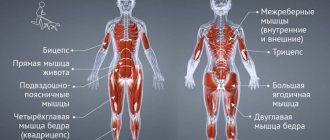
Body recomposition is a long process of restructuring the body, which is based on the desire to simultaneously gain muscle mass and burn fat. It is impossible to recompose the body without the right approach to nutrition and training. The question arises, is it possible to turn fat into muscle? Such a process is not possible. But it is quite possible to gain muscle mass and burn fat at the same time, although this contradicts your energy needs. Building muscle requires a surplus of calories, while burning fat requires a deficit.
How to turn fat into muscle? How does it actually work? Who is able to succeed at this and who is not and why? Read on to find out how to build muscle and burn fat...
How to lose weight and build muscle?
Nothing gets people to hit the gym and take supplements more than the desire to build muscle and burn fat—body recomposition, as experts like to call it.
Body recomposition is a very long and difficult process of restructuring the body, which is based on the desire to simultaneously increase the amount of muscle mass in the body and reduce fat, which is often impossible to achieve without following strict rules in calculating calories and the amount of training.
The main thing you need to know is that muscle building and burning are two opposite processes from the point of view of the energy of our body. Building muscle requires a surplus of calories, while burning fat requires a deficit. Without the right approach, attempting to carry out these actions at the same time can lead to undesirable consequences.
Everyone says, “To lose fat, you need to do certain exercises, eat right, and take supplements,” right? You can burn fat while maintaining muscle mass, right?
Research
The study involved 15 male athletes (national and international level) who had at least 5 years of experience in competitive disciplines such as sprinting (100-200 m) and long jump. In other words, these were trained athletes with competitive experience, and not a couple of students sipping beer and pizza.
- 8 participants were placed in the fast fat burning group: 750 kcal less than required to maintain full performance. The calorie deficit was 24%.
- 7 participants were placed in the slow fat burning group: 300 kcal less than required to maintain full performance. The calorie deficit was 12%.
Is it possible to build muscle and lose fat at the same time?
Well, I have news: good and bad.
- The good news: Yes, it is possible to lose fat and gain muscle at the same time.
- The bad: this is only possible under certain conditions.
- Very bad: most of the advice on how to lose weight so that you lose fat and not muscle is no good.
Yes, those “gurus” who swear they know the secret to gaining muscle mass are almost always talking nonsense. And I can prove it.
In this article, we'll talk about how the body actually builds muscle and loses fat, and then we'll look at what you need to do to do it.
Let's start with gaining muscle mass.
Is it possible to gain muscle mass and burn fat at the same time!?
Physiology of muscle growth
Two vital processes take place in your muscles every day - protein synthesis and protein breakdown.
- The destruction of proteins means their breakdown into smaller components: peptides and amino acids.
- Protein synthesis means creating new proteins, as well as their smaller components.
When you are healthy and your diet is in order, muscle tissue remains in a fairly stable state. That is, the rate of synthesis and breakdown is more or less balanced, and you do not lose or gain significant amounts of muscle in your daily life. (Strictly speaking, you lose muscle mass as you age, but you get the idea.)
In order for muscle to grow over time, the level of protein synthesis must exceed the level of protein breakdown.
This means that the body must produce more protein than it loses, and then muscle growth increases slightly.
Then what should be done to ensure that the rate of protein synthesis exceeds the rate of breakdown?
You must take certain actions in order to start and maintain this process. Muscles undergo a fairly active metabolism (metabolism), which requires quite a lot of energy to maintain it. Without this, muscles will not grow.
And the main thing you should do here is, of course, train your muscles. Strength training damages muscle cells, which signals the body to increase protein synthesis to repair muscle tissue.
Although this does not mean that by restoring muscles, the body returns them to their previous state. It strives to adapt to new stimuli—training—and produces new muscle cells, increasing muscle size and strength.
Research shows that progressive overload is the key to muscle growth.
“What is “progressive overload”?” you ask? This is a gradual increase in the level of tension in muscle fibers. When you systematically give your muscles more and more load, they constantly adapt to it, becoming bigger and stronger.
Like a true weightlifter, you must get stronger if you want to get bigger.
Of course, muscles can become stronger without increasing in size (due to increased neuromuscular activity), but there will come a point when more muscle fibers are required to achieve your training goals.
Pumping is great and can be included in a training program, but high rep ranges and exhausting sets should never be the focus. This training significantly increases metabolic stress, which promotes muscle growth, but not as much as progressive overload does.
