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
- 5-minute exercise therapy for the lumbar region
- Exercise therapy for the lumbar region with a fitball
- Exercise therapy of the lumbar region according to the method of Bubnovsky and Evdokimenko
Exercise therapy for the lumbar region is one of the most effective methods of treatment and prevention of complications of spinal diseases.
Physical therapy exercises take into account all the features of the pathologies of this zone. But in order to defeat the disease, you need not only to ensure that they are performed correctly, but also to be aware of the existing contraindications.
What are the benefits of exercise therapy for the lumbar region?
Nowadays, almost everyone has heard about spinal osteochondrosis. According to the World Health Organization, 80% of the Russian population has pathologies of the musculoskeletal or musculoskeletal systems. This applies not only to older people, but also to the younger generation aged 29 to 49 years.
Many people feel back pain. It causes discomfort and reduces performance. After therapy, some patients never manage to return to their previous lives, because the disease becomes chronic. This significantly interferes with the return of performance to the previous level or even provokes its cessation.
Back pain is most often related to osteochondrosis. The pathology is very common and can affect anyone.
Osteochondrosis is accompanied by metabolic disorders in intervertebral cartilage and discs. As a result, the muscular and skeletal systems change. It has been proven that the spine has a significant impact on the internal organs, which means they are also subject to pathological transformations. Many doctors say that the most effective therapy for osteochondrosis is physical activity. Therefore, we advise you to pay special attention to exercise therapy for the lumbar spine.
How does osteochondrosis develop?
The spine contains from 33 to 35 vertebrae, and between them are elastic discs. Due to them, it has flexibility and elasticity. The disc has a core covered with cartilage above and below, and along its contour there is a fibrous ring.
Osteochondrosis negatively affects blood circulation and metabolism in the spine. In this regard, the discs dry out, decrease in height, and become less durable and elastic. The fibrous ring does not cope with its function of holding the spine, which leads to its protrusion. In addition, a rupture may occur, resulting in an intervertebral hernia. The consequence of these disorders can be mobility and curvature of the spinal column.
A healthy spine is a reality, but only with an active lifestyle and moderate sports activity. Considering that the age of modern technology forces us to spend most of our time sitting at a computer, do not forget about exercise therapy for the lumbar region. After all, this is the most effective method of treating spinal diseases, as well as their prevention.
Therapeutic exercise has a positive effect on the trophism of elastic discs. As a result, joint mobility improves, the spine is saturated with blood, and its bone components are destroyed more slowly. Exercise therapy for the lumbar region helps to recover after surgery and helps strengthen the back muscles.
Physical therapy is especially recommended for the following population groups:
- Elderly people.
- For those who have previously had vertebral injuries.
- People diagnosed with flat feet and club feet.
- For those who are constantly in a non-standard position.
- People with weak muscles and ligaments.
Osteochondrosis according to the place of occurrence can be classified into osteochondrosis of the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral spine.
Why does stooping occur and what to do about it?
In this paragraph we will not touch upon congenital causes: if a person has different leg lengths, the structure of the intervertebral discs is disturbed, or abnormal muscle development, exercises cannot correct this, or they are too specific. Let's talk about acquired disease.
In childhood
In children, stooping usually appears after 6-7 years, when the thoracic spine is finally formed. The reason is long hours spent with a tablet or phone in hand, when the child leans towards the screen, or carrying a heavy backpack on one shoulder.
If you don’t notice anything, the child may develop kyphosis or scoliosis, but at this age everything is easily corrected: the joints and vertebrae are flexible, and daily 20-minute exercises are enough to strengthen the muscles.
However, sometimes the reasons are psychological. It is useless to shout “Don’t slouch!” if the reason is fear, uncertainty, or emotional tightness. In this case, to remove stoop, it is better to do gymnastics together, or to understand the reasons for internal tightness.
During adolescence
A young body begins to grow quickly, and sometimes bones develop faster than muscles. That is why a teenager should be sent to swimming or introduced to some kind of sport, this will help make the figure harmonious.
Sometimes children are embarrassed by their height and cannot stop hunching over, as if trying to be smaller. This is solved psychologically. The body is still growing, and if we take it in time, everything can be fixed.
In adults
The problem here, most often, is a sedentary lifestyle or work where you need to bend over a table, machine, equipment, etc. How to fix a slouched back? Exercises, special exercises for stooping, and constant monitoring.
