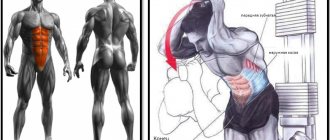
A crossover is a simulator that looks like this: these are two fixed metal columns that are connected by a crossbar. Under the crossbar there is a horizontal bar that can be used for pull-ups with different grip options.
On both sides of the vertical columns, weights are suspended from metal cables. Thanks to such devices, you can perform a large number of very effective exercises, such as moving your legs back in a crossover, while using many muscle groups.
Taking the leg back
This is an isolated exercise that targets the gluteal muscles. In general, it is considered auxiliary and is needed for additional work on the muscles of the buttocks. In its pure form, it can be useful if the knee is damaged and it is not possible to do more complex exercises for the buttock muscles.
In parallel with the gluteal muscles, receiving a slight load, the thigh muscles, in particular the biceps, also develop. It should also be noted that the exercise is not entirely deservedly considered purely feminine. The reason for this is that it basically gives a beautiful shape to the gluteal muscles. But for men it is also useful for the general strengthening of the entire complex of gluteal muscles and the development of their quality.
Tips for maximum efficiency
- Before performing leg extensions in the simulator, you should do a set of WARM-UP EXERCISES. Paying special attention to the hip and knee joints, as well as the lumbar region.
- This exercise does not require the athlete to work with extreme weights; the emphasis is more on technique.
- This exercise is isolated and targets small muscle groups. Therefore, it is best performed in a multi-repetition mode. It is generally recommended to do 15-20 times in 3-4 approaches.
- Leg raises are best performed at the end of a workout aimed at developing the legs and pelvis. This will allow you to squeeze out all the juices from already tired muscles. Some athletes place it before the basic ones, to pre-tire the gluteus medius and minimus, so that during the same SQUATS or LEG PRESS, the emphasis can shift to the hips.
- Be sure to set aside time for a COOL-DOWN at the end of your workout. Stretching after a workout will help flush out lactic acid from your muscle tissue. Thanks to this, the recovery process will be less painful.
I think you have slightly changed your views on such an exercise as leg raises in the simulator. Yes, it will not give you a huge increase in mass, as the base does. But it is fully capable of strengthening the hip abductor muscles. It’s not for nothing that many iron sports gurus say that there are no bad exercises. The main thing is to use his strengths correctly.
Good luck to everyone in your training!
Exercise technique
To start the exercise, you should take the starting position, having first put a special cuff on your leg, to which a cable with a weight is attached to the crossover. To take the starting position, grab the crossover pillars with your hands and lean forward slightly, keeping your spine straight.
Being in the starting position, you need to take a deep breath, and then, exhaling, move your leg back by only isolated tension of the buttock muscles. The leg should be pulled straight back (with the heel), slightly straightening the knee joint.
Then, as you inhale, return your leg to its original position. In this case, the body must remain motionless. After you have completed the required number of repetitions for one leg, you can begin exercises for the other. Do not do the exercise too sharply or jerkily and keep your spine straight throughout the entire process.
Efficiency can be increased by abducting your legs without interruption. While one of them is working, the other is resting. It is better not to do a crossover leg move at the very beginning of the lesson, since the exercise is performed at a fairly fast pace, which can be critical for unwarmed muscles.
Target muscles
“Hydrant” has an accentuated effect on the gluteal muscles, namely on its middle bundle. The gluteus maximus and minimus muscles receive indirect load.
In addition, the exercise, thanks to the lateral abduction of the legs, helps to tighten the inner thighs. The abs, deltoids and arm muscles are responsible for stabilizing the body in the “on all fours” position, which helps to strengthen them overall.
Common mistakes
Despite the apparent ease, mistakes are still made during the exercise, which reduces the overall effectiveness of the exercise.
We list them to know and avoid when pumping the gluteal muscles:
- Rounding the back. Unfortunately, when performing this exercise, people sometimes do not keep their spine straight, but rather arch it, thereby reducing the load on the buttock muscles. Additionally, rounding your spine can be hard on your lower back muscles.
- Jerks during execution. Because of the desire to pull the weight at all costs, many beginners make such a common mistake as jerking. Due to energy, the load on the gluteal muscles is reduced, which reduces the overall effectiveness of the exercise.
- Leg bending. Also a common mistake. The exercise must be performed with a straight leg. When bending, part of the load is transferred to the thigh, which immediately makes the exercise easier to perform.
