The male skeleton weighs 13-14 kilograms, the female skeleton weighs 9-10 kilograms - these are the average human bone mass. If we convert these data into a percentage relative to the total mass of the body, they will look like this:
- The weight of a man's bones is 17-18% of his body weight;
- The weight of a woman’s bones is 16% of the total mass;
- The weight of a child's skeleton is 14% of the child's weight.
The skeleton, translated from ancient Greek as “dried”, indicates the methods of its manufacture - drying in hot sand or in the sun.
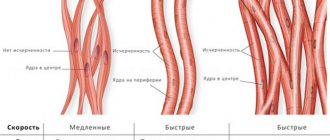
The bone basis of the human body is a unique and perfect invention of nature. The design features of the bones are such that they “know how” to withstand loads similar to a steel structure.
But, if the human skeleton were “made” of steel, then it would weigh at least 200 kg and the person simply would not be able to move. The individuality of the structure of bone tissue lies in the fact that it has a porous structure, due to which the skeletal mass is lightened several times, but the strength indicators do not change. The skeleton is the shock-absorbing basis of the human body: with increasing physical activity, the musculoskeletal system is able to stretch elastically and reduce pressure on other organs. The strength and plasticity of bones is determined by their structure:
| Name of the substance contained in bone tissue | Quantity, % | |
| 1. | Water | 50 |
| 2. | Fats | 15,75 |
| 3. | Organic matter | 12,25 |
| 4. | Inorganic substances | 22 |
The male skeleton weighs 13-14 kilograms, the female skeleton weighs 9-10 kilograms.
The organic matter of bone tissue is ossein, a protein that is a type of collagen and forms the basis of bone. The bulk of inorganic substances are calcium salts, in the form of hydroxyapatite crystals, from which the lattice structure of bone tissue is formed. The bones of an adult and a child differ in their internal contents: in children, organic substances predominate in the bone tissue, providing the skeleton with flexibility and elasticity; in an adult, the main component is mineral salts, which are responsible for strength.
How much can an adult human skeleton weigh?
Greetings to all lovers of a healthy lifestyle and sports!
It’s interesting, but here are people who work out in the gym according to training programs to increase muscle mass or, on the contrary, to lose weight, burning fat (how to find out how much fat is in the body?) with proper nutrition.
They know very well the working weight of barbells, dumbbells, exercise machines, but do they know how much a human skeleton ? Precisely the design of your own body.
If the news is new to you, then read the article to the last line and find out all the details.
How much does the skeleton of an average adult human weigh?
People who regularly visit a gym or fitness center have noticed that each person has an individual body structure. Someone has a wide chest bone, another athlete has a narrowed chest. It's very easy to check. Wrap your wrists with tailor's tape. From 16 to 19 cm, average reading.
More than 19 cm, then you are a giant! Exercises with barbells and free weights suit you. If you don't yet know the shape of your muscular body, take a look at this article. Hence, having little May knowledge of not only what muscles the bodybuilder’s body consists of, but bone tissue.
You can build a training complex to get results more effectively.
The quantitative indicator of human skeletal mass depends on gender, age, and height of live weight. At birth, on average, the weight of a newborn’s skeleton is 11% of the mass; as the child grows, the figure changes to 18%. As you grow older, this figure reaches 20% and lasts for a long time. For older people, the number decreases.
Skeletal structure of Homo Sapiens
Includes 206 bones connected by ligaments and joints. There are paired specimens and 33 unpaired specimens. The cruciate region consists of fused 3-5 bones; the number of vertebrae in the cervical region varies.
table
| Name | quantity |
| skull | 23 |
| spinal column | 26 |
| torso (ribs, chest) | 25 |
| upper limbs | 64 |
| lower limbs | 62 |
Bone tissue as a living organism changes, increasing both the qualitative and quantitative aspects. The main organic substance is ossein, a protein, and the inorganic substance is calcium salt.
In an adult, inorganic materials predominate, giving strength; in a child, organic materials predominate, providing flexibility. The interconnection of elements occurs throughout time. By connecting some are destroyed, others are created.
