Share:
Each of us is individual - this is an axiom. However, often two different people absolutely match each other in terms of body type and physique. In such cases they speak of an identical self-type. In this article we will tell you what body types there are, how to determine yours and how to “correct” it through exercise.
What influences body type?
One of the criteria for assessing development and health is the proportionality of the body. If the proportionality is disturbed, then we can assume chromosomal, endocrine disorders that have an impact on the growth process.
The constitution of the human body is a set of characteristics of the body, formed from hereditary and acquired properties, many of which become obvious at an early stage of child development. Some children have a fragile physique, others have an excess of fat tissue over muscle tissue, and still others are endowed with strong muscles.
As you grow older, body features become fixed and by the age of 11 you can determine the type of constitution of the child.
Over the years, scientists have determined body types based on body proportions, but their classification is not an exact science.
- Normosthenic. This type includes people whose body sizes correspond to age parameters.
- Asthenic. People with this body type have elongated limbs, narrow bones, a thin layer of fat, and poorly developed muscles.
- Hypersthenic. In this case, people have well-developed muscles, average height, and transverse dimensions predominate in the existing body proportions.
Classification of species is not an exact science, and there are often many variations within a single “type.” The medical term “physique” includes the constitution, height, and weight of a person.
Practical meaning of the human constitution:
- Medicine. Knowledge of proportions helps diagnose diseases and is used in medical anthropology.
- Physical education. Helps you decide on the choice of sports activities.
- Industrial production. Body parameters are taken into account in the production of clothing and shoes.
Features of the endomorph
In people classified as endomorphs or hypersthenics, the transverse dimensions of the body prevail over the longitudinal ones. Their characteristic features:
- broad shoulders;
- wide, barrel-shaped chest;
- relatively short limbs;
- wide pelvis;
- bones and joints are thick and massive.
The muscles are sufficiently developed, as is the subcutaneous fat layer. This is why hypersthenics do not look athletic - they look massive. In general, endomorphs are genetically adapted to perform brute force work; their musculoskeletal and endocrine systems are designed for this.
Tendency to accumulate fat mass
Endomorphs have high levels of testosterone and insulin. It is this combination that allows representatives of the described type to gain weight. At the same time, hypersthenics have a relative predominance of the parasympathetic nervous system, so they love to eat and have sufficient or increased appetite.
People with this body type are more likely to suffer from obesity and related problems - diabetes, atherosclerosis, hypertension.
This feature imposes on endomorphs the obligation to be very strict about their diet - nutrition for an endomorph must be carefully selected and balanced so as not to once again cause the appearance of excess fat on the body.
It is advisable for people with this somatotype to choose typical strength sports - bodybuilding, strongman, crossfit, rugby. Anything that provides typical work for hypersthenics is suitable - strength and preferably for a certain period of time, sufficient for the increased concentration of cholesterol and blood glucose to be used for energy needs.
Large meals are undesirable for endomorphs: the more the intestinal walls are stretched and the more toned the parasympathetic system is, the greater the reaction of enkephalin and insulin release. Therefore, the classic diet plan for bodybuilders, consisting of 6-8 meals in small portions with a minimally sufficient amount of carbohydrates, is well suited for hypersthenics - both in order to look better, and in order to feel better and avoid a number of the above diseases.
Specifics of the central nervous system
Due to the low level of hormones of the sympathetic system, as well as due to the low manifestation of androgenic activity of testosterone, hypersthenics are not aggressive and are relatively slow. The muscle composition is dominated by glycolytic muscle fibers. Thanks to this, hypersthenics are capable of performing powerful power movements, but in a limited time period. Simply put, hypersthenics by nature don’t have very much endurance.
However, with appropriate training, the mitochondrial apparatus can be developed in glycolytic muscle fibers, which will help correct this deficiency. Impact martial arts are not for them. Endomorphs will feel more comfortable in various types of wrestling, especially where there is a tough ground game - jiu-jitsu, judo, classical wrestling. The limbs of hypersthenics are short, the muscle bellies are thick, the levers are not long - it is easier for hypersthenics to demonstrate maximum strength due to the reduced amplitude. For the same reasons, endomorphs will feel comfortable in arm wrestling and powerlifting.
Areas of sports implementation of an endomorph
A large amount of adipose tissue may lead to the idea that hypersthenics need more cardio exercise. This is not true at all. The joints of endomorphs are large, formed by the joints of fairly thick bones. Such structures, even at rest, require significant blood supply, which they receive from the surrounding muscles. Cardio loads the joints, while not only not increasing, but even decreasing the amount of muscle tissue.
