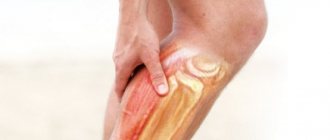
A calf muscle strain is a rupture of individual fibers or muscle bundles as a result of injury or excessive physical activity. Clinically, the pathological condition is manifested by acute pain, crunching, swelling and hemorrhage of varying intensity. To diagnose a sprain and determine the degree of its severity, a number of instrumental studies are performed - MRI, CT.
Anatomy.
The effectiveness of treatment and the speed of recovery of the victim depend on the prompt provision of first aid. The therapy uses cold compresses, fixing bandages, external agents with a cooling effect, and painkillers. During the rehabilitation period, ointments for sprains, physiotherapeutic procedures, exercise therapy, and no stress on the ankle are indicated. Surgery is performed for severe injuries when most of the calf muscle is damaged.
Causes
The most common strain occurs at the junction of the calf muscle and the Achilles tendon. The ankle muscles are usually injured in people involved in active sports: tennis, basketball, acrobatics, volleyball, football. At a certain point, they experience a load that they are unable to withstand. Even the elastic calf muscles of professional athletes have a certain strength limit. Its excess causes fiber rupture. Sudden movements during running, especially at the start, or high or long jumps lead to injury. Almost all injuries to the calf muscles in athletes are considered acute, caused by powerful contractions of the muscle-tendon system.
Pay attention to the location of the injury.
The risk group also includes amateurs who decide to actively engage in sports, but do not have the necessary knowledge and skills. Injury is caused by a combination of factors:
- lack of pre-warming of muscles before a long run or jump;
- low elasticity of muscle fibers, ligaments and tendons, significantly reducing tensile strength.
Calf muscle strain is often diagnosed in people predisposed to this type of injury. The likelihood of damage increases with flat feet and joint hypermobility associated with improper collagen biosynthesis. During sports, sometimes only individual fibers are torn. People attribute the resulting pain to muscle strain and fatigue. Such microtrauma significantly reduces the functional activity of the muscle. Soon a situation arises where a small amount of physical activity is enough to cause serious damage.
In untrained people, only a sprain of the calf muscle is rarely detected. It may be accompanied by violations of the integrity of the bone, fascia, periosteum, partial rupture of the tendon or its complete separation from the bone base.
Mechanism of development of gastrocnemius muscle cramp
To understand the mechanism of development of calf muscle cramps, it is necessary to understand some of the features of its structure. So, this muscle is represented by many myofibrils. Each myofibril is a strip with hundreds of rows of muscle cells. They are called myocytes.
Each muscle cell (myocyte) has a contractile apparatus consisting of several proteins. The main one in them is actin, and the auxiliary ones are troponin, myosin and tropomyosin. Myosin and actin are intertwined with each other like filaments. Their mutual approach, and therefore muscle contraction, occurs under the influence of ATP, calcium ions, troponin and tropomyosin.
This is a multi-level process that goes through several stages:
- An impulse arises in the brain, which is sent along the nerve to the calf muscle.
- With the help of acetylcholine, the electrical impulse from the nerve passes to the surface of the muscle.
- This impulse then spreads throughout the muscle fiber and penetrates its deep structures through T-shaped channels.
- From the channels, the impulse passes to the cisterns (cells containing calcium ions). Calcium channels open and calcium leaves the cells.
- Calcium activates tropin and tropomyosin, which in turn cause actin and myosin filaments to move closer together. ATP takes part in this process.
- Muscle contraction occurs at the moment when the myosin and actin filaments come as close as possible.
If a failure occurs at any stage of this complex process, it will lead to seizures.