Renewal of bone tissue indicates the ability to exercise with heavy loads in the gym without fear of injury. But with age, this trend declines. Therefore, a person's age is important before visiting a fitness center.
Younger people are easier to bear stress on their joints. The skeleton itself acts as a shock absorber for the body. When an athlete increases the load, the bones stretch elastically, reducing pressure on the internal organs. A simple example.
When you wake up in the morning, measure your height, carry out a similar procedure in the evening, and make sure your height changes. This change occurs due to the fluid within the bone structure. During the night, the accumulated fluid pulls out the bone, you become 1 cm taller.
What does the bone structure of the human skeleton consist of?
Table
| Name | percent |
| water | 50 |
| fats | 15,7 |
| organic matter | 12,2 |
| inorganic substances | 22 |
How much does the average human skeleton weigh?
The adult skeleton itself is very light. The main weight load is taken by muscles - 43% (a very important point when building muscles), internal organs - 19%, skin + subcutaneous fat - 17.5%, human brain - 2%.
The structure of a man and a woman are different, so the weight of the bones is different. In men – 18% of the mass, in women – 16%. On average, a man weighs 10 kg, and a girl weighs 7 kg. For information, your live weight of the girl is 55 kg, which means the bones together will weigh 8.8 kg. With a guy weighing 80 kg, the bone structure will be 14.4 kg.
After overcoming the age of 40 years . The structure of bone tissue changes. The walls become fragile, which is why I recommend consuming more foods containing calcium to strengthen bones. After all, you need to maintain the strength of the main body frame, which is 3 times stronger than granite. Exercise regularly and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Speaking about the weight of the skeleton for a person’s height (160 cm, 170 cm, 180 cm), you need to know the type of build; pay attention to the photo. Determine your build for yourself. Hypersthenics are 10 percent heavier than other types.
Please note that the girls go to the gym together. The first one, with dimensions of 160 by 60, looks more attractive than the girlfriend with dimensions of 160 by 48 kg. But here you need to take into account the width of the bone. Covering a wide pelvis will require more skin, muscles, and subcutaneous fat. Of course, many conclusions vary. Everyone has their own point of view.
To the question of how much a human skeleton weighs depending on its height. People of different heights may weigh the same. The difference occurs in the density and width of the bone structure. Bulk specimens contain a higher percentage of water and are heavier.
Source: https://sergosport.ru/zdorovie/skolko-mozhet-vesit-skelet-vzroslogo-cheloveka.html
How many bones are there in a person?
How many bones are there in a person?
The question of how many bones a person has is purely medical in nature, and oddly enough, there is no definite answer for it . It is possible to indicate the number of bones only if you take into account the person’s age and his individual characteristics.
Thus, an adult’s skeleton usually consists of 206 bones, and at the same time, a child’s skeleton has about 300 bones . But why is there such a difference, and how does a child’s skeleton differ from an adult’s? Why can an adult also have more or less bones? Medicine has answers to these questions.
Why can an adult have more or less bones?
The fact is that in an adult, many bones fuse together, becoming a single whole, and at the same time, in a child, the same bones can consist of separate fragments, connected to each other only by cartilaginous tissue. This is where this age-dependent difference arises. The fusion of a number of bones begins in infancy, and later, with the advent of late adolescence, this process ends.
Variation in the number of bones in an adult is observed due to the fact that some bones under certain conditions may not fuse, or fusion may occur of bones that in most people remain separately located until the end of their days. In addition, for a number of reasons, additional bones may appear.
Interesting:
Why do we laugh when we hear jokes?
So, for example, there is such a disease as polydactyly. In this case, a person may develop sixth fingers - on one hand, on both hands, or on both hands and feet.
An extra finger is an extra bone that will remain in the body unless a person undergoes surgery to remove the extra finger. Here is one example that clearly demonstrates variations in the number of bones.
And this is not to mention injuries that can lead to an increase or decrease in the number of bones in the body. Each person is individual, and in terms of the skeleton this is also true.