- A man is often more comfortable working out in the gym, where he pumps up his muscles so that they keep the spine straight.
- The girl will most likely benefit from home gymnastics. Women by nature are more flexible, they enjoy going to yoga, they try to maintain their posture so that their tummy does not stick out and their breasts seem more attractive.
- In older people, problems with posture often arise against the background of other diseases of the spine or internal organs, and most often, general treatment is required. But a gentle warm-up, stretching and simple exercises without strain can relieve pain and allow you to straighten up.
The effectiveness of exercise therapy for the lumbar region and the main contraindications
During movement, the lumbar and sacral regions of the spine receive the main load. The vertebrae of the first zone are very mobile, unlike the vertebrae of the second zone. The latter are a fixed articulation of five vertebrae. Exercise therapy for the lumbosacral region helps strengthen the muscle corset, helps muscles that are constrained by spasms, and relieves pain in them after a pinched nerve.
Gymnastics alternately relaxes and tenses the muscles, which leads to improved blood flow. After an illness, the tissue receives stress and becomes stronger. Classes involve performing various exercises to train specific muscle groups. Exercise therapy is used for hernia of the lumbar spine.
Carrying out physical therapy of the lumbar region on a regular basis contributes to:
- Relief from lower back pain.
- Training of spinal muscle tissues.
- Normalization of joint mobility and blood flow in them.
- Relaxation of spasming muscles.
- Improving blood circulation in the pelvic organs.
- Increasing immunity and general tone of the body.
Exercise therapy for the lumbar region will be effective only if the exercises are performed correctly. Let's look at the basic rules:
- If you are doing physical therapy for the first time, be sure to contact an instructor. Your goal is the right exercises, not quick results.
- In case of exacerbation of the disease, you need to adhere to a special training program and only under the supervision of a trainer.
- Warm up your muscles and ligaments thoroughly before starting exercise. Massage the sacrum, because it bears the greatest load.
- Increase the difficulty gradually. The first workout should include a warm-up and the simplest movements. Duration no more than 20 minutes.
- It is not recommended to eat 1–1.5 hours before class.
- Perform exercise therapy for the lumbar and sacral region on a regular basis. Avoid long breaks. Only in this case can the disease be overcome.
Recommended articles on the topic:
- How to massage the abdomen for weight loss: different techniques for health and beauty
- Stone massage: description, benefits, methods
- MRI of three parts of the spine: when is it necessary and what are the features of the procedure
Undoubtedly, physical therapy is very useful, but not for everyone. Exercise therapy for the lumbar region has a number of contraindications:
- Any bleeding of the body, including uterine.
- The presence of malignant tumors.
- Increased body temperature.
- The period of exacerbation of any chronic disease.
- Swelling and cramps, poor circulation in the legs.
- In the presence of an inflammatory process of any organ. May be accompanied by general malaise or fever.
If, while performing exercise therapy for the lumbosacral region, you notice at least one of the symptoms listed below, consult a doctor immediately. The lesson plan may need to be adjusted:
- Sharp pain.
- Receiving microtraumas and other damage.
- Malaise and deterioration of health.
- Exacerbation of a disease associated with the spine or lumbosacral region.
Exercise therapy on the horizontal bar
A horizontal bar or crossbar in a doorway is a universal device for strengthening the back muscles, including those located in the lower part. With its help, you can effectively stretch the muscle fiber, thereby making the lower back more flexible. Hanging on a horizontal bar does not require special skills or knowledge; the absence of contraindications is sufficient. Exercises on the horizontal bar are allowed for scoliosis in the early stages, osteochondrosis, and postural disorders in the sagittal plane. The use of a crossbar for intervertebral hernia and vertebral deformities is dangerous.
Exercises with a horizontal bar are quite simple. You should clasp the handrail with your palms and hang, relaxing your muscles and allowing your spine to stretch. This helps to relax all the tension and improve the condition of the spine. 10-15 repetitions are enough to get a good result. If desired, the approaches can be made more difficult by pulling the body up, or raising the legs in front of you, forming a “corner”. This will strengthen the back muscles as a whole and improve the condition of the muscular corset of the spine.
Features of exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
Most often, pain is felt in the lumbar spine, since it bears the main load. This is due to the anatomy of the human body structure.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region include pain in the legs and lower back. Their cause lies in irritation of the spinal nerve roots. Swelling forms around the irritated area of the root, increasing the pain and causing it to spread to the muscles. The affected area is affected by the resulting spasm. The process is a vicious circle. But it can be interrupted by influencing the muscle system and strengthening the muscle corset.
