A light gait, straightened shoulders, a flexible spine are signs of youth. If you store them carefully, youth will last for a long, long time. To do this, you need to make it a rule to regularly train the muscles that support the spinal column, endure loads without failure, and skillfully relax after them. Physical stress, overload, fatigue are manifested by pain in the lower back, neck, thoracic, and shoulder regions. This is how the body asks you to pay attention to it. An effective way to prevent pain is to stretch your back. It is enough to add fifteen-minute exercises to your daily routine and enjoy the ease that lasts youth.
Flexibility exercises for the lower back
Lying on your elbows
Rise up on your elbows as high as possible. Don't lift your hips off the floor. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Back stretch
Tilt your chest towards the floor as much as possible. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Lumbar rotation
Position – lying on your back, legs together, knees bent. Turn your knees to the sides. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Lifting extension
Position is as shown in the picture. Don't lift your hips off the floor. Relax your lower back and buttocks. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Angry cat
Tilt your chin down and tighten your stomach, arching your back. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Exercises for the pelvis and back
Straighten your back, tensing your abdominal and back muscles. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
One leg to chest
Pull your leg bent at the knee towards your chest. Stretch your psoas and gluteal muscles. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Knees to chest
Bring your bent knees towards your chest. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Why does my back hurt?
Most adults experience back pain in one way or another, especially in the lumbar region. Discomfort may be accompanied by spasms of the muscles located along the spine, numbness, and tingling. There are several reasons for this condition.
- Muscle tension occurs due to muscle weakness or overuse.
- Sprains occur due to inaccurate and sudden movements, causing pain. Ligaments connect the vertebrae and provide stability to the spinal column.
- Poor posture leads to muscle fatigue, joint compression and intervertebral disc tension.
- Age-related changes lead to a decrease in the density, strength and elasticity of bones, muscles and ligaments.
If the pain arises as a result of injury (you fell, turned unsuccessfully or lifted something heavy), then you should first ensure yourself peace: if possible, do not move or do any exercises and be sure to consult with a specialist, he will prescribe an examination if necessary and draw up a treatment and rehabilitation plan .
You can apply ice (but not heat!) and take painkillers. After the pain has subsided (usually within a few days to several weeks), you can begin to perform rehabilitation physical exercises. If the condition does not improve, you should consult a medical specialist.
There are several simple causes of pain:
- If you feel pain in your back, but you definitely haven’t fallen or made sudden movements, this means that you are overloading your spine or incorrectly.
- If your occupation mostly involves sitting (at the wheel, at a computer, at a desk), then you need to do light exercises every hour.
- If your job involves heavy physical labor, you need to learn how to properly load your back.
- Don't forget to lie comfortably. If you are lying on your back, place pillows under your knees. If you like to lie on your stomach, place a pillow under your hips. If you choose the side position, hold a pillow or blanket between your knees.
- If you experience difficulty urinating or defecating after an injury, numbness in the genital area, severe weakness in the legs and unsteadiness, consult a doctor immediately!
Through regular physical activity, any person can maintain their musculoskeletal system in good shape and minimize the risk of back pain.
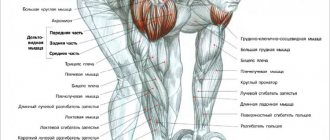
Exercises to strengthen the lower back
For back muscles (1)
Raise your arm forward without bending your neck. The back is straight. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
For back muscles (2)
Raise your leg parallel to the floor. The neck and back are straight. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
For back muscles (3)
Tighten your abdominal muscles. Raise your leg and opposite arm at the same time. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
For neck and abdominal muscles (1)
Position – lying on the floor. Hands are brought together in front of you. Feet rest on the floor. The back is straight. Raise your head and shoulders off the floor. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
For neck and abdominal muscles (2)
Position – lying on the floor. Hands are brought together in front of you. Feet rest on the floor. The back is straight. Raise your head and shoulders off the floor, turning them to the sides. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
How to train properly
Training at home is no less effective than training in equipped gyms. By adhering to a number of basic rules, you will be able to achieve equally impressive results:
- Perform exercises to work your back muscles no more than 2 times a week. Intense daily training will not give your muscles time to recover. There simply won’t be the desired effect from such training.
- At the initial stage, until you learn to feel the tension in the loaded areas of the body, perform the movements in 3 sets of 10-12 repetitions. No need to overdo it. Only experienced athletes with good physical fitness can exercise to failure. Video exercises for the back will help you quickly understand the rules:
- Do not include strength loads in the initial phase of training. Insufficient muscle warming can lead to injury.
- Remember that muscles can adapt to a certain level of impact. Therefore, training programs must be alternated. In addition, the variety will not let you get bored during classes.
