What is (and is) fat used for? Is fat always bad? Should you strive for a minimum body fat percentage?
Fat is much more than just passive energy storage. Although fat cells are surprisingly well adapted to this role, fat is also an active tissue that influences metabolism.
Fat cells are called adipocytes. Most of them are under the skin, this fat is called subcutaneous. There is also fat in the abdominal cavity around the organs, this fat is called visceral, and its excess threatens health problems (for example, the risk of cardiovascular diseases increases). There is very little fat in the muscles.
The human body can contain between XXX and YYY billions of fat cells, with a diameter ranging from 70 to 120 microns (a micron is one millionth of a meter).
80-95% of fat consists of triglycerides (a glycerol molecule linked to three chains of free fatty acids). The remainder of the cell is water, as well as various cellular “equipment” that produces enzymes and various other substances that cells need to function.
What is visceral fat
There are two types of fat in our body:
- subcutaneous (or white) - mobile fat that is located on the surface of the skin, so you can grab or pinch it;
- visceral (or brown) - fat located deep in the abdominal cavity, it surrounds the stomach, liver and intestines.
It is this location that makes visceral fat the most dangerous. Its excess leads to what scientists call obesity of internal organs. Such fat has greater metabolic activity. This means that it releases a lot of toxins, which then go straight to the organs.
According to the Cleveland Clinic (USA), excess visceral fat increases the risk of developing heart and liver diseases, and also leads to the development of diabetes.
Gennady Shpalikov absorbed the spirit of the 60s, leaving us his poems (video)
Luxurious chicken coops that were built with love and imagination (photo)
Surveillance from the USA? Russians warned of dangers from WhatsApp
How do you know if you have excess visceral fat? It accumulates mainly in the abdominal area. Measure your waist. For women it should not exceed 90 cm, and for men - 100 cm. If your waist is wider, you are more likely to have excess visceral fat.
The main difficulty in losing weight is that the body hardly burns visceral fat, but quickly accumulates it. Therefore, it is first important to stop its formation, and only then start losing weight.
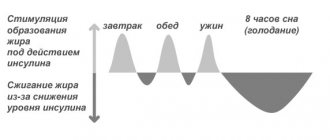
Fat is where energy is stored
The main role of fat cells is energy storage. And until 1994, it was believed that this was their only function - a passive storage room for excess energy coming from food. And in 1994, the hormone leptin was discovered, which plays a very important role in metabolism, which is discussed below.
When it comes to storing energy, fat cells are simply ideal. A kilogram of fat contains 7,000 calories of stored energy. Assuming you could use 100% fat as fuel (which doesn't happen in the real world), that would be enough energy for a 70kg person to walk 56km.
A slim man weighing 72 kg and with 15% body fat has 11 kg of fat, i.e. about 84,000 calories of stored energy. If his metabolic rate is 2400 calories/day, then even with complete fasting he will use up his fat reserves in 35 days. And the fat reserves of obese people will help them live without food for several months.
For comparison, another place where energy is stored is muscle and liver glycogen - this is only about 500 grams. Each gram provides 4 calories of energy, so that's a total of 2,000 calories. For some, this is not enough just to cover the body’s energy needs for one day. So fat is ideal for storing energy.
In addition, the fat cell can greatly increase in size and “deflate” when we lose weight. That is, it does not disappear and is always ready to fill up again.
Reduce your sugar intake
Fructose or glucose causes fat cells to mature faster, especially in visceral fat. Therefore, try to reduce your sugar intake. To make up for its deficiency, the body will begin to burn fat itself, thereby causing weight loss. It is enough to give up sweet cola or not add sugar to tea. Remember that it is also found in regular foods. For example, there is a lot of sugar in white bread or refined cereals.
She was married to a groom and an oligarch: how does the great-niece of Leo Tolstoy live?
