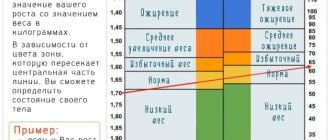
When it comes to weight loss, patients are primarily interested in the numbers they see on the scale. And such an important indicator as waist circumference often remains beyond attention. However, it is this indicator that is taken into account in the diagnosis of obesity and metabolic syndrome, also known as the “deadly quartet.”
The accumulation of visceral fat is associated with a higher risk of certain metabolic (eg, type 2 diabetes) and cardiovascular (eg, coronary artery disease) diseases.
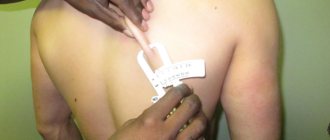
How to correctly measure your waist circumference?
When measuring, it is important to position the measuring tape correctly! Absolutely everyone has a waist , you just need to determine the guidelines.
To measure the waist circumference, we find along the mid-axillary line the middle of the distance between the top of the iliac crest and the lower edge of the last rib.
You should not take measurements after a heavy lunch, with flatulence, or with severe edema - the error in such situations can be significant.
What body type is dangerous?
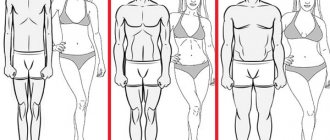
Excessive fat accumulation in the abdomen (also known as “apple” obesity) poses a higher health risk than fat in the thighs (lower or “pear” obesity) and is associated with diabetes, hypertension, atherosclerosis and other dangerous consequences.
Classification and causes of hypogonadism
The main cause of hypogonadism is a decrease in volume or impaired production of sex hormones. This may be caused by diseases of the testicles or problems in the regulation of hormone synthesis at the level of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Depending on the cause, primary and secondary hypogonadism are distinguished. Primary is one that is caused by problems in the testicles, and can be caused by:
- genetic defects that cause underdevelopment of the glands;
- the influence of harmful factors on a woman during pregnancy;
- infectious diseases such as epididymitis, mumps, vesiculitis;
- toxic effects of high doses of certain drugs (tetracyclines, hormonal);
- chemotherapy for malignant diseases;
- radiation injury;
- testicular injuries due to torsion of the spermatic cord, varicocele, excision of a hernia, etc.
Secondary hypogonadism is caused by diseases of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. These could be tumors, inflammation, vascular problems. Common reasons include:
- adenoma or prolactinoma of the pituitary gland;
- dysfunction of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus after surgery or injury;
- age-related changes leading to a decrease in testosterone levels (age-related hypogonadism);
- hemochromatosis (iron metabolism disorder).
The primary and secondary forms are distinguished by the level of gonadotropic hormones (hormones of the anterior pituitary gland - FSH (follicle-stimulating) and LH (luteinizing), regulating the gonads. Depending on this, they are distinguished:
- Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism, i.e. the primary form in which the level of gonadotropes is increased.
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, i.e. a secondary form, which is characterized by a decrease in the production of gonadotropins.
- Normogonadotropic hypogonadism. With this form, the level of gonadotropins is normal, and the disease is manifested by a decrease in testosterone production in the testicles. The cause of the disease is hyperprolactinemia.
From here it is easy to conclude that the hypergonadotropic form is caused by a disruption in the functioning of the testicles, and the hypo-and normogonadotropic form is caused by problems in the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
Causes of a large waist circumference
Endocrinologists treat obesity, including visceral obesity.
But very often we need the help of colleagues: gastroenterologists, gynecologists, nutritionists, oncologists, surgeons. Since an increase in waist circumference does not always mean an accumulation of visceral fat! There are other situations that are quite dangerous for humans, which may be accompanied by an increase in this indicator. Let's look at some of them.
- Ascites. This is the name given to the accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity. It may develop slowly and unnoticed over several months. Detection of ascites by conventional clinical methods (inspection, palpation, percussion) is possible only with a significant amount of free fluid (several liters). In the early stages, a good assistant in diagnosis is the ultrasound method.
- Flatulence. Intestinal bloating is one of the common causes of abdominal discomfort that occurs with an increase in waist circumference. Treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract accompanied by bloating leads to a rapid and significant change in volume downward.
- Tumors. Some formations of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs can reach significant sizes and affect the configuration of the abdomen. In some cases, even upon examination and palpation it is possible to suspect which organ this formation is growing from. The diagnosis is clarified using research methods such as ultrasound, CT, MRI.
