for every novice bodybuilder, and simply curious people, to learn the anatomy of human skeletal muscles in order to navigate strength training programs, especially when it comes to split training, and also so that we can understand each other when you ask questions about , how you can pump up a particular muscle group.
In addition, knowledge of muscles will help you in the future to better work out all parts of the body with the help of selected exercises, due to the fact that you will no longer have a one-sided understanding of the structure of muscle groups.
For example, many athletes, still in pursuit of ball-shaped shoulders, do not know that the deltoids consist of the front, middle and rear heads, so in order to pump up your shoulders like a ball, you need to do all the exercises that develop all three deltoids, and not just favorite barbell/dumbbell press up with an emphasis on the front and middle deltoids .
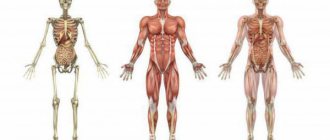
In total, there are more than 600 skeletal muscles , and they all consist of fibers of different lengths (up to 13 cm) and thickness (from 40 to 80 microns), but we will consider only the main groups, since knowledge of the rest does not have any practical benefit for bodybuilding.
Major human muscle groups
The structure of muscles and the principles of their work
Each muscle is not a separate organ, but part of a single system. It consists of many interconnected cells - myocytes, they are covered with loose and dense connective tissue - fascia.
There are two zones in the structure of each muscle:
- Abdomen.
- Tendon.
The main work is done by the first part. The abdomen consists of myocytes that are capable of contracting. Therefore, the function of this zone is active, contractile.
The tendon performs passive work - it is a dense connective tissue with which the muscle is attached to bones or joints.
The human musculoskeletal system works in close interconnection. Bones are not only a place for muscle attachment, but also a source of calcium for their contraction.
In turn, muscles during work improve bone nutrition, accelerating blood circulation and metabolic processes in the periosteum area.
The mechanism of muscle fiber functioning was discovered in the middle of the 20th century. It was called the sliding thread theory.
Contraction and relaxation are regulated by nerve impulses using calcium and magnesium ions.
Magnesium is like a brake fluid, allowing muscle fibers at rest not to waste energy.
When a nerve impulse passes, calcium ions are released, which stimulate fiber contraction.
Nutrition is carried out through thin capillaries that pass between the fibers. There are also nerve bundles through which the signal is sent. The source of energy is glucose or fatty acids.
The presence of oxygen ions is also required. Moreover, these substances must constantly enter the body from the outside. Muscles are not able to accumulate much ATP. With a lack of energy, their exhaustion and fatigue quickly begin, and lactic acid accumulates.
The structure of human muscles
A muscle fiber is a single cell consisting of threads of different thicknesses.
It is multinuclear, but the fibers interact only in a certain area. It is called a sarcomere and usually makes up 30% of the length of the muscle. It is in this area that it contracts or stretches. Elasticity is provided by the proteins collagen and elastin.
Be sure to read my detailed article about collagen for joints. I'm sure you'll like it.
The sheath of muscle fibers is covered with myofibrils. The speed of muscle contraction and their strength depend on their quantity. Training leads to an increase in the thickness and number of myofibrils. When they grow 2 times, muscle strength increases 3 times.
The myocytes themselves consist mostly of water; muscle cells contain 70-80%. They also contain proteins, glycogen, and mineral salts. And the shell, on which the work of the fibers depends, has a more complex structure. It contains several substances:
- actin - an amino acid that makes up thin filaments, is responsible for contraction;
- myosin makes up thick filaments and is a polypeptide chain of 2 thousand amino acids;
- actinomyosin is a complex of proteins formed by their interaction.
Thanks to such a complex structure, each muscle fiber is able to withstand severe loads. Muscle strength depends on the number of myocytes, as well as on the trace elements they contain.
If their cells do not receive proteins, glucose, fatty acids and oxygen, their ability to contract will decrease and they will decrease in size.
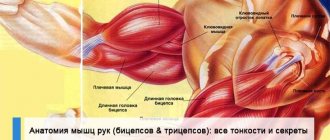
Anatomy of arm muscles
The anatomy of the arm muscles includes the muscles of the shoulder and forearm. The shoulders are divided into two groups: posterior (extensor) and anterior (flexor).
