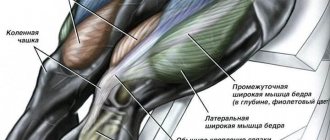
Quadriceps femoris[edit | edit code]
Quadriceps [rectus femoris, vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius (white arrows)]
Home[edit | edit code]
- Vastus medialis: medial labrum of the linea aspera, distal part of the intertrochanteric line, medial intermuscular septum of the thigh
- Vastus lateralis: intertrochanteric line, lower part of the greater trochanter, gluteal tuberosity, upper half of the linea aspera of the femur, lateral intermuscular septum of the thigh
- Vastus intermedius: anterior and lateral surface of the femur
Attachment[edit | edit code]
- Base and lateral edges of the patella. Patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity. The lateral parts of the vastus medialis and vastus lateralis muscles participate in the formation of the medial and lateral suspensory ligaments of the patella and are attached to the anterior surface of the tibia
Innervation[edit | edit code]
- Lumbar plexus, femoral nerve, L2-L4
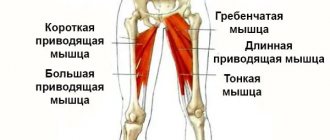
Inner thigh, muscle names
It is considered the most problematic. The skin here is somewhat thinner, which affects the appearance, especially of the fair half of humanity. In addition, stretching and tearing often occur here.
Another name is adductors. Simply put, the main function is to bring the legs together. Strengthening them is very important; training programs are based precisely on this action. Let's look at each in more detail.
Comb
The structure is similar to a quadrangle. Attaches to the line of the same name in the femoral region. Located diagonally. Works while running, walking and squatting.
Thin
This is a long bundle located in the pubic area. Crosses the knee and attaches to the tibia. Extends and rotates the lower leg. Works in conjunction with other adductors (from the Latin adductor - leading).
Short adductor
Flat, small in size, stretches from the pubis downwards, to the rough line. Flexes and rotates the limb outward. Often injured during sports. It is necessary to warm up so as not to provoke tears and sprains. Healing takes quite a long time. The pain syndrome is localized in the groin area.
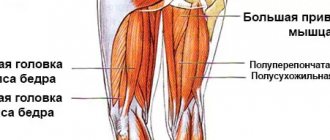
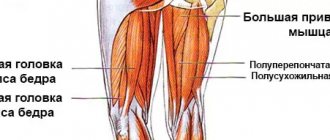
Adductor magnus
The fibers are located deep. They pass from the pubic symphysis. Fills the inner space of the femoral area. One of the most difficult to palpate. Its main task is to stabilize the pelvis and align it relative to the lower extremities. This is due to the characteristics of the fastening. Weakness and underdevelopment leads to hypertonicity and overstrain of neighboring areas.
Long adductor
Flattened, looks like a triangle. It is located on the anteromedial side and expands inferiorly. Most convenient for palpation.
Interestingly, the adductors are called “guardians of virginity” or “moral muscles.” Because their increased work and overexertion is associated with disturbances in the regulation of sexual activity. This “leg contraction” function leads to suppression of sexual arousal. It is especially developed in females, as this is a natural defense mechanism.
Participation in sports[edit | edit code]
During normal physical activity, this muscle performs both static work (prevents bending of the knee joint when standing and walking - in the front and back support phases) and dynamic work (extends the lower leg when walking - in the swing phase), especially when the step length increases or walking speed. In running, skiing, speed skating and bobsleigh, this muscle determines the length and frequency of the step in the support and push phases. Also involved in take-off during long jump, high jump, pole vault or triple jump and in movements during basketball, volleyball, rowing, ski jumping, diving, javelin and discus throwing, shot put, fencing, cycling, striking on goals in football, gymnastics, breaststroke and water polo. Performs eccentric and concentric contractions to stabilize the axis of the limb during triple jumps, fencing and contact sports and then shortens again. Due to static contractions, it participates in holding the torso in a straight position when skiing. The vastus medialis and lateralis muscles, due to their influence on the rotation of the lower leg, are involved in maneuvering on alpine skis.
| Kind of sport | Movement/hold | Function | Load | Types of abbreviations |
| Walking | Front and back support phases, leg swing | Shin extension | Strength endurance | Dynamic concentric and static |
| Running, cross-country skiing, speed skating, bobsleigh acceleration | Support and push-off phases | Shin extension | Fast, Max, Strength Endurance | Dynamic concentric |
| long jump, high jump, pole or triple jump, basketball, volleyball, ski jumping, diving | Repulsion | Shin extension | Fast, explosive, strength endurance | Dynamic concentric |
| Rowing | Wiring phase | Shin extension | Strength endurance | Dynamic concentric |
| javelin and discus throw, shot put | Push and extension of the lower limb, final acceleration | Shin extension | Fast, explosive | Dynamic concentric |
| Cycling | Pushing the pedals | Shin extension | Strength endurance, fast, explosive when sprinting | Dynamic concentric |
| Football | Shot on goal | Shin extension | Fast, explosive | Dynamic concentric |
| Gymnastics | Jump, elements with jumps in floor program | Shin extension | Fast, explosive, reactive | Dynamic concentric |
| Fencing, contact sports (karate) | Push-off with a variable step, stabilization of the knee joint with a variable step during an attack | Shin extension | Fast, explosive, strength endurance | Dynamic concentric and eccentric static |
| Skiing | Descent | Shin extension | Strength endurance | Static |
| Maneuvering on skis | Vastus medialis: internal rotation of the tibia; vastus lateralis: external rotation of the tibia | Fast, explosive, strength endurance | Dynamic concentric and static |
Thigh muscle problems
Spasms, pain, discomfort are far from uncommon for most of us. Many people face one problem or another. There may be one symptom, but there are many reasons. This condition occurs due to injuries, insufficient warm-up and overload. It is important to take sports seriously. Be sure to study the relevant literature or consult with trained trainers. The muscles of the anterior and posterior inner surface of the thigh, their anatomy and functions are very diverse, as are the problems with them.
