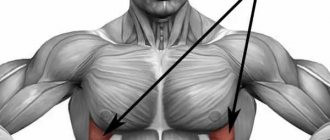
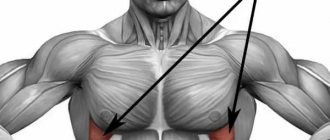
Triceps brachii (triceps)
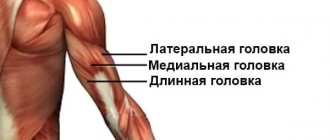
located on the back surface of the shoulder from the shoulder blade to the elbow and is responsible for moving the arm back and bringing the shoulder to the body, and also participates in the extension of the forearm. The triceps (extensor muscle) consists of three heads - long, lateral and medial. The long head begins with a wide tendon from the subarticular tubercle of the scapula. The lateral and medial heads originate on the posterior surface of the humerus. All three heads unite into a flat, wide tendon, which is attached to the olecranon process of the ulna. Triceps injuries are more common in men than in women. Most common for people involved in sports.
Triceps brachii[edit | edit code]
Triceps brachii
Home[edit | edit code]
- Long head
: subarticular tubercle and lateral margin of the scapula - Lateral head
: posterolateral surface of the humerus, lateral and proximal to the groove of the radial nerve - Medial head
: posteromedial surface of the distal two-thirds of the humerus, medial and distal to the groove of the radial nerve and medial and lateral intermuscular septa
Attachment[edit | edit code]
- Olecranon
- Posterior wall of the elbow joint capsule
Innervation[edit | edit code]
- Radial nerve, C6-C8
Training[edit | edit code]
Read separate article:
Triceps - exercises and training features
Participation in sports[edit | edit code]
As an extensor of the forearm, this muscle performs dynamically (pole vaulting, javelin throwing, handball, volleyball, basketball, shot put, swimming (backstroke, crawl, butterfly), weightlifting, boxing, fencing, kayaking, tennis, alpine and cross-country skiing , Figure skating (lifts) and luge, as well as static work: artistic gymnastics (holding exercises), weightlifting, archery, cycling, figure skating. As a shoulder extensor, it is active in rowing, kayaking and swimming (all types) Due to adduction at the shoulder joint, this muscle plays an important role in breaststroke swimming, gymnastics and wrestling.In weightlifting, it pulls the head of the humerus upward and stabilizes it in the glenoid cavity.
| Kind of sport | Movement/hold | Function | Load | Types of abbreviations |
| Pole vaulting | Movement of the lower hand when jumping and pushing off when flying over the crossbar | Forearm extension | Fast, explosive, strength endurance | Dynamic concentric |
| Shot throw, shot put | Final phase - final effort (movement) | Forearm extension | Fast, explosive | Dynamic concentric |
| Handball, volleyball, basketball | Throw | Forearm extension | Fast, explosive | Dynamic concentric |
| Boxing | Direct hit | Forearm extension | Fast, explosive, strength endurance | Dynamic concentric |
| Fencing | Injection | Forearm extension | Fast, explosive | Dynamic concentric |
| Kayaking | Opal nodding | Forearm extension | Strength endurance | Dynamic concentric |
| Tennis | Serve and backhand | Forearm extension | Fast, explosive, strength endurance | Dynamic concentric |
| Skiing | Sticking sticks in and adjusting the position with sticks | Forearm extension | Fast, explosive | Dynamic concentric |
| Cross-country skiing | Pushing | Forearm extension | Strength endurance | Dynamic concentric |
| Figure skating | Support | Forearm extension | Strength endurance | Dynamic concentric, eccentric and static |
| Gymnastics | Pommel horse, parallel bars, uneven bars, horizontal bar, handstand | Forearm extension | Strength endurance, maximum | Dynamic concentric, eccentric and static |
Muscles and landmarks lying adjacent (muscle topography) to the triceps brachii.
The triceps is a superficial muscle and is clearly visible. In the area of the origin points, it is slightly overlapped by the deltoid and teres minor. And the latissimus dorsi muscles, at the point of their attachment to the upper limb, pass under the triceps muscle.
Diagnostic tests for the triceps brachii muscle.
Two manual muscle tests:
Manifestation of triceps brachii imbalances.
