September 29, 2022 Admin Home page » Tips and tricks
Features of sprint running and its technique. What are the benefits of sprinting? Safety precautions when sprinting.
At the Summer Olympic Games, one of the most spectacular sports is sprinting, which is performed both over long distances of 400 m and shorter distances of 60, 100 and 200 m.
Despite the minimum race time, spectators get a real explosion of emotions, because sprint running is considered the most dynamic discipline and is not for nothing considered the most spectacular.
The nuances of sprinting
Running in the sprint style is the most difficult discipline in athletics; I activate the entire reserve of the body and work at maximum capabilities, coordinating movements, high-speed endurance and maximum speed are included in the work as much as possible. All these indicators determine the final success of the race.
Maximum speed
Speed is the basic component of sprinting. A short distance forces the development of maximum acceleration, which develops from an early age throughout the entire sports life.
Speed is affected by 2 main components:
- stride length;
- step frequency.
Competent coaches begin to develop the frequency of movements in young athletes from early childhood, usually this happens between 10 and 16 years. At this time, the body adapts well to the load, which improves running speed in the future, but sprinting can be improved even in adulthood.
Speed endurance
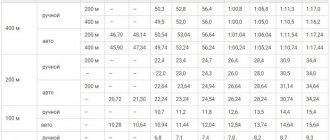
Allows you to maintain maximum speed for a certain period of time. To obtain maximum results, athletes use a signature technique: if the competition is held at a distance of 100 m, then training for maximum endurance takes place at a distance of 200 m, if the competition is at 200 m, then speed endurance develops accordingly during the preparation period for a distance of 400 m.
This will create a reserve of endurance and prevent it from falling at the most crucial moment at the finish line.
Coordination
Responsible for the accuracy of all movements and correct balance during running.
It needs to be improved and developed for 2 important reasons:
- so as not to run into someone else’s path - otherwise even stepping onto the opponent’s line threatens to disqualify the athlete;
- improving muscle function - this will reduce the load from less loaded muscle fibers and redistribute it to those areas that bear the maximum load.
The development of all 3 components will allow you to achieve maximum speed results.
How to incorporate such workouts into your regular schedule
1. Complement your ultra-speed workouts with fast free running. Studies have shown that immediately after completing such a workout, free running speed increases. You have about 10 minutes to run a free sprint to reap the greatest benefits.
2. Make sure that the ultra-fast running pace does not exceed the free sprint pace by more than 10%. Everyone has experienced this at least once: you rush down a slope at incredible speed and cannot stop. This can cause serious injury, so it is important not to overdo it.
3. Work on your sprinting technique to achieve maximum speed.
Sprinting technique
The sprint distance itself is divided into 4 stages, which are taken into account when drawing up a running strategy. Professional sprinters pay close attention to each stage, which is why they achieve success at the finish line.
So what is included in these stages:
Start
Divided into 2 types - high and low:
HIGH – most often used for young runners or in the absence of special sports equipment. This type of start is also good for beginners, as it does not require special skills, otherwise, without special training, a starting movement from a low position can lead to a loss of body stability and balance, which ultimately threatens a fall.
LOW – used by professional sprinters, which makes it possible to take a more comfortable position and make a powerful starting push. To start from this position, it is necessary to have pads, which are adjusted individually for each athlete.
The general rule for any position is as follows:
♦ a stronger leg is placed forward for a powerful starting pushing movement;
♦ arms are bent at the elbows;
♦ the shoulders are not tense and relaxed;
♦ after the command steps on the stronger leg, part of the body is transferred in front and a powerful push is made with further full straightening of the leg.
Starting acceleration
After making a push and lifting the leg from the pads, acceleration begins over 3 steps. It is necessary to pay special attention to the position of the body, which is directed forward, while the head looks down. Only this positioning of the body will allow you to gain maximum speed in a minimum time.
Then you need to remain in approximately this position for 30-40 meters, after which the body gradually levels out.
This is interesting! The maximum speed officially registered for the competition was 44 km/h!
Central part of the run
The battle for the podium is mainly determined in this segment, when 50% of the way is already left behind. When half of the path is completed, the sprinter, with his head raised, looks forward, the torso tilt is practically not noticed and is only 5-10 degrees.
It is a mistake to tighten the muscles of the shoulder area too much, because this reduces speed at maximum speed. You need to run with your shoulders wide, which will immediately affect the final result.
Finish
The emotional part of running, where the winner can be determined by hundredths of a second. For this complex task, when the human eye cannot clearly determine, a photo finish is used with a clear moment of the end of the running distance.
Currently there are 2 ways to finish:
⇒ sideways – when, at the moment of crossing the finish line, the sprinter turns sideways and thus crosses the finish line faster;
⇒ chest - literally 0.5-1 m before the finish, the runner sharply straightens his chest and moves his arms back, which allows him to shorten the finish by a split second.
The sideways finishing option should not be used if the coordination of movements is not perfected, otherwise loss of balance can lead to a fall and possible injury!
How to run correctly
Proper foot placement during sprinting reduces the likelihood of injury. When running, you should not feel any kickback in your foot. There are three types of foot placement techniques:
- with emphasis on the toe, without touching the ground with the heel;
- with emphasis on the entire foot;
- with emphasis on the heel, with a gradual transition to the forefoot.
The first technique of planting the foot, in which the spring effect is triggered, is considered the most effective. This achieves the best shock absorption when the foot hits the ground, and the foot is pushed upward without delay on the surface. You can figure out the correct placement of the foot by jogging barefoot on a hard surface. Each person’s foot has its own individual characteristics and, in this case, the best option for positioning the foot will be suggested by nature itself.
