Among modern strength sports, powerlifting is especially popular. Its name, when translated from English, means “lifting (weights) with force.” In training and competition, a powerlifter continually lifts heavier weights by performing the three basic barbell exercises of powerlifting: the squat, the chest press, and the deadlift.
Today, powerlifting has a huge number of followers who regularly visit sections, sports clubs and gyms to set a personal record for themselves or take part in a strongman competition. You can study either with a professional trainer (recommended) or without one, guided by methodological literature.
Powerlifting Principles
A key training goal for powerlifters is to increase the weight they lift as much as possible. Athletes do not have a goal to develop endurance. There is no desire to gain weight and build a sculpted body.
To achieve an impressive effect, you need to achieve results according to the following principles:
- Training should be varied. It is important to alternate them in intensity. For example, a high-intensity session is replaced by a less intense session with less weight, and for the next workout, more weight is taken again and the load increases. Such changes are necessary for timely muscle recovery.
- Avoid unplanned weight gain, even if lifting the current one seems easy. Strict adherence to the chosen program is the key to success. It is important to leave the working weight unchanged for at least two weeks, because this way the muscles will maintain and increase strength.
- There is no need to perform formed repetitions. We are talking about the last presses performed through force. A powerlifter doesn't have to be tough. Moreover, if you use too much weight, performing forced repetitions will lead to injury, so performing them is extremely undesirable.
- No additional exercises are required.
- You should always stick to the program strictly.
These 5 principles are time-tested: they have helped more than one generation of athletes achieve good results.
How the training goes
Before you begin strength training, you need to warm up your muscles, joints and ligaments. Every workout begins with a warm-up.
An approximate list of general physical warm-up exercises includes:
- squats;
- exercises for the abs;
- bending to the sides;
- push-ups from the floor and from parallel bars;
- pull-ups on the bar;
- jumping rope;
- jumping out of a squat.
At the end of the warm-up, stretching is mandatory.
The group method is used for training. Beginners practice their lead-up exercises one by one. The coach corrects their execution and points out mistakes.
The main condition of the process is maintaining regularity of training and performing the full complex from start to finish.
The coach makes sure that the guys increase the load gradually. This applies to the number of approaches and adding weight to the projectile. The technique is practiced with medium weight.
At the end of each month of classes, competitions are held within the group. Competitions identify errors, make adjustments and develop a further training program.
A first year student must:
- master the technique of classical exercises;
- is in excellent physical shape;
- be able to read training plans;
- dose the load;
- know the terminology and name of the exercises.
Second year athletes train in pairs. They develop independent work skills. Partner insurance is required.
After practicing the entire complex at each workout, athletes perform hanging on the bar to relax the muscles and stretch the spine. Additionally, children can exercise on simulators.
Visiting the pool once or twice a week is very helpful in relieving stress on the spine.
The benefits and harms of powerlifting
Powerlifting has the following positive aspects:
- strengthening all muscle groups, creating an athletic figure;
- improvement of strength indicators;
- development of coordination and flexibility;
- posture correction;
- A differently tuned diet helps you lose weight or, conversely, increase muscle mass;
- a powerlifter builds a good foundation that allows him to engage in other sports.
There are also negative points:
- those who practice with a careless approach or inattention run a high risk of injury;
- duration and severity of training;
- the emergence of dependence on working weight and competitive results, as a result, the athlete uses sports pharmacology irrationally, he develops mental problems, which primarily applies to beginners.
However, it is worth remembering: any of the listed dangers occurs only when the powerlifter himself violates the principles.
Preparation stages
The stages of preparation in this sport are:
- initial;
- educational and training room;
- sports improvement;
- supreme sportsmanship.
The focus of sports programs is shown in the table.
| The name of the program | Age, years | Study time, year |
| Modified | 10-18 | 2 |
| Experimental | 15-18 | 1 |
Competition rules
The rules divide all competing athletes into categories based on gender, weight and age. Each exercise is limited to three approaches. To calculate the final result, the indicators of all elements are summed up. The basis for winning is lifting the most weight compared to your opponents. The age of admission to participate in the competition is 14 years.