The first group includes three muscles:
- Coracobrachial.
- Biceps.
- Brachial muscle.
Second muscle group:
- Triceps brachii muscle.
- Elbow muscle.
The brachialis is a thick muscle that sits underneath the biceps, pushing it outward. Attaches to the elbow joint. The main anatomical functionality includes flexion of the forearm at the elbow joint.
The coracobrachialis muscle is a flat muscle, covered by the short head of the biceps. The main anatomical functions include raising the arms, flexing the shoulders at the shoulder joint and bringing the arm to the body.
The biceps is a biceps muscle, consisting of two heads: long and short. They start from the shoulder blades (in different places) and ultimately form one abdomen, resembling the shape of a spindle.
Anatomical functionality:
- Performs flexion at the shoulder joint.
- Bends the elbow at the shoulder joint.
- The inwardly rotated forearm turns outward (supination).
- The long head is involved in abduction of the arms.
- The short head takes part in adducting the arm.
The posterior muscle is represented by the following muscles:
The anconeus muscle is a small pyramidal muscle that is a continuation of the medial head of the triceps. Location - in the area of the olecranon process. Anatomical functionality - participates in extension of the forearm at the elbow joint.
The triceps is a large, long muscle that occupies almost the entire back of the shoulder. The triceps consists of three heads:
- long;
- lateral;
- medial.
The main anatomical features include extension of the forearm at the elbow joint and reduction of the forelimbs to the body.
- To properly work your arms, you need to pay great attention to muscles such as biceps and triceps.
- Exercises for pumping up your arms: standing biceps curls, push-ups from a bench.
Types of human muscles
Depending on the structure, functions and location, all muscle tissue in the human body is divided into three groups.
- Smooth muscles make up the walls of internal organs and blood vessels. They work automatically, continuously, regardless of consciousness. With their help, the food bolus moves through the digestive system, the bladder works, and blood pressure rises or falls.
- Cardiac muscles are located only in the heart and serve to pump blood. They also work continuously and rhythmically.
- Skeletal muscles or striated muscles make up the framework of the body. It is these muscles that are interesting to us, because... These are the ones we are trying to pump up. They are responsible not only for various movements, but also for maintaining balance and a certain position. Even at rest, when a person sits or lies, many of them work. By force of will, a person can force them to contract or relax. These fibers actively respond to nerve impulses; with the help of loads, their strength and volume can be increased. But continuous work leads to their fatigue.
Physical training is aimed at strengthening skeletal muscles. But everything in the body is interconnected.
A strong muscle corset supports the proper functioning of internal organs, which leads to improved digestion. Thanks to this, muscle fibers receive more nutrients and can withstand even greater loads.
Skeletal muscles are also related to the work of the heart. During training, the heart muscle is strengthened. This leads to improved blood circulation and oxygen supply to myocytes.
Properties of skeletal muscles
Human striated or skeletal muscles have the most complex structure. They form part of the musculoskeletal system; physical training is aimed at them. These muscles perform many important functions:
- support the posture;
- participate in movement;
- in moving body parts;
- protect internal organs;
- regulate breathing, blood circulation, body temperature.
They are able to conduct nerve impulses and contract under their influence. The ability of these fibers to relax and maintain a state of rest is also important. They are characterized by the following properties:
- elongation - increasing length under the influence of force, most fibers can stretch by 150%;
- elasticity - restoration of the original appearance after the cessation of force;
- contractility – the ability to contract, usually by 30-50% of the length;
- strength - holding a certain load
Skeletal muscles can function in a dynamic mode, when they actively contract and stretch, as well as in an isometric mode. This is a static voltage that does not lead to a change in the length of the fibers.
This is how the muscles work that maintain the vertical position of the body and work to overcome the force of gravity.
The characteristics of skeletal muscles also depend on the type and structure of the fibers.
