In fact, fast carbohydrates are a household term. There are simple carbohydrates (that is, carbohydrates with a simple structure of their constituent molecules) - as well as complex carbohydrates (molecules with a complex structure), which have a rapid absorption rate during digestion.
For example, the starch contained in potatoes is quite a complex carbohydrate. However, in the form of mashed potatoes, the rate of absorption of such starch is quite high. Plus, many refined (processed) carbohydrates are actually simple.
The benefits of carbohydrates for the body
The main benefit of carbohydrates is to provide the body with energy. Carbohydrates have advantages over other nutrients in terms of absorption rate. The breakdown of saccharides begins in the mouth, while fats are digested in the stomach and proteins in the intestines.
Carbohydrates are necessary for the normal functioning of the body. The list of foods containing these nutrients is huge, so there is something for everyone.
- Glucose is extremely necessary to nourish the brain. People who completely eliminate carbohydrates from their food (not only sweets, but also vegetables and pasta) become more irritable due to “starvation” of the brain and nervous system. It is not uncommon for mental illness to develop against the background of such restrictions.
- Glucose is necessary for the normal functioning of the liver. From it the organ forms glycogen. During periods of insufficient nutrition, the body first of all breaks down glycogen and obtains energy from it.
- Coarse fiber - fiber ensures intestinal cleansing and peristalsis. Fiber or cellulose is not absorbed by the body at all, but only participates in cleansing processes. Pectin is also needed for cleansing.
What are these organic substances?
As everyone knows, carbohydrates are divided into two groups: fast (in our case, easily digestible) and slow. Each of them differs in structure, nutritional value and rate of absorption by the body. Every food product, be it a potato or a piece of meat, consists of all kinds of substances that the human body really needs to ensure normal functioning of all organs and systems. Carbohydrates are the most important nutrient found in sugar and various plant foods.
As already mentioned, these substances provide our body with the necessary energy. Each person has his own carbohydrate norm, which depends on the person’s activity and the consumption of energy reserves. Those carbohydrates that are not used up throughout the day are converted into fat cells, disrupting the functioning of internal organs and increasing the level of “bad” cholesterol in the blood.
The main types of easily digestible carbohydrates:
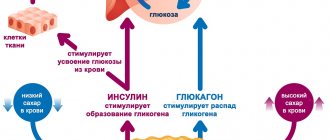
- Glucose (dextrose) is the most common and well-known representative of carbohydrates, participating in almost all metabolic processes. Thanks to glucose, our body is provided with the necessary energy. In order for dextrose to enter the body from blood cells, insulin is needed - a substance that is produced in certain quantities by our body. A deficiency of this organic substance can cause irritability, increased fatigue, decreased performance, dizziness, nausea, and sometimes fainting. Glucose can be obtained from fruits and some types of vegetables.
- Fructose is partially converted by the liver into glucose. You can find it in cherries, melons, apples, currants, and various types of honey.
- Galactose - when interacting with glucose, it forms a disaccharide. You can get galactose from fermented milk products such as milk, cheeses, cottage cheese, kefir and others.
- Lactose is the only carbohydrate of its kind that is of animal origin, which makes this milk sugar an incredibly valuable component of every person’s diet. You can get lactose from milk.
- Sucrose - found in various types of sugar: beet, cane and brown. Sometimes this substance can be found in ripe fruits and vegetables, but its amount will not be large (less than 10%).
- Maltose is a sugar of natural origin, formed during the formation of malt and fermentation of grapes. This organic compound is found in beer products, granola and citrus fruits.
Complex carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates include:
- starch;
- cellulose;
- sucrose;
- glycogen.
When digested, they are broken down into simple carbohydrates (glucose, maltose) and only then absorbed. They do not have a pronounced sweetness. But since the process of their breakdown begins directly in the mouth, upon contact with saliva, a sweetish taste appears.
A distinctive feature of complex carbohydrates is that they give a feeling of fullness for a long time.
Carbohydrate diets are quite popular. The diet consists of foods rich in slow carbohydrates. Fast carbohydrates are completely excluded. The number of meals per day is about 4-6. As for liquids, you can only drink pure water or tea. It is recommended to have dinner before 19:00.