Ants are afraid of the smell of unrefined oil: how to make a trap for them
5 zodiac signs who can't keep other people's secrets, no matter how much you ask
Fat white, brown, beige
Kirill Stasevich “Science and Life” No. 11, 2014
Doctors have every reason to believe that being overweight is not a good thing. As a rule, a whole range of disorders are associated with increased body weight: from cardiovascular to metabolic. And the number of people with one form or another of obesity is constantly growing.
How can you keep your weight within normal limits? The answer, it would seem, could not be simpler - eat less, move more. No one doubts the effectiveness of these remedies, but they do not help everyone. Some people have metabolic characteristics such that fat accumulates with any diet. Sometimes we simply cannot resist the feeling of hunger: the brain requires calories without regard to excess weight. It is also not always possible to follow instructions regarding physical activity, especially for city residents.
Therefore, obesity has become one of the most studied topics in modern medicine, and the efforts of many researchers are aimed at finding a remedy that would help prevent the accumulation of fat. You can, for example, try to change eating behavior through the brain and neuroendocrine system. Another way to prevent the accumulation of fat is to influence the intestinal microflora, since it largely determines what from food will be absorbed into the blood and what will not. Finally, excess lipids can simply be burned, that is, they can be broken down in some metabolic processes.
Meanwhile, fat is different from fat. What is deposited on the buttocks and waist is white adipose tissue, consisting primarily of white adipocytes (fat cells). Their function is to store a variety of lipids, and they look like a huge drop of fat. They have cytoplasm, nucleus and other components of the cell, but they huddle somewhere between the lipid mass and the membrane. Brown fat cells look different: they have several fat droplets, and in the cytoplasm there are a lot of mitochondria, which, thanks to iron-containing proteins, give the cells a darker, brown color.
From a biochemical point of view, brown fat cells are arranged in a senseless way at first glance. In their mitochondria, the connection between the oxidation of organic molecules (that is, lipids) and the synthesis of energy molecules ATP is broken. As is known, during the oxidation of molecules in mitochondria, a proton gradient is created on their internal membranes: there are more protons on one side of the membrane than on the other. This gradient is necessary for the enzyme built into the membrane to work for the synthesis of ATP: the energy stored in the chemical bonds of ATP is easily released and used in the vast majority of molecular processes in the cell. But in brown fat, the energy from oxidized products is almost not stored in ATP. But it is not wasted either, but goes into warmth.
All cells, to one degree or another, allow some portion of the energy they receive to leak into heat, but brown fat cells are specialized for this very function - creating heat from stored lipids. It is easy to guess that brown adipocytes serve as an important element of the thermoregulation system in warm-blooded animals. In fact, zoologists have long noticed that brown fat is especially developed in animals that hibernate. “Sleeping” animals cannot maintain body temperature using other mechanisms, such as shivering, and brown fat comes in handy.
Brown fat also protects infants from hypothermia - in them it makes up up to 5% of their body weight. In adults, as was believed until recently, brown adipocytes cease to perform their function, lose mitochondria and turn into something like ordinary white fat cells.
However, a few years ago, brown fat was also found in adults. It turned out that some part of it remains in the area of the neck, shoulders and upper chest. Moreover, it turned out that the amount of brown fat in adults increases in the cold, which is understandable, because brown fat is needed specifically for heating.
And since the “furnace” of brown fat works on lipids, the idea arose: could it be used to get rid of excess weight? But then we need some kind of “switch” that would activate brown adipose tissue when needed. To realize this idea, it is necessary, firstly, to understand the molecular and cellular mechanisms that ensure the appearance of brown fat in the body, and secondly, to make sure that it really helps against obesity and related metabolic problems.
When a person feels cold, the brain signals white adipocytes to break down triglyceride fats, and the resulting fatty acids are carried into the blood into brown fat, where they are “burned.” Muscle exercise also contributes to the transformation of white fat cells into brown ones.
