- July 21, 2018
- Health
- Ksenia Leonidova
When a person wants to describe someone's figure, they most often use one of three definitions: thin, normal, plump. Everyone has their own idea of the difference between these characteristics: someone may think one person is thin, while someone will say that he is quite normal. Of course, everyone’s concept of beauty is different, but there are also scientific studies that have described human body types for quite some time, and, as they say, you can’t argue with science. Scientists distinguish three body types: asthenic, normosthenic, hypersthenic. Each group has its own pros and cons, knowing which you can build your diet and training in the most constructive way possible. Therefore, before working for results, find out your physical characteristics. You can determine your body type at home. The most common way is to determine body type by wrist. This method was described in 1917 by the domestic doctor G. A. Solovyov. The Solovyov index is a relative indicator of bone thickness, by which you can make a conclusion about your figure. Before answering the question of how to determine your body type by wrist, we list the features of all three body types.
Body types
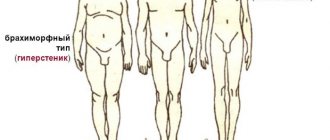
There are three traditional body types, one of which a person is assigned at birth. Along with it, everyone gets a certain metabolism, the ratio of fat and muscle tissue and the width of bones. Thin-boned, thin people with a high metabolism are asthenics. Proportional, harmoniously developed individuals with medium or wide bones and having an average metabolism are normosthenics. Overweight, big-boned people with a slow metabolism are hypersthenics. Since physique is primarily a classification of the skeleton, one type cannot change into another. People with age (and not only) gain excess weight, but this does not mean that they all become hypersthenics. This only demonstrates that there are some shortcomings in their lifestyle and habits, or indicates other processes occurring in the body.
Main models
A bracelet is a classic piece of jewelry that is worn on the hand. Being widely known since Paleolithic times, it was present in the cultures of various peoples. It was assumed that wearing special hoops on the wrists could protect against evil spirits, damage and the evil eye, and all kinds of troubles and adversities.
These unique accessories have not lost their relevance today, being divided into several types and categories. Thus, bracelets are usually distinguished by:
- shape - spiral, round (hoops), bracelets-clips, bracelets-half-rings and bracelets-chains;
- material – gold, silver, platinum or costume jewelry;
- manufacturing method - closed, hinged, chain, spring, braided.
Chain accessories are those made by connecting chain links in series.
Hinged - those that are secured using a special hinge.
Closed - one-piece bracelets that do not have additional fasteners or inserts.
Spring - tightly wrapping around the hand, stretching under mechanical influence. Made on the basis of elastic threads.
Braided - made on the basis of beads or beads by stringing.
How to determine your body type based on your wrist?
To determine the constitution of the body you need to perform a few simple manipulations:
Option 1. Take a tape measure and measure the circumference of your wrist.
Option 2. If you do not have a centimeter, then you can use thread, tape, etc. and attach the resulting segment to the ruler.
Option 3. The easiest way is to clasp your wrist with the thumb and forefinger of your other hand: if the fingers touch with reserve, then you are asthenic, if without reserve, you are normosthenic, and if they do not touch at all, then you are hypersthenic.
This is how you can easily and simply determine the body type of men and women based on their wrists. The width of the wrist is considered a constant value, independent of the current weight and amount of muscle mass. You need to measure the narrowest part of the wrist. Next, we look at the result obtained and its meaning.
Types and rules of measurements
Wrist circumference in women and men is knowledge that will be needed not only to determine the somatotype, but also when purchasing (tailoring) clothes, as well as watches, jewelry, in particular, a bracelet - a fashionable accessory today. The exact values of this parameter will help you choose the product that will be most convenient.
The algorithm for measuring wrist circumference in all these cases is not fundamentally different from the one given above, but has its own nuances.
Measurements for a bracelet without clasp
A bracelet has a number of requirements, compliance with which largely depends on its length. It, in turn, is determined based on the circumference of the wrist.
In particular, the decoration should:
- do not slip off your hand spontaneously;
- easy to take off and put on;
- do not squeeze your wrist;
- do not restrict movement.