Authorized products:
- beans;
- cereals;
- vegetables;
- fruits;
- vegetable and fruit juices;
- dairy products;
- lean meat;
- whole wheat bread.
One meal should contain about 150 g of carbohydrates in total.
The benefits of the diet are that blood glucose levels are reduced. The food is quite dense, so there is no feeling of hunger, and the diet is well tolerated. Products containing complex carbohydrates. Complex carbohydrates, a list of products containing them is shown below, help reduce body weight.
| Product | Mass of carbohydrates per 100 g of product mass (g) |
| Hercules | 50 |
| Pearl barley | 66,5 |
| Brown rice | 65,1 |
| Pasta made from durum wheat | 68,4 |
| Corn | 22,5 |
| Buckwheat | 68 |
| Barley grits | 71,7 |
| Wheat bread | 53,4 |
| Beans | 54,5 |
| Soybeans | 26,5 |
| Lentils | 53,7 |
| Bran crispbread | 70,6 |
| Crackers | 72,4 |
| Pine nuts | 20 |
| Peas | 21,1 |
| Beet | 9,56 |
The entire process of digesting complex carbohydrates takes about 40-50 minutes. During this time, complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple monomers and absorbed by the body.
Types of carbohydrates and their composition
Easily digestible carbohydrates have a high glycemic index.
Depending on the chemical composition, carbohydrates are divided into simple and complex.
Simple ones include:
- Monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, galactose). In a complex reaction they break down to water and carbon dioxide.
- Disaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose). They consist of two or more monosaccharides, which are connected to each other using hydroxyl groups.
Simple carbohydrates are quickly absorbed in the body, which leads to adverse consequences.
Complex carbohydrates are made up of three or more units.
These include polysaccharides:
- Plant origin (starch, fiber).
- Animal origin (glycogen).
Before the process of food absorption begins in the body, complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple components. This requires energy and time.
Be sure to read: Complex carbohydrates: list of products, table, beneficial properties, what you need to eat for weight loss
List of easily digestible carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
| Name | Description | Effect |
| Glucose | A colorless crystalline monosaccharide | Upon penetration into the blood, it becomes a source of nutrition for the brain, liver, and muscles. |
| Fructose | The sweetest of all carbohydrates | Does not lead to excess sugar. Converts to glycogen faster than glucose |
| Galactose | Not found in free form, together with glucose it forms lactose | As a result of its oxidation, complex carbohydrates are burned in the body and metabolic processes are regulated |
Disaccharides
| Name | Description | Effect |
| Sucrose | Dissolves quickly. Composed of glucose and fructose | Accumulates in the body as reserve fat |
| Lactose | Milk sugar | Promotes more active absorption of B vitamins, ascorbic acid, calcium |
| Maltose | Is malt sugar. Formed during the breakdown of starch | Easily absorbed by the body, saturating it with amino acids and B vitamins. Promotes the production of energy necessary for brain function |
Fast carbohydrates
Fast carbohydrates, a list of products containing them is presented below, are absorbed by the body in the shortest possible time. Sugars have a pronounced sweetness in taste, easily dissolve in water, and are also a nutritious product for brain neurons and the nervous system in general.
A distinctive feature of fast carbohydrates is that they are absorbed almost immediately, within 10-20 minutes. After eating food rich in fast carbohydrates, the level of glucose in the blood rises sharply and the production of insulin is activated, strength and energy appear.
This rise passes as quickly as it comes. But simple carbohydrates from fruits - fructose - do not cause the production of insulin, because it is absorbed without it.
Products containing fast carbohydrates
| Product | Mass of carbohydrates per 100 g of product mass (g) |
| Chocolate candies | ≈54,2 |
| Caramel | 77 |
| Pasta made from soft wheat varieties | ≈72 |
| Cake | 45-70 |
| Butter buns | ≈55 |
| Cakes | ≈64 |
| Dark chocolate | 52 |
| Milk chocolate | ≈50 |
| White chocolate | ≈60 |
| Grape | 14 |
| Banana | 21 |
| Apple | 9,8 |
| Plum | 9,6 |
| Prunes | 57,5 |
| Apricot | 10,8 |
| Dried apricots | 62,64 |
| Dates | 69,2 |
| A pineapple | 10,6 |
| Candied pineapple | 17,9 |
| Raisin | 65-75 |
| Peach | 9,54 |
| Cherry | 12,18 |
| Cherries | 11,5 |
| Jams and preserves | ≈70 |
| Fast food | ≈70 |
| Honey | ≈80 |
In addition to food, fast carbohydrates are also found in alcoholic drinks.
| Drink | Mass of carbohydrates per 100 g of drink mass (g) |
| Liquor | 53 |
| Vermouth | 16 |
| Semi-sweet white wine | 5,9 |
| Dry red wines | 2,3 |
| Sparkling wines and champagne | 1,4 |
| Dry white wines | 0,2 |
Where can you get easily digestible carbohydrates?