Video: neuropathologist on the causes and treatment of seizures during sleep:
Clinical picture
Treatment for a calf strain depends on the severity of the symptoms. Treatment of first-degree pathology is carried out at home. And if an injury of the second or third degree of severity is diagnosed, the patient is indicated for hospitalization for medical care in a hospital. Symptoms of a calf muscle strain include:
- first degree. It is diagnosed when no more than 25% of the muscle fibers are torn. Victims do not immediately consult a doctor, since the pain that occurs during the injury quickly subsides. Discomfortable sensations occur only during walking and make it difficult to fully rest on the foot. The main symptoms appear after 5-12 hours. Severe swelling and an extensive hematoma form in the ankle area. The functional activity of the calf muscle is noticeably reduced: the victim experiences difficulty when trying to lean on his toe, and while moving he is forced to limp in order to reduce the load on the sore leg;
- second degree. With such a stretch, up to 75% of the muscle fibers are torn. At the time of injury, acute pain occurs, the intensity of which decreases slightly when lying down. Muscle rupture provokes a violation of the integrity of nearby blood and lymphatic vessels. Blood enters the subcutaneous tissue and soon a large hematoma forms in the area of the ankle and ankle. The swelling is so intense that the contours of the foot and ankle change. The victims are not able to fully flex and extend the foot and ankle joint, and use outside help when moving;
- third degree. It is detected when more than 75% of the muscle fibers are torn or the gastrocnemius muscle is completely torn off in the area of its attachment to the Achilles tendon. During injury, a crunching sound may be heard, reminiscent of the cracking of dry branches being broken. The pain is so acute and piercing that the person often loses consciousness. Within a few hours, swelling and hematoma form. The stability of the joint is completely disrupted, the range of motion in it is noticeably reduced. The victim is unable to bend or straighten his foot, ankle, rise on his toes, or move independently.
High-grade calf strains are most often associated with other types of injuries, usually fractures. In this case, ligaments, tendons, and joint structures are seriously injured. With such damage, the likelihood of bleeding into the joint and nearby soft tissue increases. Only quickly provided first aid and going to the emergency room will help prevent traumatic shock.
Why do muscles cramp?
The reasons can be divided into two groups. The first includes those that do not have any underlying diseases. So, if the calf or gluteal muscles cramp in a dream, there is no physiological pathology in this. The seizure in this case is a parasomnia, that is, a phenomenon associated with sleep. Spasms that occur during increased physical activity also do not indicate an abnormality.
In other cases, such discomfort may be caused by:
- neurological disorders;
- compaction of muscle fibers against the background of physical inactivity;
- metabolic disorders;
- micronutrient deficiency;
- dehydration;
- poisoning (including cramps from a hangover).
There is also a disease called hypoparathyroidism. It is characterized by a convulsive syndrome that immediately affects muscle groups. This condition is caused by hypofunction of the parathyroid glands.
First aid
First of all, the person needs to be laid down and calmed down. To relieve acute pain, you can use analgesics and antispasmodics, but it is best to give the victim a tablet of any non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (Ibuprofen, Nise, Ketorol, Diclofenac, Ortofen). What to do next:
- limit the mobility of the injured leg. If you have the skills, it can be fixed using a splint or elastic bandage. In their absence, the person should be provided with complete rest. Traumatologists advise raising the limb by 30-40 cm, for example, placing a tightly rolled cloth under it. This will help avoid the formation of severe edema and compression of sensitive nerve endings;
- use cold compresses. The procedure will prevent the formation of edema and hematoma and reduce the intensity of pain. This is done using a plastic bag filled with ice cubes. A piece of frozen meat or a package of mixed vegetables is also suitable for cooling. The package must be wrapped in several layers of thick fabric to avoid frostbite. The compress is applied to the calf muscle for 15 minutes. Then you should take a half-hour break.
If first aid is provided correctly and in a timely manner, the victim’s well-being will improve significantly. Sometimes he even refuses hospitalization, which is absolutely unacceptable. Signs of a sprain may mask symptoms of a fracture, dislocation, rupture of ligaments and (or) tendons. To determine the type of injury, diagnostic measures are necessary.
It is advisable to elevate the leg and give it rest.
First aid for calf cramps
If leg cramps are not associated with an epileptic attack, then you need to perform the following simple measures:
- The leg must be elevated to improve blood flow and eliminate existing stagnation.
- You need to grab the toes of the lower limb and bend them towards the knee. First, they are bent halfway and relaxed, and then bent as far as possible and held in this position. This will stop the seizure.
Following these recommendations allows you to stretch the calf muscle, due to which it, like a sponge, absorbs blood saturated with oxygen. Foot massage can improve blood circulation through small blood vessels. Movements should be light and smooth. They come down to pinching and stroking the limb.
Injecting soft tissues with a pencil or other sharp object (without damaging the skin) allows you to interrupt the reflex chain and stop the spasm. This technique is actively used by professional swimmers, who always carry a pin with them. In this way they get rid of the cramp that happened at depth.
After the attack of cramp has been stopped, it is necessary to give an intensive massage to the muscle and stretch it.