Although brown fat cells were found not only in special “depots”, but also in the thickness of white fat, it was believed that they still had their own special precursors, which then developed into brown adipocytes. However, researchers from ETH Zurich have found that white fat and brown fat can directly convert into each other. The experiments were carried out on mice in which individual white fat cells were monitored: when the temperature decreased, these cells “turned brown”, and when the temperature increased, they “turned white.” It turns out that brown fat can be formed directly from white fat.
Brown adipose tissue is densely permeated with blood vessels; they not only bring her fuel, but also take heat with them. It was even possible to find nerve cells that give a signal for the breakdown of fats - they turned out to be some neurons of the hypothalamus. They controlled specifically the metabolic activity of brown fat cells. That is, appetite and food consumption remained the same, but more calories were burned in the brown fat “furnace”.
The brain can control brown fat not only through neural signals itself, but also through neuropeptide hormones called orexins. These neuropeptides are synthesized again in the hypothalamus, participate in the regulation of sleep-wake cycles and affect energy metabolism and appetite. It turned out that orexins directly act on white fat cells, promoting their transformation into brown adipocytes. (It is possible that the matter is not limited to just one direct effect, since orexins are included in a complex system of several neuropeptides that control metabolism and can act on brown fat through their “agents of influence.”) If the orexin genes were turned off in mice, the animals gained weight even when moderate diet.
However, you should not think that brown fat is under the care of just a couple of neuropeptides and a group of nerve cells. The immune system takes an active part in the transformation of one adipose tissue into another. Several years ago, researchers from the University of California, San Francisco (USA) discovered that macrophages present in white fat cause fat cells to turn brown when the temperature drops. Macrophages are commonly thought of as “cleaner” cells that clean up the effects of “immune wars,” and their active role in metabolism has only recently become clear. Under the influence of special signaling proteins, macrophages force adipose tissue to burn its reserves. And just recently it was possible to link the immune signals that control macrophages with muscle function. During physical exercise and again when the ambient temperature drops, a special hormone (called meteorin-like hormone) is released from the muscles, which, through the immune signaling proteins interleukins, acts on macrophages located in adipose tissue, and then everything unfolds according to the scenario described above.
Deciphering the mechanisms that control brown fat usually involves searching for molecular “magic buttons”—regulatory proteins that can be used to activate the appearance of new brown cells or enhance their activity. Thus, recently researchers from Virginia Commonwealth University (USA) published an article in which they proposed the enzyme Tyk2 kinase to play the role of the brown fat switch. Until now, this enzyme has been studied as one of the promising anticancer proteins. (Here we may recall that obesity often develops along with cancer.) There are many such examples, reports of proteins that activate brown fat appear regularly. Naturally, in each such work their effect on excess weight is tested. So far, everything that activates brown fat helps to get rid of excess weight. But does brown fat help reverse the metabolic problems that accompany obesity?
Researchers from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (USA) answered this question in the affirmative. They found a protein that links heat-burning calories to inflammation that begins in overgrown fat tissue. It is inflammation that is believed to provoke resistance of tissues and organs to insulin, which is a direct path to type 2 diabetes. It turned out that the TRPV4 protein, contained in white adipocytes, interferes with fat burning and promotes inflammatory processes in adipose tissue. If the synthesis of TRPV4 was suppressed, then there was no obesity or inflammation in the experimental animals, although they ate high-calorie fatty foods. In fact, other studies have also noted a connection between the activation of brown fat and the disappearance of signs of diabetes, but it was necessary to find a specific molecular link. It turned out to be TRPV4. However, it must be taken into account that research of this kind is not limited to just one link, and usually molecular biologists extract a whole signal chain by catching a link, each member of which can become a target for drugs.