- Red or slow fibers contain many mitochondria. They are located deep, mainly abductor and extensor muscles. They are excited slowly and require external stimulation. The speed of nerve impulse conduction is up to 8 m/s. They actively use oxygen, oxidize carbohydrates and fats, and participate in heat exchange.
- Fast or white muscle fibers are located superficially. These are flexors and adductors. Able to work in oxygen deficiency. They contract quickly, the speed of impulse transmission is up to 40 m/s. But which fibers are involved in the movement depends not on the speed, but on the force applied.
It is believed that the ratio of different muscle fibers is determined genetically. This may explain people's natural inclination towards certain sports. But with the correct distribution of the load, you can force the muscles to adapt and perform any work.
Classification of muscles of the human body
In anatomy, all skeletal muscles are classified according to shape, position in the body, function, direction of fibers and type of interaction with each other. The shape is divided into short, long and wide. By location - external or superficial, deep, internal, as well as lateral and medial. These types differ in the direction of the fibers:
- parallel;
- oblique;
- transverse;
- circular;
- one, two and multipinnate;
- semitendinosus;
- semimembranous.
This classification distinguishes straight, ribbon-shaped, spindle-shaped. These are simple muscles.
There are also biceps, triceps and quadriceps muscles. They are classified as complex. This group includes comb, serrated, square, deltoid, trapezoid.
But the most famous division of all muscles according to their functions. Groups are determined depending on the type of movement performed:
- flexors and extensors;
- abducens and adductors;
- tilting left and right;
- pronators and supinators;
- raising - lowering.
There are also several types depending on how they interact with each other.
- So the muscle that takes on the main load is called an agonist.
- Everyone who helps her complete this action, working together, is a synergist.
- Those that oppose the movement, working in the other direction, are antagonists.
- There are also stabilizers or clamps. They are needed to keep the joints in the correct position during exercise.
Anatomy of the muscles of the shoulder girdle
The deltoid muscle is a thick muscle, again shaped like a triangle, covering the shoulder joint and part of the shoulder muscles. Its large tufts fan-like converge to the very top of the downward-pointing triangle. The muscle begins from the axis of the scapula, acromion and lateral part of the clavicle, and is attached to the deltoid tuberosity of the humerus. Under the muscle itself there is a subdeltoid bursa.
The muscle itself consists of three bundles:
- front;
- average;
- rear.
Anatomy of the muscles of the shoulder girdle: functionality
- Front delta - bends the shoulder, turning it inward, raises the lowered arm up.
- Rear delta – extends the shoulder, turning it outward, lowers the raised arm down.
- Middle delta - moves the arm back.
The remaining muscles of the shoulder girdle include the major, minor, teres, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and subscapularis muscles.
- From the above list, the deltoid muscles are more susceptible to growth.
- By shaping the shoulders, you can achieve the best V-shaped symmetry.
- Recommended exercises are military press, barbell press from different positions.
How many muscles are in the human body
Human muscles form a complex system. They differ from each other in size, functions, and location. It is generally accepted that there are 640 muscles in the body. These include smooth, skeletal and cardiac. But according to some estimates there may be up to 850.
Muscle names
The name of the muscles reflects either their appearance - latissimus, rectus, or location - sternocleidomastoid.
Many of them are named according to the functions they perform - extensor finger.
Some names have been preserved since the Middle Ages, for example, the sartorius muscle is the one that is involved in flexing the hip, this is the position in which tailors sat at the machine.
Often the name also reflects the location.
According to localization, several groups are distinguished: muscles of the head, neck, torso, upper extremities, lower extremities. Not all of them participate in physical activity.
But you need to know the location of the most famous muscles that are most often involved in training.
Let's take a look at the main muscles in our body that we strive to transform more than others through training and nutrition:
- Trapezoid (Trapezius).
- Deltoid.
- Biceps.
- Rhomboid.
- Large round (Teres major).
- Triceps.
- Extensor carpi radialis (Extensor carpi radialis).
- Extensor digititi minimi.
- Extensor carpi ulnaris (Extensor carpi ulnaris).
- Latissimus dorsi muscle.
- Extensor digitorum.
- Serratus anterior muscle.
- Rectus abdominis muscle.