Age and weight categories
Separately among men and women there are 4 age categories:
- adult (14+, no restrictions on weight categories);
- youth (14–18 years, until the first day of the year in which they turn 19);
- junior (19-23, until the first day of the year in which you turn 24);
- veteran
The last category, veterans, is divided into 4 groups for men and 3 groups for women.
Men's groups of veterans by age:
- 40–49 years old.
- 50–59 years old.
- 60–69 years old.
- 70+ years.
Women's groups of veterans by age:
- 40–49 years old.
- 50–59 years old.
- 60+ years.
In terms of weight, for boys/girls and juniors/juniors there are separate categories up to 52 kg and up to 44 kg, respectively. The categories are further divided into adult males and females.
Men's adults start at 52 kg and have no further restrictions, as do women's, starting at 44 kg.
Weighing order
Participants weigh in two hours before the competition along with representatives of their weight category. Sometimes organizers and judges combine and weigh participants of different weight categories in one competitive stream.
The weighing order is determined by drawing lots. Drawing lots is also used when it is necessary to determine in what order the participants ordering the same weights will appear on the platform.
The duration of the weigh-in is 1.5 hours. The athlete chooses how to do it - without taking off his underwear or in the nude.
All athletes are weighed once. The commission allows the athlete to re-weigh if his indicator exceeds or, conversely, is less than the permissible limits. Athletes are allowed to adjust their results by weighing themselves an unlimited number of times, but this must be done within the established time limits and following the drawing of lots.
Initially, each athlete is placed in a category corresponding to his performance, but the athlete has the opportunity to change it to one that is lighter or heavier.
Checking the height of the racks (for squats, bench presses) and, if necessary, blocks (stands) is carried out by athletes before the start of the championship is announced. The result is recorded in the protocol.
Equipment
The support suit is registered and approved by the technical committee.
The non-supportive suit is made of elastic material and is similar to a jumpsuit. You don't need permission to use it because it doesn't break any rules.
Each athlete is required to wear a half-sleeve T-shirt under his suit if he performs bench presses or squats. This rule does not apply to traction.
Underpants. They can be a standard factory bandage or swimming trunks (cotton + polyester + nylon). Wearing any type of support garment is prohibited.
The length of the socks should not allow them to come into contact with the knee wraps and knee pads. Deadlifts should be performed in long socks that protect the shin well.
The belt is worn on top of the suit. It should be made of multi-layer non-stretch materials that are stitched and glued (leather, vinyl, etc.). The maximum width is 10 centimeters, the main part is 13 millimeters.
Footwear – sports boots (shoes), special boots, sneakers, slippers for traction.
A bandage or bandage is permitted only if it is made of elastic single-layer fabric material: cotton, polyester, medical crepe. The bandage cannot exceed 1 meter in length and 8 centimeters in width.
The knee bandage should not exceed 2 meters in length and 8 centimeters in width. This requirement does not apply to socks or tracksuits.
Basic exercises and reasons for failing results
The first exercise is a squat. It is divided into three main phases:
- The barbell is removed from the racks and the starting position is taken.
- A squat is performed and the athlete rises back to the starting position.
- The barbell returns to the rack.
Lifting weight in a squat will not be counted if the athlete:
- did not comply with the referee's signals;
- performed other movements when standing up;
- did not take the correct vertical position with legs straightened;
- stepped;
- in the starting position, moved the bar lower by a distance greater than its thickness (diameter);
- spotters (assistants) touched the bar during the exercise to make it easier;
- touched the leg with the elbow or shoulder;
- dropped or dropped the barbell to complete the squat.