When purchasing in a jewelry store, you always have the opportunity to try on the product, but if you are purchasing it online, you will have to take several measurements yourself:
- the main measurement is the girth of the wrist: you need to measure it along the wrist joint, and not between it and the hand, as when determining your body type: the difference, although insignificant, is there. Another difference: measurements are taken on the hand for which the jewelry is intended;
- for a bracelet without a clasp, you will also need to measure the volume of your hand, to do this, press your thumb against your palm and measure in the widest part of your hand;
- When buying a double or triple bracelet, you need to measure your wrist in several places (just above the wrist joint).
Usually this data is enough for the seller to select the desired sample: for this, 1-3 cm is added to the circumference of the wrist.
The specific amount of the increase depends on the following factors:
| Factor | Description |
| Hand girth | If the hand is narrow, the increase should be minimal, otherwise the bracelet will slip off the hand. |
| The presence or absence of elastic inserts on the bracelet | If they are, the increase is minimal. |
| Material of manufacture | For example, massive voluminous stones or wooden or plastic beads will create additional volume and require a significant increase. Otherwise, the bracelet will be tight. The most difficult thing is choosing the right size of a leather bracelet, since this material can stretch or shrink depending on humidity and operating conditions. |
| Shape of bracelet elements | If it consists of large wide fragments, then it must cover the hand tightly enough, otherwise the product will lose its decorative effect, and a thin chain is allowed to hang freely from the hand. |
| Design features | For double and triple bracelets, the premium is always higher. |
| Availability and possible number of charms | Small removable pendants: the more of them, the larger the diameter of the bracelet should be. |
| Client's wishes | Some people like the bracelet to fit tightly around their hand, while others, on the contrary, prefer freedom. |
The decision regarding the length of the bracelet must be made based on the totality of all these data.
Measurements for bracelets with a clasp with a small margin
To select a bracelet with a clasp, provided that its length is not much greater than the circumference of the wrist, you do not need to measure your palm; otherwise, the algorithm is the same as described above.
As a rule, for thin metal bracelets with locks of the most popular type P-Lock (a latch in the form of a decorative bead that opens when pressed), the increase in length is approximately 2 cm. For other types of bracelets, the dimensions of its elements and the material of manufacture are taken into account.
If, when measuring the wrist, a fractional number is obtained, when choosing the length of the bracelet, its design features and the client’s requirements regarding the tightness of the product to the hand are taken into account.
Bracelets sizes for women
As a rule, all the necessary calculations are performed by the jewelry seller. The buyer is only required to provide him with wrist circumference, but there may be exceptions. To eliminate errors, this point should be clarified.
Measurements for knitting gloves, mittens
When knitting gloves and mittens, the main parameter is the circumference of the palm, measured at its widest part (at the base of the fingers). A tight fit of the cuff to the wrist is achieved through the use of elastic knitting.
If there are concerns that the product will be too tight or loose on your hand in this place, you can do the following:
- Measure the circumference of your palm.
- Knit the prototype with the main knitting stitch.
- Using a prototype, determine the knitting density (the number of loops in 1 cm of fabric) and calculate the number of loops that need to be cast on.
- Cast on the required number of stitches on the knitting needle and knit a few centimeters with an elastic band.
- Measure the length of the resulting canvas.
- Measure your wrist circumference and compare the resulting values: ideally, they should match (since the knitted fabric is elastic, no increases are required).
- If necessary, add or subtract a few loops. After the elastic band is knitted, perform the reverse operation, then knit the product with the main stitch.
Measurements for knitting gloves, mittens
In addition to the circumference of the palm and the circumference of the wrist, to knit mittens you will need to measure the length of the thumb and the distance from its base to the tip of the middle finger. When knitting gloves, things are a little more complicated.
You will need to take the following measurements (without allowances):
- hand circumference;
- wrist circumference;
- distance from the wrist to the base of the thumb;
- distance from the wrist to the base of the little finger;
- distance from the wrist to the base of the middle and index fingers;
- the length of each finger.
All these parameters are needed in the case when you have to knit “in absentia”. If the product can be tried on at any time, usually only the wrist circumference necessary to calculate the required number of loops is used, and all other parameters are determined during fitting.