All food products whose index exceeds 65 units are considered easily digestible.
All food products whose index exceeds 65 units are considered easily digestible.
The maximum amount of carbohydrates of this type can be obtained from bread, potatoes, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, sweets, cakes, honey, cereals, etc.
Table of easily digestible foods with their calorie content
The table below shows foods containing easily digestible carbohydrates:
| Name | Kcal (100g) |
| Alcoholic drinks | From 33 |
| Bread | 250 |
| Starch | 320 |
| Honey | 300 |
| Potato | 105 |
| Dried fruits | 480 |
| Sugar | 350 |
| Carbonated drinks | 27 |
| Porridge | From 105 |
| Muesli | 320 |
| Baking | 350 |
| Rice | 360 |
What foods contain large amounts of carbohydrates?
In some foods, most of the nutrients come from carbohydrates.
Grocery list:
- bakery products;
- pasta and noodles;
- confectionery;
- cookies, biscuits, snacks;
- fast food;
- honey;
- caramel;
- chocolate (especially milk chocolate);
- potato;
- flour;
- dried fruits (especially dates);
- bananas;
- jam;
- granulated sugar and refined sugar.
Easily digestible foods for children
For the normal growth of children, proper nutrition is especially important, which should provide the growing body with everything necessary. The more varied the menu, the healthier the food. Recently, it is becoming increasingly common to see overweight children.
The main reasons are a sedentary lifestyle and poor diet. As a rule, children receive an excess amount of calories from food. For a child under 3 years old, 1540 kcal is needed, and from 3 to 7, 1970 kcal is needed daily.
Easily digestible foods must be present in the daily menu. Fruits and berries should be eaten every day; they contain a large amount of vitamins and minerals. They contain easily digestible carbohydrates.
Fruits and berries in baby food:
- in its natural form;
- in juices, fruit drinks, compotes;
- in puree.
It is recommended to give preference to fresh berries and fruits, and in winter to use frozen fruits, juices, and compotes.
Vegetables should be present in children's diet every day. If you add cabbage, carrots, beets, and potatoes as a side dish to meat and fish, then such food will be better absorbed.
Dairy products are beneficial for a growing body due to their composition. They contain the necessary substances. In addition, there are easily digestible fluorine and calcium salts. Pediatricians say that any preschooler should consume at least 500 g of milk and fermented milk products per day.
We recommend a video about healthy foods for babies:
Products with minimal carbohydrate content
Carbohydrates are found in minimal quantities in animal products (fish, pork, beef, poultry, etc.), mushrooms, vegetables, herbs, herbal teas and black and green tea.
Animal products with minimal carbohydrate content:
- pork,
- beef/veal,
- mutton,
- minced meat,
- cow/goat milk,
- cheeses,
- chicken/quail/ and other eggs,
- fish (catfish, pink salmon, herring, capelin, halibut and others) smoked, canned, salted or home-cooked,
- turkey,
- duck,
- chicken,
- goose,
- butter,
- cottage cheese,
- unsweetened/Greek yogurt,
- kefir,
- sour cream.
Plant-based products with minimal carbohydrate content:
- any mushrooms,
- zucchini,
- cucumbers,
- tomatoes,
- cauliflower,
- chard,
- celery,
- arugula,
- asparagus,
- spinach,
- sorrel,
- apricots,
- avocado,
- watermelon,
- strawberry,
- grapefruit and other citruses,
- pumpkin seeds,
- Pinto beans and other legumes,
- soy milk,
- walnuts, hazelnuts, cashews, peanuts.
Low carbohydrate drinks:
- black and green teas,
- almond milk,
- tomato juice.
