Not sure about how much carbohydrate you should consume before and after your workout? Build your own schedule with this complete guide to the types and timing of different carbohydrates!
Often referred to as the "devil macro" or the "instant weight gainer," carbohydrates are the subject of heated debate in the fitness community, especially when it comes to their role in building muscle or burning fat. With so many opinions on whether or not you should take carbohydrates - basically, only at certain times or only from certain sources - it is not surprising that many people do not have a clear understanding of what carbohydrates are.
The first thing you need to remember is that carbohydrates act as a source of fuel for the brain and body. During exercise, carbohydrates that are stored in the muscles (in the form of glycogen) are broken down into glucose (sugar) and sent to the muscles to provide energy. The more intense the training session, the more your body relies on carbohydrates for energy.
Carbohydrates play an important role in performance during exercise, but not all carbohydrates have the same characteristics, and some carbohydrates are more effective than others at certain times. Don't worry if everything seems too complicated for now! This article's simple guide will tell you the best carbohydrates to consume before, during, and after workouts for peak performance.
Carbohydrates replenish glycogen stores
The main reason to consume carbohydrates post-workout is to replenish the muscle glycogen you burned during your workout. When you exercise, your main source of fuel is muscle glycogen . Glycogen is a storage form of glucose storage , which consists of long chains of branched glucose molecules.
Glucose is released from the glycogen chain as needed to produce ATP , which carries energy and is key for muscle contraction . Research confirms that the best way to replenish muscle glycogen stores after exercise is high-glycemic carbohydrates [13]
Some “experts” claim that regular gym workouts don’t burn enough glycogen to warrant replenishment . However, it is not. When you deplete any amount of muscle glycogen, you should take care to restore , especially if muscle growth is your main goal. If a trainer claims that people don't need to worry about glycogen replenishment , then their training is weak and at very low intensity, or they haven't looked at any research. [12]
A study on glycogen utilization during strength training found that workouts that included 6-20 sets of approximately 15-30 minutes depleted muscle glycogen stores by approximately 30-40 percent . If your workouts last 60-90 minutes , you need to move quickly between exercises, or you prefer high-intensity workouts like cardio or Tabata, then such workouts will deplete your muscle glycogen by as much as 60-75 percent. [2] So take your post-workout carbohydrate intake seriously and be sure to your muscle glycogen stores If you don't do this, you are cheating your muscles and limiting their recovery. Based on the study, delaying carbohydrate consumption by just 2 hours showed a reduction in the rate of glycogen replenishment by as much as 50 percent! [2]
Some experts also argue that most people in the gym don't do this because there is evidence that, whether you consume carbohydrates immediately after exercise or two hours later, glycogen levels replenish themselves within 24 hours . However, there is no significant evidence of this information. Therefore, the fastest way to replenish glycogen stores is to consume carbohydrates with a high glycemic index immediately after exercise.
Full restoration of glycogen levels as soon as possible after exercise is essential for muscle growth. Glycogen stored in muscle cells attracts water into them, thereby increasing the volume of the muscle cell and thus the fullness of the muscle fibers. [9]
Considering that you pump up your muscles during exercise, which also increases the amount of water in the muscle cells and therefore their volume, then quickly replenishing muscle glycogen can help you maintain high muscle cell volume over a long period. This may be important because evidence suggests that high muscle cell volume triggers changes in muscle that also lead to long-term muscle growth. [3]
The next benefit of eating carbohydrates, and especially high-glycemic carbohydrates such as dextrose, immediately after an intense workout is that you will feel energized . Carbohydrates help get rid of lethargy after a hard workout and give you energy . Also, eating high-glycemic carbohydrates post-workout tends to satisfy cravings for sweet or starchy carbohydrates without negatively impacting your diet. [9]
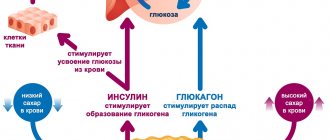
What about insulin?