Is bone dead inorganic tissue or a living organ?
The bones raise many other questions. For example, not all people know whether these are living parts of the body, or whether they are simply some kind of fossilized base on which soft tissues rest, preventing the human body from turning into a jellyfish? In fact, bone is living tissue, it is an organ that performs its own functions in the body .
It is also worth noting that in childhood and adolescence there is more living tissue in the bone, and less inorganic elements, and because of this the bone can grow, and it is more plastic and less prone to fractures.
Closer to old age, inorganic elements become much more numerous than living tissue, and therefore the bone becomes brittle and vulnerable.
Interesting:
Why do you need to go to bed on time? Description, photo and video
Structure and functions of bones
Bone structure
The main part of living bone tissue is bone marrow. And it not only represents the core of the bone, it plays a huge role in the body. Thus, bone marrow is known for its hematopoietic functions; it is responsible for the formation of red blood cells. Also, substances accumulate in the skeleton, which are then used by the body.
The bone marrow also produces special cells, which then become the spongy tissues of the body. These are the functions of the skeleton that are not related to the support and support of the body. Bones also play a protective function, providing protection to internal organs and protection from blows. It provides the dynamics of the body, if we consider joints and ligaments together with it.
All this is extremely important for the human body.
Dynamics of bone tissue development
It is worth noting that in infancy, bones take up a significant percentage of the weight, more significant than in adulthood. In a baby, 20 percent of a baby's body weight is formed by bone mass. But at the same time, a premature baby has smaller bones than a full-term baby, and this is also the norm.
Initially, a baby's bones are flexible. Otherwise, he would have gotten stuck in the birth canal and could not be born, leading to the death of the woman in labor. Many women get scared when they notice that the baby was born with a melon-shaped head - but this is completely normal.
During labor, the bones of the skull are flattened, and the presence of fontanelles, that is, cavities filled with cartilage tissue, between them, creates the possibility of such deformation without harm to the child, and the brain is also adapted for this.
Subsequently, the bones straighten and take their normal position, and the baby’s head becomes rounded. This is a feature of the bones of a newborn baby.
Interesting:
Why is the crescent moon considered a symbol of Islam?
In infancy, the baby can be so flexible that he manages to suck his toes. And this is also the norm; he succeeds due to the flexibility of his joints and bones.
In the future, such opportunities are lost, and the bone and joint systems become more rigid.
After all, an adult must withstand physical stress and other external negative influences, from which a strong bone primarily protects him.
Interesting video about human bones
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Source: https://kipmu.ru/skolko-kostej-u-cheloveka/
Heavy bone: truth or myth?
“I look slim, but at the same time I weigh 5-10 kilograms more than a girl with a similar figure, because I have very heavy bones” - you’ve probably heard similar phrases more than once in your life.
Very often people blame the heavy weight of the skeleton. But what does a heavy bone even mean, is it a myth or true?
Can bones be heavy in some people and light in others?
Let's turn to science and find out whether heavy bones occur in humans in nature?
- Are there heavy ones? How much does a human skeleton weigh?
- Density
How much does a human skeleton weigh?
In 2014, fitness expert Matt Marshall turned to scientists at Michigan State University, where he was examined using a densitometry method, which is designed to measure bone mineral density and also allows you to calculate your weight.
It turned out that the weight of the bones of Marshall, who at that time was in good physical shape and weighed 80 kg, was only 3.6 kg.
For comparison, we took densitometry data from another person whose weight was 118 kg. Of these, 46 kg. accounted for fat and only 4.2 kg. on bone tissue.
Data obtained from an obese woman weighing 96 kg were compared in the same way. Her skeleton weight was 3.2 kg. Similar ratios were obtained for 50 other obese adults.
As a result, it turned out that in percentage terms the skeleton (bones only, excluding fat, water and minerals) occupies approximately 6-7% of the body weight of an adult. Average values for bone mass density in adults are in the region of 1.0 - 1.2 g/sq.cm. Roughly speaking, this is about 10% for different people.
