Start and Attachment
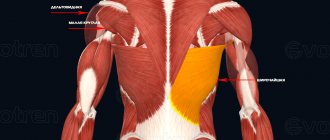
The PSM originates on the anterior surface of the eight or nine upper ribs and is inserted on the medial border of the scapula.
We recommend reading: How to get rid of 30 extra kilograms and believe that it’s never too late to change
Conventionally, this muscle is divided into three parts:
- Upper: 1st-2nd rib → upper corner of the shoulder blade.
- Middle: 2nd to 3rd rib → medial edge of scapula.
- Inferior: from the 4th to the 9th rib → medial edge and lower angle of the scapula. This is the most powerful and outstanding part.
Innervation and blood supply
The PZM is innervated by the long thoracic nerve (C5-C7 roots of the brachial plexus). The blood supply to this muscle is provided by the lateral thoracic, superior thoracic and thoracodorsal arteries.
Diagnosis of muscle damage
To confirm a muscle tear, the patient must undergo an ultrasound. An ultrasound examination will confirm or deny the presence of injury. If confirmed, ultrasound will detect a hematoma if it has formed. This is very important in order to evacuate blood from it in time and prevent inflammation.
It is also possible that the hematoma may not be detected. In such cases, the specialist prescribes a nerve block with novocaine to numb the injured muscle. The blockade is performed either every day or every 2-3 days, according to the doctor’s decision and in the presence of severe pain.
Features of pumping the serratus anterior muscle
In bodybuilding, there are no specific exercises for developing the serratus anterior muscle, because it is completely impossible to work it separately: after all, it plays a role in all exercises that are aimed at working the pectoral and deltoid muscles and is involved in back training .
It is also important to emphasize that the group of people who have learned to feel this muscle at the time of exercise . Naturally, such a feeling comes to us over time, when we accumulate experience and acquire basic knowledge.
Moreover, the most important aspect of the development of the serratus anterior muscle is considered to be static training. It can be carried out with or without load.
Jaw Information
The jaws are a pair of bones that form the base of the mouth and teeth (see Figure 1).
- The maxilla is the upper jaw bone.
- The mandible is the lower jaw bone.
- The temporomandibular joint is where the lower jaw attaches to the skull.
- The masseter muscle is the muscle that connects the lower jaw to the skull.
Figure 1. Bones and muscles of the jaws
The opening and closing of the mouth is controlled by many muscles and nerves located around the jaws. Most people can open their mouth 35–55 millimeters (1.4–2.2 inches), which is the width of three fingers (see Figure 2).
Figure 2. Normal open mouth height
to come back to the beginning
How to pump up the serratus muscles
In bodybuilding, as in many sports, aesthetics and ideal body proportions are important. Many people forget about this and just chase muscle mass.
Now let's look at a small muscle group located on the ribs, called the serratus muscles. Although they are small in volume, they play a significant role in the overall picture. Relief and voluminous muscles on the ribs perfectly emphasize pumped up abs.
To understand how to pump up the serratus muscles, you need to understand at what points they work.
We recommend reading: Transverse abdominis exercises
Having studied the anatomy and basic functions in detail, you will understand that it will not be possible to select targeted exercises for the serratus, they simply do not exist. They actively work only in certain movements, for example, pumping the pectorals and deltoids. The serratus muscles cannot be pumped up with isolated movements, but there is a group of exercises that load them as much as possible.
Anatomy and function of the serratus muscles on the ribs
Located in the front of the chest, the upper part of the serratus is covered by the pectoral muscle, and the lower part is on the surface of the ribs. The muscle fibers are directed backward and upward, covering the outer surface of the ribs and passing under the shoulder blade. Performs the following functions:
- Moves the scapula forward and outward;
- With the participation of other muscle groups, raises arms above the horizon line;
- Promotes chest expansion.
Considering the functions performed, we can assume how to pump up the serratus muscles, namely, which exercises are more suitable for these muscles. In training, you need to do movements that are physiologically characteristic of them.
Now you need to determine how the serratus anterior muscle swings; the exercises will be aimed at pumping the pectorals, deltas and back.
As you understand, it will not be possible to isolate and pump up the serratus muscles alone; they work as an additional muscle in various exercises.