Basically, such experiments are carried out on mice, so it would be reasonable to ask the question to what extent the results obtained can be extrapolated to humans. But literally in July of this year in the magazine Diabetes
An article was published in which employees of the medical department of the University of Texas at Galveston (USA) write about a clear connection between the amount of brown fat in a person, the level of glucose in the blood and the response of cells to insulin. The more active brown fat was, the more it was, the more calories were burned and the more actively glucose was absorbed from the blood into tissue cells. So brown fat could really be a good medical tool in the fight against obesity and diabetes, and it is not in vain that scientists are looking for a means with which they can quickly and effectively activate brown adipose tissue.
Most of these searches are aimed at target molecules involved in the management of brown fat. Different approaches differ in their effectiveness and likelihood of side effects. For example, biotechnological employees claim that they can activate brown adipocytes and normalize metabolism with just one injection of antibodies that activate cellular receptors for the hormone FGF21 (fibroblast growth factor 21). In diabetic mice that received the injection, their glucose levels remained normal for a whole month, and the mice themselves lost 10% weight. However, these antibodies have so far only been tested on animals. On the other hand, researchers from Cambridge (UK) believe that preference should be given to “their” protein called BMP8B, which not only activates brown fat, but does it very specifically - that is, by acting on BMP8B with some drug, we almost never we risk affecting another molecular cellular process. It is also worth mentioning the recently discovered hormone irisin - it saves against obesity and diabetes by turning white fat into brown, and at the same time promotes the growth of muscle tissue. That is, the effect of this hormone is similar to going to the gym: minus fat, plus muscles.
Among the various tips on how to activate brown fat, the proposal to use Viagra looks original. The fact that this legendary drug also helps against obesity was reported by researchers from the University of Bonn (Germany), who published an article last year in The Journal of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology
. Viagra, or sildenafil, increased the amount of brown fat in mice and also suppressed inflammation in white adipose tissue.
Well, can a person himself help increase the proportion of brown fat in the body, without waiting for medications to appear? There is such a way, and it is sports and physical education. We have already mentioned above about the meteorin-like hormone, which is released from the muscles during physical stress. Also, muscle loads increase the synthesis in muscles of the transcription factor PGC-1α, which turns on genes in white fat cells that convert them into brown adipocytes. (The protein factor PGC-1α works in a signaling chain associated with the TRPV4 protein, which has been used to “link” brown fat with diabetes.)
If you don’t want to spend time on physical exercise, your friends will help you lose weight. In 2011, researchers from Ohio University (USA) found that increased social activity helps fat mice lose weight, and protects thin ones from obesity, even if fed fatty foods. Communicating with other mice increased the proportion of brown fat in the animals' bodies, and the connecting molecular link was a fairly well-known protein called brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), the level of which increased in nerve cells during intense social life.
Finally, another way to activate brown fat, which naturally suggests itself, is cold. Indeed, if the activity of brown fat cells is increased by cold, then why not freeze for therapeutic purposes for those who are overweight? Employees of the University of Maastricht (Netherlands) tried to evaluate the effectiveness of this method. For 10 days, they forced volunteers to sit in a room with an air temperature of 15°C for six hours every day. The brown fat of the experiment participants was actually activated, they stopped freezing, and their energy expenditure increased by 30%. However, it is still unclear whether such activation is enough for truly significant weight loss.
But if brown fat alone is not enough, white fat will help - as it turns out, it can also break down fat and release heat if it gets cold around. Researchers from Harvard (USA) found that white adipocytes themselves, without the intervention of the nervous system and independently of brown fat, can sense cold and participate in thermoregulation.
To be fair, there is some evidence associated with brown fat that may dampen enthusiasm for it. For example, oddly enough, in some experiments it increased the risk of atherosclerosis, provoking an increase in the proportion of “bad” fats - low-density lipoproteins - in the blood. However, these results still need to be confirmed in clinical studies.
It is possible that the diversity of lipid tissues is not limited to white and brown fat. Two years ago, employees of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (USA) discovered that there is also beige fat in the human body. Its cells are similar to brown fat cells and also burn excess lipids to produce heat, but differ in some significant biochemical and genetic characteristics. It is possible that those adipocytes that are considered brown in humans are actually beige. However, even if adult brown fat is indeed fake, researchers will just need to switch to beige fat, which can also be used to regulate metabolism and prevent obesity.