Wrist measurements for sewing clothes with long sleeves
The correct choice of sleeve width is one of the prerequisites for the comfort of clothing, its attractive appearance and high heat-saving qualities (the latter is important for jackets and coats). When performing the necessary calculations, you need to start from the girth of the wrist, which is measured by the wrist joint on the leading hand.
Wrist measurements for sewing clothes with long sleeves
Next, the following types of additions must be made to the result obtained:
- freedom of fit;
- on the clasp (if any);
- on an insulating lining (for demi-season and winter clothing);
- on the seams (directly when cutting the fabric).
An increase in freedom of fit, due to which a gap is created between the arm and the sleeve (or cuff), is necessary to ensure freedom of movement.
Taking sleeve measurements
Its value depends on several factors, in particular:
- type of clothing: shirt, dress, coat;
- its seasonality: for cold or warm seasons;
- silhouette type: close-fitting, semi-fitting, loose;
- design features: method of designing the bottom of the sleeve (cuff, without cuff);
- material: in this case, the degree of its elasticity is important;
- the presence or absence of a fastener.
When sewing a men's or women's shirt with cuffs, the following allowances are recommended: fit - 2 cm, fastening - 3 cm, seams - 0.5 cm on each side. With a wrist circumference of 17 cm, the optimal cuff length is 23 cm; for sewing you will need a strip of fabric 24 cm long (including seam allowance).
Indicators
Of course, each person is unique, but numerous studies and measurements have allowed scientists to determine average parameters that can be used as a guide. The table below lists wrist widths for men and women.
| Body type | men | women |
| asthenic | less than 18 cm | less than 15 cm |
| normosthenic | 18-20 cm | 15-17 cm |
| hypersthenic | more than 20 cm | more than 17 cm |
[poll][medicine] Can you do this?
There are several symptoms that are associated with heart disease, the symptoms are quite acrobatic:
Thumb sign. If you press your thumb to your palm and clasp it with your other fingers, then normally the thumb does not protrude beyond the ulnar edge of the hand.
Wrist symptom. If, with a little effort, you clasp your wrist with your thumb and little finger, and the little finger overlaps the thumb by at least 1 cm, then you can talk about going beyond the norm.
Hypermobility of joints. Normally, the fingers cannot be bent back, but if you go beyond the normal limits, you can easily bend the finger back so that you can touch the back of the palm of the same hand with the tip of your finger. also, if you go beyond the norm, you can reach your thumb to the wrist of the same hand. Knees and elbows can also be susceptible to hypermobility (flexion of these joints over 190° degrees can be considered beyond the normal range).
Can any of the LOrovites demonstrate at least two of the three named symptoms?
>Wrist symptom. If, with a little effort, you clasp your wrist with your thumb and little finger, and the little finger overlaps the thumb by at least 1 cm, then you can talk about going beyond the norm.
how to grab it like that?
>how do you grab it like that?
I understand the wrist of the other hand
Neither of. The second option is kind of unrealistic, this is how you need to lose weight so that your wrist becomes so thin. However, about 5 years ago the first two points could have worked for me.
> Thumb sign. If you press your thumb to your palm and clasp it with your other fingers, then normally the thumb does not protrude beyond the ulnar edge of the hand.
Wrist symptom. If, with a little effort, you clasp your wrist with your thumb and little finger, and the little finger overlaps the thumb by at least 1 cm, then you can talk about going beyond the norm.
one and a half centimeters. however my fingers are very long
Hypermobility of joints. Normally, the fingers cannot be bent back, but if you go beyond the normal limits, you can easily bend the finger back so that you can touch the back of the palm of the same hand with the tip of your finger. also, if you go beyond the norm, you can reach your thumb to the wrist of the same hand. Knees and elbows can also be susceptible to hypermobility (flexion of these joints over 190° degrees can be considered beyond the normal range).
I can’t reach the back of my hand, but my little finger is pulled towards it to a distance of a centimeter and a half. the thumb does not reach the wrist just a little. but my brother could previously, without lifting his palm from the plane, turn it 360 degrees clockwise.
and the topic is something like “most people can’t bite their elbow.”