- External oblique abdominal muscle.
- Lumbar fascia (Thoracolumbar fascia).
- Gluteus maximus muscle (Gluteus maximus).
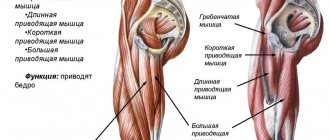
- Long adductor muscle (Adductor longus).
- Gracilis muscle of the thigh.
- Vastus lateralis muscle.
- Vastus medialis (vastus medialis).
- Semimembranosus femoris muscle.
- Tibialis anterior muscle.
- Semitendinosus muscle.
- Peroneus longus muscle (Peroneus longus).
- Biceps femoris (biceps femoris).
- Calf muscle (Gastrocnemius).
- Soleus muscle.
- Extensor hallucis brevis (extensor hallucis brevis).
- Short extensor of the toes (Extensor digitorum brevis).
- Sartorius muscle.
- Pectineus muscle.
- Rectus femoris muscle.
- Tensor fasciae latae.
- Gluteus medius (gluteus medius).
- Palmaris longus (Palmaris longus).
- Extensor carpi radialis (Flexor carpi radialis).
- Brachioradialis muscle.
- Pectoralis major muscle.
- Sternocleidomastoid muscle (Sternocleidomastoideus).
Anatomy of the back muscles
The anatomy of the back muscles covers the entire back of the body. This is a very large muscle group. The back muscles are paired and divided into two parts: deep and superficial.
The superficial ones are located in two layers, making up a smaller part of the dorsal mass. From the point of view of proportions (the outline and relief of the back), the muscles of the first and second layers are of greatest interest. It is a trapezoid, diamond-shaped and serrated.
The trapezius muscle is a flat, wide muscle that occupies a partial position in the back of the neck and upper back. The shape of this muscle is similar to a triangle.
Anatomical functionality:
- Raising and lowering of the shoulder blades.
- Bringing the shoulder blades closer to the spine.
You can train the trapezius muscle with lifting exercises and bringing the shoulder blades closer to the vertebra. Particularly suitable are dumbbell chin rows and barbell shrugs.
The latissimus dorsi muscle is also shaped like a triangle, but only large. It is located in the lower back, and in bodyman slang it is called “wings”. They give it a “V” shape and perfectly highlight the athlete’s entire figure.
Anatomical functionality:
- Bringing the shoulder to the body.
- Pulling the muscles of the upper limbs back (toward the midline) and pronating them (inward rotation).
You can train it using a variety of exercises designed to abduct and retract the shoulder blades. These are regular pull-ups on a horizontal bar or an exercise in the gym on a special “vertical pull-down” machine.
Rhomboid muscles. They resemble the shape of a rhombic plate and lie under the trapezoid. They originate from the cervical and thoracic vertebrae and attach to the scapula above the level of the bone. Anatomical functions - traction of the scapula towards the spine and at the same time its movement to the top.
Serratus muscles. Thin and flat muscles, slightly covered by the rhomboid muscle. They form three layers: superficial, middle and deep and make up the main part of the dorsal mass. They are directly involved in breathing, raising and lowering the upper and lower ribs. Much interest has been shown in the superficial part of this muscle.
The longus muscle is the longest of the back muscles and the strongest. It consists of a pair of “pillars” stretching along the lumbar spine. The lumbar region is divided into three parts:
- spinous;
- longest;
- vertebral-costal.
Anatomical functionality:
- Flex and straighten the torso during bilateral contraction.
- Tilts to the side during unilateral contraction.
The muscles of the superficial layer are the strongest, they perform the hardest work and occupy large surface areas.
Various types of exercises are suitable for developing the back - the main thing is that the load is persistently connected with the burden on the spine. For example, deadlift or hyperextension.
Functions of human muscles
Every athlete who wants to build muscles and change the shape of the body must know their anatomy and functions. You need to understand what exercises you need to do, how to increase the working weights in the exercises. There are several muscles that are most often involved in training.
Neck
You can pump up the sternocleidomastoid muscle from the neck muscles. She is responsible for tilting the head in all directions, as well as turning. Strengthening it is important for those athletes who play football, boxing, and wrestling.