- Spine pathology. Diseases that occur with a decrease in the height of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs can have a significant impact on the waist. For example, with compression fractures, the ribs may descend towards the pelvic bones until they touch. This leads to displacement of internal organs, changes in the tone and configuration of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, and deformation of not only the spine, but also the entire torso.
- Press. The condition of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall is a modifiable factor, which is significantly influenced by physical activity. A well-chosen training regimen can significantly reduce your waist circumference. But, in case of problems such as diastasis, hernias, consultation with a surgeon and surgical treatment may be required.
So, a simple and understandable method that can be done at home can direct you to consult a specialist. Bearing in mind that obesity is a disease, and not just a feature of the figure, in the fight against it you should start with a visit to an endocrinologist.
Author of the article: ASTAFYEVA MARIA ALEXANDROVNA – ENDOCRINOLOGIST, CATEGORY I
Main symptoms and manifestations of the disease
Hypogonadism develops due to a lack of sex hormones. Due to deficiency, the organs that depend on these hormones suffer. Symptoms of hypogonadism can manifest in different ways. The age of onset of the disease and the reason for the decrease in the amount of hormones are important.
If puberty has not started
If the failure occurred before the onset of puberty, then it occurs with a delay. The boy is very tall, his arms and legs look too long, and his chest is small compared to other parts. Male pattern hair growth also does not occur, since it depends on sex hormones.
Obesity in hypogonadism is another characteristic feature. Due to a lack of testosterone, it develops according to the female type. In addition, gynecomastia is formed - enlargement of the mammary glands, and an underdeveloped penis of small size is observed.
At the end of puberty
If the production of hormones was disrupted after puberty, the signs of hypogonadism are not so pronounced. A man's testicles become smaller, body hair decreases, and obesity begins to develop with female-type fat deposition. The skin loses its elasticity and becomes thin, problems with sexual function appear, and infertility may develop.
The very first sign is a decrease in the size of the testicles. This does not happen only if the disease began to develop recently. As it progresses, spermatogenesis—the development of male germ cells—is disrupted. The testicles lose their basic function, which leads to infertility with the cessation of testosterone production. Secondary sexual characteristics gradually regress. Against this background, a man may experience weakness, fatigue and weakening of muscles.
Age and body fat
Doctors generally believe that with age, fat mass in the body increases, and muscle mass decreases.
In nature, this phenomenon is not observed in animals. In nature, with age, an animal becomes weaker, produces less, eats less and loses total body weight: both muscle and fat.
In people, as they age, a person moves less, but gets as much as he wants, so fat grows with age and muscle disappears. This is a normal but unnatural phenomenon.
People who increase the amount of physical activity with age also experience an unnatural phenomenon - they begin to look younger than their peers, having a percentage of fat and muscle similar to that of young athletes.
Useful fashion - determining the percentage of fat
Determining your body fat percentage is becoming very popular today because it clearly and effectively shows the state of not only your physical fitness, but also your health!
The photos below will help you determine the approximate percentage of body fat, which will help you more accurately define your goal.
Well, when the goal is known, all that remains is to make a plan for achieving it and... start acting!
By the way, keep in mind that fat is not distributed equally on everyone’s body.
Therefore, two people with the same body fat percentage may look different.
Most women have more fat on their thighs, most men have more fat on their belly.
12-20% fat content in men
12-20% body fat is a normal body fat percentage for women. A man with such a percentage of fat, even if he goes to the gym, looks feminine: the veins are not visible, and the muscles look smooth.
With this percentage of fat, several centimeters already hang over the belt.
Most modern men have this percentage of body fat. For example, most often, a man 180 cm tall and weighing 80 kg looks exactly like this.
Create a program to reduce body fat mass
The Effect of Different Rep Ranges on Hypertrophy
Now that we have an understanding of some basic information, we can evaluate the effects of different rep ranges on muscle growth.
First, we need to find studies that controlled for set tension, so that we don't take into account groups that did not work to failure (and therefore did not recruit and fatigue all available fibers), and only count groups that performed all sets to failure.
Next, we need studies that control for training volume (sets X reps) or number of sets. If one group performed one set to failure while another group performed 10 sets to failure, we cannot tell whether the differences in strength and mass are due to rep range or differences in the number of sets.