Source
Asthenic body type
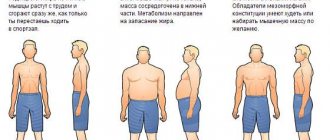
As can be seen from the table, if a girl’s wrist is 14 cm, then she is asthenic. People with this body type are also called ectomorphs. These are graceful individuals who have naturally thin bones. It is not difficult to visually identify asthenics; they have:
- narrow shoulders and chest;
- thin long neck;
- relatively short body;
- small breasts;
- angular body contours;
- elongated limbs;
- underdeveloped muscles;
- small amount of subcutaneous fat.
It is believed that ectomorphs are not strong and resilient enough, so physical activity aimed at developing endurance is more suitable for them. If the goal is to gain muscle mass, then cardio exercises should be abandoned in favor of strength exercises. Since the metabolism of ectomorphs is very high, to preserve energy for a long time, it is better for them to eat foods rich in complex or plant carbohydrates, and increase the number of meals to 5-6 times a day. Fortunately for asthenics, fat deposits are practically not formed on their body, but it is also quite difficult to gain muscle mass. However, with the right diet and proper training, ectomorphs can achieve impressive results.
What is a somatotype
Somatotype is the constitutional body type of a person. “It is laid down by nature and cannot be radically changed,” explains Ekaterina Zhuravleva, an expert in the X-Fit group programs in Russia .
“Everyone at birth is given relative proportions of fat, muscle, bone tissue, as well as limb length and height.” But it is worth understanding: the somatotype determines not only appearance, but also affects physical development in general. “This is not just a physique, but also a program for his future physical development,” says Ekaterina Kalinina, a gastroenterologist, specialist in dietology and nutrition at the SportMedica sports medicine clinic . — A person’s physique changes throughout life, it is influenced by: age-related changes, diseases, increased physical activity, etc. Whereas the somatotype is genetically determined and remains unchanged from birth to death.”
Normosthenic body type
To the question about what body type girls have with a 15 cm wrist, we answer that it is normasthenic. The figure of mesomorphs, as normosthenics are also called, is the standard figure. Such people are proportional, their genetic potential is enormous: subject to diet and regular exercise, their body quite easily acquires a sporty appearance. Those with wrists of 16 cm and 17 cm are also normosthenics. Characteristics of mesomorphs:
- developed muscles;
- the body and limbs are proportional;
- the shoulders are well developed, the chest is of medium size;
- pronounced waist;
- the fat layer is present, but in moderate quantities throughout the body;
- the skin is elastic, dense.
Normosthenics are distinguished by the fact that they quickly gain weight and lose it just as quickly. The diet of normosthenics should contain equal amounts of proteins and carbohydrates, and fats should not be excluded. Any type of activity is suitable for a mesomorph.
Weight index
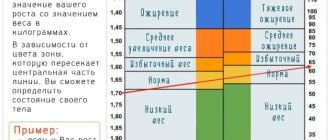
Determining a woman's weight index or body mass index (abbreviated BMI) allows us to assess the compliance of a woman's basic anthropometric indicators - height and body weight - and determine the need for weight correction by changing diet or physical activity.
In general, the formula for calculating the mass index is:
BMI = M/H2,
Where:
- M – weight, kg;
- H2 – height in meters, squared.
For example, if a woman’s height is 1.7 m and her weight is 50 kg, then:
BMI = 50 / (1.7 x 1.7) = 17.
To correlate this indicator with the norm and establish deviations, the following interpretation of values is used (according to WHO):
- up to 16 kg/sq. m – pronounced deficit weight;
- from 16 to 18.5 kg/sq. m – deficient weight;
- from 18.5 to 25 kg/sq. m – weight within normal limits;
- from 25 to 30 kg/sq. m – there is a tendency to obesity;
- from 30 to 35 kg/sq. m – presence of obesity;
- from 35 to 40 kg/sq. m – high degree of obesity;
- from 40 kg/sq. m and more – a pronounced, severe form of obesity.
Accordingly, the resulting value is 17 kg/sq. m falls under the indicator of deficit weight.
This formula has large errors and does not take into account the characteristics of a particular somatotype, which may significantly go beyond the preset BMI values.