You can do exercises with weights.
Torso
From the torso, special attention is paid to the abdomen, back, pectoral muscles, and neck.
- The pectoralis major is responsible for adducting the upper limbs, lifting up, and lowering. You need to do push-ups from the floor or parallel bars, abducting your arms on a block, and chest press. By the way, I have an article about how to pump up your breasts at home.
- The rectus abdominis muscle is responsible for bending the torso forward. A beautiful relief can be created by performing crunches from a lying position. I advise you to read my article about how to quickly pump up your abs at home.
- The external obliques help with forward bending and also perform lateral bending. They train while throwing the javelin, playing tennis, performing side bends and twisting.
- Trapezius - it helps lift the shoulders, move the shoulder blades, as well as the head back and forth and to the sides. Trained by weightlifters, gymnasts, during rowing and while pressing. Here is an article about how to pump up your trapezius.
- Latissimus – bending the torso to the sides, moving the arms back. Works during rowing, gymnastics and weightlifting. You can train using pull-ups on the bar. Read the link in detail about how to pump up your back.
Upper limbs
Mostly men try to pump up their arm muscles, but women will also find it useful to know the following information. To create a beautiful relief, you will need to work on the following types of muscles of the upper limbs:
- Biceps (biceps) – bending at the elbows, turning the wrist. Train for any exercises that include arm curls, as well as during rowing. Here is an article about how to pump up your arms.
- The coracobrachialis is responsible for raising the arms. You can train during bowling, arm wrestling, javelin throwing.
- Brachial – adduction of the forearm. To train it, you need to row, climb a rope, and perform weighted arm curls. Here is a detailed article about how to pump up your forearms.
- The triceps (triceps) is responsible for moving the upper limbs back. You need to do handstands and exercises involving extension of your arms.
- The deltoids are responsible for lifting the upper limbs. They train during gymnastics, weightlifting, and throwing. You can also do presses and lifting weights. Read the article about how to pump up deltoids.
Lower limbs
It is easier to train the leg muscles; there are many sports that put stress on the lower limbs.
- The quadriceps is responsible for rotation and supination, straightening in the hip joint. All types of squats, presses, leg extensions with weights are useful. He also trains for cycling, football, and athletics. Here is an article about how to pump your legs.
- Biceps hamstrings – for leg curls. To pump up, you need to do any exercises related to this movement. The most effective exercise for the hamstrings is the barbell deadlift.
- The gluteus maximus rotates the hip. Swimming, skiing, cycling are useful. Read the article about how to quickly pump up your buttocks.
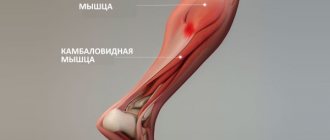
- The gastrocnemius is involved in the work of the knee joint and the rotation of the foot. Half squats, jumping, running, cycling are useful.
- The soleus extends the foot. Trains with calf raises.
- The tibia and fibula are involved in turning and other movements of the foot. You need to do a calf raise.
Exercises to develop skeletal muscles
All exercises for the development of skeletal muscles can be divided into two types, isolating (involving one joint) and basic (involving two or more joints). You should first of all focus on training a particular muscle group on the basic ones, because they grow muscle mass most effectively.
Human Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
Isolating exercises are well suited for separation and muscle relief, which at the initial level of training of a bodybuilder should not worry at all.
Trapeze
trapezius muscle belongs to the upper back and is involved in raising and lowering the shoulders.
The best exercise for training the trapezius is the barbell shrug.
Exercises for trapezius muscles
Latissimus dorsi muscles
They give a triangular shape to the back (especially when the waist is narrow), the wider the back, the larger the latissimus muscles.
The main function is adduction and extension of the shoulder, internal circular movement (rotation) of the shoulder, and also helps lower the shoulder girdle.
The best exercise for the back is wide-grip pull-ups.
Exercise for the latissimus dorsi muscles
Longus dorsi muscle
This muscle group is one of the strongest in the human body, located in the form of two “ pillars ” that stretch along the lumbar region.