These values vary depending on age, gender, race, level and type of physical activity, nutritional status, body condition, presence of diseases, etc. The total mass of human bones, excluding fat and fluid content, is something around 4-5 kg in adult men and 2-3 kg in adult women.
Add to this water, which makes up about half the mass of the skeleton, and substances of organic nature, the share of which is 28% of the mass, and you get about 15% of the total mass of a person.
Within these boundaries, the mass may fluctuate depending on the bone mass density, but this difference will be negligible up to a maximum of 1 kg ! By the way, in medicine and anatomy there is not even such a thing as a heavy bone!
More precisely, the body has the heaviest bone in relation to others - the femur . This is the main “lever” that can withstand enormous loads when walking and running (up to 3 tons, stronger than concrete). Its length in an adult is 45 cm or more, and its weight is determined by the person’s height and the peculiarities of the bone structure.
In addition, keep in mind that the bone structure of women is lighter than that of men. So male bones will indeed be heavier compared to female ones.
Factors such as physical activity and genetic characteristics also have an influence. But let us repeat for better understanding: all these factors can change the mass of the skeletal system by no more than 10%, i.e. no more than 1 kg to total body weight .
Experts use such a parameter as the value of estimated bone mass. The indicator characterizes the net weight that the bones of the skeleton have. It is determined taking into account the calculation of the volume of non-fat tissue using special methods.
Modern research has shown that:
- in women 20-40 years old, the weight of the adult skeleton is:
- up to 50 kg – 2 kg;
50-75 kg – 3.5 kg;
- from 75 kg – 3 kg.
- in men from 20 to 40:
- up to 65 kg – 2 kg;
65-95 kg – 3.5 kg;
- from 95 kg – 3 kg.
In addition, the weight of the skeleton is affected by the height and age of a person. But at the same time, studies prove that 15% of the population, having a larger skeleton than average, will not show a significant difference in weight.
Deviations of 1-1.5 kg in bone mass cannot cause an additional 30-45 kg. And bone density itself does not affect bone size. Therefore, it is impossible to justify excess weight with wide or heavy bones.
By and large, talk about a person having wide or heavy bones is simply a myth, not a reality, which is usually used to explain excess weight, the amount of fat in the body, or a genetic predisposition to weight gain.
If you eat diligently and a lot, but move lazily and little, then it doesn’t matter what shape of bones you have, the average 3-4 kg of bones you have will easily accommodate hundreds of kilograms of fat.
It is important to talk not about the weight of the bone, but its density and not in the context of weight. This indicator is the most important indicator of the health of your skeletal system and will be of great importance to you as you age.
Density
It is the density of bones (the amount of calcium in them) that indicates their strength. As calcium leaches from bone tissue, it becomes brittle, leading to osteoporosis, a disease that affects connective tissue.
Bones with osteoporosis lose strength, which threatens a person with frequent and complex fractures. But why do bones lose density? There are several main non-pathological reasons for this:
- In fact, the only root cause of calcium leaching from bone tissue is bone cell death. There is nothing static in the body, and even bone cells are also born, live (on average 4 months) and die.
This brings us back to the issues of anabolism and catabolism (more about metabolism: the 2 main misconceptions of those losing weight about metabolism .
This is a normal process, because... the death of old cells gives life to new ones. The problem begins when the formation of cells goes wrong.
With age or with certain metabolic diseases, the process of birth of new bone cells slows down in a person. The structure of a person's bones changes throughout his life. After birth it increases, reaching a peak at 25-30 years.
From 30 to 45 years, bone density remains virtually unchanged, and after 45 years, regardless of whether a person is sick or healthy, the natural physiological process of rarefaction of the bone structure begins.
Because of this, the overall number of young cells in the bone decreases, namely, they contain calcium.
Accordingly, there are also fewer obsolete bone cells, which means that the amount of calcium in the blood, from which young cells absorb it, also decreases.