We recommend
Anti-wrinkle facial massage: 10 effective techniques Read more
How to do this? Exercise therapy for the lumbar region, massage and useful habits in everyday life will help you here. If pain is observed in the lower back or legs, it is necessary to perform gymnastics in a lighter form.
The objectives of exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine are to:
- relax and stretch tense back muscles;
- strengthen lymph and blood circulation in the lumbar region.
Follow the principles of gymnastics described above. Clearly remember what not to do, and then exercise therapy for the lumbar region will be useful and effective.
Is it possible to pump up the muscles of the lower back?
The development of the muscles of the lower back and sacrum is considered mandatory for everyone who cares about their health and functionality in the future. Strengthening the area is also the first step in a strength sport before performing heavy compound movements (deadlifts, squats, etc.). For those who do not play sports, training the lower back and all the core muscles is also a must. This will allow you to efficiently perform any “life” movements, from getting out of bed and bending over, to being in a standing position.
If the question of whether an area can be pumped up is purely visual in nature, then such training is unlikely to be effective. The fact is that the entire area is covered by the latissimus muscle, which, even with a low percentage of fat, does not stand out as either massive or relief. Therefore, it is recommended to pump the muscles in the lower back only with the aim of increasing physical capabilities and stabilizing the area by creating a powerful muscle corset.
What you need to know about exercise therapy for the lumbar region
The basic requirements for physical therapy are as follows:
- Classes can be started only after pronounced pain has been eliminated.
- During an exacerbation of osteochondrosis, it is recommended to do only simple movements.
- Training should be carried out on a regular basis during remission of the disease.
- Increase the range of motion and number of repetitions gradually.
- Watch your breathing, it should be measured and calm.
- Movements should be smooth. If you feel pain, you should end the session.
- The first training should be carried out strictly under the supervision of an instructor.
- Before classes, contact a specialist for advice and a program.
- Wear only breathable clothing.
If you have problems with the lumbar spine during exercise therapy, it is prohibited to:
- Use maximum loads at the very beginning of your workout.
- Make movements that lead to painful sensations.
If osteochondrosis worsens, perform exercises only in bed.
During exercise therapy for hernias and protrusions of the lumbar and sacral regions, it is contraindicated to lift weights while standing, do leg presses while lying down, jump and run.
Harmful exercises
Not all physical impacts on the lumbar region develop its flexibility and lead to improvement in condition. Incorrect technique leads to a completely opposite effect, the back becomes overly strained and begins to hurt a lot. Basic errors that can lead to dangerous consequences:
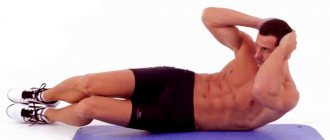
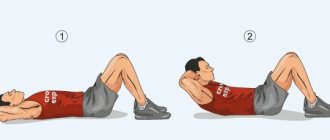
- Classic crunches for pumping the abs. It is not allowed to lift the body, lifting the lower back off the floor; only the shoulder blades should rise.
- Hyperextension. During the process, it is important to monitor the position of the upper body so that it maintains an even leg-shoulder line.
- Lying leg raises. Here athletes often make the angle between the floor and their legs more than 45 degrees, which is not necessary. The amplitude must be kept within these limits.
- Deadlift. It is unacceptable to round your back when bending over; your posture should always be maintained in an even position, with your knees slightly bent.
It is recommended to end the gymnastics with a contrast shower; you should avoid hot foods; a contrast shower is suitable for enhancing the effect. To relieve inflammation in muscle tissue and relax, immediately after training, douse yourself with water and rub your skin with a towel.
How to prepare for lumbar exercise therapy
Physical therapy may be prescribed by a doctor after the results of the examination. Don't forget about the rules that will help you make it effective:
- The best time for classes is before lunch. The last meal should take place 1.5 hours before they start.
- Every workout should start with a warm-up. It helps warm up muscles and ligaments, prepares the heart for stress.
- During the exercise, use a roller under your knees at the correct height (the thigh and shin are perpendicular to each other).
- Record the exercises you perform in your diary and monitor the results.
For osteochondrosis, there is a whole complex of gymnastics. Exercises vary in difficulty and stages. Follow the lesson plan without combining them with each other.