The triceps brachii muscle is a structural and functional unit of the extension chain of the upper limb. It should be said that according to the laws of neurology, the function of flexion takes priority for the function of the hand and the flexors prevail over the extensors (we see the opposite picture in the lower limb). Accordingly, dysfunction of the triceps is characterized by inhibition, i.e. decreased functional capabilities (decreased intermuscular and intramuscular coordination, which will primarily be expressed in an increase in the development of strength indicators, as well as in the development of pain syndromes in the glenohumeral area). We remember that the arm extension chain is a functional extension of the posterior intersecting chains of the core and work in combination to transmit force through the latissimus and scapula. Therefore, when considering the causes of decreased triceps functionality, we must first evaluate the stability of the scapula. At the level of the scapula, we must pay attention to the functionality of the lower portion of the trapezius muscle, which is the basis for performing traction efforts (pull-ups, pull-downs, etc.), providing a pattern of posterior descent of the scapula. With insufficiency of the lower trapezius, the lower angle of the scapula is displaced laterally i.e. to the side. With this configuration, the traction efforts are carried out due to the work of the teres major and minor muscles, as well as the traction of the long head of the triceps (“pulled up by the arms”). Long-term work in this mode leads to a decrease in the functionality of the triceps and the development of inflammatory processes (tendinitis) in the tendon of the long head, up to a tear. The second most important link for triceps inhibition is the arm flexors in the biceps brachii muscle. Having functional priority, the biceps will take credit for the lengthening, leading to functional suppression of the triceps muscle. Accordingly, instead of extending the forearm, the triceps will engage in extension of the shoulder (bringing the elbow closer to the body when pulling up). Which will aggravate the above manifestations. Conclusion - to normalize triceps function you need to:
- activate the scapular region;
- restore mobility of the scapula (mobilizing exercises);
- activate the lower trapezius muscle (accented rows with fixation at the maximum point with an expander);
- formation of the correct technique of pull-ups and rows;
- performing isolation exercises for the triceps with control of the scapula.
Violation of daily movements and manifestations outside of training.
Distal triceps tendinitis is a condition in which the triceps tendon becomes inflamed, causing pain in the back of the elbow. Symptoms:
- discomfort and pain along the length of the tendon;
- discomfort and localized pain at the site of attachment to the olecranon process;
- pain and/or weakness during movements requiring increased elbow extension;
- There may be swelling around the elbow.
Manifestation of triceps imbalances in exercises.
Rear push-ups. In this exercise, with an imbalance of the triceps, we can observe the following deviations: - tilting the body forward - lifting due to extension of the legs - the movement of the body and pelvis is not strictly downward, but moving the pelvis forward - incomplete extension at the elbow joint French bench press. In this exercise, with an imbalance of the triceps, we can observe the following deviations: - when extending the arms at the elbow joint - flexion of the shoulder joint - when bending the arms at the elbow joint - extension of the shoulder joint and, as a result, excessive lowering of the equipment behind the head - compensation of movement due to the muscles of the back and press (bending in the lower back when bending the arms and something like a crunch when extending the arms) - incomplete extension in the elbow joint Extension of the arms in a block (triceps block press) In this exercise, with an imbalance of the triceps, we can observe the following deviations: - when extending the arms, tilting the body forward - when extending the arms, excessive extension of the shoulder joint, thereby moving the elbow joint behind the line of the body backwards - when bending the arms, flexion of the shoulder joint, thereby moving the elbow joint forward beyond the line of the body - extension of the arms due to a jerk - incomplete extension in the elbow joint Extension of the arms at an angle (with/without support) In this exercise, with an imbalance of the triceps, we can observe the following deviations: - extension of the arm due to a jerk - compensated movement of the back (like a cat exercise) - incomplete extension in the elbow joint Push-ups on uneven bars Imbalances will manifest themselves as follows: - Strong tilt of the body forward - A jerk of the legs at the bottom point when rising to the top - The elbows are strongly pressed to the body and then the movement occurs due to the tilt of the body forward. Close-grip push-ups Imbalances will affect the exercise as follows: - Elbow abduction to the sides to include the pectoral muscles to help - Arching in the back, no neutral body position - Downward movement only with the body, not with the whole body
Exercise options for the triceps brachii muscle.