Krepatura or delayed onset muscle pain syndrome
A fairly common phenomenon among athletes. Unpleasant sensations arise due to increased physical activity. It usually appears after 8–12 hours. Disturbs at rest and when using overstrained muscles. Another striking sign is a decrease in endurance.
Why does this happen and how dangerous is this condition?
For a long time, the pathology was associated with the irritating effect of lactic acid. Anabolic loads promote the oxidation of glucose and the active release of metabolic products. In trained people, this process practically does not manifest itself.
However, recent research has put forward a new theory, which is considered the most reliable. According to her, the cause is a change in the structure of the muscles and the resulting inflammation. Muscle fibers are made up of myofibrils. These elements provide the strength and speed of contraction. It is their deformation that occurs.
At the initial stage of playing sports, such a reaction is understandable and normal. In other cases, overexertion does not bring any benefit to the body. To prevent this, you need to warm up thoroughly and objectively evaluate your preparation. Regular anti-inflammatory drugs will help relieve symptoms.
It is important to differentiate this condition correctly
Myositis
This is inflammation of muscle tissue. The main symptom is severe pain and weakness; there may be the following accompanying manifestations: redness of the skin, swelling, increased temperature of the whole body. This happens due to: various injuries, hypothermia, vascular disorders or spinal defects.
If such symptoms are detected, you should consult a specialist. Only he will be able to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. As a possible surgical intervention.
Breaks
The thigh muscles are most susceptible to this effect. It is characterized by limited mobility, sharp pain immediately after a blow or excessive tension. An extremely dangerous condition. Some types of it require surgical intervention.
Sprains
Improper training or falls often cause deformity. Unpleasant sensations can be accompanied by hematomas or even a “click”, this indicates severe injury.
First of all, you need to apply a compress for 15–20 minutes. Ice or a cloth moistened with cold water will do this. Then make a fixing bandage, an elastic bandage or compression stockings will help. This will reduce swelling. Try to limit your movements. If it does not get better within 24 hours, contact the clinic.
Hypotrophy
This is a condition that occurs due to metabolic disorders. The muscles are literally “starving.” A rather dangerous disease that can lead to disability.
The main reason is insufficient supply of nutrients. This occurs due to: burns, hypothermia, intoxication, prolonged displacement, and can also be a congenital pathology. Symptoms are as follows: frequent pain, weakness, inability to perform usual actions, loss of body weight. Which leads to discomfort. To solve the problem, complex measures are used. Eliminate the primary factor, stimulate trophism, normalize metabolic processes.
At the “I Want to Walk” prosthetics center, we offer rehabilitation and adaptation to children with musculoskeletal disorders, give them the opportunity to join a full and vibrant life in society, demonstrate their abilities and talents, and master everyday and professional skills.
Piriformis syndrome
This is a neurological pathological manifestation characterized by a pulling action in the area of the buttocks and lower extremities. In this case, numbness, burning and increased tension in the knee area are also possible.
Occurs due to compression of the sciatic nerve. This can be provoked by: hypothermia, physical activity, an incorrectly placed injection, a defect in the spine or hip joint, or muscle strain.
It is extremely difficult to independently determine the correct diagnosis. It's best to leave this to a qualified professional. He will palpate and identify areas of pain and flattening. In the absence of serious pathology, a few days of rest will be sufficient; in some cases, medication, exercise therapy or massage are prescribed. Find out more about how to get rid of spasms here.
Iliopsoas syndrome
The disease is of a tonic nature, the cause is injury to the fiber or adjacent areas. However, this effect can affect innervation. Which leads to loss of sensitivity and motor function.
The clinical picture is very clear: involuntary contractions, weakness on the affected side, especially in the hip girdle. Active activity is impossible in this case.
The pain can be localized in various places. In the intestines, legs, lower back, it completely disappears when lying down.
It is treated with specially designed exercises that should be performed only as directed. They relieve tension, improve the patient’s general condition, promote relaxation, and restore tone and blood circulation. It is also possible to use drug therapy.
Features of adductor training
We offer recommendations that will help increase the effectiveness of adductor muscle training:
- Work your adductors on the same day as your glutes workout. This will avoid shortening the adductors;
- After your workout, do some light stretching. This will also help avoid shortening and improve the ductility of the fibers;
- To pump up the hip adductors, use high weights and low repetitions (for men);
- To strengthen the adductors and get rid of cellulite , work with light weights for a large number of repetitions (for women);
- Women are allowed to do stretching, yoga, and Pilates on their free days to improve the flexibility of the adductors.