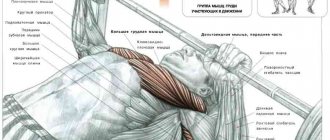
The second exercise is the bench press:
- Lie down on a bench and place your feet shoulder-width apart. The feet should be pressed firmly to the floor, the emphasis should be on the heels.
- This is followed by maximum retraction of the shoulder blades.
- The head, both shoulders and buttocks are completely pressed against the bench.
- Bend your lower back and check that the bar is at eye level.
- Grasp the bar with the desired grip.
- Extended arms hold the barbell above your chest.
- Inhale, lower down, touching the bar to your chest, and raise again.
Lifting weights on the bench press will not be counted if the athlete:
- changes the starting position while performing the exercise (raises (lifts from the bench) the head, buttocks, shoulders, moves the legs along the platform or hands on the bar;
- raises or lowers the bar after fixing it on the chest;
- straightens arms unevenly;
- moves the barbell down while performing a bench press;
- does not straighten his arms completely, completing the exercise;
- touches the feet with the support or the bench itself.
The third exercise is deadlift:
- Shoulder extension and shoulder blade retraction. The position of the legs is no wider than hip level. The shins touch the bar. The feet are parallel, the bar goes above their center.
- Pulling the pelvis back and straightening the back while squatting, and bringing the knees behind the toes are prohibited.
- Hands take the bar with a wide classic grip.
- By placing the shoulders and chest in front of the bar line, the quadriceps and buttocks lift the bar upward.
- The lower back straightens, the pelvis is pushed forward, and the position is fixed.
- Before lowering the bar, to prevent unpleasant contact with the knees with the bar, the hips are pulled back.
- The body moves back down, the position of the spine is neutral (it does not arch or sag).
- The knees bend only after the bar reaches their level.
Deadlift weight lifting will not be counted if the athlete:
- moves the barbell in a different direction until reaching the final position;
- a vertical position in which the shoulders are pulled back is not accepted;
- completing the exercise, does not fully straighten the legs at the knees;
- when lifting the barbell, supports it with your hips;
- stepped;
- lowered the bar without receiving a signal from the referee;
- when lowering, he let the barbell out of his hands, rather than carefully placing it down.
In all three exercises, strict adherence to technical requirements is important.
The order of the competition
When performing an exercise, a corresponding round is allocated for each approach: the first - the first, the second - the second, the third - the third.
The starting weight for each exercise is stated by the athlete or his coach during the weigh-in. The athlete performs the first approach in the exercise, after which he or the coach orders the weight for the next one. When performing the third deadlift approach, you are allowed to re-order the weight twice.
With each new round, the weight of the barbell increases. The weight should not decrease.
When an athlete fails to lift a weight, he waits for the next round, where he uses a similar or greater weight.
You can only change the weight on the first set of each exercise once.
The declaration of the second and third approaches is made by the athlete after finishing the first in 1 minute. If he did not declare the weight, then 2.5 kilograms are automatically added (when the approach was unsuccessful, the weight remains unchanged).
The size of the group in the competition stream is up to 14 people. Rest before the next exercise is usually 15 minutes. With the simultaneous participation of two or more groups, only technical breaks are announced, during which the platform is prepared and equipment is installed.
Responsibilities of insurers
Assistant (insurer):
- adjusts the height of the bench press and squat stand;
- sets the weight of the bar;
- ensures that order is maintained on the platform;
- clears the platform or bar as directed by the senior judge.
The number of belayers on the platform ranges from two to five people.
An assistant helps the athlete remove the barbell from the racks and return it back. Touching the barbell or the athlete while he is performing an exercise is prohibited unless there is a risk of injury. In the latter case, after the judge’s command, they help the athlete free himself from the barbell. When the case is particularly dangerous, you should not wait for the judge’s signal.
When squatting, there are at least two assistants. They are located on both sides of the athlete. If the weight is too heavy, up to five belayers are allowed.
When pressing, everything is similar.