Height and weight standards by body type
Women's body types have their own characteristics and distinctive features, based on which the ideal weight norm for each somatotype is determined. Moreover, this norm may vary depending on the age of the woman.
| Height, cm | Permissible weight limit, kg | ||
| for asthenics (ectomorphs) | for normosthenics (mesomorphs) | for hypersthenics (endomorphs) | |
| Up to 148 | 42,5 – 51,2 | 45,3 – 54,9 | 53,4 – 60,0 |
| 148 – 150 | 43,2 – 52,2 | 49,8 – 57,4 | 54,6 – 62,4 |
| 151 – 153 | 44,7 – 52,6 | 51,2 – 57,2 | 53,8 – 62,7 |
| 154 – 159 | 47,2 – 56,3 | 52,1 – 61,3 | 56,4 – 65,8 |
| 160 – 163 | 50,9 – 57,4 | 54,8 – 68,2 | 58,8 – 68,7 |
| 164 – 169 | 52,9 – 61,0 | 57,4 – 65,6 | 62,2 – 72,4 |
| 170 – 173 | 55,6 – 63,1 | 60,2 – 68,3 | 65,1 – 75,7 |
| 174 – 179 | 57,1 – 65,6 | 62,4 – 71,1 | 66,6 – 78,4 |
| 180 or more | 61,2 – 68,7 | 65,3 – 73,6 | 69,7 – 81,6 |
These indicators are suitable for the category of women aged 18 to 35 years. If the age is greater, then to the indicated values you need to add:
- 3 kg for ectomorphs;
- 4 kg for mesomorphs;
- 5 kg for endomorphs.
In this case, the norm is understood as the average value of mass, which can fluctuate in the region of the segment between the maximum and minimum limit points, and differ depending on the formulas used for calculating the ideal weight.
The classic formula for determining BMI taking into account the somatotype
The BMI calculation formula recommended by the World Health Organization has been refined over time and takes into account the somatotype of women.
It looks like:
- for asthenics BMI = (M + 10%) / H2;
- for normosthenics BMI = M / H2;
- for hypersthenics (M – 10%) / H2.
Thus, in the presence of a hypersthenic or asthenic physique, a preliminary adjustment of body weight by 10% is required in the direction of decreasing or increasing, respectively.
For example:
- The woman has an asthenic somatotype with a weight of 47 kg and a height of 162 cm.
BMI = (47 + 10%) / (1.62 x 1.62) = (47 + 4.7) / 2.6244 = 19.7
Accordingly, the weight is within normal limits (according to WHO).
- The woman has a mesomorphic somatotype with a weight of 63 kg and a height of 168 cm.
BMI = 63 / (1.68 x 1.68) = 63 / 2.8224 = 22.3
Which corresponds to normal weight.
- A hypersthenic woman with a weight of 76 kg and a height of 164 cm.
BMI = (76 – 10%) / (1.64 x 1.64) = (76 – 7.6) / 2.69 = 25.4
In this case, there is already a trend towards obesity.
Weight index according to Broca's formula
The fundamental formula for determining the ideal body weight was developed by the French surgeon P. Broca back in the second half of the 19th century.
It looks like this (for women):
IV = Height – 100
For the calculation, take the height value in centimeters.
As we studied somatotyping, significant disadvantages of this method were identified:
- only suitable for the average woman with a height of 155 cm to 175 cm;
- not suitable for female athletes;
- not suitable for women suffering from conditions associated with weight loss or weight gain.
Broca–Brugsch weight index based on body type
The previous formula was modified by the German scientist T. Brugsch for women whose height does not fit into the range of 155 - 175 cm.
- with a height of less than 165 cm, IV = Height – 100;
- with a height of 165 – 175 cm, IV = Height – 105;
- with a height of over 175 cm, IV = Height – 110.
These formulas are suitable for mesomorphic women. For the asthenic type, it is recommended to add 10% to the obtained IV, and for the hypersthenic type, subtract 10% from the result.
For example:
- The woman has a normal (mesomorphic) build with a height of 167 cm.
IW = 167 – 105 = 62 kg – ideal body weight.
- With an asthenic physique with the same height:
IW = (167 – 105) – 10% = 62 – 6.2 = 55.8 kg – ideal weight.
- With a hypersthenic somatotype and a height of 162 cm in a woman:
IV = (162 – 100) + 10% = 62 + 6.2 = 68.2 kg.