Clinical relevance
Pterygoid scapula
Dysfunction of the serratus anterior muscle is one of the causes of pterygoid scapula. Weakness of the scapula leads to overactivity of the shoulder abductors, resulting in downward and internal rotation of the scapula and anterior tilt during shoulder abduction and flexion. If this position is maintained for a long time, adaptive shortening of the pectoralis minor may occur, causing the scapula to tilt further forward and rotate internally. Thus, the pterygoid scapula is caused by weakness of the PZM.
Scapula protrusion during wall push-ups
The most common cause of PSM paresis is damage to the long thoracic nerve (C5-7). The long thoracic nerve descends along the lateral chest wall, making it susceptible to injury during surgery on the anterolateral chest.
Other causes of isolated PPM palsy include trauma, strenuous work, athletics, anesthesia, infection, and idiopathic causes. Neuropraxia of the long thoracic nerve may result from compression or stretching.
Subacromial impingement
Weakness of the rotator cuff leads to dysfunction of the rotator cuff muscles, which increases the risk of subacromial pain syndrome.
You can read more about subacromial pain syndrome here.
In addition, the PSM is necessary for scapular upward rotation, posterior tilt, and, to a lesser extent, external rotation of the scapula. This is necessary to maintain the volume of the subacromial space and reduce the risk of subacromial impingement.
Myofascial lesion of the serratus anterior muscle
Chronic chest pain of noncardiac origin is a heterogeneous disorder. For example, one of the reasons may be myofascial pain syndrome, in which several functional muscle units are often affected (so-called trigger points are formed in them). The syndrome includes a set of symptoms, one of which is pain localized in the area of the 5th-7th ribs in the midline. Referred pain may spread along the anterior chest wall and medial arm, reaching the little and ring fingers. This pain may be intermittent or constant.
Trigger point PZM syndrome may also occur
- pain between the shoulder blades,
- golfer's elbow,
- pain in the ribs and arm.
Differential diagnosis
Intercostal neuralgia
This condition can be differentiated by palpation. In the case of PPM syndrome, palpation of trigger points will cause pain that occurs spontaneously. With intercostal neuralgia, palpation does not cause pain, because Neuralgia pain is located along the dermatome.
How to pump up the serratus anterior muscle
- Take the correct position - feet shoulder-width apart, stand straight, rest your hands on the sides of your body;
- The whole process will develop in the upper body. Start by tensing your latissimus dorsi while simultaneously arching your lower back and pushing your pecs forward;
- First, the shoulder girdle will move back and then forward along with the elbows;
- The shoulder blades should be spread out to the sides as much as possible.
Having felt the maximum tension, you need to maintain it and hold it for as long as possible. It is at this moment that the serratus muscles on the ribs receive maximum static load. Do at least three of these repetitions, stretching after each time to relax all muscle groups. Here is an example of how to pump the serratus muscles by posing
It is clear that a small number of athletes will suffer from such an exercise, while the rest need to tie the training to the hardware.
How to pump up serratus muscles with weights
There are a huge number of exercises that include stress on the rib muscles. For a general understanding, we list them all in main groups:
We recommend reading: Workouts for smart people: how fitness classes affect the brain
- Bench press. Any pressing exercise for the pecs helps develop the serratus. The inclination of the bench can be different, as can the choice of equipment, even in a simulator;
- Wiring. Any incline of the bench will engage the target muscle, use dumbbells, a cable machine or a butterfly;
- Press up. Any deltoid press pumps up the serratus. Whether you use a barbell, dumbbells, machines, or special techniques like the Arnold or Bradford press, all of this involves gears;
- Standing flyes and rows to the chin.
In fact, the entire complex aimed at pumping up the chest and shoulders can pump up the serratus muscle, even at home. There is one exercise called a pullover, it makes the muscle in question work the hardest. Having understood it, you will increase your knowledge of how to pump up the serratus muscles on the ribs, and you will be able to use it effectively.
There are various techniques for performing a pullover: with dumbbells, a barbell, an incline bench, straight arms, and so on. Let's look at the classic version with dumbbells; this exercise is very valuable for young athletes, because it can make the chest deeper, which will make the pecs more attractive. The best age to get maximum effect is 15-28 years old.
The pullover is aimed at developing the pecs and includes the latissimus dorsi, triceps and serratus anterior.