When deadlifting, no assistants are required, since avoiding injury depends only on the technically correct execution of the exercise.
Judging system
The athletes’ results are assessed by three judges: the central (senior) and two side judges. The duty of the central judge is to give the necessary signal in each exercise (there are three in total): visible - with the help of a hand, sound - with a voice or clap.
The judge communicates his decision using light signals: white indicates good execution, red indicates unsuccessful execution.
Before the start of the competition, the judge checks the equipment and equipment for serviceability and compliance with the rules. Athletes also weigh themselves under the supervision of judges.
The main task of the panel of judges during the competition is to monitor the correctness (technicality) of the athletes performing the exercises.
Sports titles and standards
The International Powerlifting Federation and all organizations that have membership in it assign titles to athletes in accordance with age:
- the title of master of sports is awarded to an athlete provided that he has reached 16 years of age;
- the title of master of sports of international class is awarded to an athlete, provided that he has reached 17 years of age;
- Assignment of sports categories (1-3 and CMS) begins at the age of 10.
Men's standards for all ranks are assigned separately for 9 weight categories (from 53 to 120+), women's - for 8 (from 43 to 84+). For the lower weight category for men and women there are no standards for MSMC and MS. The value of the weight lifted increases with the weight category and rank. The minimum requirements are put forward for the III youth category, the maximum - for a master of sports of international class.
Equipment and supplies for powerlifting
In training and competitions, powerlifters use:
- a barbell (bar), the total length of which does not exceed 2.2 meters;
- discs whose diameter should not exceed 45 centimeters;
- auxiliary rack for bench press;
- stand on which the squat is performed;
- the platform on which the deadlift is performed (its size should not be less than 2.5 × 2.5 m, more than 4 × 4 meters and higher than 10 centimeters);
- a bench on which the bench press is performed (more than 1.23 meters long, more than 29 centimeters wide, more than 42 centimeters high).
In addition to the parameters described above, an important requirement for equipment is its strength.
How to choose a section
The choice of section should be treated very responsibly.
First of all, you should get to know the coach. A lot depends on this person in the training process, first of all the child’s health and his psycho-emotional state.
Particular attention should be paid to the technical equipment of the club. You can talk to the guys who study in the section. Take an interest in their successes and achievements.
It is important that the spirit of collectivism and a friendly, friendly atmosphere reign in the club.
Nutrition
Huge, strong muscles require special nutrition. For this reason, when drawing up powerlifting training programs, the following recommendations must be taken into account:
- only natural products are allowed (the complete exclusion of synthetic semi-finished products is necessary);
- Constantly consuming unhealthy drinks and very sweet foods is prohibited, because they increase the level of insulin, which is undesirable for a powerlifter;
- breaks between meals for 2-3 hours (observance of such a schedule gives the greatest growth to muscle mass in the shortest period of time and prevents increased fat production);
- Protein must be consumed in sufficient quantities (in cottage cheese, milk, eggs, protein supplements, legumes, cheese) at every meal;
- you need to combine animal proteins with plant proteins throughout the day;
- use raw vegetables to enrich your daily diet (they will speed up metabolism, remove toxins and increase overall performance, and therefore increase overall strength);
- the consumption of fast carbohydrates is allowed only after training;
- do not consume trans fats;
- Only healthy fats are allowed: vegetable oils (directly pressed), nuts, red fish, food additives rich in fatty acids.
Compliance with all these rules indirectly affects the overall tone of the athlete’s body and his readiness for heavy power loads.
Contraindications
The main contraindications to powerlifting are:
- problems with the spine;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- myopia;
- cardiac arrhythmia;
- cystic diseases.
Before you start training, you must undergo a full medical examination and obtain permission from doctors.
Powerlifting Federations
The most famous worldwide is the International Powerlifting Federation. It is the only international organization that has membership in the General Assembly of Sports Federations and is part of the World Games Association.