Try to get enough sleep every day
Poor sleep can also cause the accumulation of visceral fat. Its deficiency changes the production of leptin and ghrelin. These are hormones that regulate our appetite. When they are in excess, we feel hungry more often, which leads to systematic overeating. Lack of sleep triggers the production of cortisol, the stress hormone. It not only forces us to eat more, but also contributes to the accumulation of fat in the abdominal cavity. To stop it from building up, try to sleep at least seven to nine hours a night.
Dark chocolate
Dark chocolate is one of those rare health foods that tastes incredible.
It is very fatty, about 65% calories.
Dark chocolate is 11% fiber and contains more than 50% of the recommended daily intake of iron, magnesium, copper and manganese.
It's also so rich in antioxidants that it's one of the highest rated foods tested, even beating blueberries.
We offer you: 20 foods high in vitamin C
Some of the antioxidants it contains have powerful biological activities and may lower blood pressure and protect LDL cholesterol in the blood from oxidation.
Research also shows that people who eat dark chocolate 5 or more times a week are less than half as likely to die from heart disease compared to people who don't eat dark chocolate.
There is also some research showing that dark chocolate can improve brain function and protect your skin from damage from sun exposure.
Just make sure to choose quality dark chocolate, at least 70% cocoa.
Summary: Dark chocolate is high in fat but rich in nutrients and antioxidants. It is very effective in improving cardiovascular health.
Exercise regularly
Sport is the best way to quickly burn fat, including visceral fat. Exercise regularly to prevent it from building up. A 2022 study published in the scientific journal Nutrients found that exercise reduces the amount of visceral fat, even if you're not currently losing weight.
Viewers are disappointed: on the show “The Voice. Children" ignored real talent
Rockets in honor of the first space flight: how else were sites set up in the USSR
Destiny 2 finally added the final quest with Raven: it wasn't without problems
How is this possible? Physical activity reduces circulating insulin levels. Namely, it forces our body to accumulate fat. Roughly speaking, sport forces our liver to burn visceral fat. A 2022 research review confirms this. Strength exercises and moderate-intensity cardio are most effective in burning visceral fat.
Cheese
Cheese is incredibly nutritious.
This makes sense considering that one thick slice of cheese requires a full cup of milk.
It is an excellent source of calcium, vitamin B12, phosphorus and selenium, and also contains many other nutrients.
It's also very rich in protein: one thick slice of cheese contains 6.7 grams of protein, the same as a glass of milk.
Cheese, like other high-fat dairy products, also contains powerful fatty acids that have been linked to all sorts of benefits, including a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes.
We bring you: 12 High Carb Foods That Are Incredibly Healthy
Summary: Cheese is incredibly nutritious, and one slice contains the same amount of nutrients as a glass of milk. It is an excellent source of vitamins, minerals, quality proteins and healthy fats.
Add more protein to your diet
Any fat comes from the energy that is released during the breakdown of sugar or other carbohydrates. Their processing provokes a rapid surge of insulin in the blood, which makes us feel hungry. If you want to stop fat accumulation, try to eat more protein foods. They saturate the body longer, preventing overeating. They also help burn belly fat. Protein improves the health of the intestinal microbiome, that is, it increases the number of beneficial intestinal bacteria. This improves food absorption. A healthy microbiome also contributes to the loss of visceral fat, even if you are not losing weight.
Fat cell growth
Previously, it was believed that new fat cells do not grow in adults. That is, a person is born with a certain amount of them, and it can only increase during puberty or during pregnancy, and in other cases the cells are either filled with fat to a large size or blown away. Today we know that the adult body can create new fat cells throughout life.