Why are carbohydrates needed?
It should be remembered that all carbohydrates in foods are broken down in the body into glucose, which is a source of energy, stimulates thinking and mental activity, nourishes nerve cells, starts the processes of digestion and respiration, and is spent on physiological needs.
Therefore, it is not recommended to give up carbohydrates under any circumstances. You just need to determine which carbohydrates are healthy and which are harmful.
A deficiency of carbohydrate-containing foods in the diet leads to diseases of the heart and blood vessels, impairs memory, provokes headaches, muscle cramps, reduces concentration and the ability to perform mental stress. Therefore, it is important to know the optimal carbohydrate intake.
Glycemic index
The glycemic index is usually used to denote the relative effect of carbohydrates contained in food on blood glucose levels. The glycemic index of foods containing complex carbohydrates is lower than the GI of foods containing fast carbohydrates.
Foods are classified by glycemic index in the following way:
- 55 and below – low;
- 56-69 – average;
- more than 70 – high.
| High GI foods | GI indicator | Medium GI foods | GI indicator | Low GI foods | GI indicator |
| Chips | 85 | Melon | 60 | Sunflower seeds | 8 |
| Mashed potatoes | 90 | Banana | 60 | Lettuce leaves | 10 |
| Fried potatoes | 95 | Boiled beets | 64 | Tomatoes | 10 |
| French fries | 95 | Raisin | 65 | Onion | 10 |
| Fried croutons | 100 | A pineapple | 66 | Broccoli | 10 |
| Confectionery | 100 | Muesli | 66 | Eggplant | 10 |
| Cookies, biscuits | 100 | Oatmeal | 66 | Mushrooms | 10 |
| Bagels | 103 | Croissant | 67 | Hazelnut | 15 |
| Beer | 110 | Unleavened flatbread | 69 | Walnuts | 15 |
| White bread | 136 | Pistachios | 15 | ||
| Rice bran | 19 | ||||
| Peanut | 20 | ||||
| Cherry | 22 | ||||
| Sausages | 28 | ||||
| Peaches | 30 | ||||
| Apples | 30 | ||||
| Peas | 35 | ||||
| Oranges | 35 | ||||
| Fish fingers | 38 |
Synthesis of glucose from polysaccharides
The body can obtain simple carbohydrates from complex carbohydrates. In this process, one of the important energy units is glucose. It is synthesized by the body independently from polysaccharides. Reserves include:
- glycogen is a substance that accumulates in the cells and muscles of the liver. We get glycogen from sweets, flour products and fruits;
- starch - it is the basic source used for the synthesis of glucose. It is no secret to many that this polysaccharide is found in large quantities in potatoes and cereals.
Structural polysaccharides include:
- Pectin is another source of glucose, as well as a body cleanser. In marmalade and similar confectionery products, pectin is contained in high concentrations. In the food industry, such a substance is used as a thickener and is labeled as E440;
- Cellulose is a specific type of carbohydrate that is not digested, but can provide cleansing of the body and normal digestion. Cellulose (fiber or dietary fiber) is found in vegetables, fruits, bran and grain products.
Which foods contain the most beneficial carbohydrates?
A list of foods with the most healthy carbohydrates is presented below.
- oat, rice, buckwheat, wheat cereals;
- wholemeal bread;
- vegetables (bell peppers, tomatoes, cucumbers, cabbage, broccoli, eggplant, zucchini);
- greens (arugula, parsley, dill, basil, spinach, sorrel)
- fruits (except dates, bananas and grapes);
- berries;
- almond;
- Walnut.
Nutritionists call healthy carbohydrates complex (slow) carbohydrates, cellulose and fructose, which are absorbed without the participation of insulin.
Easily digestible foods for diseases of the stomach and pancreas
Not all easily digestible foods may be suitable for nutrition for diseases of the stomach and pancreas.
So, vegetables and fruits without heat treatment are rich in fiber, and this can injure the mucous membrane of a diseased stomach and negatively affect the pancreas.
Experts recommend consuming the following products:
- white, lean meat;
- baked apples;
- bananas;
- dairy products;
- sea fish;
- rice, buckwheat, oatmeal porridge;
- steamed or boiled vegetables;
- compote, jelly;
- non-acidic berries.