The lumbar exercise therapy program is divided into blocks that are intended for a specific stage.
The first stage is carrying out exercise therapy in the acute period . As simple and slow movements as possible.
The second stage is the subacute period . If the pain has decreased, you can increase the load, but gradually.
The third stage is remission . The pain has stopped, complex exercises are included.
Choose loose clothing that will not interfere with your workout. We recommend paying attention to a cotton T-shirt or tank top, shorts or sweatpants. If you exercise outside in cold weather, use woolen items.
Inventory you will need:
- Gymnastic ball.
- Swedish wall.
- Pillow for the knees.
- Fitness mat.
Reviews
How much these or other exercises help strengthen the lower back can be determined by reviews from ordinary people who included them in their workouts.
Alena M., 32 years old “I didn’t purposefully strengthen the lower back; the complex included approaches for the entire back, which made it possible to train this area as well. I stopped exercising during pregnancy, and gradually problems appeared. The Bubnovsky complex helped to quickly recover, the doctor prescribed it.”
Elena T, 45 years old “I had pain in the lower back since I was young, but I chalked it all up to overexertion. When osteochondrosis was diagnosed, the doctor recommended exercise therapy. At first the complex seemed simple, but gradually the load increased, although I did not get tired in the process, the result was already in a month. And now I try not to miss training.”
Anton P, 36 years old “I constantly strengthen my lower back after an injury, I select exercises only with a doctor. The complex includes various techniques, including yoga, Bubnovsky, and Dikul. But without correcting nutrition, lifestyle and normalizing weight, they would not have given a good result, so we had to focus on this too.”
The lower back is one of the most vulnerable places in the human body, since it bears the maximum load during movement and performing various physical exercises. It can be strengthened using various modern techniques and exercises. The process requires strict implementation of technology so as not to cause harm or cause injury.
Effective exercise therapy for the lumbar region depending on the stage of the disease
1. Acute period.
Exercise therapy for exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine should be carried out only under the supervision of a trainer. Make slow movements. If pain occurs, training should be stopped. The exercises are performed from a lying position.
- It is necessary to develop the feet by performing movements of flexion and extension. First together, then after each other. Increase the pace whenever possible. Clench your fingers into a fist and then unclench them.
- I. p. – bend your legs at the knee joint. Extend one leg, your heel should slide across the bed. Repeat for the other leg. Do eight reps.
- Raise your hand up. Once you lower it, repeat for the other hand.
- Bend your left leg and move your right leg to the side. Repeat, switching the position of your legs with each other. The exercise loads the lumbar region. Avoid sudden movements. They can put increased pressure on nerve cells and aggravate osteochondrosis.
- I. p. – put your hands on your shoulders. Move in a circle. First clockwise and then counterclockwise.
- Rest your thighs on the bolster. Straighten your legs at the knee joint one at a time.
- As you exhale, bend your arms, trying to touch your shoulders. As you inhale, straighten, touching your thighs with your fingertips.
- I. p. – bend your legs at the knee joint. Move one knee to the side and return to the starting position. Repeat the same with the other one.
- Stretch your arms up. At the same time, pull your socks towards you. After lowering your arms, relax.
- I. p. – bend your legs at the knee joint. Spread and bring your knees together. You can diversify the movements by moving your knees first to one side, then to the other.
- Try to pull your bent knees one after the other towards your stomach. Help with your hands when doing this.
We recommend
Therapeutic massage for the back: features, indications and contraindications More details
2. Subacute period.
If there is an improvement in the course of the disease, the pain has subsided, you can diversify exercise therapy for the lumbar spine with more dynamic movements.
- I. p. – bend your legs at the knee joint. Straighten your right one up. Repeat for the left, four times on each. Do not straighten your leg completely if you experience pain.
- Lean on the bed with your arms bent. Try to arch your chest as much as possible. After completing the exercise, relax.
- In a lying position, you need to bend your legs and raise your back area in the sacrum area. Try to lean on your lower spine.
- Tighten and relax your buttocks.
- Bend your legs one after the other. While straightening them, press down on the bed with your foot and try to arch your lower back a little.
- Lie down and bend your legs. Raise your head while contracting your abdominals and buttocks. If the exercise is easy, try raising your pelvis a little.
3. Remission.
Exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine in remission can be supplemented with complex movements. At the same time, the load increases, which means you need to carefully monitor your condition even without pain. Physical overexertion is dangerous and can lead to a sudden exacerbation of the pathology.