- Do the basic exercises first.
- Increase the load gradually. Don't try to lift heavy weights or do as many reps as quickly as possible.
- Watch the technique of performing movements. Remember - it’s better to do fewer (repetitions, approaches), but correctly. Otherwise, you will not achieve the desired result. And what’s even worse is that you get injured during class.
Exercises for neck flexibility
Neck retraction
Tilt your head back, maintaining the level of your eyes and lower jaw. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Trapezius muscle strain
With one hand, tilt your head to the side. The second hand is placed behind the back. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Neck flexion and extension
Gently bend and straighten your neck, making nodding movements. Try to stretch your neck. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Neck flexion
Tilt your head down and return to the starting position. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Neck twists
Slowly turn your neck to the left to see your left shoulder. Then also to the right. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Neck extension
Pull your neck back and return to the starting position. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Shrug
Move your shoulders up and down, then forward and back. Repeat 10 times.
Neck sprain
Hold your arm extended downward at the wrist with your opposite hand. Gently turn your head towards the holding hand. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Video exercises for the back at home
Below we invite you to consider two types of exercises aimed at working the back muscles: with and without sports equipment. When drawing up a training plan, they can be combined.
Exercises with dumbbells First of all, we list several movements that require sports equipment (dumbbells).
Bent-over row
Timeless classic. The exercise is ideal for home training. Allows you to work the latissimus dorsi muscles, making your lower back and hips stronger and stronger. The optimal solution for experienced and beginner athletes.
Bench-supported row
Makes it possible to reduce the load on the lower back and biceps femoris muscles. During the process, each side is worked on in turn. In addition to the latissimus muscle, the work includes: the rear deltas, quadriceps, and forearm muscles.
Deadlift
When performing this exercise, almost all muscle groups are included in the work. The main load falls on the extensors (paravertebral columns), lower back, and legs. The material “exercises to strengthen the back muscles video” will help you understand the technique.
Dumbbell plank row
The movement is aimed at working the latissimus muscles and increasing the endurance of the body as a whole. Recommended for inclusion in the training plan for athletes with good physical fitness.
Exercises to strengthen the neck muscles
Sipping
The hand is located at the back of the head. Move your head back, offering resistance with your hand. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Lateral flexion
The hand supports the head from the side. Tilt your head to the side, providing resistance with your hand. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Flexion
Support your forehead with your fingertips. Tilt your head forward, resisting with your hand. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Rotation
Place your fingertips on your temple. Turn your head, trying to see your shoulder. Use your hand to resist. Hold for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Flexibility and health
If you look up the meaning of the word flexibility in the dictionary, it will become clear that this concept means a person’s ability to perform various movements with a large amplitude. How does this opportunity affect health? Direct.
Table. The importance of flexibility for health.
| Meaning | Description |
| How much energy does a person spend per day? Whatever this figure is, which depends on the individual, energy costs can be reduced. Each muscle in the body can be in two states. When it contracts, a person is tense, when it is stretched, he is relaxed. The more time a muscle spends in the contraction position, the more energy it requires. This is why a person who does not know how to stretch his muscles experiences occasional or constant fatigue. Increasing muscle flexibility not only relieves tension, but also frees up the energy used to keep the muscles contracted. |
| Flexibility not only gives relaxation, but also gives muscle tone. And since the tone is distributed evenly when the free muscles are not tightened, coordination of movements increases. A flexible person can acquire any physical skills much faster than someone who is not highly flexible. |
| Tense muscles actively signal to the nervous system that they are in a state that is far from normal, causing the consciousness to become distracted, tired, and the nerves to wear out. Stretching and relaxing muscles leads to relaxation of the body and stops sending alarming signals about overexertion to the brain. Nerves become more resilient, concentration increases. |
| Blood vessels consist of two important components - muscular and elastic. When flexibility develops, elasticity is trained, because if it is poorly developed, blood flows poorly through the vessels and varicose veins develop. Flexibility exercises thus help promote good blood flow, which makes it easier for the heart to work and prevents bleeding. |
| If the body does not have flexibility, the vessels in it are used unevenly. Some of them do not work at full capacity, while others take on the entire load. When muscles become flexible, blood vessels stretch, distributing blood flow evenly and regulating blood pressure. |
| During exercises that increase flexibility, the body sends many signals to the central nervous system, receiving reflex responses in all organs. This stimulates and improves the quality of their work, improving the functioning of the immune, genitourinary, cardiological, nervous and respiratory systems. |
By the way. In Chinese culture, maintaining and improving health begins with developing flexibility in the muscles of the entire body, especially the back muscles.