So the most optimal would be a special training program for endomorphs, combining heavy strength training and volumetric bodybuilding training. In this case, the diet should be complete, providing growing muscles with sufficient energy. But it is better to reduce the amount of carbohydrates - this way we will reduce insulin emissions, reduce the amount of adipose tissue and allow testosterone to more effectively perform its task in building muscle and reducing the percentage of subcutaneous fat.
Let’s not forget that “drying” will be much more difficult psychologically and physically for a hypersthenic person, which will have a very negative impact on the latter’s health.
Indices and types of bodily proportions
The constitution of the human body is a set of sizes of some parts of the human body and their ratio. One of the common ways to determine proportions is the index method, when the smaller size is determined as a percentage. This method calculates the relative width of the shoulders to the total length of the body and the length of the lower limbs.
Based on calculations, 3 types of human physique were identified:
- Brachymorphic. This species is characterized by powerful, highly developed shoulder muscles, a shortened but wide chest, and a large slope of the pelvic angle. The body of a typical representative may be long, but the height is low due to short legs.
- Dolichomorphic. A representative of this type has elongated limbs and a narrow body. High growth is ensured by long limbs, and these people also have a small pelvic angle.
- Mesomorphic. Determined by the average values of previous species.
The calculation methodology for physical development using indices includes:
- Thoracic height index , I=T– 0.5 L (I – index, T – chest circumference after a sigh, L – body length in cm). For men +5.8, for sports women +3.8 cm.
- Weight-height index , I=P/L (P – weight, L – length). For men = 360-400 g/cm, and for women 320-370 g/cm.
- Vital index , I=VC/P (I – index, vital capacity of the lungs, P – body weight in kg). The male index is 60-62 ml/kg, the female 50-52 ml/kg.
HOW DO SCALES WITH BODY COMPOSITION ANALYZER WORK?
When analyzing the composition of the human body on Tanita analyzer scales, the method of bioelectrical tissue resistance using weak electrical impulses is used.
These pulses come from special electrode plates built into the Tanita analyzer platform. To undergo a body composition analysis, it is enough to stand on such scales for a short time (feet should be bare for better conduction of impulses; you cannot stand on the scales with wet feet).
The nutritionist will have to enter the client's height, age and gender before weighing.
Next, the scales independently process the data read from the person using programmed mathematical formulas. As a result, the dietician/nutrition consultant receives a range of body composition indicators for the client being examined.
OUR ADVICE: TANITA BC 582 scales are perfect for home use, and TANITA BC 587 scales for professional use (weigh up to 200 kg).
Kretschmer's typology of human physique
The German psychiatrist and psychologist E. Kretschmer, in his famous work “Physique and Character,” put forward the theory that certain mental disorders are common among people of certain physical types.
According to the scientist, only genetic factors influence the human constitution. Social reasons do not affect the development of the somatotype. The scheme developed by E. Kretschmer was offered only for men.
He divided personalities into 4 types:
| Somatotypes | Traits inherent to this type |
| Sports or athletic | These people have good skeletal and muscular development and a slender body. Height is average or above average. These people have the personality traits of introverts and are more susceptible to serious mental disorders, schizophrenia. |
| Picnic | People of this type are characterized by large abdominal cavity sizes and numerous fat deposits. Their figure is compact and their height is short. They have the personality traits of extroverts. Such people are more susceptible to mental disorder, manic-depressive psychosis. |
| Asthenic | Tall men with narrow shoulders and underdeveloped muscles fit this type. They are energetic and aggressive, comparable to ambiverts and prone to mental disorders. |
| Leptosomatic | Leptosomatic (from Greek leptos - “fragile”, soma - “body”) - asthenic. The shape of the body is cylindrical, the physique is fragile, the height is tall. The shoulders are narrow, the legs are long and thin. The face is elongated, egg-shaped. |
The psychiatrist suggested that lanky asthenic types, and to a lesser extent athletic types, are more prone to schizophrenia, while picnic types are more prone to developing manic-depressive disorders. His work was criticized, but Kretschmer's ideas to some extent entered popular science and spawned further psychological research.
DNA interrogation
For a long time, excavations did not yield anthropological material. In general, very few human fossil remains have been found in the world. Each such find is a great holiday for archaeologists.
For Siberian scientists, it came in 2008, when in the 11th layer of the Denisova Cave - where a fragment of a bracelet and other Upper Paleolithic items were found - a human nail phalanx was found, presumably a girl 5-8 years old.