Another benefit of high glycemic index carbohydrates is the insulin release . While insulin is classified as an anabolic hormone , its role in the muscle growth process is increasingly debated. Although it was once considered one of the crucial factors for muscle protein synthesis and reducing muscle tissue breakdown. Some modern research suggests that this is characteristic of amino acids . [3] [9]
Scientists recently compared eating protein post-workout to eating protein along with carbohydrates . The study found that adding carbohydrates to a protein shake did not increase muscle protein synthesis reduce muscle protein breakdown any more than any other protein shake. [5] [6]
However, insulin is still important immediately after exercise. Insulin attaches to specific receptors on muscle cells , and this allows glucose, amino acids, as well as carnitine and creatine to enter muscle cells. Research also shows that both carnitine and creatine depend on insulin to be able to enter muscle cells to produce beneficial effects. [eleven]
If you start taking these two supplements post-workout, you'll likely want to get the maximum insulin spike in your bloodstream if your main goal is muscle growth. As mentioned above, this does not apply to the diet period when carbohydrates should be limited, including after training, since in this case protein shakes and BCAAs will provide the necessary surge of insulin to the muscles. [9]
Sample menu
For those who want to build muscle, the following sample menu is suitable.
Monday:
- 1st breakfast : oatmeal with nuts and apple.
- 2nd breakfast : chicken with vegetables and potatoes.
- Lunch : cottage cheese with banana.
- Afternoon snack : fish with vegetables and rice.
- Dinner : tuna with vegetable salad.
- Snack : fruit salad.
Tuesday:
- 1st breakfast : buckwheat porridge with milk and honey; nuts; orange.
- 2nd breakfast : veal baked with vegetables and boiled pasta.
- Lunch: kefir with whole grain bread.
- Afternoon snack : cottage cheese with kiwi and honey.
- Dinner : baked mackerel with vegetable salad.
- Snack : Peanut butter and yogurt with strawberries.
Wednesday:
- 1st breakfast: oatmeal with apple; nuts; banana.
- 2nd breakfast : lean veal with vegetables and potatoes.
- Lunch : omelet with black bread and an apple.
- Afternoon snack : milk smoothie with fruit.
- Dinner : turkey with rice.
- Snack : cottage cheese with jam.
Thursday:
- 1st breakfast : rice with milk and nuts, apple.
- 2nd breakfast : veal and vegetable soup.
- Lunch : kefir with whole grain bread.
- Afternoon snack : fruit salad.
- Dinner : turkey with baked potatoes.
- Snack : vegetable salad.
Friday:
- 1st breakfast : omelette with chicken fillet and vegetables.
- 2nd breakfast : lean veal with potatoes and banana.
- Lunch : cottage cheese with apple and jam.
- Afternoon snack: fruit smoothie.
- Dinner : vegetable and chicken stew.
- Snack : Peanut butter and yogurt with strawberries.
Saturday:
- 1st breakfast : oatmeal with banana and nuts.
- 2nd breakfast : potatoes with chicken and vegetables.
- Lunch : kefir with whole grain bread.
- Afternoon snack: cottage cheese with kiwi honey.
- Dinner : buckwheat porridge with baked mackerel and vegetable salad.
- Snack : fruit salad.
Sunday:
- 1st breakfast : omelette with chicken and vegetables.
- 2nd breakfast : veal with vegetables and apple.
- Lunch : cottage cheese with banana and jam.
- Afternoon snack: fruit smoothie.
- Dinner : rice with chicken and vegetables.
- Snack : vegetable salad.
Fast carbohydrates are foods that can instantly convert amino acids into building blocks for muscle growth. They must be eaten during the open anabolic window (in the first hour after training). Eating this way also promotes rapid muscle development.
Dextrose is the best source of post-workout carbohydrates
Consuming pure glucose, also called dextrose, after exercise means your body doesn't have to digest it . Glucose is absorbed into the blood instantly, immediately after administration. And this allows it to be delivered to the muscles as quickly as possible, which ensures faster and more complete restoration of muscle glycogen. This will maintain muscle glycogen stores until your next workout and water flow to muscle cells to maximize muscle size. [4]
How to cook meals
Sprouted wheat added to dishes will be a source of additional arginine and chromium. It is useful to season vegetable salads not only with sunflower oil, but also with its seeds.
When cooking, it is better not to bake or fry foods, but to:
- steam;
- stew;
- cook
Vegetables and greens are eaten raw. 2-3 hours before strength training, eat protein-carbohydrate meals.
Immediately after performing the exercises, drink special cocktails for sports with:
- minerals;
- protein;
- vitamins.