French bench press. The triceps in this exercise work eccentrically by flexing the forearm and lowering the weight (barbell) down toward the forehead. Further, during extension, the triceps fibers are shortened and a concentric contraction occurs. It is important that the shoulder blades remain pressed against the bench and help stabilize the shoulder joints. Dips. This exercise can be performed either in a special Gravitron simulator, or on regular parallel bars with your own body weight (in some cases, with additional weights). The elbows should be fixed above the wrist joints throughout the entire exercise. When lowering the body down, the triceps lengthens and works eccentrically. When squeezing the body upward, the forearm is extended at the elbow joint and the shoulder is partially flexed at the shoulder joint. The fibers of the triceps muscle work concentrically. Bent-over arm extensions (Kick-back). In the starting position, the shoulder is already in partial extension. For this reason, a long head does not utilize its full elongation potential. Movement occurs only at the elbow joint. When lowering the weight down, the forearm bends and resists the force of gravity, working eccentrically. When lifting the projectile upward and, accordingly, extending the forearm, the triceps works in an overcoming mode, i.e. concentrically. Arm extensions on a block (Triceps press). As in the previous version, the movement occurs strictly due to the extension of the forearm at the elbow joint. But, if the body is fixed in a slight forward tilt, maintaining a neutral position of the spine, then the shoulder may go into partial flexion. This will slightly lengthen the fibers of the long head, but will limit their contraction during the extension phase. When lowering the block down and, accordingly, lifting the handle up with flexion of the forearm, the triceps works eccentrically. When lifting the block and extending the forearm, the muscle works concentrically.
Read also[edit | edit code]
- Muscles - anatomy and functions
- Arm muscles
- Triceps - exercises and training features
- Triceps brachii muscle - training and exercises
- Biceps brachii
- Brachialis muscle
- Brachioradialis muscle
- Elbow muscle
- Arch support
- Pronator quadratus
- Pronator teres
- Extensor carpi radialis
- Extensor carpi ulnaris
- Flexor carpi radialis and palmaris longus muscles
- Flexor carpi ulnaris
Treatment options
The method of treatment in each specific case will be different, since the cause of damage to the triceps muscle or its anatomical components can be any factor - infection, injury, professional muscle fatigue, degenerative diseases.
Plasma therapy
An innovative method of therapy based on the introduction to the patient of orthoplasma, rich in vitamins, platelets, growth factors, and hormones. Orthoplasma is prepared from a person’s own plasma.
The essence of the technique is to activate the body’s own reserves and start the process of tissue regeneration. Sometimes just three injections are enough for the muscles and surrounding tissues to stop hurting and then recover.
Physiotherapy
There are several types of physiotherapeutic effects on muscle tissue:
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation , conducted through the skin, restores the contractility of damaged muscles and tendons. Suitable for the treatment of post-traumatic conditions, as well as neuralgic problems.
- Magnetotherapy. The device creates a magnetic field that stimulates blood circulation in the muscles.
- Myostimulation is exposure to weak electric currents. Restores tissue metabolism and fiber structure.
- Amplipulse therapy – relieves pain, restores lymph flow and blood circulation.
- UHF therapy is exposure to ultra-high waves.
- Laser therapy is a directed light flux that can restore self-regulation processes in the body.
- Pulsed short-wave therapy is used to treat the consequences of bruises, hematomas, and sprains.
The most accessible is electrophoresis with drugs , which are introduced into tissues under the influence of direct electric current and have a much stronger effect.
Massage
Massage of the triceps brachii muscle is carried out at the stage of rehabilitation and recovery after injury . Special massage movements can relieve swelling due to disruption of the integrity of the lymphatic vessels.
Procedures are especially relevant after surgery on the triceps, when the doctor dissects the vessels and the fluid pours into the soft tissues. While the integrity of the lymphatic vessels is restored, the patient may be concerned about lymphostasis - swelling of the shoulder muscles.
Valeria
General doctor
Ask a Question
Massage gives the best results at the stage of myalgia, before fibrous cords appear inside the soft tissues. A course of massage can completely eliminate pain.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is used for complete separation of the triceps , as well as for old tears . Such an injury occurs very rarely, since the triceps brachii muscle has one of the most powerful tendons in the body, which is designed to withstand heavy loads. Surgery is necessary if, due to degenerative processes, the tendon is still torn from its place.
Fresh injuries heal better and faster than old ones. With old tears, it is sometimes necessary to free the tendon from scar tissue and plastic. Rehabilitation after such an operation is long, and the risk of re-injury is much higher.