The World Raw Powerlifting Organization specializes in holding raw powerlifting competitions. Its goal is to identify and support the strongest athletes who have shown record results. In addition, its most important task is to increase the attractiveness of strength sports. She holds championships both in powerlifting in general and separately in deadlift and bench press.
The Russian Powerlifting Federation has the status of a member of the International Organization. It is also accredited by the Russian Ministry of Sports. Each competition is strictly regulated by the rules established by the International Organization. Doping control is required. The FPR holds competitions in both equipped and unequipped (classical) types of powerlifting.
History of powerlifting
Powerlifting originated in that distant past, when humanity was just beginning its journey. Every nation is the creator of tales, legends, whose heroes have extraordinary power. Ancient Egyptian, Greek, Chinese and Iraqi bas-reliefs, drawings, written sources and mosaics show the desire of men to demonstrate their own strength.
When the Chu dynasty ruled in Ancient China, all conscripts were tested for strength qualities before being sent to serve in the state troops: they had to lift the greatest weight.
The ancient Greeks were especially passionate about physical exercise. They also founded the ancient Olympic Games - a set of competitions that included lifting additional weights. The incredible strength achievements of the Greek people are confirmed by many testimonies.
The province of Croton gave the state the most Greek strongmen. This is the birthplace of the famous strongman Milo, who could put a four-year-old bull on his back and walk with him throughout the Olympic Stadium.
In England XIV-XV centuries. Pushing a beam made of iron was a mandatory exercise for soldiers.
Physical strength was especially held in high esteem by the Scots. They tested all the young men for maturity. The test consisted of lifting and placing a 100-kilogram stone to a height of 120 centimeters. Having passed this test, the young man received the right to be called an adult and could wear a headdress made of bear skin (the bear personified strength and courage).
The first outstanding strength achievement in England was achieved by Thomas Topham. His record was lifting a weight of more than 800 kilograms: the athlete held 3 thick barrels filled with water using straps attached to his shoulders.
The typical strongman of the New Age was clumsy and heavy, relying not so much on technique as on brute strength. To “promote” himself, he could exaggerate his abilities by deceiving the audience at a performance. Frequent instances of deceit on the part of heavyweight athletes have made the public more skeptical of records on stage. This attitude has continued to this day.
The title of the most famous strongman of the 19th century goes to the Canadian Louis Cyr, who weighed more than 100 kg. Sir is the first athlete to perform a bench press while lying on a bench.
Another type of competition for athletes was strength endurance.
- The first one-arm 50kg barbell press was performed by William Couture.
- Henry Sarteriel can bench press a 33-kilogram barbell with one hand 118 times.
- Using a special device, Gilman Lowe managed to lift more than 450 kilograms with his back over 1 thousand times in about 35 minutes.
- Lowe's record was later broken by Lou Travis, who managed to lift a similar weight in no more than 10 minutes.
1964 was marked by the holding of the first official powerlifting championship by the United States of America. This is his date of birth. As soon as powerlifting became established as an official sport, the formation of organizational structures and federations began. The name of the very first of them (created in the United States) is ADPFA.
In the USSR, powerlifting, like bodybuilding and martial arts, was considered a bourgeois sport. The pronunciation of its very name was seditious. Athletes-enthusiasts trained in specially equipped basements. Due to the threat of closure and punishment, they renamed powerlifting to artistic gymnastics.
Later, athletic gymnastics was criticized and banned: some strength qualities were developed through the use of ordinary brute force, without requiring mental activity. The program changed, supplemented with “intellectual” exercises: standing long jumps, pull-ups, etc. The deadlift was completely excluded because it was a “bourgeois” exercise that did not require “great mental abilities.”
The holding of men's championships at the international level began in 1971, women's - in 1980.
The first all-Union tournament was held in Siauliai, Lithuania (1979) and since then has been held annually. Groups of juniors performed triple jump and bench press, men - squats and bench press.