Fortunately, there is a large body of research available that does what we need to do. I have summarized the results in a table (see below). All sets in all of these studies were performed to failure.
When reviewing these studies, several features emerge. In a study by Campos et al, light loads did not produce as much hypertrophy (or any hypertrophy) as high loads. However, the low-load group performed fewer sets than the high-load group to keep the total load volume comparable. Assuming that there are no differences between loads (probably a dangerous assumption, but safer than taking into account the entire literature reviewed), this seems to show that the number of sets is decisive for hypertrophy. However, in Schoenfeld's (2014) study, one group did 3 sets of ~10 reps and the other group did 7 sets of ~3 reps (again a comparable volume). If the number of sets matters, there should be more hypertrophy in the 7 x 3 group, but this was not the case. Taking a closer look, the low-load group actually completed 9 sets to failure per body part, while the high-load group actually completed 21 sets per body part per week. When the number of sets stimulating each muscle is taken into account, it can be assumed that 9 or fewer sets to failure per week for a muscle group may produce maximal hypertrophy in this specific training population, and the additional 18 sets performed by the high-load group contributed little ( if at all) contributed to additional hypertrophy.
Studies evaluating repetition ranges and their effects on muscle hypertrophy, strength and endurance
| Study | Controllable factors | Estimated Rep Range | Effect on hypertrophy | Impact on strength | Impact on endurance |
Weiss et al, 2000 (7,  | Volume-load | 3-5/13-15/23-25 | No differences between groups | Larger gains at 3-5 RM, smaller gains at 23-25 RM | Not rated |
| Campos et al, 2000 (9) | Volume-load | 3-5/9-11/20-28 | No difference between 3-5/9-11, no hypertrophy at 20-28 | More in group 3-5 | More in the group 20-28 |
| Alcaraz et al, 2011 (10) | Number of approaches | 6 in both groups, but rest 30s/3 minutes | No differences between groups | No differences between groups | Not rated |
| Mitchell et al, 2012 (11) | Number of approaches | 3 sets 30% RM/3 sets 80% RM/1 set 80% RM | No differences between groups | More in the 80% PM group | More in the group 30% |
| Schoenfeld et al, 2014 (12) | Volume-load | 2-4/8-12 | No differences between groups | More in group 2-4 | Not rated |
| Van Roie et al, 2014 (13) | Volume-load | 10-15/80-100/60 reps at 20% RM after 40% RM until failure | No differences between groups | More for 10-15 and unusual group | Increase only in group 80-100 |
| Schoenfeld et al, 2015 (14) | Number of approaches | 8-12/25-35 | No differences between groups | More for 8-12 | More in the group 25-35 |
Van Roie's study also assessed volume-load rather than number of sets but found no difference in hypertrophy.
The remaining studies tended to match the number of sets across groups, and help fill in the gaps in our model: different rep ranges had similar effects on hypertrophy. Not only in these studies, but in all other studies, populations of untrained, well-trained, and even elderly people are represented, so the similarities in hypertrophy hold true for all cases considered.
The next feature is that large working weights allow trainees to show better results with significant weights, and smaller working weights lead to better results when lifting small weights, even if muscle gains are similar. This may be due to a variety of factors not explored in the literature: neural adaptation to specific loads, fiber type-specific hypertrophy, aerobic/anaerobic adaptation of muscle fibers, and so on. I personally lean towards a predominant effect on the nervous system, with really minimal differences in muscle adaptation, but this is just my humble guess and the real answer remains to be seen. I believe that lighter loads preferentially stimulate hypertrophy of type I fibers, which I observed in the Campos work where direct measurements were taken. There are several studies examining muscle fiber types in competitive clean weightlifters (15) and powerlifters (16) where the ratios of fiber types were found to be very similar. A few more studies have assessed fiber types in bodybuilders and found very high type I fiber content (17, 18), but these were conducted in competitive, untested, high-level athletes with extremely small sample sizes, so the potential for doping and other factors such As differences in muscle groups between studies do not allow us to come to clear conclusions. Additionally, none of the studies evaluating fiber types were training studies, so the actual effect of a given rep range on fiber types may not be known anyway.
The third feature that stands out, at least to me (and is based primarily on studies not included in the table) is that more sets increases the effect on strength and muscle mass (19). For example, in the Campos study, the two higher-load groups did more sets than the low-load group due to the investigators' control for volume-load, and hypertrophy was not observed in the low-load group. However, in a number of other studies we can find that lighter weights actually stimulate hypertrophy as more sets are performed.