- Not full leg extension. Some people are too lazy to lift their leg completely. And being able to raise it 90 degrees, they raise it only 70. Thus, you do not force the muscles to work at full strength. The longer the leg travels, the better it is for the buttocks.
- The cuff is loose. Elementary, due to a poorly secured cuff, the exercise can cause discomfort, rubbing the lower leg. To avoid this, always secure the cuff tightly.
What muscles does the leg raise in the simulator use?
The main work when performing leg raises in the simulator falls on the medius and minimus . It is due to their contraction that the hips are moved away from each other. Also taking a slightly lesser part are:
- Tensor fascia lata. Together with the gluteal muscles, it spreads the legs to the sides. In addition, it participates in pronation of the hip, that is, it rotates it outward, allowing the femur to move freely in the joint.
- Piriformis muscle. A small muscle that is also involved in hip abduction and slight external rotation.
- Adductor magnus muscle . Acts as pelvic stabilizers. Of course, she will not receive the same load as, for example, when performing LEG CUTS IN A SIMULATOR.
- Spinal extensors. Stabilize the body by holding the spine.
- Press. Together with the back extensors, it is responsible for maintaining the spine.
Weight and number of repetitions
For men (beginners)
Having mastered and tested the technique of performing this exercise, beginner men should decide on the weight and number of repetitions when performing it. For male beginners, it is recommended to apply a load of 5-10 kilograms on each leg. In this case, the number of repetitions should be from 10 to 15, and the number of approaches should be 3.
For men (advanced)
It all depends on your level of performing this exercise. After all, weight is selected individually. Here you need to focus on the number of repetitions that you can do with this weight. If you can perform 3 sets of 10-12 repetitions with it without violating the exercise technique, then this weight should be used.
For women (beginners)
Beginner women, unlike men, are allowed slight concessions in terms of weight. So they are recommended to start doing this exercise without weight or with a load of a maximum of five kilograms. The number of repetitions is the same as for men – 10-15. And you need to do at least 2-3 approaches.
For women (advanced)
The rule of individual weight selection also applies here. The main thing is to calculate your strength so that with three sets of 10-12 repetitions, you cope with the existing weight and do not feel a strong sense of discomfort or workload.
Thus, we see that one of the most important things when performing this exercise on a crossover is the technique of performing it. It is needed in order to do everything efficiently. After all, moving the leg back is not exactly an exercise where there is a risk of injury or where you need to chase a lot of weight.
Yes, of course, there are many alternative ways to pump up the gluteal muscles by moving your legs back. This can be exercises on a bench or on a machine. But the crossover will help you perform it with maximum efficiency, strengthening your gluteal muscles.
To summarize, we note that the main thing is:
- choose the appropriate option for performing the exercise;
- observe technique;
- avoid common mistakes;
- distribute weight according to your capabilities.
Varieties
Let's consider alternative options for performing the "hydrant" exercise.
"Hydrant" with straight leg
Technique:
- Get on all fours, straighten your back.
- Stretch one leg to the side, lower your toes to the floor.
- Exhale and, without bending your knee, lift your limb until it is parallel to the surface.
- Hold this position for 1-2 seconds, then inhale and slowly lower your leg.
- At the bottom point, try not to place your foot on the floor. This will allow you to better load the target muscles.
The exercise can be made more difficult by wearing soft sand weights on your ankles.
Static "hydrant"
Technique:
- To perform this you will need a rubber expander loop.
- Secure the shock absorber above your knees and get on all fours.
- Raise your hip to the side as high as possible and hold for 10–15 seconds (or longer).
- Repeat 10 times, then switch sides.
Instead of an expander, it is allowed to use soft weights attached to the ankles.
"Hydrant" with leg extension
Technique:
- Lower yourself to the starting position on all fours.
- Straighten your back and arms.
- While kneeling, exhale and gently move your hip to the side.
- When you reach the top point, straighten your leg and hold for a second.
- Then bend the limb and inhale to return to the starting position, but do not place your knee on the floor.
The element can also be complicated by using sand weights worn on the shins.
"Hydrant" with an expander
To perform this you will need an elastic expander loop. Technique:
- Secure the shock absorber above your knees and lower yourself onto all fours.
- Exhale and, keeping your leg at a 90° angle, move your hip to the side.
- Freeze for a second in the upper position, then inhale and lower the limb, but do not place it on the floor.
Instead of an expander, you can use a crossover. To do this, get on all fours next to the lower block, secure the cable to your thigh using a soft cuff and perform lateral abductions.
What other exercises is the crossover trainer designed for?