High speed during sprinting is regulated by frequency and stride length. During the race, your hips must be separated from each other as wide as possible - this will allow you to take longer steps. You don't need to fully extend your knees, as fully straightening your legs when running will affect your speed and lead to rapid fatigue.
As you lower your leg, your torso must be kept vertical, directly above the point where your foot contacts the surface. This position will allow you to make a strong push and continue to accelerate. The movement of the hands is free, they should move as nature dictates. Your back should be kept straight and your torso should remain motionless.
The benefits of sprinting
♦ reaction speed and explosive power develops. Sprinting should be used at a young and mature age, but should be excluded in the elderly and elderly, because the heart and blood vessels receive a greater load;
♦ running at maximum speed over short distances involves a large number of muscle fibers and allows you to burn a huge amount of calories.;
♦ allows you to strengthen your legs and buttocks in the shortest possible time, because explosive movements actively engage the deepest areas of the muscles, which remain “dormant” during normal jogging;
♦ sprint actively develops the respiratory system, because maximum load forces you to consume a large amount of oxygen, which in turn leads to an increase in lung volume.
If sprinting has not been practiced before, you need to get into it gradually. Start with a regular run of 200-400 meters and speed up from workout to workout. Only after this reduce the distance and increase your running speed.
For example, for week 1, run 400 meters every other day, for week 2, reduce the distance to 350 m, and so on, reduce it by 50 meters every week, while increasing your speed.
How to increase your running speed
If you want to take up sprinting, you must first train regularly and increase the overall endurance of the body. Running speed can be increased only by strengthening your muscular corset, the strength of the muscles and ligaments of both the lower and upper limbs.
You need to increase the pace of training gradually so as not to cause harm to the body. The psychological aspect and the mindset to win are very important. You can increase your overall motivation with the help of regular small victories; it’s enough to set yourself feasible goals every day and achieve them. This will help significantly increase self-confidence and increase determination and passion for winning in sports.
The importance of training muscle strength in running disciplines[edit | edit code]
Each individual push-off in sprinting involves the application of a certain amount of force, especially fast force. However, an important role is played by the fast force and the maximum force that determines it only at the moment of start and during the first phase of acceleration, when it is necessary to overcome significant resistance in order to move from a state of rest to acceleration. With increasing running speed, since the support phase is shortened, power capabilities begin to weaken very quickly, coordination and technique, or speed abilities determined by the characteristics of the central nervous system, become decisive. However, in the phases of development of high and maximum speed, strength qualities are still necessary to perform pushes and jerks, as well as to overcome the braking force in the first support phase (landing shock absorption).
Sprint[edit | edit code]
Sprinting or short distance running
, is an area of athletics that covers all types of straight running, steeplechase and relay races over distances of up to 400 m.
Within athletics, sprinting, or speed running, has a special position due to the fact that it determines the results of many other disciplines (for example, in horizontal jumps, long jumps and triple jumps) or has a significant influence on them (for example, in running). medium distances). For this reason, sprinting can largely be considered the main discipline of athletics. Sprint, or high-speed running, is of decisive importance in achieving high results not only in other athletics disciplines, but also in many other sports.
Based on the results of numerous studies of sprinting, the following typical phases of running in a straight line can be distinguished:
- reaction/start;
- acceleration phase;
- maximum speed phase;
- decreasing speed phase.
As the results of recent studies have shown, the acceleration phase in a short sprint (100 m) can be divided into intense acceleration and acceleration.
Short distance steeplechase
(100 and 110 m hurdles) or steeplechase (400 m hurdles), unlike running in a straight line, is a complicated race, with overcoming obstacles determined by the conditions of the competition. Each athlete must individually adapt to these given conditions in terms of the number, length and rhythm of his steps. Due to the specific conditions of obstacle racing, the phase structure of this discipline can be represented as follows:
- reaction/start;
- first acceleration phase;
- maximum speed phase;
- decreasing speed phase;
- second acceleration phase.
The second phase of acceleration refers to the increase in speed after overcoming the last obstacle (the end of a controlled run) to the finish line.
The reaction/start and (first) acceleration phase are the same in straight running and obstacle course running/sprinting, and the second acceleration phase is practically the same as the first and maximum speed phases.
Running tactics for 100 and 200 meters
The choice of tactical techniques depends on the goal set by the athlete: to take a specific place in the competition or to win. The athlete preliminarily assesses the capabilities of his opponents and analyzes their strengths and weaknesses. When running a 100 m race, the athlete’s muscles work in optimal mode for up to ten seconds.
During the race, various tactics are used:
- pursuit of a competitor;
- leading at a distance;
- final dash in the last hundred meters;
- acceleration in the middle of the distance.
The leader, using leadership tactics, imposes a running pace on his opponents. There are no obstacles when turning, so it is possible to stay close to the edge. The final effort doesn't require wasting energy on overtaking.
Disadvantages of leadership tactics:
- Forced overcoming the force of the wind.
- Lack of knowledge of the opponents' plan.
- Loss of protection during unexpected overtaking.
Pros of stalking tactics:
- It’s easier to run behind because the leader takes on some of the air resistance;
- It’s easier to adapt to someone else’s not-so-fast pace than to offer the same to yourself;
- it is possible to deliver an unexpected “blow” to the leader at any moment.
Disadvantages of stalking tactics:
- Behind the leader, there is always a fight between the participants for the closest places.
- High risk of injury.
- Time is wasted on extra meters of distance to the finish line.