Proper nutrition for a number of diseases can significantly improve a person’s condition.
Daily intake of carbohydrates
It is important to consume a normal amount of carbohydrates per day. After all, even healthy slow carbohydrates, when consumed in excess, can lead to weight gain.
| Norms for carbohydrate intake for children | |
| Age | Quantity (g) |
| Children under 1 year | No more than 15 g |
| Children aged 1 to 1.5 years | No more than 160 g |
| Children aged 1.5 to 2 years | No more than 190 g |
| Children aged 2-3 years | 210-215 g |
| Children aged 5-7 years | 250-300 g |
| Children aged 8-11 years | 350-400 g |
| Teenagers aged 12-14 years | 400-450 g |
| Teenagers aged 15-18 years | 450-500 g |
| Carbohydrate intake standards for adults | |
| Age | Average quantity (g) |
| 18-29 years old | 378 |
| 30-39 years old | 365 |
| 40-59 years old | 344 |
| 60-74 years old | 333 |
| 75 + | 290 |
The consumption rates presented in the table are advisory in nature. The exact consumption rate is calculated taking into account lifestyle, activity and body weight. For people with mental work, 5 g of carbohydrates per 1 kg of body weight are recommended, and for people with moderate physical work - 8 g per 1 kg of body weight. With strong physical exertion, the rate is increased.
For pregnant women, the norm for carbohydrate consumption per day is 450 g for the first half of pregnancy. In the second half of pregnancy, the norm is reduced to 350-400 g per day.
For women during lactation, the carbohydrate consumption rate is 4-5 g per 1 kg of body weight. On average, a woman needs to consume about 320 g of carbohydrates per day with food. In the first six months of lactation, this norm is increased by ≈40 g. And remains the same in the second half of the year.
Slow carbohydrates
Why slow?
They are also called complex carbohydrates - they take longer to break down into simple sugars than fast ones.
Glycogen is processed by the liver into glucose.
When the body does not receive the required amount of carbohydrates, this product can be formed from proteins and fats.
This substance can be obtained from pork, beef, and chicken liver. There is plenty of glycogen in yeast cells, as well as in crab meat.
Starch – thanks to catalysts, it is converted into dextrose and maintains its level in the body. These substances are found in potatoes, grains and legumes.
Fiber – 2/3 of this component passes through the digestive tract and leaves the body naturally, “taking” with it “bad” cholesterol and other harmful substances. Helps protect the intestines from various diseases.
Inulin is formed from fructose residues.
Acts as a reserve carbohydrate for most plants. For example, inulin can be found in chicory and artichoke cells.
This substance is used as a replacement for granulated sugar for people suffering from diabetes.
Pectin plays the role of stabilizing products.
Unripe fruits and vegetables contain propectin, which is converted into pectin when they ripen.
Complex carbohydrates are a broad class of compounds that include starch, glycogen, fiber and many other polysaccharides.
They gradually release their sugar into the blood, helping to maintain normal energy levels.
Thanks to this product, the feeling of satiety with the food consumed remains for quite a long time.
By using complex carbohydrates, you can reduce the amount of calories your body needs, which will help you lose weight.
In addition, polysaccharides will be an excellent source of nutrition for active physical activities.
When is the best time to eat carbohydrates?
There are many opinions about the timing of carbohydrate intake. Some nutritionists believe that you can consume fast carbohydrates (all kinds of sweets, sugar, etc.) only in the first half of the day, that is, before 12 o’clock. It is recommended to eat slow carbohydrates (in the form of pasta, potatoes) between 12 and 16 hours, and all kinds of cereals for breakfast.
In the evening, it is recommended to completely avoid carbohydrate foods, except vegetables.
Other nutritionists believe that complex carbohydrates can be consumed throughout the day, and fast carbohydrates only before lunch. But there is no precise scientific research on the timing of carbohydrate consumption. That is, it has not been scientifically proven that eating foods rich in carbohydrates at night leads to weight gain faster than eating carbohydrates in the morning.
In addition, some nutritionists are of the opinion that in the evening you should not limit your food intake, because the stomach is constantly working and its work is not interrupted at night.
What carbohydrates are healthy?