Bringing hands together
Good for chest muscles. In particular, for the lower, middle part of the chest. With a crossover, the muscles are isolated and allow you to perform the exercise with high amplitude, while the concentration on the process itself is quite high. The tilt of the body during the exercise may differ - it depends on the position.
The greatest load is placed on the muscles if you perform the exercise in a lying position. This way the muscles will be more isolated. Indeed, in the same position, standing and sitting, the athlete involuntarily helps himself with other muscles and weight. And if you do the exercise while lying down, it will be more “clean”.
Reduction of hands for the lower block
This exercise is suitable for the upper part of the pectoral muscles and the inner edge. Helps make muscles more prominent and emphasize them. It is better to perform standing or bending over.
Performing a tilted crossover
In addition, crossover exercises performed in a tilted position are effective. To perform it, you need to bend over so that your back is parallel to the floor and bend your knees. The main thing is to fix this stance so that other muscles are not involved when performing the exercise.
Doing exercises for biceps
The exercise is performed in a standing position. Using an underhand grip, take the upper handles and lower your arms so that they are parallel to the floor. The position of the legs and back remains fixed, the arms should be slightly bent at the elbows.
Development of deltoid muscles
This exercise should be done standing and will especially help train the middle deltoid muscles. It should be done alternately on each hand. With your free hand, hold on to the counter, fixing your body in this way. The working arm, bent at the elbow, should be raised up and to the side.
Foot pain
Gout
Arthritis
Diabetes
50024 05 March
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Foot pain: causes, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
The foot consists of 26 bones, which, when connected to each other, form several joints, held together by numerous elastic muscles and strong ligaments. It bears the entire weight of the human body, so pain in the foot causes not only discomfort, but in many cases limits motor activity.
Foot pain is a common symptom that can be caused by a variety of reasons.
In some cases, when collecting anamnesis, the doctor needs only such characteristics of pain in the foot as its location and conditions of occurrence, as well as the presence of concomitant diseases and other symptoms that accompany this pain (numbness of the foot, itchy skin, etc.). In others, finding the cause of pain requires a thorough laboratory and instrumental examination.
Types of foot pain
Based on duration, they are distinguished:
- Acute
pain in the foot - this phenomenon is most often associated with injuries - bone fractures, ruptured or sprained ligaments, severe bruises. - Chronic
pain that bothers the patient for a long time, in some cases, in the absence of proper treatment, a person develops a forced type of gait, which is associated with attempts to maintain the function of movement, while sparing the affected limb. The causes of this condition can be both diseases of the foot itself and pathologies of various body systems.
According to localization they distinguish:
- Diffuse
pain – affects the entire foot. - Local
pain – clearly limited to a specific area.
Possible causes of pain in the foot
One of the main causes of pain is
traumatic injuries to the foot
(bruises, sprains, bone fractures). With fractures, the pain is sharp, and swelling is rapidly increasing. In many cases, the supporting function of the foot is lost. Bruises and sprains are characterized by moderate pain, swelling and hematomas. Support is preserved, sometimes limited.
The next reason is inflammatory processes
affecting the joints of the foot. These include gout, chondrocalcinosis (pseudogout), rheumatoid arthritis.
Gout is a disease that occurs due to a disorder in the metabolism of uric acid. The deposition of uric acid salts in the joints is called gouty arthritis. With this disease, the first metatarsophalangeal joint is most often affected, which is manifested by a severe attack of pain, redness of this joint, swelling, and fever. Typically, an exacerbation of gouty arthritis lasts 6–7 days.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease that also affects the joints of the feet and hands. Characterized by morning stiffness and pain in the hands and feet.
Pain in the foot can be a symptom
of pathology of bone structures
. In this case, we can talk about diseases such as osteomyelitis, osteoporosis, bursitis of the metatarsal head, etc.
Osteomyelitis can result from open fractures, infected wounds, or surgical interventions on the foot. It manifests itself as an increase in pain and a deterioration in general condition. The pain is throbbing, bursting, intensifying with any movement.
In osteoporosis, bone strength is compromised due to decreased bone density. This condition is promoted by hormonal changes in women during menopause and during pregnancy, some endocrine diseases, insufficient supply of calcium and phosphorus from the outside, as well as excessive stress on the musculoskeletal system.
Pain in the feet with this disease is constant and intensifies with movement.
Bursitis of the metatarsal heads is a change in the articular capsules of the foot joints, associated with their increased trauma due to age-related thinning of the fatty layers that protect them. It manifests itself by the appearance of painful “bumps” in the projection of the joints of the feet.