This is why the biggest athletes in the gym are usually also the strongest, and why those who are chasing pumps by doing supersets, drop sets, giant sets, etc., do not have the same physical capabilities.
Your main goal in training should be to constantly increase your working weight.
If you don't do this, you won't get the benefits of progressive overload and will gain little muscle mass no matter what else you do (unless you use chemicals, of course).
Heavy training and progressive overload do not guarantee muscle growth because you also need to eat right.
You've probably heard that you need to eat a lot to get bigger, and there's some truth to that.
You must consume enough protein, which provides the basis for muscle growth, and also consume enough calories, which ensures that protein synthesis is as efficient as possible.
However, before we talk about diet, let's look at the other side of body recomposition, namely fat burning.
Physiology of Fat Burning
How to force the body to burn fat? Losing fat is easier than you thought.
- Don't get hung up on diet.
- There is no need to avoid carbohydrates, or indeed any other food.
- You should not eat a strictly defined number of meals per day on a schedule.
- Don't try to manipulate hormones.
In order to avoid mistakes when losing weight, you need to properly understand the mechanics of this process - how to burn fat correctly.
The first and most important mechanism is energy balance.
This means the relationship between the energy you provide to the body through food and the energy that is expended in cellular and physical activity. This ratio is often measured in kilocalories.
As evidenced by weight loss trials over the past 100 years, the truth is this: you must expend more energy than you consume.
You've probably heard it all before, and if you're disappointed, let me explain how to properly burn fat, not muscle.
When you eat food, you provide your body with a relatively large amount of energy in a short period of time. It burns some of this energy and stores some as fat for later use.
Scientifically, this process of nutrient absorption is called “postprandial”. "Fasting" means "after" and "prandial" means "having to do with food." In this postprandial state, fat burning does not occur because the body is in fat storage mode.
The reason for this is simple: why does the body burn fat to produce energy if you provide it with the required amount and even more?
Eventually, the body completes digestion and absorption of food, which takes several hours, and then enters a state that scientists call “post-absorptive.”
The energy obtained from food has ended, but the functioning of the body must continue. What can the body do to meet its energy needs?
That's right - it can burn fat. The body must now go into “fat burning mode” to work while it waits for the next meal.
Every day, your body moves from a postprandial to a post-absorptive state and back again, storing and burning fat.
Here is a simple graph that clearly demonstrates this:
The light parts of the graph show what happens when you eat food: insulin levels rise to help absorb nutrients, and fat burning stops.
The dark areas show what happens when the energy from food runs out: insulin levels drop, signaling the body to start burning fat.
What happens if these two parts of the graph are more or less balanced? That's right - the fat level will remain the same. The body will burn approximately the same amount of fat as it stores.
What happens if the light parts exceed the dark parts? Then fat reserves will exceed the amount of fat burned, and fat deposits will increase.
What happens if the dark parts collectively exceed the light parts? You burn more fat than you store, which means your overall fat mass decreases.
This is why losing significant amounts of fat requires expending more energy than you take in.
It doesn't matter how many "unclean" foods you eat or when you eat them. Your metabolism operates according to the first law of thermodynamics, which means that fat stores (energy) cannot be increased without providing excess energy and cannot be decreased without limiting energy intake, thereby creating an energy deficit.
- That's why research shows that low-calorie diets result in clinically significant weight loss, regardless of the macronutrients they rely on
- That's why Professor Mark Haub was able to lose 12 kg while on a diet of protein shakes, cakes, cookies, chips and pastries.
When it comes to simply shedding extra pounds, calories are still calories. The body uses a certain amount of energy, and if you give it less than it needs, then it has no choice but to continue burning fat to maintain life.
What if your goal is more than just losing weight? What if you want to lose fat but not muscle? In this case, calories are no longer just calories. Some types of calories become more important than others here.
I have already written about this in detail in my books and articles, so I will briefly outline the essence.
When you're cutting calories to lose fat, make sure you're consuming enough protein.
Research shows that when calories are reduced, high protein diets are more effective in reducing body fat, and these diets also help preserve muscle and increase feelings of fullness.
How much protein should you consume?
Special government agencies recommend 0.8 g. per kilogram of body weight, but research shows that doubling or tripling this amount will not be enough to maintain muscle mass while dieting.
Instead, I prefer to follow the advice of scientists at Oxford University. This is the conclusion they came to:
“The protein requirement for athletes involved in strength training and dieting will be approximately 2.3-3.1 grams. per kg. body weight without fat deposits and will increase depending on the severity of the diet and the increase in muscle mass.”