In the 80s, the Lithuanian tournament gained popularity throughout the USSR. In the youth age group (18-23), a biathlon was held, focusing on the bench press and squats, and in the men's age group, a triathlon was held, which added deadlifts.
The championship held in Estonia was said to be the most progressive competition. They were carried out according to international rules, the number of weight categories was 11 (from 52 to 125 kg and above).
At the end of January 1988, the Yenisei Sports Palace in Krasnoyarsk became the venue for the first RSFSR Championship, where athletes from allied countries competed in powerlifting. The number of participants was 87 people, each team had 16, there were 8 weight categories.
In February 1998, the Athletic Federation of the Soviet Union held the First Cup, held in the city of Tyumen. The number of athletes participating in the Cup was 123 people. The number of participants in the team championship is 16.
In July of the same year, the teams of the Soviet Union and the United States of America met twice in the city of Leningrad - on the 24th and 27th. The performance of the Soviet athletes surprised the Americans, because they worked with a barbell in a high position and did not wear equipment. There was no technique as such: weightlifting left its mark.
In February 1989, Chelyabinsk hosted the second RSFSR Athletes' Championship, in which 140 athletes and 24 teams managed to take part. Each competitive exercise was limited to two attempts. Due to the inexperience of the coaching staff, many athletes failed to correctly distribute their own strength, and they received zero results. A third of the participants were unable to lift the starting weight. Two participants entered the category up to 56 kilograms. Unfortunately, both applicants received a zero score.
In 1990, Russian athletes, representing the national team of the Soviet Union, made their debut at the world championship. The silver medal went to Alexander Lekomtsev (weight category - 82.5 kg), who showed a result of 792.5 kg. Valery Kuznetsov (category – 90 kg) had a similar result, but with a bronze medal. The USSR national team was awarded 3rd place. Considering that she competed at the World Championships as a debutant, the result was very good.
In the early spring of 1991, Russian athletes successfully competed at the European Championships for men, which began in May in France. The Soviet Union national team was again awarded third place.
December 1991 Due to the collapse of the Union of the Russian Powerlifting Federation, it was necessary to send a request to the European and International Federations to become its member. The request was granted - in January 1992, Russia became a temporary member of these organizations. Russian national teams received the right to participate in championships held by these federations.
In February 1992, the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation registered the Powerlifting Federation as an independent public organization that can officially develop this sport in Russia.
In April 1992, Russia became a full member of the European Powerlifting Federation, and in November - a member of the International Federation.
Books on powerlifting
The book “Powerlifting” by Leonid Ostapenko, a personal powerlifting trainer, has good reviews. The author talks about the right start to powerlifting training. He recommends starting with regular strength training and athletic training and then moving on to the circuits described in the book. However, Ostapenko also gives systems from scratch for complete beginners, for whom it is important to correctly adapt the body to high loads.
Frederick Hatfield's Comprehensive Guide to Strength Development focuses entirely on powerlifting. The manual by the author-scientist not only provides ready-made training regimens, but also addresses their scientific basis, touches on the rules for handling anabolic steroids and other issues.
The book by V. L. Muravyov “Powerlifting. The Path to Strength” addresses the problem of stagnation in an athlete’s training, when ordinary loads do not produce an increase in results. Increasing the number of workouts or approaches is not the answer. What to do? It is this question that is relevant for athletes that the author answers.
Thus, powerlifting is a strength sport that focuses not just on developing strength, but on achieving a specific result. The athlete’s task is to constantly increase the load and set new records. Therefore, powerlifting is often called a sport of strong-willed and purposeful people.
At what age can you start training?
For parents, the pressing question is: at what age can children start powerlifting? Coaches recommend that children start training at the age of ten.
There are cases when 7-8 year old children are brought to the section. However, their muscle corset is not yet fully formed and there is a risk of injury. Such guys can carry out a program to prepare the body for stress.
13-14 year olds can participate in professional competitions.