- I. p. - lying on the side. Pull one thigh toward your stomach first, then the other. Try to do the exercise all the way, thereby stretching the lower back muscles as much as possible. Perform five to seven repetitions on each leg.
- I. p. - on all fours. Imagine an obstacle and carefully crawl under it.
- I. p. - sitting on a hard surface, hands on knees. The back is straight. Slowly lean back, tensing your abdominal muscles. Stay a while. Return to the starting position at the same pace.
- I. p. - on all fours. Arch your back while lowering your head. Make reverse movements: arch your back, raising your head up.
- Stand up straight. Bend forward, trying to reach your toes with your hands. The chest should be pressed against the hips as much as possible. The exercise is also effective from a sitting position.
- I. p. - on all fours. Raise your legs bent at the knee joint and bend your lower back slightly. Movements help relieve symptoms of osteochondrosis.
- The legs are bent at the knee joint. Sit on them, and your heels should be level with your buttocks. Reach up and interlock your fingers. Sit on the floor, changing direction: first left, then right.
- I. p. - on all fours. Raise your arm and opposite leg. Stay in this position for a while. After returning to the starting position, repeat with the other limbs. Do five times for each side.
Reasons to start exercising today
The first impression of a person is formed by his appearance. Slouched, hunched figures repel people and do not motivate them to get to know each other further. Women subconsciously prefer men whose broad figure they can hide behind; next to them they feel protected.
Do you want to be successful with the opposite sex? Save the poetry and your interesting, deep personality for later. Start to amaze with your beautiful curves and strong body constitution.
Often the fair sex undeservedly ignores these areas, placing more emphasis on the legs, buttocks and abs. But this is a completely wrong decision, because it is a strong core that contributes to the correct implementation of power loads on other muscle groups, and is also an excellent strength for the spine and all internal organs.
They are also repelled by the fear of losing their femininity, because a wide back is the calling card of men. But these fears are unfounded, because specially designed trainings for women help the formation of a seductive V-shaped silhouette without overload.
By the way, especially for the fair sex, I recommend reading an article about the main issues in fitness that concern girls.
Gentle physical therapy exercises for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
1. Lying on your back.
- Hands at your sides, legs together. As you inhale, pull your arms up, and as you exhale, lower them. Number of repetitions – 4-5.
- Bend and straighten your feet while clenching and unclenching your fists. Do it 10 times.
- Rotate your feet in a circle. In each direction 4-6 times.
- Pull your knees to your chest one at a time. Do 6-8 reps.
- Move your right arm and leg to the side, for example. Repeat in the same way for the left limbs. Do 4-6 repetitions.
- Clasp your fingers in a “lock” at the back of your head. Raise your head while pulling your toes towards you. Number of repetitions – 8.
- Hands at your sides. As you inhale, stretch your arms up, while simultaneously pulling your toes in the opposite direction from you.
- Place your legs bent at the knee joint, shoulder-width apart. Use your knee to touch the opposite foot, and vice versa. Do 4-6 times.
- Exercise “bicycle”, simulating pedaling. Repeat five circles back and forth.
- Place your hand on your stomach. Take a deep breath into your belly and then exhale slowly. Number of repetitions – 3-4.
- Stretch your left hand along your body, and stretch your right hand up. Repeat the exercise, changing the position of your hands. Do 10–12 times.
- Spread your arms to the sides, feet shoulder-width apart. With your left hand, reach your right hand. Repeat the exercise for opposite limbs. Number of repetitions – 6–10.
- Pull your knees towards your chest with your hands. First the left knee, then return to the starting position and repeat the exercise with the right. Do 6-8 times.
2. Exercise therapy lying on your side.
- Swing your arm and leg upward. Repeat about five times.
- Pull your knees to your chest: 6-8 reps.
- Swing your leg forward and backward. Repeat 6-8 times.
Perform the exercises in the same way, lying on the other side.
3. Exercises while standing on all fours.
- First move one hand to the side, then the other. Do 10–12 reps.
- Swing your leg back, straightening it. Repeat with the other leg. The quantity for each is 8–10.
- Pull your left knee towards your right hand. Repeat, switching sides of limbs. Do 6-8 times.
- Pull one knee toward your chest. After this, take your leg back, the toe should slide along the floor. At the same time as this movement, you need to sit on the opposite heel. Perform the exercise in the same way with the other leg.