Simply put, I recommend consuming 2-2.4 grams. per kg. body weight while restricting calories in order to lose fat.
If you have a lot of body fat (a man with 20%+ body fat or a woman with 30%+ body fat), you can reduce this amount to 0.8 grams and you will be fine.
So now you know how the body builds muscle mass and stores and burns fat. Let's see what happens when these 2 processes occur simultaneously.
The science
Physical activity speeds up your metabolism because your need for extra energy increases. The body begins to use up stored fuel. Any food, with the participation of oxygen, decomposes into three chemical components: water, carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is a universal source of energy for all biochemical processes occurring in living systems. A certain amount of ATP is constantly available in the muscles and is used up when necessary (this is why our muscles are able to tense without preparation and the need to increase the oxygen content in the blood through deep breathing). ATP stored in muscles is burned quickly and to synthesize new portions of ATP, the body uses the following sources, in order of priority:
- carbohydrates (carbohydrates) – stored in the form of glucose in the blood, glycogen in the liver and muscles;
- fat – in the blood, muscles and in the body in the form of subcutaneous fat;
- protein – tissue protein.
This process occurs in our body every time we take a deep breath during exercise. In doing so, we exhale carbon dioxide, which is a byproduct of burning the actual weight (i.e. fat) we lose converted into CO2. If you've ever wondered where fat goes from your body, now you know - we literally breathe it out.
How to gain muscle mass and burn fat at the same time
There is a lot of talk around gaining muscle mass and burning fat at the same time.
People sell pills, powders, programs based on super-secret technologies. Skeptics say that this is completely impossible. The truth, however, is somewhere in the middle. Some can achieve recomposition, some cannot. How to lose weight correctly so that you lose fat and not muscle?
The main determining factors are the level of training and experience of the athlete. Here are 2 general principles:
- If you're new to strength training or starting up again after a break, you shouldn't have trouble gaining muscle mass and burning fat at the same time.
- If you train for at least 6-8 months without much rest, you probably won't be able to achieve recomposition.
The exception to point 2 are those who have been training for a certain amount of time, but have not focused on compound exercises with heavy weights. They are likely, like beginners, to make rapid progress in the beginning, including muscle growth while on a calorie deficit.
“Why are there such rules?” you ask. – “Why can’t anyone achieve success in body recomposition, no matter the circumstances?”
Because from a physiological point of view, there is an irreconcilable discrepancy between fat loss and muscle growth. Their mutual incompatibility stems from their relationship to the body's energy balance.
When the body is in a negative energy balance (calorie deficit), it reduces fat mass, but also has the unwanted side effect of reducing the body's ability to synthesize proteins.
You lose muscle mass when you diet to burn fat. The body is not able to synthesize enough protein to balance the processes of its formation and breakdown.
So, if your goal is to maximize muscle growth, make sure you are not in a calorie deficit. And since it is impossible to accurately determine daily energy expenditure, athletes who want to gain muscle mass deliberately overestimate the body’s energy needs, thus maintaining a small excess of energy.
This is the science behind the claim that you should eat more to get bigger. Although it would be more accurate to say that you must consume a little more energy than you expend in order to become bigger. This creates the basis for muscle growth.
This is why it is so difficult to burn fat and gain muscle at the same time. You're restricting calories and losing fat, but you're also limiting your body's ability to build and repair muscle tissue.
As you've probably realized by now, building muscle in a calorie deficit requires very high levels of protein synthesis (or very low levels of protein breakdown, or both). In short, anything you can do to increase your body's ability to synthesize protein and decrease its rate of protein breakdown will greatly help you in your quest for recomposition.
This is why beginners or those returning to exercise can be so successful at losing fat and building muscle. Their bodies are “hyperresponsive” to exercise, and this outweighs the restrictions on protein synthesis that a calorie deficit imposes.
Over time, these “privileges” of the beginner disappear, however, the restrictions on synthesis become more and more until they finally become insurmountable. You simply won't be able to stimulate synthesis and inhibit breakdown, maintaining the balance necessary for muscle growth. This is why the goal of experienced weightlifters is to maintain muscle and strength while burning fat, not gain it.
So, we've fully covered the theory of body recomposition, now let's move on to practice and talk about what you should do to achieve it.
Maintain a moderate calorie deficit
This is the basis of body recomposition. How to lose weight so that you lose fat and not muscle? You need to be in a calorie deficit to lose fat, but you shouldn't eat so little that you accelerate muscle loss.