To carry out genetic analysis, the material was sent to the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (Leipzig), where a team of scientists led by Professor Svante Pääbo has accumulated significant experience in conducting paleogenetic work, in particular, they read the nuclear genome of the Neanderthal.
Colleagues in Leipzig isolated mitochondrial DNA from the phalanx, deciphered it and came to a completely unexpected result: its structure differs from both the DNA of modern humans and the DNA of Neanderthals.
Publishing these data in Nature
- one of the most influential and authoritative scientific journals in the world - created a real sensation in the scientific community: they even began to talk about the need to revise textbooks on paleoanthropology.
In order to confirm or refute the conclusions obtained from the study of mitochondrial DNA, the laboratory of Svante Pääbo began deciphering nuclear DNA. As is known, this type of research gives more accurate results. Recently, geneticists completed their work - their main conclusions were confirmed. (A new paper forthcoming for Nature
.)
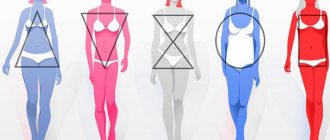
What types of physiques are there in men, their distinctive features
The term somatotype is used in the classification system of human physical types developed by the American psychologist W. Sheldon. According to his classification system, a person can be correlated with one of the body types: endomorphic or round type, mesomorphic or muscular type, and ectomorphic or thin, linear type.
Sheldon proposed a theory of personality that correlated temperament and body type. He divided people into three categories called "soma types", which were named after the germinal layers of the body of multicellular animals.
- Endomorph. Corresponds to the inner layer, the endoderm, from which the digestive system was formed.
- Ectomorph. The name is compared with the outer ectoderm from which the formation of the skin, glands, and nervous system occurred.
- Mesomorph. The name of the type is derived from the mesoderm, from which the cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems were formed.
Most people do not have a pure match in somatotype characteristics. A person always has average characteristics that take into account gender, age, and developmental characteristics.
The constitution of the human body is not only external morphological characteristics, but also physiological indices. It is difficult to find pure representatives of all body types, since the indicators of certain parts of the body can be classified with different options.
Ectomorphs
Individuals belonging to this group have the following characteristics:
- thin face with a high forehead and drooping chin;
- narrow chest and toned abdomen, with no subcutaneous fat;
- thin, rather long arms and legs;
- narrow body.
Ectomorphs demonstrate greater social anxiety and introversion, and have the makings of analytical thinking. They have a fast metabolism, which requires more calories and more training. These people are hardy, very flexible and dexterous. A person belonging to this group gains weight easily. If he becomes fat, he is still considered an ectomorph, just overweight.
Endomorphs
An individual of this group is characterized by a round shape, his body is almost spherical, and he also has:
- large round belly;
- large internal organs corresponding to its size;
- rather short limbs;
- full shoulders and hips;
- thin ankles and wrists.
Gains weight easily, has a higher percentage of body fat, and is prone to obesity. Under normal conditions, such a person has a lot of fat, but if he starves, he remains endomorphic, only becomes thinner.
Mesomorphs
This physical type is characterized by good muscle development.
Mesomorphs in their pure form have:
- big head;
- massive muscular chest, shoulders;
- minimum body fat;
- pronounced muscles on the lower and upper limbs;
- excellent posture;
- narrow hips and broad shoulders.
This somatotype easily gains muscle mass, it has strength, speed, and endurance. An example of a mesomorphic person in sports would be a weightlifter, shot putter, or sprinter.
conclusions
In fact, there are exactly as many body types as there are people in the world, but the theory of somatotypes is a good starting point for studying your body. The most important thing you can do for your body is to realistically assess the initial data, know your characteristics and purposefully go to your maximum.