To minimize the likelihood of cramping during exercise, your muscles should be warmed up and stretched before you begin. To do this, perform bends with lunges, body bends without lunges, and squats. While bending, exhale and only after that you need to stretch the muscles.
Video: 3 ways to relieve cramps:
What to do if your calf muscle cramps in water?
If a cramp catches a person while swimming in a pond, then under no circumstances should you give in to panic. Whenever there is such an opportunity, you need to loudly call for help. In this case, you must continue to swim towards the shore, actively working with your hands.
The simplest solution is to roll over onto your back. At the same time, you need to breathe deeply and continue to swim towards the shallows using your hands.
If a person is confident in his abilities, then he can relax in the water, taking the form of a starfish. While floating on the water, you need to massage the calf muscle until the cramp goes away. You need to be prepared that in such a position a person will have to plunge headlong into the water from time to time. Therefore, this method can only be put into practice by a swimmer who feels confident at depth and knows how to hold his breath.
So, immediately after a cramp occurs, it is necessary to direct all efforts to eliminate it. After all, this condition is stressful for the body and needs to be eliminated as quickly as possible. Only after this should you search for and treat the cause of calf muscle cramps.
Diagnostics
An external examination of a patient with muscle fiber rupture is not very informative due to the similarity of symptoms of almost all ankle injuries. Differential diagnosis is carried out to exclude a fracture of the tubular bone, dislocation or damage to the Achilles tendon. What diagnostic tests can be performed:
- radiography. An X-ray examination reveals fractures and cracks in the bones;
- MRI or CT. The study is informative for establishing damage to any connective tissue structures: muscles, ligaments, tendons, soft tissues.
Diagnostics is also necessary to identify the inflammatory process that occurs during injury, the degree of its intensity and localization. The victim is also shown general blood and urine tests, the results of which make it possible to assess the general state of health.
Types of seizures
If involuntary contraction of muscle fibers is caused by overexcitation of the cortical part of the brain, such convulsions are classified as epileptic. Non-epileptic ones are provoked by diseases of the central nervous system, imbalance of nutrients, and unfavorable external conditions.
Also, involuntary muscle contractions can be classified according to their nature:
- tonic – long-term, turning into a state of tension;
- myoclonic – short;
- clonic - jerky, cyclically repeating and alternating with relaxation.
Based on localization, these phenomena are divided into generalized and local. The former cover a significant part of the body (arms, legs, face, neck, side, torso, and sometimes extend to the respiratory tract). The latter occur in separate areas (for example, only in the back or only in the buttock).
General principles of conservative treatment
In case of injury of the first degree of severity, the victim is prescribed bed rest for 1-2 days. A cane or crutch is used to move around the room. At the rehabilitation stage, rigid or semi-rigid orthoses are used. Wearing orthopedic devices helps reduce the load on the damaged muscle and speed up the recovery of torn fibers. As the ankle heals, it is secured with elastic bandages or bandages. How else can you treat a calf muscle strain at home:
- in the first days, actively use cold compresses or ointments with a cooling and distracting effect, for example Ben-Gay;
- after 2-3 days, external agents with a warming effect (Finalgon, Viprosal, Capsicam) are included in the treatment regimen to improve blood circulation and accelerate regeneration processes;
- Throughout the entire therapy, the use of venoprotectors and venotonics (Troxevasin, Lyoton, Troxerutin) is recommended to reduce the severity of edema and hematoma.
NSAIDs and analgesics should only be taken to relieve severe pain. If you follow all medical recommendations, the discomfort gradually disappears. Warming ointments have a distracting effect, significantly reducing pain.
A little anatomy
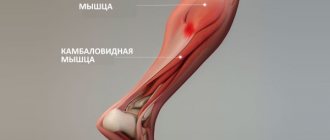
First, let's get acquainted with the structure of the lower leg. The lion's share of it is occupied by the gastrocnemius muscle, consisting of two heads - medial and lateral. It is their development that gives the main volume of the lower leg. Below the gastrocnemius is the soleus muscle - it is flat but wide, so its development can add width, both in side view and in frontal positions.
An important difference between the gastrocnemius and the soleus is that the former crosses the knee joint and is attached to the femur, while the soleus does not cross the knee joint and is inserted within the tibia. This means that the calf muscle is maximally activated in a standing position, but is virtually inactive when the leg is bent at a 90-degree angle. At these moments, the soleus muscle takes over the baton.