- Swing your straight leg up and back. At the same time, pull your opposite hand up. Repeat similarly for the other leg and arm. Do 6-8 times.
- The legs are fixed in one position, and move your hands to the right and left sides. Repeat five times in each direction.
- Without lifting your hands from the floor, try to sit on your heels. The exercise is performed slowly. Do 6-8 times.
- Without lifting your hands from the floor, sit first on your left buttock and then on your right. Repeat 6-8 times.
- Place your hands on the floor and raise your head. Arms straight. Lower your head to your chest and arch your back, then arch it back. Make movements at a slow pace. Number of repetitions – 8–10.
Exercise therapy training exercises for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
For exercise therapy of the lumbar region, training exercises are indicated while the pain subsides. During the acute stage they are prohibited.
Tasks:
- Completely form the muscle corset.
- Normalize the range of motion in the leg joints.
- Repeat the number of exercises that include movements in the lumbar region strictly in accordance with the training plan.
1. Lying on your back.
- Bend your legs at the hip and knee joints. The shins should rest on the support. Join your fingers behind your head into a “lock.” Lift your head and shoulders off the floor. Do 6-8 times.
- The shins rest on the support. Hold the ball between your feet. Move it to the left, then to the right. Do 6-8 reps.
- Hold the heavy ball with your feet. The shins rest on the support. Your task is to pull your knees towards your chin, lifting your head off the floor. Perform 6–8 times.
- Bend your legs at the hip joint. The shins should rest on the support. Take dumbbells in your hands and stretch them along your body. Try to sit down. Do 6-8 times.
- Take dumbbells in your hands and move them to the right. At the same time, tilt your knees to the left. Repeat 6-8 times.
- Bend your knees and hold the ball between your feet. Take dumbbells. Try to sit down and hold this position. Do 6-8 reps.
2. Lying on your stomach.
- Stretch your hands in front of you. Raise your head and shoulders at the same time. Move your right arm behind your back, accompanying this movement by turning your torso to the right. Repeat the same with your left hand.
- Place your arms straight behind your back. At the same time, lift your head, shoulders and upper body off the floor. Raise your legs with your knees bent. Repeat 6-8 times.
- The legs need to be bent and then straightened at the knee joint in turn. Only 15–20 times.
Don't forget to take your heart rate before and after your workout. Its optimal value is 120–140 beats per minute. Exceeding the normal heart rate indicates that the load is high for you.
What muscles does the back consist of?
They are divided into two groups: deep and superficial. The first ones consist of:
- Transverse spinous muscles (provide movement of the ribs). In turn, they include: rotator cuffs, multifidus and semispinalis muscles.
- Extensor muscles (provide movement of the torso). These are, first of all, the longissimus and iliocostalis muscles.
- Belt muscles.
- The erector spinae muscle (the strongest and most important because it holds the body upright).
The rotator cuff muscles are divided into cervical and lumbar rotators. Thanks to them, we can rotate our head or body accordingly. The multifidus muscles are involved in lumbar extension. The iliocostalis is attached to the entire spine and ribs; it, like the longissimus muscle, is responsible for the “straightness” of the spine.
Deep and superficial muscles
Muscles responsible for posture
Superficial muscles are, first of all:
- Latissimus muscles (“wings”). They perform all kinds of hand movements.
- The quadratus lumbar muscles are responsible for lateral flexion of the body.
- Rhomboid muscles. Regulate the movements of the shoulder blades.
The superficial muscles also include the trapezius muscles. They are involved in the movement of the shoulder blades, head and neck. They are often simply called "trapezoids" because they have a similar shape. The trapezium is divided into upper, lower and middle parts. But during intense training, it is the upper one that is most clearly visible. When you stoop, the upper part is constantly under tension, hence the nature of constant headaches. This is also why it is very important to do exercises to achieve a straight posture.
Shape and location of trapezoids
5-minute exercise therapy for the lumbar region
- Lying on your stomach, legs straight, bend your arms at the elbows and press them to your body. Lean on your straight arms and lift your upper body off the floor. Turn your head first in one direction, then in the other. Return to the starting position and relax. Do 2-3 repetitions.
- Lying on your stomach, stretch your arms forward. Legs remain straight. Raise your torso while simultaneously performing a crawl motion with your arms. Repeat 4-6 times.
- Similar to the previous exercise, move your arms using the breaststroke technique. Do 4-6 reps on each arm.