To diseases of the ligamentous apparatus
foot pain syndromes include, for example, plantar fasciitis. The calcaneal fascia is a plate of connective tissue that starts from the heel bone and ends with attachment to the heads of the metatarsal bones. With increased loads, excess weight, and flat feet, the fascia is stretched and injured, which causes inflammation to develop in it. This condition is called plantar fasciitis and causes pain in the instep and sides of the foot.
A distinctive feature of this disease is also that the pain occurs in the morning, after a night's rest, intensifies with exercise, and in some situations can lead to lameness.
A condition where the fascia ossifies where it attaches to the heel bone and causes severe pain in the heel when walking is called a heel spur.
Diabetes may be a cause of foot pain
– a disease in which the microvasculature also suffers due to impaired glucose metabolism. Diabetic osteoarthropathy (a type of diabetic foot) primarily affects the metatarsal joints. The pain in the feet is not intense at first, but as the pathological process develops it becomes prolonged, appears even at rest, and severe deformation of the feet develops.
In the neuropathic form of diabetic foot, zones with hyperkeratosis are formed, and painful ulcers and cracks form in their place.
The ischemic form of diabetic foot is characterized by pain when walking, persistent swelling of the feet, and weakened pulsation of the arteries.
Diabetic foot with the development of gangrene, along with obliterating atherosclerosis and endarteritis, is one of the most serious complications of diabetes.
Flat feet
characterized by a change in the shape of the arch of the foot, which leads both to a redistribution of the load on the bones and muscles of the foot, and to compression of the vessels and nerves passing through that part of the sole that is not normally involved in the act of walking. The reasons for the development of flat feet include rickets suffered in childhood, wearing incorrectly selected uncomfortable shoes, weightlifting, congenital weakness of connective tissue, congenital difference in leg length, etc.
Inflammatory processes in the soft tissues of the foot
also cause pain. If infection gets into small wounds during a pedicure or the skin of the toes is injured, panaritium (purulent inflammation of the periungual tissues) may develop.
Panaritium is characterized by shooting pain in the affected finger, disturbing sleep, discharge of pus from the wound, redness and swelling of the finger.
An ingrown nail (onychocryptosis) is the ingrowth of the nail plate into the lateral edge of the nail fold. This condition manifests itself as jerking pain in the affected finger, swelling; a possible complication in the form of infection.
Which doctors should I consult for foot pain?
Pain in the foot brings significant discomfort and often makes it difficult to move, so you should decide in advance which doctor to see in order to avoid long standing in lines and unnecessary trips to the clinic. As a rule, an orthopedist is involved in the diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of people with deforming or traumatic damage to bones, joints, muscles, and ligaments of the musculoskeletal system. However, patients with diabetes first need to make an appointment with, and with vascular problems - with a phlebologist. Rheumatologists treat diseases associated with chronic connective tissue lesions. A traumatologist consults patients with foot injuries. If symptoms appear that resemble an ingrown toenail, osteomyelitis or panaritium, you should consult a surgeon.
In most cases, assistance can be provided on an outpatient basis, but sometimes hospitalization is required.
Diagnostics and examinations for foot pain The diagnosis of “Osteoporosis” is made on the basis of x-rays of bones and blood tests for calcium, phosphorus and other necessary indicators.
Technique for performing exercises in the simulator
Leg abduction in the simulator. We study all the subtleties and secrets
The element refers to an exercise of an initial level of complexity, and since it is performed on a special simulator, preliminary preparation for the training is necessary. First, you need to set the weight. For Men it will be 20-25 kilograms, for Women - 10-20 kilograms. In order for the weight to be selected correctly, you need to set the average value using the block system and perform 10-15 repetitions. Signs of a properly selected weight are a successfully completed set and a burning sensation in the muscles of the legs.
The technique for performing the leg extension exercise in the simulator will be as follows:
Step 1. We take the starting position
We sit on the simulator, pressing our back tightly against it and placing our hips between the side stops. We grab the handles with our hands and slightly spread our legs to the sides. Keep your back straight and your chest straight.
Step 2. On inhalation, we strain the press, and on exhalation we spread our legs as much as possible to the sides. We linger at the extreme point for a few seconds.
Step 3. We return to the starting position. At the same time, the legs should move towards each other, resisting the cushions of the simulator.
We do 15-20 repetitions, rest for half a minute and proceed to the next approach. It is advisable to do three sets.