This exercise with additional weights strains the serratus muscles to a greater extent than the others.
Therefore, it is the best and will help in achieving expressive, sculpted muscle forms on the ribs. Let's move on to the technique and take a closer look at how to pump up the serratus anterior muscle on the ribs:
- You need to place your upper back across the bench and brace yourself. Place your feet firmly on the floor with your knees at a 90-degree angle. Instead of a bench, you can use a chair, bench or fitball;
- Take a dumbbell on one side with your palms facing the plates (as in the picture) and lift it above your chest;
- Maintain a slight bend in your elbows to avoid possible injury. Position yourself so that your pelvis is below shoulder level;
- Lower the dumbbell behind your head as you inhale, maintaining a slight bend in your elbows. Lower until you feel a strong stretch in your back. The greater the amplitude of movement, the stronger the serratus anterior muscles contract;
- Use an optimal weight so you can do 12-15 reps, 3-4 sets. Raise the dumbbell in the opposite direction as you exhale.
The pullover was a popular exercise during the golden era of bodybuilding for a reason. See how to pump up the serratus muscles with a pullover using an example:
Calculate your ideal sports weight!
How to pump up the muscles on the ribs with crunches
The beauty of a muscular body is also emphasized by the prominent muscles on the ribs, or rather the intercostal muscles. Any training for the abdominal muscles helps to pump up the intercostal muscles, so it’s enough just to pump up your abs.
Of course, the emphasis of the load increases if you do exercises with an emphasis on one side. For example: lateral crunches, diagonal crunches, leg raises on the horizontal bar, in general, all types of exercises aimed at pumping up the lateral press.
Now you also know how to pump up your intercostal muscles at home, because you don’t need a gym to train your abs.
- Look how Yuri Spasokukotsky pumps the intercostal muscles:
- Masses and relief to you!
In case of spasm of the masticatory muscles when opening the mouth
The sooner you begin treatment for spasms of the masticatory muscles, the easier it will be to resume normal jaw function. If you experience tension in your jaw, call your healthcare provider immediately. He or she may refer you to a specialist, as described below.
- See a speech and swallowing specialist, a physical therapist, or both. They will help you maintain your ability to open your mouth and regain any lost abilities. These professionals use a variety of techniques, such as exercise, stretching and massage. They may also recommend that you use special devices to help open your mouth.
- See a rehabilitation doctor. He will evaluate how well you can open your mouth. He or she may prescribe medications for pain or spasms (sudden, strong muscle contractions), suggest other treatments, or recommend medical devices to help you.
Your healthcare provider will discuss with you which specialist referral would be most beneficial for you.
to come back to the beginning
Features of the training
In fitness, there are no secret exercises to pump up your serratus muscles. They are involved in most movements that are aimed at developing the pectoral, deltoid and back muscles. The muscle is also partially involved in some abdominal movements. Therefore, you can often come across the wording “serratus abdominal muscles” (although anatomically it is not correct).
The main problem on the way to pronounced hypertrophy of the desired muscle is its function. It is very difficult to perform a movement in which the rest of the muscles do not take on the entire load. This requires special conditions when performing exercises, as well as carefully selected weight (mostly the work is carried out with light weights).
The main sports in which this muscle is involved:
- Strength sports (bodybuilding, weightlifting, powerlifting).
- Swimming (works in all styles and techniques).
- Disciplines where there are throwing and pushing elements.
- Artistic gymnastics (while holding on rings, uneven bars, etc.).
- Martial arts and other sports in which the shoulder girdle is actively involved.
Therefore, the main sport in which muscles are trained to increase volume is bodybuilding. Mostly we are talking about a competitive career, where the form can give an additional advantage and give aesthetics to the figure in some positions.
It is also worth noting that the pronounced serratus muscle in professional bodybuilders is largely the result of competent posing than targeted development. Genetics also plays an important role, which determines the shape (for some athletes it stands out noticeably even without additional exercises).
1.What is a muscle tear?
The skeletal muscles of our body weave around the bone frame, supporting it in the desired position and providing precise movements. Based on our internal feelings, we can always assess whether the load associated with a particular task is feasible. However, in a number of cases - in extreme cases, in emergency situations, when events develop at lightning speed and protective reflexes are triggered, the load exceeds the allocated resources. The muscles perform excessive work even to their own detriment and, as a result, get injured.