Instead, you need to maintain a moderate (20-25%) calorie deficit, which will allow you to quickly lose fat while maintaining muscle mass.
If you don't know how to do this, here is a simple formula that I provide in my books for maintaining a daily calorie deficit of about 20% if you exercise 4-6 hours a week.
- 2.4 gr. protein per kilogram of body weight per day;
- 2 gr. carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight per day;
- 0.4 gr. fat per kilogram of body weight per day.
This is a good starting point for most people, but may need to be adjusted if you exercise more than 4-6 hours per week, or if you are a fairly thin woman (you may need to reduce carbs to 1.5g/kg and increase fats up to 0.5 g/kg).
Once you determine these numbers for yourself, create your daily nutrition program.
Focus on basic exercises
The idea that isolation exercises and high rep ranges will produce maximum results is a myth perpetuated by many athletes.
Get rid of fat deposits and you will look sculpted. One training style does not provide more definition than another.
When you're in a calorie deficit, you need to do the exact opposite of what many people say: you need to emphasize heavy compound exercises. Especially if you want to gain muscle mass and burn fat.
You should perform squats, deadlifts, military presses, and bench presses every week, and should do the majority of your work with a weight that is 80-85% of your 1RM (4-6 or 5-7 reps).
This is a key type of training for natural athletes looking to increase muscle mass and strength. The main “secret” to the effectiveness of high rep ranges and high volume training that fitness models talk about is the use of chemistry. And period.
If you go this route as a natural bodybuilder, you will not achieve your goals.
Do HIIT workouts instead of regular cardio
You shouldn't do cardio if you want to gain muscle, but at some point you'll have no choice but to incorporate cardio into your routine. Ultimately, you will simply need to expend more energy each week to continue burning fat, since you can only do so much strength training before you overtrain.
When this moment comes, you should not start doing regular low-intensity cardio training for 1-2 hours, 5-7 days a week. Sure, it uses up energy and helps you lose fat, but it also reduces muscle mass.
Instead, perform 1-2 hours of high-intensity interval training ( HIIT) once a week . Yes, you understood everything correctly: you can work on relief by doing cardio no more than 2 hours a week.
Don't believe me? Here's the "summer version" of my body that I achieve and maintain by doing strength training for 4-5 hours per week and HIIT training for 2 hours per week.
I find that short (20-25 minute) HIIT workouts burn more fat and maintain muscle and strength better than long, low-intensity cardio sessions.
There aren't many shortcuts to health and fitness, but HIIT training seems tailor-made for burning fat. Use it.
Get enough sleep
This point is often overlooked, but is extremely important for gaining muscle mass and burning fat.
Not getting enough sleep for a week will be enough to reduce levels of testosterone, growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which play an important role in gaining and maintaining muscle mass and burning fat.
The amount of sleep a person needs varies, but the National Sleep Foundation (USA) recommends that adults get 7-9 hours of sleep at night to avoid the effects of sleep deprivation.
Unloading phase
Using a value of 2970 kcal per day for a 90 kg athlete, a fasting week would look like this:
30% calories from protein
- 2970 x 0.3 = 891 kcal
- 891 / 4 = 223 grams of protein.
This means you need to consume 223 grams. protein per day.
40% calories from carbohydrates
- 2970 x 0.4 = 1188 kcal
- 1188 / 4 = 297 g carbohydrates
This means you need to consume 297 grams. carbohydrates per day.
30% calories from dietary fat
- 2970 x 0.3 = 891 kcal
- 891 / 9 = 99 g fat
You should consume 99 grams. fat per day.
Let's combine the obtained data:
- 2970 kcal per day;
- 223 gr. protein per day;
- 297 gr. carbohydrates per day;
- 99 gr. fat per day.
Remember, a fasting phase can be added after 4 consecutive weeks on the diet. Be patient, monitor your weight changes, take measurements if necessary and lose weight through fat, not muscle.
Take the Right Fat Burning Supplements
I'm talking about supplements last because taking them only makes sense if you're dieting, exercising, and getting enough sleep.
And let me be clear: you don't need supplements to achieve body recomposition, but they will help you achieve it if chosen correctly.
Specifically, you should achieve 3 things with supplements:
- you must maintain the intensity of your training, which will help maintain muscle and strength;
- you must improve your body's ability to maintain and build muscle mass and strength;
- you want to burn fat as quickly as possible, which minimizes the amount of time you spend in a calorie deficit.