Quetelet index taking into account body type and age
According to A. Quetelet, per 1 cm of a woman’s height there is a certain amount of weight, which varies depending on the somatotype and age. The formula involves calculating the ideal weight for women of reproductive age from 15 to 40 years.
The formula looks like:
- IV = K x Height,
where K is the weight coefficient in grams per 1 cm, determined from the table.
| Age, years | Weight per 1 cm of height, g | ||
| Asthenic | Normosthenic | Hypersthenic | |
| 15 – 18 | 315 | 325 | 355 |
| 19 – 25 | 325 | 345 | 370 |
| 26 – 39 | 335 | 360 | 380 |
If you are less than 160 cm tall and under 20 years of age, it is recommended to reduce the result by 10%.
For example:
- The normal weight for a woman 170 cm tall and 30 years old with a hypersthenic physique will be:
IV = 380 x 170 = 64600 g or 64.6 kg.
- The ideal weight for a 17-year-old girl with a height of 165 cm and an asthenic body type will be:
IV = 315 x 165 – 10% = 46.8 kg.
Formula Humvee
A popular way to determine ideal weight is calculated in inches and looks like this (for women):
IV = 45.5 + 2.2 x (Height – 60)
She suggests that the optimal weight for a woman 60 inches (152.4 cm) tall is 45.5 kg. If a woman's height exceeds 60 inches, then for every additional 1 inch there is 2.2 kg of weight.
For a better understanding, you can convert the formula into the usual centimeters, based on the generally accepted values of 1 inch = 2.54 cm. It turns out that for every 1 cm of height (if it exceeds 152.4 cm) there are 2.2 kg / 2.54 cm = 0.87 kg mass.
The final formula in centimeters will look like:
IV = 45.5 + 0.87 x (Height – 152.4)
This option is suitable for calculating the ideal weight for a normosthenic physique. If a woman is asthenic, then 10% must be subtracted from the result obtained, and if she is hypersthenic, then 10% must be added to the total.
For example:
- A woman 165 cm tall has an asthenic body type.
IV = (45.5 + 0.87 x (165 – 152.4)) – 10% = 51 kg.
- The woman is 170 cm tall and belongs to the mesomorphic somatotype.
IV = 45.5 + 0.87 x (170 – 152.4) = 60.8 kg.
The ideal weight of a woman is a rather vague and conditional concept, for the calculation of which many formulas have been invented. Moreover, not all of them take into account belonging to a certain type of physique and are calculated only on the basis of 1 - 2 values, which is why large errors arise.
Information about the acceptable weight norm and knowledge of your somatotype allows you to adjust your appearance, work out problem areas of your figure, determine the right lifestyle and prevent the occurrence of many diseases.
Author of the article: Anna Lalochkina
Article design: Svetlana Ovsyanikova
Hypersthenic body type
What is your body type with a wrist of 18 cm or more? That's right, hypersthenic. Another name is endomorphs, they are predisposed to obesity, and slow metabolism makes it difficult to burn subcutaneous fat. Visual characteristics of endomorphs:
- curvaceous;
- wide chest, large breasts;
- voluminous shoulders and hips;
- short limbs;
- heavy bones;
- fat mass predominates over muscle mass;
- loose skin.
For endomorphs, it is best to limit fat intake and increase physical activity. To avoid injuring your joints, exercise in the pool is ideal: swimming or aerobics. Only regular cardio training and a healthy diet can reduce subcutaneous fat in hypersthenics.
Modern body beauty standards
The standards of a modern man combine the features of an ancient warrior, a young man of the Renaissance and the ideas of modern times.
The typical image of a handsome man is associated with a number of criteria:
- developed V-shaped back, prominent arm muscles;
- long neck, broad shoulders;
- clear waist and elastic abs;
- narrow hip area;
- muscular legs;
- The upper half of the body and the bottom are the same length.
Ideal proportions for athletes
Strength sports require the athlete to have strength, endurance, and developed muscle structure.
A professional level of physical fitness does not involve too much bulk, as in bodybuilding. The athlete must be of strong build and have clearly defined and proportional muscle atlas.