Obesity
Obesity is a disease characterized by an excess of fatty tissue in the body . Currently one of the most common metabolic diseases in the world. Diagnosed and treated by dieticians and nutritionists.
The causes of obesity can be physiological and psychological. If the former are innate characteristics of the body, for example, a predisposition to obesity, then the psychological prerequisites for the development of obesity are a product of the socialization of the individual.
There are a number of genes that fix lipid (fat) metabolism in the human body. They determine the speed of its flow, the efficiency of the breakdown of fatty acids, the mechanisms of use and the “comfortable” fat mass.
In the vast majority of cases of obesity, it is psychological overeating . It can be caused by poor eating habits, ignorance of the basics of healthy eating, a sedentary lifestyle, or as a result of eating disorders.
The complications and consequences of obesity include:
- Metabolic disorder.
- Diabetes.
- Stroke.
- Heart attack.
- High blood pressure.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Lack of libido.
- Fatty liver.
- Tumors.
- Mental disorders.
Often, people who adhere to proper nutrition and keep their weight normal or underweight through severe restrictions soon break down. They reach even more weight than they did when they started losing weight.
The classification of the disease depending on the percentage of adipose tissue in the body is presented in the table:
| BMI (Body Mass Index) | Diagnosis |
| 25-30 | Obesity |
| 30-35 | Obesity (I) |
| 35-40 | Acute obesity (II) |
| 40 or more | Morbid obesity (III) |
Morbid obesity is the most severe degree of the disease. It is much less common and is often caused by serious metabolic pathologies. Patients can reach 150 kilograms or more.
Obesity prevention is carried out at the state and municipal level. Thus, schools hold special events dedicated to promoting a healthy lifestyle and conscious nutrition. Many universities include in the educational program such disciplines as “culture of health” or “healthy lifestyle”, “nutrition”.
In order to stay in shape, it is enough to adhere to the following rules:
- Maintain daily physical activity (exercise, walking).
- Add regular physical activity (workouts in the gym, at home).
- Avoid high-calorie, refined foods.
- Prepare homemade meals, avoid quick snacks and fast food.
- Follow the basic principles of conscious nutrition, reflect the feeling of hunger.
- Reduce the amount of salt and sugar you consume.
- Limit fatty foods, replace saturated (animal) fats with unsaturated (vegetable) fats.
- Add more vegetables, fruits and fiber-containing foods to your diet.
Another preventative measure for obesity can be a high percentage of muscle mass. It consumes more energy than connective and adipose tissue.
It is important to follow the norms for the values of all types of fabrics. An imbalance of metabolic processes in both men and women can cause serious consequences. Before starting training and changing your diet, it is better to consult a specialist.
What are the causes of muscle fatigue?
Fatigue during resistance training is still a very sticky topic. However, we do know that when muscles contract, they produce metabolic byproducts. Additionally, during contractions or any time a muscle is under load, blood flow into and out of the muscle is restricted and metabolites are removed more slowly. When the increase in metabolite production exceeds the cardiovascular system's ability to remove them, concentrations increase and begin to interfere with muscle contraction. It is also likely that they stimulate pain sensations, and our brain may recognize this pain and reduce motor unit recruitment. It is almost certain that the events occurring are a combination of effects on the muscles and the nervous system.
These assumptions are best illustrated by a technique called muscle blood flow restriction training. It uses a cuff to reduce blood flow throughout the entire approach. You can perform significantly fewer repetitions with lighter weights this way, but muscle gains have been shown to be similar to those seen when lifting heavier weights without restricting blood flow (6).
So why is this concept important? Because at least for now it is known that in order to grow, muscle fibers must be recruited and experience at least some fatigue. Something in the process of fatigue gives a signal for the onset of hypertrophy. I like to think of every instance of fatigue as a stimulus for a small amount of hypertrophy, so it's not just a few instances—sets to failure—that accumulate and cause more significant hypertrophy.
So, more about male fat percentage
3-4%
This is the level of a competitive bodybuilder. For me, this is somewhere beyond... both physical health and... it’s difficult for us ordinary people to understand this.
6-7%
This is still an extreme level. As Mark says, with this percentage of body fat, your face becomes very skinny and your family members become very worried about you.
This is what fitness models usually look like when they dry off for a cover shoot.
10-12%
This is what most men strive for and what most women like