When existing adipocytes reach their limiting size, their stretching stimulates the release of various signaling substances. They tell the body to make new fat cells from preadipocytes, i.e. "dormant" fat cells.
And if these new cells also become too large, the body will continue to make new ones. Unfortunately, the only way to get rid of newly created fat cells is through surgery.
By the way, a new class of diabetes drugs (TZDs) works exactly like this - by stimulating the production of new fat cells, which makes it possible to "move" glucose and fats out of the bloodstream to a safer place. This is extremely important for people with diabetes.
Whole eggs.
Whole eggs used to be considered unhealthy because the yolks were high in cholesterol and fat.
We offer you: 7 healthy foods high in vitamin D
One egg contains 212 mg of cholesterol, which is 71% of the recommended daily value. Additionally, 62% of the calories in whole eggs come from fat.
However, new research has shown that the cholesterol in eggs does not affect blood cholesterol, at least not in most people.
What we're left with is some of the most nutrient-dense food on the planet.
Whole eggs are rich in vitamins and minerals. They contain a little bit of almost all the nutrients we need.
They even contain powerful antioxidants that protect the eyes and are high in choline, a brain nutrient that 90% of people don't get enough of.
Eggs are also good for weight loss. They are very healthy and contain large amounts of protein, the most important nutrient for weight loss.
We offer you: 12 healthy foods high in iron
Despite the high fat content, people who replace breakfast grains with eggs end up consuming fewer calories and losing weight.
The best eggs are those rich in omega-3s or pasture-raised. Just don’t throw away the yolk, almost all the nutrients are there.
Summary: Whole eggs are among the most nutrient-dense foods on the planet. Despite their high fat and cholesterol content, they are incredibly nutritious and healthy.
Extra virgin olive oil.
Another fatty food that almost everyone considers healthy is cold-pressed. olive oil.
We offer you: 10 products that will help you look younger
This fat is an important component of the Mediterranean diet, which has been shown to have many health benefits.
Extra virgin olive oil contains vitamin E and vitamin K and is rich in powerful antioxidants.
Some of these antioxidants may fight inflammation and protect LDL particles in the blood from oxidation.
It has also been shown to lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol markers, and have all sorts of benefits related to heart disease risk.
Of all the healthy fats and oils in the diet, extra virgin olive oil is king.
Summary: Extra virgin olive oil has many health benefits and is incredibly effective at improving cardiovascular health.
Fatty fish.
One of the few animal products that most people agree is healthy is fatty fish.
This includes fish such as salmon, trout, mackerel, sardines and herring.
These fish are rich in heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids, high-quality proteins, and all sorts of important nutrients.
We offer you: 20 healthy fruits that are very nutritious
Research shows that people who eat fish tend to be much healthier, with a lower risk of heart disease, depression, dementia and all sorts of common diseases.
If you can't (or don't want to) eat fish, you may want to consider a fish oil supplement. Cod liver oil is the best and contains all the omega-3s you need as well as plenty of vitamin D.
Summary: Fatty fish like salmon are rich in important nutrients, especially omega-3 fatty acids. Eating fatty fish is associated with improved health and a reduced risk of various diseases.
Chia seeds
Chia seeds are not typically thought of as a "fatty" food.
However, 28 grams of chia seeds contain 9 grams of fat.
We offer you: 20 best foods high in soluble fiber
Given that almost all of the carbohydrates in chia seeds are fiber, most of their calories come from fat.
In fact, chia seeds are about 80% fat in terms of calories. This makes them an excellent fatty plant food.
They're not just fats, most of the fats in chia seeds are made up of heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids called ALA.
Chia seeds may also have many health benefits, such as lowering blood pressure and being anti-inflammatory.
Plus they are incredibly nutritious. Chia seeds are not only rich in fiber and omega-3, but also rich in minerals.
Summary: Chia seeds are very rich in healthy fats, especially an omega-3 fatty acid called ALA. They are also rich in fiber and minerals and have many health benefits.