April 25, 2017
| no comments
In recent years, one trend in women's fitness has developed very steadily and today it has eclipsed all other types of training. Of course, we are talking about training the lower body, in particular, beautiful legs and especially buttocks. There is hardly a single girl who would not strive to do squats for beautiful buttocks.
However, not only do many girls train frankly incorrectly, which prevents them from achieving the desired results, but they can also seriously harm their health.
Some instructors are not very concerned about the health consequences that will appear over time, because few people realize full responsibility for their actions. Therefore, if some trainer advises you to lean heavily on squats from the first day, and even constantly increase the weight, as per the textbook, it is better to run away from him or ignore such advice, at least you will thank yourself in the future.
Naturally, squats are by far the best exercise you can find not only for the legs, but for almost the entire body.
But it is extremely important to do it correctly and in this article we will look at everything that will allow you to become an expert in such an exercise as the squat with a barbell (or any other weights). We will look at not only the main topic: how girls can progress in squats, but also what “correct” squats are, what squat techniques are, consider exercises that complement squats, and also talk a little about the benefits of squats.
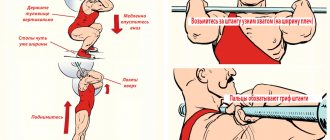
Squats: technique
It doesn't matter how much you go to the gym. Even if you just arrived and an empty bar is your limit, or you can already easily squat with a weight of 40-45 kg, this can still be considered a “beginning”.
Why?
Yes, because many girls, mastering the technique of squats in the gym, progress only in weight, excluding the most important stages.
THEREFORE, YOUR PATH FROM START TO 100+ KG IN THE SQUT WILL LOOK LIKE THIS:
- Practicing the correct technique without weight (that is, bringing it to perfection);
- General development of the legs and gain of muscle strength (in addition to squats, it is important to do other exercises, but more on that later);
- Progression in squats.
The last point implies:
- thinking through micro and macro cycles,
- changing the load (classical and front squats),
- improving stretching (Romanian deadlift + stretching exercises),
- and much more.
If you skip any of the stages and immediately start improving your squat weights, you will very quickly reach the limit, after which your progress will stall and you will have to get out of this “stagnation” for months. Not to mention that it is quite risky for your health.
There is a rather interesting paradox with exercise. Even with many training videos on the Internet, most gym goers often don’t even think about such a concept as “technique,” doing everything haphazardly. Meanwhile, the correct squatting technique is 100% effective or vice versa.
FOOT POSITION
Let's start with the banal - positioning of the legs. It can completely change the nature of the exercise, help you take on more weight or shift the main load to a specific part of the legs.
Among the main ones, there are 4 options:
- Standard (slightly wider than shoulder level);
- Wide (much wider than shoulder level);
- Sumo (wide, toes turned to the sides);
- Narrow (narrower than shoulder level, the load falls mainly on the quadriceps).
- Each of them is needed and periodically try to vary the exercises from workout to workout to ensure even development of the leg muscles.
For example, the sumo style will allow you to perfectly work out the inner thighs (they are usually the lagging behind), a narrow stance will allow you to work out the quadriceps, etc.
- It is also important to remember that you need to sit down as deeply as possible, that is, as far as your stretching and chosen style of execution allows.
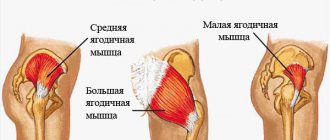
Deep squats, when performed classically, perfectly load the buttocks and are considered the best exercise for this muscle group. If you only sit down to the level where your thigh is parallel to the floor (a popular misconception), then your buttocks will not receive enough load, which means they will progress more slowly than you would like.
- This is why it is important to work on stretching, which will allow you to sit lower, reduce the risk of injury and increase the weight on the bar faster.
In addition to regular stretching exercises, try alternating squats with Romanian deadlifts, or even sometimes combining both movements into supersets.
Related articles:
Squats (without weights): guaranteed toned buttocks and slender legs Squats (with weights - a barbell): guaranteed toned buttocks and slender legs Squats with dumbbells - an effective exercise for the legs and gluteal muscles
How to choose weight
In order for a beginner to calculate the appropriate total weight of the weights on the barbell, you need to start with a load of 40 kg (20 kg on both sides). With this weight, it is important for the athlete to try his hand at squatting (with proper technique) about 10 times. If failure occurs on the 8th or 9th time and the person feels that it is becoming very difficult for him to perform the exercise, then the weight is calculated correctly. If the movements were difficult even on the first squats, then you need to lighten the barbell by evenly removing several weights on both sides. If the loaded squats were easy to perform, then you can safely add 5 kg on both sides until failure occurs on the 8th-9th squat.
Squats for girls: different techniques
LET'S TALK ABOUT YOUR BACK
If we talk about the back and what the squatting technique should be, then hardly anyone will be surprised by the requirement that...
- The back should be straight, maintaining a natural arch.
- You shouldn’t tilt your head down and “peck” at the floor, just as you shouldn’t lift it up.
- The eyes should look straight ahead.
- To maintain a deep squat arch, it is very important to move your pelvis back during the squat. This is necessary so that you do not fall forward with the weight, providing yourself with stability, and also so that your technique is not disturbed (back, heels not lifted off the floor, etc.).