Literature
1. SHELDON, WH and STEVENS, SS and TUCKER, WB (c.1940) The varieties of human physique. Oxford, England: Harper 2. HEATH, BHJE and CARTER, JEL (1967) A modified somatotype method. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 27(1), p. 57–74 3. McARDLE, W. et al. (2000) Essentials of Exercise Physiology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 4. Peter Attia, MD, Good science, bad interpretation 5. Ebbeling, Cara B., et al. “Effects of dietary composition on energy expenditure during weight-loss maintenance.” Jama 307.24 (2012): 2627-2634. – A calorie is not a calorie. Isocaloric feeding experiment showed that after 10% weight-loss low-carb diet leads to the least depression of TEE and BMR 6. Rosenbaum, Michael, et al. “Effects of changes in body weight on carbohydrate metabolism, catecholamine excretion, and thyroid function.” The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 71.6 (2000): 1421-1432. 7. Małgorzata Drywien, Joanna Frackiewicz, Magdalena Górnicka, Justyna Wielgosz, Anna Sobolewska, Stanisław Kulik, Influence of the somatotype on intake of energy and nutrients in women 8. Peter Attia, MD, The great disconnect medical 9. Levine JA, Lanningham- Foster LM, McCrady SK, Krizan AC, Olson LR, Kane PH, Jensen MD, Clark MM, Interindividual variation in posture allocation: possible role in human obesity. 10. Tom DiChiara, Do Some People Get in Shape Easier Than Others? 11. Michelle Kerns, Somatotype Meal Plans 12. AT Ali, NJ Crowther, Factors predisposing to obesity: a review of the literature 13. Smith SR, The endocrinology of obesity. 14. Myers MG Jr, Leibel RL, Seeley RJ, Schwartz MW, Obesity and leptin resistance: distinguishing cause from effect. 15. Scarpace PJ, Zhang Y., Leptin resistance: a prediposing factor for diet-induced obesity.
Types and signs of female physiques
The constitution of the female physique was systematized by Professor M.V. Chernorutsky in his works. He identified 3 main types of female body. But the constitutional characteristics of most women cannot be reduced to these three types. This division gives only a general idea of the range of fluctuations in the structure of the human body.
Asthenic appearance
Women in this category have a proportionate figure, long legs, a thin waist, and are of average or slightly above average height. People of this type lack endurance and strength because their muscles are not sufficiently developed. But they are graceful, energetic, and do not tend to be overweight, since the percentage of fat deposits in the body is minimized.
Normosthenic appearance
Normosthenic women have proportional body sizes. This is a balanced and harmonious type of build.
Nature has endowed individuals with such a constitution with fast, sharp movements and well-developed muscle mass. They are slightly taller or average in height, and they rarely develop chronic diseases.
Hypersthenic appearance
Physiological factors that determine women of this type: slightly shortened limbs, the presence of a wide chest, dense bones, height is often below average. A low metabolic rate contributes to rapid weight gain.
Hypersthenic women are hardy and have considerable strength, but lack grace and flexibility.
Types of body constitution according to Ayurveda
Indian traditional medicine, Ayurveda, offers its own idea of the human constitution. According to the teaching, there are three types of body energy, corresponding to the elements of fire, air and earth. They are all present in the human body, but the human constitution is determined by one or two, the dominant ones. They may change over the years, but maintaining the balance of the three elements depends on the person himself.
cotton wool
This type of energy belongs to the element of air. Representatives of Vata are creative, extraordinary individuals. They are fueled by the energy of the air, impulsive, sensitive, and are often visited by feelings of anxiety and restlessness.
They have a refined appearance, a slender, flexible body, and tall stature. According to teaching, such people should maintain energy balance with the help of yoga, Pilates, and race walking.
Pitta
People belonging to the element of fire are decisive, quick-tempered, and have all the signs of a leader. They are ambitious, hardworking to the point of exhaustion, filled with emotion and passion. Often individuals with pitta energy are prone to aggression.
According to Ayurveda, these are fair-skinned people, of average height, with red hair, pointed features. The muscular system is well developed, their height is average. The reason for their frequent aggression is an imbalance in their internal balance, so they are recommended to engage in meditation and water sports.
Kapha
People with predominant kapha energy or the earth element are balanced and calm. They strive to achieve harmony, so they are often characterized by laziness and lack of initiative.
They have a strong build, a round figure, and tend to be overweight. They have a large supply of energy, so they are recommended to do jogging, strength training, and aerobics.
Modern methods of somatotyping
Modern science includes at least 60 somatotyping schemes. For classification, estimates of both the component composition of the body are used: bone, fat, muscle, and overall size.
Typical features of a normosthenic body type
Individuals of this type are characterized by proportional body sizes.
The main parameters of a normosthenic:
- classic body type;
- the muscles are clearly expressed and prominent;
- predisposition to obesity is average;
- good endurance, stable body strength.
The complexion of men and women of this type often looks larger than that of asthenics, but this is due not to fat, but to well-developed muscle tissue. Normosthenics have good health and enhanced metabolism.
Typical features of a hypersthenic body type
Hypersthenics have a slow metabolism, which leads them to rapid weight gain.