- I. p. - lying on your stomach, hands pressed to your chin. Crawl on your bellies. The movement involves pulling the knee towards the elbow. Repeat 4-6 times.
- The situation is similar to that described above. Lift one of your straight legs up, point your toes down. Repeat the exercise with the other leg. Do 4-6 times.
- Raise your arms and legs at the same time. Hold this position and after a few seconds return to the starting position. Relax. Do 3-4 repetitions.
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
Anatomy of the serratus anterior muscle
Start and Attachment
The PSM originates on the anterior surface of the eight or nine upper ribs and is inserted on the medial border of the scapula.
Conventionally, this muscle is divided into three parts:
- Upper: 1st-2nd rib → upper corner of the shoulder blade.
- Middle: 2nd to 3rd rib → medial edge of scapula.
- Inferior: from the 4th to the 9th rib → medial edge and lower angle of the scapula. This is the most powerful and outstanding part.
Innervation and blood supply
The PZM is innervated by the long thoracic nerve (C5-C7 roots of the brachial plexus). The blood supply to this muscle is provided by the lateral thoracic, superior thoracic and thoracodorsal arteries.
Exercise therapy for the lumbar region with a fitball
- "Locust". Lie on the fitball with your stomach and take turns lifting your arms and legs.
- Hyperextension. The stomach and thighs lie on the ball. Hands behind your head, legs extended back. As you inhale, bend forward, and as you exhale, return to your starting position. The exercise affects the back, do it smoothly.
- Half bridge. I. p. – lying on the floor on your back, put your feet on the fitball at an angle of 90 degrees. As you exhale, you need to straighten your legs and raise your pelvis. While inhaling, take the starting position.
- I. p. similar to the previous paragraph. Grab the ball with your feet, clasp your hands behind your head. Pick up the exercise ball.
- Twist/"flugel". Back on the floor, feet on a fitball. Hands are spread to the sides. Roll the ball with your legs in different directions. Your goal is to touch your knees to the floor.
Effective exercise therapy for the lumbar region involves repeating these exercises about 20 times.
Exercise therapy of the lumbar region according to the method of Bubnovsky and Evdokimenko
Sergey Bubnovsky is a rehabilitation specialist by profession, the author of a large number of exercise therapy complexes for joints, recognized by official medicine.
Pavel Evdokimenko is a rheumatologist, a member of the highest level of the Academy of Medical Sciences of the Russian Federation. Among his works are a huge number of books that describe recommendations for the treatment of arthritis and arthrosis.
Doctors Bubnovsky and Evdokimenko developed an effective set of exercises. You can familiarize yourself with the technique of their implementation, which will make physical therapy of the lumbar spine more effective, in the video.
- Lying on your stomach, reach your buttocks with your heel, bending your legs one at a time. The head is turned in the opposite direction. Hold the position for 10 seconds. After this, relax for a few seconds and repeat the movement again.
- I. p. - on all fours. Arch your back and hold this for five seconds. After that, relax. Performing the exercise from the side resembles the behavior of a cat on its hind legs, which is why it has a similar name.
- I. p. - lying on your back. First pull one leg towards your stomach, then the other. Help with your hands. Tighten your muscles for seven seconds and then relax.
- I. p. - lying on your back. Wrap your arms around your legs and pull them towards your stomach. Tighten the muscle tissue for 10 seconds, then relax.
- I. p. - sitting on a chair. Bend over slowly. Your task is to thoroughly stretch your back. As you inhale, tighten your lower back muscles for six to seven seconds, and as you exhale, relax.
Video instructions for exercise therapy of the lumbar spine:
.
Nowadays, you no longer have to spend a lot of time performing complex and unpleasant procedures at home. It is much easier to seek help from real professionals - the Veronika Herba beauty and health center, equipped with effective and modern equipment.
Why clients choose Veronika Herba beauty and health center:
- This is a beauty center where you can take a course of exercise therapy for the lumbar region at a reasonable cost, and you will be treated not by an ordinary cosmetologist, but by one of the best specialists in Moscow. This is a completely different, higher level of service!
- You can receive qualified help at any time convenient for you. The beauty center is open from 9:00 to 21:00, seven days a week. The main thing is to agree with your doctor in advance on the date and time of your appointment.
Sign up for a consultation with a specialist by phone +7 (495) 085-15-13, and you will see for yourself!