Try a combination of maltodextrin and glucose
Maltodextrin is a complex carbohydrate found in corn, rice or potato starch, but its molecular formula is shorter than that of regular complex carbohydrates. It also consists of loosely bound glucose molecules, and like dextrose, maltodextrin is absorbed directly from the intestines . Thus, it increases blood sugar and insulin levels, just like dextrose . [13]
The only difference is that maltodextrin must first pass through the liver , breaking the bonds between glucose molecules. This affects the rate of glycogen production, which is slower than when consuming dextrose . Because it takes longer to metabolize, there is no rapid decrease in insulin and blood sugar levels as with dextrose. For this reason, a 1:1 ratio of dextrose and maltodextrin is a healthier post-workout option. [13]
List of foods for weight gain
The following foods will be important for gaining muscle mass:
- Proteins: pearl barley and buckwheat porridge; lean meat; millet; seafood; nuts and beans; all dairy; eggs.
- Fats: butter; fatty sea fish; milk fats.
- Carbohydrates: muesli; vegetables; rice; fruits; pumpkin; cereals; potato; beans; raisin; dates.
Fast carbohydrates are foods that restore athletic strength after active sports and trigger the muscle growth response during rest. The glycogen produced when consuming them replenishes its reserves. Simple carbohydrates also release more insulin than protein does, either on its own or from muscles. The latter, thanks to this phenomenon, are not destroyed.
Fructose is not fast enough
Fructose, which makes up 50% of the sugar in most fruits, honey and sucrose, is actually a low glycemic index carbohydrate . Fructose is a type of sugar that the body doesn't use very well. Due to its structure, it cannot be directly converted into muscle glycogen like glucose.[4]
So when you consume fructose in the form of fruit or high fructose corn syrup, it is not immediately absorbed into the bloodstream like dextrose. Instead, most of it is forced to move to the liver , where it can be converted into glucose and stored as glycogen. This occurs when the liver deems it necessary to blood glucose levels [4]
Because glucose does not optimize muscle glycogen recovery, it is not the best post-workout option. This is one of the main reasons why you should choose gummies and candies instead of fruits or other sweets. Most candies use high fructose corn syrup or sugar as the main sweetener. ( sucrose) is approximately 50% fructose and 50% glucose , while high fructose corn syrup is approximately 55% or more fructose . In contrast, most gummy bears contain dextrose and corn syrup. Corn syrup is primarily glucose and is significantly different from the contaminant-laden high fructose corn syrup.
Eating carbs after a workout won't hurt you
Many people worry that carbs after a workout will add fat to their body , but post-workout is about the only time of day when you can be sure that carbs aren't being converted into body fat. carbohydrates immediately after training.
If you are on a diet to reduce your body fat percentage, but you consume carbohydrates at all meals, then you should not avoid eating carbohydrates after a workout. It's best to cut back on carbohydrates at other meals and save them for the period immediately after exercise.
Maybe you're afraid to eat carbs after exercise because you've heard that eating carbs immediately after exercise can lower your growth hormone and testosterone levels. However, this is not true. Why? Because growth hormone and testosterone levels peak during the training period, and when the training is completed, they plummet, regardless of whether you ate anything or not. So, eat after your workout and stop worrying about your already plummeting hormone levels. [8]
How to calculate your daily calorie intake?
To increase muscle mass, the following ratio of BJU is required - 35/30/55, that is:
- 35% should be proteins;
- 30% may be fat;
- carbohydrates in the daily diet should be 55%.
Further calculations are carried out using the Geor formula, namely:
- Body weight in kg is multiplied by 10.
- Height in cm is multiplied by 6.25.
- Age in city is multiplied by 5.
- The results of points 1 and 2 are added up, and then the number from step 3 is subtracted from the result.
- Men add 5 to the result, and women subtract 161 from it.
- The resulting number is multiplied by A, where A is a coefficient that indicates the physical level of human development:
- 1,2 – practically absent (no sports activities);
- 1,375 – weak (with 1 or 3 workouts in 7 days);
- 1,55 – average (3-4 trainings per week, 1 hour each);
- 1,7 – high (with daily training);
- 1,9 – hyperactive (with numerous sets every day).
Next, the resulting calories are converted into grams, given that 1 g of fat is 9 calories, and 1 g of carbohydrates or protein is 4 calories. So, for example, the result of 1300 is multiplied by 0.35 or 0.55, and then divided by 4 - the daily amount of protein or carbohydrates per g is obtained. Fats in g are calculated using a similar scheme, only divided by 9.