- In addition, bone density depends on weight loss or weight gain : scientists have calculated that for every 1 kg of body fat lost, an average of about 16.5 grams is lost. minerals in the bones, and when you gain the same 1 kg of fat, approximately the same amount is restored, but only with training!
- However excess fat harms bone health and strength. Scientists from the University of North Carolina have found that “obese” bone marrow increases the risk of fractures. It turned out that the higher the fat content in the bone marrow, the lower the mineral density of bone tissue!
According to the results of scientists' experiments, with obesity, the fat content in the bones increases in the same way as visible fat in the body and negatively affects human health.
However, do not rush to be sad: your skeleton can and, strictly speaking, needs help! And it’s easier to do this not with the help of expensive supplements or rare pills, but just by doing strength training!
The fact is that the ability to create bone cells is directly related to testosterone levels. This hormone is present in both men and women, but, of course, in different concentrations and has a direct anabolic effect on bone tissue, that is, it starts the process of bone cell division and allows new cells to be born.
Men have ten times more testosterone than women. Therefore, men have stronger bone tissue. But women have cell receptors for testosterone tens of times stronger than those of men. In addition, female sex hormones estrogens increase the sensitivity of bone cells to testosterone.
For this reason, it is necessary to do strength training 2-3 times a week, especially for people over the age of 50.
How to lose weight for a woman after 50 years:
[Total: 3 Average: 5/5]
This article was reviewed by a certified nutritionist who has a bachelor's degree in nutrition and dietetics, D. G. Veremeev.
Source: https://kost-shirokaya.ru/kak-pohudet/tyajelaya-kost/
Big bones and obesity: debunking the myths
Content
- How much do the bones weigh?
- Thin bones and wide bones
- Bones, fats and health
“It’s not me who’s fat, it’s my big bones,” overweight people continue to say. This is how they explain to themselves and others their unsuccessful attempts to lose weight and the pointlessness of physical and dietary “violence” over the body. And indeed: a large body weighing 100 kg cannot be supported by the same skeleton as that of a fragile girl with her 45 kg! MedMe understood the bone-fat paradoxes of the human body.
Thin bones and wide bones
No one argues that the weight of skeletons will vary from person to person. For example, the bones of a tall person weigh more than the bones of a short person the same age. And even the very concept of “broad bone” deserves the right to exist. It is enough to measure the circumference of the wrist or ankles with a centimeter - in these places a person has little fat and muscle, mainly skin and bones - to be convinced: there are people with both “thin” and “wide” bones.
Women 157-158 cm tall:
- “thin bone” - wrist circumference less than 14 cm;
- “normal bone” - from 14 to 14.6 cm;
- “broad bone” - wrist girth more than 14.6 cm.
Women 159-166 cm tall:
- “thin bone” - wrist circumference less than 15.2 cm;
- “normal bone” - from 15.3 to 15.9 cm;
- “broad bone” - 16 cm or more.
Women 167 cm tall and above:
- “thin bone” - wrist circumference less than 16 cm;
- “normal bone” - from 16 to 16.5 cm;
- “broad bone” - 16.6 cm or more.
Men 167 cm tall and above:
- “thin bone” - wrist circumference from 14 cm to 16.5 cm;
- “normal bone” - from 16.6 to 19 cm;
- “broad bone” - 19.1 cm or more.
In 2011, experts from North Carolina State University confirmed that the femoral neck of obese people is wider than that of people of normal weight. This is explained by the fact that, firstly, large people move in a special way, and secondly, the body gradually adapts to heavy weight, which leads to thickening of the femoral neck - one of the most vulnerable places in the human body in relation to fractures.
But even with the above data, research shows that only 15% of people have a slightly larger skeleton than the majority of the population. The difference in the weight of the skeleton will still not be so great that one can say that it is the “heavy bone” that puts pressure on the scales: a 1-1.5 kg difference in bone mass does not justify the extra 30-40 or more kg.
And one more important point: bone density does not affect their size. Osteoporosis can make your bones a little lighter, but it does not make them shorter or thinner. In this disease, calcium is washed out of the bones, but their structure itself, the frame, remains unchanged.