Most guys strive to achieve a pumped up athletic figure. A large back with a clearly defined trapezoidal part, sinewy arms with a sculpted shoulder area, elastic abs and strong legs with pronounced quadriceps and hamstrings are considered indicative.
The standard of beauty for a male model
In the modeling world, there are laws. For a young man to walk along the catwalk, his height must be at least 182 cm.
At the same time, an overly muscular figure is not welcome. Most of all, young guys with clothing sizes 46-48 are in demand. Preference is given to fit guys or even slightly thin guys. Attractive and regular facial features play an important role.
Ideal male body proportions for women
Girls are attracted to broad-shouldered young men of medium or tall height, with proportionally developed muscles. However, the requirements for a man's physique are much more varied than the standards of female beauty.
Details are important:
- Strong arms;
- narrow hips;
- sculpted torso;
- piercing look.
For representatives of the fairer sex, male appearance is largely determined by the overall impression and silhouette as a whole. For women, an image that inspires confidence and a sense of security is considered masculine, regardless of the specific indicators of a particular part of the body.
Ideal parameters of a male figure: height, waist, shoulders
There are no generally accepted criteria for appearance. In different nations, due to genetic characteristics, the norms of male body structure will differ. In addition, the indicators of a modern ideal figure and healthy appearance also vary.
Table No. 6 Male physique parameters.
| Data | Standard for men in the Russian Federation (cm) | Collective standard (based on global trends) (cm) |
| Height | 178-180 | 180-185 |
| Waist | 95 | 90 |
| Shoulders | 7.5 cm wider than hips | 10 cm wider than hips |
Other ways to determine body type
We have looked at how to determine body type by wrist, but there are other ways that will help in this procedure:
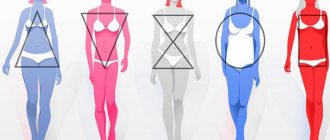
- Visual. Quite often, a simple glance at your reflection in the mirror is enough to determine the constitution of your body. In the case when the shoulders, chest, waist and hips are approximately on the same line without significant differences, you are most likely asthenic. If the hips and shoulders (for girls) are on the same line, and the waist is clearly defined, then you are more likely to be normosthenic. A wide waist, full arms, legs and stomach indicate a hypersthenic type of build.
- Along the intercostal angle. For normosthenics this angle is close to 90 degrees, for asthenics the angle is straight, and for hypersthenics it is obtuse.
- Elbow width. To do this, you need to extend your arm in front of you, bend it at the elbow at a right angle, with your fingers pointing upward, your palm open and facing your body. Next, with the thumb and index finger of the other hand, you need to touch the most protruding places of the elbow joint (for the index finger this will be the ulna bone) and measure the resulting distance between the fingers using a ruler. The higher the number, the greater the chance that you are an endomorph.
- Measuring certain parts of the body and subsequent calculation using special formulas. This is the most accurate method that can be done at home or in fitness centers.
- Online calculators that can help you find out your body type.
How to choose the right Pandora bracelet size
This decoration is a kind of construction set. Charms and clips are placed on a traditional hard bracelet made of precious or other metal, leather or other materials. The number of additions is individual, each of them has a specific meaning.
Before determining the size of a Pandora bracelet, it is important to consider how it will be used (wrap tightly around the wrist, fall below the wrist, or sit above it). Then the measurements described above should be carried out. Please note that a leather bracelet, unlike a metal bracelet, stretches a little.
In order to choose the size of a bracelet for charms, it is important to know that each of the charms or clips placed on the hoop slightly reduces the useful diameter of the hoop. It is ugly and unacceptable when a hoop bracelet and charm pendants dig into the skin, leaving an unsightly mark and painful sensations.
Only by imagining what material the jewelry will be made of and with what charms and clips can you understand the size of the Pandora bracelet.
Celebrities with different body types
To better imagine all three body types, let us give examples of famous personalities who have asthenic, normosthenic and hypersthenic body types.
Star asthenics are Keira Knightley, Victoria Beckham, Ingeborga Dapkunaite, Emma Watson and others.
Popular normosthenics are Sophia Loren, Scarlett Johansson, Kim Kardashian, Halle Berry, etc.
Famous hypersthenics - Ashley Graham, Adele, Anfisa Chekhova, Irina Pegova, etc.