The main function is to hold the muscle corset, and is also responsible for flexion and extension of the torso.
If you have problems with the spine, or just a weak back, then you simply need to strengthen these muscles.
The best exercise for strengthening the “pillars” is hyperextension.
Hyperextension for long back muscles
Pectoral muscles
The pectoral muscles are involved in the process of inhalation, and also pull the scapula forward, down and inward and indirectly contribute to the elevation of the ribs.
The best exercise is a regular barbell bench press on a horizontal bench; for athletes who have injuries to the pectoral muscles, during the recovery period we recommend the bench press and dumbbell flyes , as well as the hands in the butterfly simulator.
Basic exercise for the pectoral muscles
Abdominal Press
The press is one of the most capricious muscles in the human body. To have beautiful, sculpted abs, you need to not only train them frequently, but also monitor your diet (a layer of fat can simply hide sculpted abs). For those interested, you can read in detail about how to build beautiful abs here.
The main function is to stabilize the abdominal muscles.
One of the most effective and proven exercises is crunches on a bench at a downward angle and straight leg raises while hanging.
Abdominal exercise in the gym
Delts or shoulders
The deltas are divided into three main bundles: anterior, middle and posterior.
The function in the body is to raise, lower, and rotate the arm.
If you want to have large, inflated shoulders , do barbell lifts while sitting/standing behind your head and in front of you with free weight, and also for additional, isolated loading of the rear deltoids, use dumbbell raises to the sides.
Basic exercise for deltoids (shoulders)
Biceps
The biceps is involved in flexing the arm and consists of a long (external) and short (internal) head.
One of the most effective exercises in the gym for building bigger and stronger arms is the standing biceps curl (with a straight bar).
Exercise for developing biceps
Triceps
The triceps performs the function of extending the arm and consists of 3 main bundles : internal, medial and lateral.
The best exercises for pumping up the mass (volume) of the triceps are bench press with a narrow grip on a horizontal bench and push-ups on the uneven bars.
Basic exercise for developing triceps
Forearms
The forearm is responsible for moving the fingers, rotating the hand and clenching the hand into a fist.
The stronger the forearm, the more weight the athlete will be able to lift in a separate exercise, when the load is placed on the corresponding muscles, for example, in the deadlift, and with the help of a strong grip you can hang for a long time on the horizontal bar, which will greatly facilitate the pull-up process.
best exercise for increasing the strength of the forearm, since they need to be trained comprehensively, in different directions and at different angles (as arm wrestlers ), as for the volume of the forearm, the leading position is occupied by the exercise of flexion and extension of the arms at the wrists.
Exercise to develop powerful triceps
Gluteal muscles
The buttocks are one of the largest muscles in the body, are involved in bending and straightening the torso, and are also responsible for inward and outward rotation of the hip.
Consists of the gluteus minimus, medius and maximus muscles.
The best exercise for pumping up elastic buttocks is deep squats with a barbell on your shoulders.
Basic exercise for the gluteal muscles
Biceps hamstrings
The biceps femoris is involved in rotation and flexion of the lower leg, as well as in hip extension and together with the gluteus maximus muscle of the trunk.
The biceps femoris muscle consists of two heads - long and short.
It is recommended to first pump up the rough muscle mass of the legs, and then hone the relief of the hamstring biceps, for example, with an isolated exercise - lying leg curls in a machine.
Isolated exercises for hamstrings
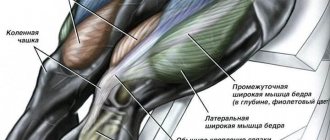
Quadriceps
The quadriceps consists of 4 heads - the rectus femoris, vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, and vastus intermedius muscles, which is why it is called the quadriceps.
The quadriceps muscle is involved in extension of the tibia at the knee joint and flexion of the hip.
Everything is the same as with the hamstrings - first you pump up the rough muscle mass of the legs by squatting with a barbell on your shoulders, and then start honing it.
The best isolation exercise for pumping up large quadriceps is considered to be a leg extension in a machine.
An effective exercise for quadriceps relief