Overall, there is almost no difference between men's and women's squats. The muscles work the same way, the development features are the same, so the main difference still lies in the weights. Firstly, it is more difficult for girls to gain muscle mass and strength, and secondly, they need to train the whole body, not just the legs.
The weak link in squats can be the back, abs and other muscle areas. It is especially important to remember the compressive load on the spine. In the case of an insufficiently powerful muscle corset, the load on the vertebrae will be higher than normal, which over time can lead to unpleasant consequences, and the spine itself will simply “age”.
SO, REMEMBER A NUMBER OF RULES:
- Progress gradually, rushing will only add unnecessary risks;
- Train your whole body, not just your legs;
- Always do a full warm-up (the whole body, not just the one you are training).
ALSO CONSIDER THE OPERATING MODE:
- With a load of 60-70% of OPM (one-rep maximum), it is worth working within 8-10 repetitions;
- C 70-80% = 5-6;
- 80-90% = 1-3.
If you decide to work with light weights in a high-repetition mode (for endurance training or in cardio cycles), then in this case you no longer need to particularly look at the number of repetitions and do it either for a while or until failure, that is, to the maximum.
The secret is that you don't have to choose. If you want powerful leg muscles, round buttocks and the standard of a modern figure, then the “strength” option will always come first.
Why is that? Because without developing strength indicators, you can forget about increasing mass. At the same time, by training in strength mode, you can always maintain such an important indicator as the aesthetics of your figure.
Also, do not assume that development and progression in strength training, that is, working solely to increase strength, will also build muscle mass. It’s worth looking at the women’s weightlifting section and seeing that with extremely high weights, not all girls have massive legs.
Those involved in fitness often have even larger hips, although powerful and firm buttocks will be guaranteed in any case and for any job (if you sit as deep as possible).
An excellent option that allows you to progress and, so to speak, “sit on two chairs at once,” is alternation. Just alternate types of workouts over the weeks, changing between strength and regular (or high-repetition) options.
For example, this week you squat 3-5 times per set, but with heavy weights, the next week - 7-10 times, but with lighter weights, or even work with about 40% of the maximum resistance to failure (15-20 times) .
The main thing is to shock the muscles so that they constantly adapt to the load they receive, this will ensure constant and rapid progression.
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
And yet, the power regime should become the main one.
The following option is ideal:
- Sets (6) – 5, 5, 5, 3, 3, 3 repetitions each with 60-70% of the maximum resistance level;
- 3, 3, 3, 1, 1, 1 – with 80-90% of OPM.
Don’t be afraid to squat 1-3 times, your muscles will receive much more load than from ten repetitions with moderate weight.
Recent studies show that priority always shifts towards weight, while the quantitative difference (with one barbell weight) is much lower. Therefore, the more weight, with the correct technique, the better.
In a strength cycle, it is better to do 6 approaches, the first 3 with 4-5 repetitions (3, if you take the extra strength version, which should be done no more than once every 3 weeks), the second 3 approaches - 2-3 repetitions. At the same time, each squat must be done as technically as possible, confidently and honestly, that is, without cheating. It’s better to work with a partner, or ask someone to back up.
If you want to add volume, then alternate the strength style with the usual, so-called “hypertrophy” training. That is, squats in the range of 8-10 reps in 4 sets with moderate weight (on average 60 to 70% of 100% max, if you take only working sets).
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
AMONG THE RELATED EXERCISES THAT NEED TO BE PERFORMED IN PARALLEL WITH SQUATS, in order to develop the entire lower body and strengthen all muscles, it is better to pay attention to:
- Romanian cravings;
- Lunges (forward and backward);
- Bulgarian squat;
- Jumping onto a pedestal (or just up) from a deep squat;
- Flexion/extension in the simulator;
- Leg raises/extensions in the simulator (optional);
- Any workout for calves (from a machine and a hack machine to a “donkey”).
The main thing to remember is that technique and safety when performing squats is always more important than weight, number of approaches and repetitions, etc. The weight on the bar is important, but it should never be chased, especially when your muscles are not yet ready for such a load.
The number of repetitions is not important if they are done to failure
Other scientists have used a similar basic training program (Study #5). 25 healthy people aged 34-44 years with at least 1 year of resistance training experience were divided into only 2 groups: low and high repetitions, the group with medium repetitions was excluded.
Ultimately, after 8 weeks of training, a 10% increase in quadriceps femoris cross-sectional area was found in both groups, with no significant differences.
A follow-up study from the same laboratory (#6) with a similar sample of subjects reported a 10% increase in quadriceps muscle size, with no significant differences between groups that used a similar training protocol.
The researchers believe that the results differ from the data we described in the previous example due to the lack of training of older people, as a result of which any type of resistance training in this population can provide a significant stimulus for muscle growth.
Notably, subsequent studies using a similar protocol in healthy young adults showed an 18% increase in satellite cell numbers associated with low-intensity (higher repetition) training. Therefore, exercises with light weights and high repetitions, done to the limit, can have a positive effect on the early stages of the muscle tissue formation process.