Just because sugar in large quantities is harmful does not mean that all carbohydrates are bad and you should completely eliminate them all from your diet. These substances can be divided into two groups:
- Simple sugars. These include rapidly digestible substances: glucose, fructose, sucrose and milk sugar (lactose). Fast carbohydrates are harmful to health, they taste sweet.
- Complex sugars or polysaccharides. This is a slowly absorbed compound consisting of many molecules. This group includes such common substances as starch, dietary fiber (pectin, cellulose), as well as gums and mucus. These are slow, correct, healthy carbohydrates that do not have a sweet taste.
Fast sugars are bad because they are absorbed and enter the bloodstream in a very short period. This leads to sudden spikes in glucose, which is very dangerous for diabetics. In addition, the body does not have time to spend the energy received so quickly and stores it “in reserve” in the form of fat. This is already a big minus for the figure.
Polysaccharides are digested gradually, releasing glucose little by little. The body completely spends the calories it receives, so slow sugars are very useful carbohydrates for weight loss.
Signs of a lack or excess of carbohydrates
In the BJU ratio, carbohydrates occupy about 50-60%. With a carbohydrate deficiency, the following occurs:
- fatigue not only after physical activity, but also after waking up in the morning or after a long sleep;
- headaches, irritability, because the brain needs glucose for full functioning;
- chills;
- the desire to eat sweets, as the brain does not have enough glucose;
- disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system due to a lack of cellulose (fiber).
The main sign of excess carbohydrates in the diet is excess weight. With a surplus of fast carbohydrates, some of them are still absorbed, and the rest is converted into fat deposits. Eating large amounts of carbohydrates can lead to a kind of “addiction.” Some people cannot do without sweets, others cannot do without flour.
Regular consumption of large quantities of simple carbohydrates leads to the manifestation of symptoms of latent diabetes. Carbohydrates themselves do not cause disruption of insulin synthesis, but they contribute to the development of diabetes in people with a predisposition to it.
People who eat a lot of simple carbohydrates are prone to fungal diseases. It is also very difficult for such people to get rid of the fungus, because it feeds on glucose.
The secret of a perfect figure
How to find an ideal figure? Photo: pixabay.com
Let's carefully monitor the behavior of simple carbohydrates in our body (we're not talking about complex carbohydrates, everything is clear with them - they only provide benefits).
For example, you had breakfast by drinking sweet coffee and a bun. A great start to the day?
After all, excess is unsafe. The body urgently gives a command to the pancreas - and it produces insulin, which removes sugar from the blood, turning it into fat. Well done: the body is protected, and you can be congratulated on the new additional grams. Well, how? A great start to the day?
This happens because simple carbohydrates give the body empty calories (the nutrient content in them, one might say, is zero, as is the energy value). The only value of simple carbohydrates is sugar and energy, but its excess instantly turns into fat.
It's a vicious circle: you consume simple carbohydrates - the body reacts to excess blood sugar with a surge of insulin - insulin accumulates sugar in muscle tissue and instructs the liver to process excess blood sugar into fat, storing it in fat cells.
Fat is not all the evil that simple carbohydrates bring us. The overall balance in the body is disrupted, and syndrome X, or metabolic syndrome, appears on the horizon.
Metabolic syndrome is characterized by three main symptoms:
- overweight;
- arterial hypertension;
- increased blood sugar levels.
Metabolic syndrome provokes the development of diseases in your body such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and some forms of cancer.
Give preference to complex carbohydratesPhoto: pixabay.com
The benefits of carbohydrates for weight loss
Complex carbohydrates are essential when losing weight. They give you a feeling of fullness for a long time and saturate the body with a large supply of energy. There are 4.1 kilocalories per 1 g of carbohydrates.
During digestion, slow carbohydrates are broken down into monomers that feed the brain. That is, the brain receives the glucose it needs, but from healthy foods.
Cellulose, which is also a complex carbohydrate but is not digested in the human body, is necessary for the normal functioning of the digestive system and cleansing the intestines of harmful substances. Pectin substances also help cleanse the body by absorbing harmful compounds.
List of products that contain fast carbohydrates
Some foods that are present in our diet every day contain easily digestible carbohydrates and are hazardous to health. The glycemic index (GI) of such products exceeds 60 units, and their quantity is so large that it is very difficult to manage with restrictions.
For those who don’t know, the glycemic index is a kind of rate at which our body digests carbohydrates.