Luckily, there are several safe, natural supplements that can help you achieve each of these goals. You will find information about them below.
Supplement #1 for body recomposition
The first thing you need is a post-workout recovery supplement that contains 2 ingredients that help achieve body recomposition:
Creatine
Creatine is a combination of 2 amino acids. Creatine is synthesized in the human body, and its source is food.
It's the most researched supplement in the sports nutrition world, and the evidence for its effectiveness is clear: it helps build muscle and strength even in a calorie deficit, and reduces muscle damage and inflammation that occurs after training.
Bottom line: If you do strength training, you should take creatine.
Carnitine
Carnitine is a substance consisting of the amino acids lysine and methionine and is involved in the production of cellular energy.
Research shows that creatine supplements reduce muscle damage and soreness that occurs after exercise, as well as improve muscle recovery.
Supplement No. 2 for body recomposition
This is a caffeine-free fat burner that helps you lose fat in 3 different ways:
- dramatically increases metabolic rate;
- enhances the effect of fat-burning substances produced in the body;
- increases the feeling of satiety.
This is achieved through effective dosages of synephrine, naringin, hesperidin, forskolin, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), hordein, salacia and 5-HTP (hydroxytryptophan).
Plus, the decaf formula means you can continue drinking coffee and your favorite caffeinated pre-workout drinks.
The conclusion is obvious: in combination with proper nutrition, a fat-burning supplement will help you lose fat faster.
Supplement No. 3 for body recomposition
A pre-workout drink containing a clinically effective dosage of 7 ingredients that work to increase energy levels, improve focus, and increase performance.
The better you can maintain your workout intensity while dieting, the easier it will be to maintain muscle and strength. Everything is very simple.
In addition, it is worth noting that caffeine directly helps you burn more fat and also enhances the fat-burning effect.
“This doesn’t work for me! I tried it a hundred times!”
Your body does not violate the laws of physics. If you "can't" lose weight, the reality is that you're eating more calories and/or burning fewer calories than you think.
Don't have time to go to the gym? Do 20-minute bodyweight workouts at home and sprint intervals outside. You can find the time. You can make time. Many people are in amazing shape despite working hard, and you can be in that shape too.
Worried about hunger? There are many simple tactics you can use to curb your appetite. Drink coffee in the morning to kill your appetite with caffeine until lunch, eat plenty of vegetables and protein, and drink plenty of water. The first few days may be tough, but hunger goes away much faster than you think.
Losing weight isn't easy, but it doesn't have to be self-tormenting. With determination and discipline, you can get healthy and build the body you've always dreamed of.
What to do if you experience a sudden weight loss
Every fourth patient out of 20 patients with cancer dies from cancer cachexia. If you lose weight, it is recommended to immediately notify your doctor in order to take therapeutic measures aimed at correcting the patient’s condition. Take advantage of the services of oncologists with extensive practical experience who see you at the Medscan clinic in Moscow.
Our medical center uses a special approach to treating cancer patients, which differs from the generally accepted ones. To prevent unintentional weight loss, an early intervention strategy is used and a multidisciplinary approach is practiced. The attending physician works in a team with an oncopsychologist and nutritionist. An integrated approach is aimed at compensating the energy balance and maintaining a high quality of life for the patient.
Is it difficult?
Do you want to know why so many guys fail there?
Because it's easier to pursue one goal. This explains why most guys find it easy to gain muscle without worrying about body fat.
And vice versa: therefore, most people can lose weight, but few of them will really look good.
By dieting, you risk losing muscle. And it's all too easy to gain fat when your weight-gaining diet in a calorie surplus contains the wrong ratio of fatty acids.
In order, as they say, to pump fat into muscles, you need to create the right balance in your training and nutrition, so that the body receives the load for growth, but has time to recover, and there is enough energy for fiber growth, and there is no excess for deposits.
Here's how to lose weight and gain weight without risking your health.
Metabolic rate
Each of us requires a certain amount of calories to maintain basic life functions such as breathing, circulation, cell production, etc.
This is called the basal metabolic rate ( BMR ). The body also burns a certain number of calories at rest, called resting metabolic rate or resting energy expenditure ( RMR or REE ).
Learning your BMR can help you gain, lose, or maintain your weight safely and effectively because it essentially gives you a starting point or helps you determine the calories you need to maintain your weight. By determining your BMR, you will see what calorie deficit you need to burn fat.