The main features of hypersthenic:
- stocky appearance, below average height;
- soft rounded facial features and figures;
- ability to quickly gain weight;
- excess amount of subcutaneous fat.
How to calculate your body type?
The constitution of the human body is a hereditary program implemented during the individual development of each organism.
To determine the type, you can use one of the following methods:
- Visual method. To do this, you should know the characteristics inherent in the main types of body structure. By looking at the figure, you can visually determine a person’s somatotype.
- The relationship between height and weight. A simple formula consists of the difference between the height index and the number 110. The resulting amount approximately corresponds to the ideal weight being measured. And the difference between your own weight and the resulting figure will indicate which somatotype the figure belongs to. All calculations are made with a height of no higher than 170 cm.
- Body measurements and calculations using certain formulas. The most common are the indices of scientists M.V. Chernorutsky, V.P. Chtetsov. To determine it, it is necessary to calculate the girth of the limbs, body mass index, and the size of skin folds.
- Determination of somatotype by wrist size.
Determining body type by wrist
The method of correlating body type by wrist was proposed by the doctor G. A. Solovyov at the beginning of the last century.
The index is based on the thickness of the bones in the wrist area, which can be used to determine your body type:
- ectomorphs – girth is 15–17.5 cm;
- mesomorphs – 17.5–20 cm;
- endomorphs – more than 20 cm.
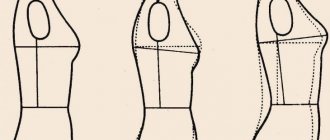
Typology based on the proportions of body parts
Scientists who study the proportions of the human body understand by them the ratio of transverse, longitudinal, girth and anteroposterior dimensions.
Bodily proportions derived by the scientist P. N. Bashkirov:
| Body type | Body parts relative to length, % | ||||
| Length | Width | ||||
| torso | hand | leg | pelvis | shoulder | |
| Brachymorphic (hypersthenic) | 33,4 | 42,6 | 50,0 | 17,4 | 24,4 |
| Dolichomorphic (asthenic) | 29,6 | 46,6 | 54,1 | 16,1 | 21,4 |
| Mesomorphic (normosthenic) | 31,1 | 44,4 | 52,1 | 16,4 | 23,1 |
Currently, many different tables and programs have been published in which the optimal weight of women and men is calculated, taking into account their constitution.
There are different types of human body types. It has been proven that the constitution of the body does not affect the condition of the body. But knowing your somatic type, you can try to improve it with the help of physical exercise, diet correction, and proper lifestyle.
Author: Belyaeva Anna
CALCULATION OF SOMATOTYPE COMPONENTS BY HIT CARTER
To calculate the components of the somatotype, it is necessary to measure:
- Body length, cm
- Body weight, kg
- Shoulder circumference in a tense state, cm
- Shin girth, cm
- Diameter of the distal epiphysis of the humerus, cm
- Diameter of the distal femoral epiphysis, cm
- Thickness of skin-fat folds:
- On the back, under the shoulder blade, mm
- On the shoulder, behind, mm
- On the side, mm
- On the shin, cm
Example
- Body length, 180.3 cm
- Body weight, 66 kg
- Shoulder circumference in a tense state, 30 cm
- Calf circumference, 37 cm
- Diameter of the distal epiphysis of the humerus, 7.2 cm
- Diameter of the distal femoral epiphysis, 9.6 cm
- Thickness of skin-fat folds:
- On the back, under the shoulder blade, 9 mm
- Shoulder, back, 8 mm
- On the side, 6 mm
- On the lower leg, 8 mm
1 step. Definition of the first component of endomorphy – D
- We find the total thickness of the skin-fat folds (on the back, on the back of the shoulder and on the side). It is equal to 9+8+6 = 23 mm.
- We turn to the table (columns 1 and 2). The resulting value falls within the range of 23-26.9 mm and corresponds to the fifth line of the table.
- In column 3, the fifth row corresponds to a value of 2.5 points.
- Therefore, component D = 2.5 points .
Step 2. Definition of the second component - mesomorphy - M
- The body length is 180.3 cm. This value is closest to the value 181.6 (4th column, 11th line). Let's mark it in the table. We calculate points relative to this value.
- The diameter of the distal epiphysis of the humerus is 7.2 cm (5th column, 14th line). In relation to the value of 181.6 cm, we moved down three lines, therefore we have +3 points.
- The diameter of the distal epiphysis of the femur is 9.6 cm (6 column 11 line). It is on the same line as the body length. Therefore we have 0 points.