The main properties of our muscle fibers are elasticity when stretched and contractility when changing body position or performing any action. During sudden movements, when falling, jumping, a mismatch may occur in neighboring muscles. They contract simultaneously, whereas normally the contraction of a part of the muscle should be combined with the relaxation of neighboring fibers. This conflict leads to tissues receiving pathological stretching and ruptures.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Exercises for pumping the serratus anterior muscle
Certain diseases of the spine cause pain in the area of the serratus muscle. The main preventive measure is regular exercise. The main exercise for pumping the upper serratus muscle is the “pullover” exercise. To do this, you need to lie on your back across a horizontal bench. Take one dumbbell in both hands at once and place it behind your head while lying down (across the bench). Then the dumbbell is raised up above your head and then lowered behind your shoulder blades. While performing the movements, you need to understand that it is the serratus muscle that is being pumped (there should be a clear feeling of training this particular muscle group, if this does not occur, that the exercise is not being done correctly).
Quite often, patients are diagnosed with osteochondrosis of the cervical or thoracic regions. This disease also manifests itself as severe pain in the neck, possibly radiating to the shoulder or arm. Pain and burning sensations are felt in the muscle fibers. Comprehensive treatment with medications is necessary. Physical activity is the main aspect in the prevention of musculoskeletal diseases.
3. Treatment for muscle ruptures of varying degrees
Depending on the severity of the injury, the patient requires different amounts of medical care. The recovery period is also very individual. Muscle tears are classified according to two criteria:
- open or closed gap;
- full or partial.
First aid for muscle fiber injury is provided on the spot and includes:
- fixing the affected area in a position that ensures maximum approximation of the separated parts of the muscle;
- applying ice to stop bleeding;
- in case of an open rupture, it is necessary to treat the edges of the wound with antiseptic agents.
First aid measures may be sufficient for a partial rupture. In this case, further fusion of damaged tissue occurs under the condition of complete rest.
However, it is difficult for a non-specialist to assess the severity of the injury.
It is recommended to take the victim to the nearest emergency room for diagnosis and obtain qualified advice. The treatment plan based on the results of the examination may include:
- applying ice to the injury area according to a specific pattern;
- subsequent heat treatment;
- painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- first rest, and then physiotherapy aimed at development and recovery.
Muscle tears require 4 to 12 weeks to heal and recover. This injury is dangerous because the muscles can heal incorrectly and form a lifelong defect. If there is any suspicion that the rehabilitation process is being delayed or is not producing the desired result, you should contact a traumatologist.
The doctor will conduct intermediate studies and make adjustments to treatment tactics.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Recommendations
- Brand, R. A. (2008). "Origin and comparative anatomy of the thoracic limb". Clinical Orthopedics and Related Research
.
466
(3):531–42. doi:10.1007/s11999-007-0102-6. PMC 2505211. PMID 18264841. - Platzer, Werner (2004). Color Atlas of Human Anatomy, Vol.
1: musculoskeletal system (5th ed.). Time. ISBN 3-13-533305-1 .CS1 maint: ref=harv (communication) - Preuschoft, H. (2004). “Mechanisms for the acquisition of habitual bipedal behavior: are there biomechanical reasons for the acquisition of an upright posture?” Journal of Anatomy
.
204
(5):363–84. Doi:10.1111/j.0021-8782.2004.00303.x. PMC 1571303. PMID 15198701.
Notes
- ^ a b c
Platzer 2004, para. 144 - Giuseppe Milano; Andrea Grasso (December 16, 2013). Shoulder Arthroscopy: Principles and Practice
. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 549–. ISBN 978-1-4471-5427-3. - Giuseppe Milano; Andrea Grasso (December 16, 2013). Shoulder Arthroscopy: Principles and Practice
. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 551–. ISBN 978-1-4471-5427-3. - Martin, R. M.; Fish, D. E. (March 2008). "Scapular wing: anatomical review, diagnosis and treatment." Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine
.
1
(1): 1–11. Doi:10.1007/s12178-007-9000-5. PMID 19468892. - For Strong, Healthy Shoulders - Functional Anatomy of the Scapula by Bill Hartman and Mike Robertson.
- ^ a b
Brand 2008, pp. 540–41 - Preuschoft 2004, pp. 369–72