From this anatomical structure of the lower leg follow the specifics of training the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles - the gastrocnemius is trained in a standing position, and the soleus in a sitting position, but more on that later.
In addition to the triceps surae, the extensor digitorum, peroneus longus, and tibialis anterior muscles are also present on the anterior surface. To directly train them, you need a special simulator, which is so rare in gyms that you can forget about it. If you have such a machine in your training room, I strongly recommend using it more often.
Surgical intervention
Treatment for a sprained calf muscle, which is characterized by rupture of most of the fibers, is only surgical. If the victim is taken to the hospital in a timely manner (within 1-3 days), the surgeon stitches the torn muscle and immobilizes the leg with a plaster cast for 2-3 weeks. After a course of rehabilitation measures, the functionality of the foot is completely restored after 1-3 months.
When a victim underestimates the severity of his condition and does not go to the emergency room, this causes shortening of the calf muscle, a decrease in its volume, and the development of degenerative processes in nearby connective tissue structures. A person is still forced to seek medical help due to the impossibility of full movement. Since muscle retraction has already occurred, its plastic restoration is necessary during arthroscopic surgery. The surgeon builds muscle tissue using a graft.
Why do muscles cramp in pregnant women?
Carrying a child leads to significant changes in the body. In particular, metabolism is rebuilt. As a result, many expectant mothers are faced with magnesium deficiency, which is why cramps appear.
Pregnant women's legs are subject to greater stress due to weight gain. Hence the involuntary muscle contractions that occur in the evenings and at night. They can also be triggered by varicose veins, which often accompany hormonal changes.
Pregnant women often complain about back pain. The lumbar spine is under constant tension, forced to bend under the pressure of the uterus, so such sensations are normal. Therefore, expectant mothers are recommended to lie on their side to relieve the load on the spine.
Rehabilitation period
To restore the active functioning of muscles, the doctor draws up a set of rehabilitation measures. Following all recommendations will significantly speed up recovery. For mild sprains, rehabilitation begins after 2-3 days, at the stage of using warming ointments. In case of serious injury, recovery begins after removal of the plaster cast. What rehabilitation doctors recommend:
- massage, classic or acupressure, to improve blood circulation and microcirculation;
- 5-10 sessions of physiotherapy: laser therapy, magnetic therapy, UHF therapy, increasing the rate of muscle fiber regeneration;
- therapeutic exercises and physical education to restore all functions of the torn muscle.
From the very beginning of treatment, patients are shown electrophoresis with analgesics, NSAIDs, and calcium solutions to reduce pain intensity. If a sprain is combined with injury to a joint or bone, then chondroprotectors are used during physiotherapy.
Traumatologists recommend going to a hospital even with mild pain in the ankle. The victim cannot independently assess the severity of the sprain or identify concomitant injuries to the bones or ligamentous-tendon apparatus. Lack of treatment will cause the injury to worsen and serious complications to develop.
Informative video about ways to recover from injury:
Prevention
The best prevention of involuntary muscle contractions is moderate physical activity. Regular exercise helps keep your muscles under control. The tissues will not suffer from physical inactivity or sudden overload. This is equally beneficial for both men and women at any age.
A set of exercises to prevent cramps always includes stretching. It is useful to do it before bed so that unpleasant symptoms do not occur at rest.
Since muscles often cramp due to hypovitaminosis and lack of microelements, it is important to eat a balanced diet. If you cannot get them in sufficient quantities from food, you should additionally take vitamins B and E, as well as magnesium, calcium and potassium supplements. It is also important to drink enough fluids, because similar discomfort occurs due to dehydration.
Circulatory disorders
Experts include the following diseases and pathological conditions of the lower extremities in this group of causes that provoke the occurrence of calf spasms:
- thrombophlebitis;
- varicose veins;
- endarteritis;
- vascular atherosclerosis.
Lack of blood supply to tissues or blood stagnation due to impaired venous outflow leads to an imbalance of potassium, sodium and magnesium. A deficiency of these microelements leads to increased nervous excitability of the muscles and causes spasms.
Spasms can be a signal of the development of dangerous vascular pathologies that require treatment.
In addition to the imbalance of microelements, disturbances in the blood supply to the lower extremities lead to a decrease in ATP levels. These are specific molecules that produce the energy necessary for muscle contraction and relaxation.
Their deficiency leads to disruption of the reaction mechanism - this is why convulsions occur.