- The girth of the shoulder without the skin-fat fold on the shoulder is: 30-0.8 = 29.2 cm. This value corresponds to 29 (7th column 9th line). We went up 2 lines relative to body length, therefore we have – 2 points;
- Calf circumference without skin-fat fold: 37-0.8 = 36.2 cm. This value corresponds to line 11 of column 8, on which our body length value is located - 181.6 cm, so we have 0 points.
- Sum of all points S = +3+0-2+0=1 point
- We determine the values of the M component using the formula: M = 4 + S/8 = 4+1/8 = 4.125 ≈ 4
Table for calculating somatotype components according to the Heath-Carter scheme
| № | Total thickness of skin-fat folds, mm | Value of the first component, endomorphy D , points | Body length, cm | Diameter of the distal epiphysis of the humerus, cm | Diameter of the distal femoral epiphysis, cm | Shoulder circumference, cm | Shin girth, cm | The meaning of the third component, ectomorphy O | |||
| bottom line | upper limit | Lower limit, conventional units | Upper limit, arb. units | Points | |||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
| 1 | 7 | 10,9 | 0,5 | 139,7 | 5,19 | 7,41 | 23,7 | — | 39,5 | 0,5 | |
| 2 | 11 | 14,9 | 1 | 143,5 | 5,34 | 7,62 | 24,4 | 28,6 | 39,6 | 40,6 | 1 |
| 3 | 15 | 18,9 | 1,5 | 147,3 | 5,49 | 7,83 | 25 | 29,3 | 40,7 | 41,3 | 1,5 |
| 4 | 19 | 22,9 | 2 | 151,1 | 5,64 | 8,04 | 25,7 | 30,1 | 41,4 | 42,0 | 2 |
| 5 | 23 | 26,9 | 2,5 | 154,9 | 5,78 | 8,24 | 26,3 | 30,8 | 42,1 | 42,7 | 2,5 |
| 6 | 27 | 31,2 | 3 | 158,7 | 5,93 | 8,45 | 27 | 31,6 | 42,8 | 43,3 | 3 |
| 7 | 31,3 | 35,8 | 3,5 | 162,5 | 6,07 | 8,66 | 27,7 | 32,4 | 43,4 | 44,1 | 3,5 |
| 8 | 35,9 | 40,7 | 4 | 166,3 | 6,22 | 8,87 | 28,3 | 33,2 | 44,2 | 44,7 | 4 |
| 9 | 40,8 | 46,2 | 4,5 | 170,1 | 6,37 | 9,08 | 29 | 33,9 | 44,8 | 45,4 | 4,5 |
| 10 | 52,3 | 58,7 | 5,5 | 178,8 | 6,55 | 9,49 | 30,3 | 35,5 | 45,5 | 46,1 | 5 |
| 11 | 58,8 | 65,7 | 6 | 181,6 | 6,8 | 9,7 | 31 | 36,3 | 46,2 | 46,8 | 5,5 |
| 12 | 65,8 | 73,2 | 6,5 | 185,4 | 6,95 | 9,91 | 31,6 | 37,1 | 46,9 | 47,4 | 6 |
| 13 | 73,3 | 81,2 | 7 | 189,2 | 7,09 | 10,12 | 32,2 | 37,8 | 47,5 | 48,1 | 6,5 |
| 14 | 81,3 | 89,7 | 7,5 | 193,9 | 7,24 | 10,3 | 33 | 38,6 | 48,2 | 48,8 | 7 |
| 15 | 89,8 | 98,9 | 8 | 196,8 | 7,38 | 10,53 | 33,6 | 39,4 | 48,9 | 49,5 | 7,5 |
| 16 | 99 | 108,9 | 8,5 | 200,6 | 7,53 | 10,7 | 34,3 | 40,2 | 49,6 | 50,2 | 8 |
| 17 | 109 | 119,7 | 9 | 204,4 | 7,67 | 10,95 | 35 | 41 | 50,3 | 50,9 | 8,5 |
Step 3. Definition of the third component - ectomorphy - O
- We calculate the value of O using the formula:
О= Body length/cube root (body weight)
- We look at the 9th and 10th columns of the table.
 The resulting value falls within the range from 44.2 to 44.8 (the line corresponds to the value O = 4 points.
The resulting value falls within the range from 44.2 to 44.8 (the line corresponds to the value O = 4 points.
Thus, the somatotype according to Heath-Carter is 2.5 - 4 - 4
This means that in our example the elements of endomorphy are weakly expressed, and the elements of mesomorphy and ectomorphy are moderately expressed.