The table below will help you quickly determine which food products are among those that pose a threat to the human body. Qualified nutritionists strongly recommend minimizing such foods.
Fast and slow carbohydrates, the cornerstone of weight loss.
If you understand what foods you eat, you will always know what in your diet helps you lose weight, and which foods, on the contrary, will help you gain weight.
I tried to collect basic information about slow and fast carbohydrates from different sources, this turned out to be quite a difficult task, because the information is quite contradictory, even regarding the same products.
List of complex carbohydrates for weight loss
Many foods contain complex carbohydrates. The list of products is very large.
Slow carbohydrates include:
- starch – saturates the body for a long time. Some diets are based specifically on increasing starch intake;
- cellulose is an indigestible (coarse) fiber necessary for removing toxins from the intestines;
- pectins - complex carbohydrates contained in fruits (apples, citruses) also cleanse the body by absorbing harmful substances. Thickeners are made from pectin;
- glycogen is one of the most important carbohydrates for the human body. It helps regulate blood glucose levels. It is synthesized by the human body from fish and animal liver.
For weight loss, only complex (slow) carbohydrates are important. They provide the body with a large amount of energy and nutrients for normal functioning.
Why is it dangerous to eat foods rich in easily digestible carbohydrates?
The formation of glucose from foods containing carbohydrates is an important physiological process. Insulin, which is produced by the pancreas, helps with this.
Easily digestible carbohydrates are processed the moment they enter the gastrointestinal tract, which causes a sharp increase in blood sugar. Physical activity leads to increased energy expenditure and, naturally, to a drop in sugar levels. The person feels hungry again and the desire to eat arises.
If there is no physical activity, glucose is stored “in reserve”, forming adipose tissue.
To avoid the accumulation of fat deposits, the consumption of carbohydrate-containing foods and physical activity must be balanced, that is, all energy supplied with glucose must be wasted.
The dangers of easily digestible carbohydrates are not only manifested in excess weight, they can affect:
- On the condition of the pancreas. She must produce a lot of insulin, and then wait for a new supply of carbohydrates. The gland working in this mode wears out, which can cause cancer.
- On mood, since blood sugar levels affect the production of serotonin, the hormone of joy. Fast carbohydrates can quickly improve your mood, but at the same speed it will deteriorate.
- For violation of intestinal acidity. A change in the acid-base balance of the intestines leads to the growth of fungi, the level of beneficial microorganisms decreases, and immunity deteriorates, which leads to various diseases.
- At risk of developing diabetes. Since sugar causes the formation of large amounts of insulin, the breakdown of fat slows down and even the formation of new fat deposits occurs.
- To the development of a condition known as hypoglycemia. It manifests itself in loss of strength, high fatigue, anemia, low blood pressure, darkening of the eyes, slow movements and causeless nervousness.
- On the development of carbon dependence. The production of insulin by lunch depends on the morning meal: coffee or tea with sugar and cookies will satisfy hunger for a short time, and after eating a normally balanced meal for lunch, satiety does not occur, since the insulin produced requires carbohydrates. Because of this, after a huge bowl of soup you want to eat candy or chocolate.
- Frequent mood swings: from immense joy to boundless melancholy. The nervous system suffers from such changes, depression, apathy, and imbalance appear.
- On the health of the cardiovascular system, since fat cells narrow the walls of blood vessels, severe obesity as a result of poor nutrition with a high content of easily digestible carbohydrates is especially dangerous.
- In appearance. Sweet and starchy foods spoil your figure and teeth if you do not carefully monitor nutritional balance and dental hygiene.
For more information about what carbohydrates are and how they affect the body, watch the video:
What to combine with foods containing carbohydrates
The ability to combine foods correctly is the basis of a balanced diet. Any cereals and rice can be combined with vegetables and fruits. Oatmeal goes well with berries - strawberries, raspberries, and fruits - apples, plums. You can add a little dried fruit to porridge, but just a little, because they are rich in glucose. You can eat a small piece of whole grain bread along with the porridge.
Also, porridge can be consumed separately, without any addition, so as not to burden already high-calorie foods. This rule is especially relevant when losing weight. Nutritionists do not recommend cooking porridge with milk, since the calorie content of the dish increases significantly, and in addition to complex carbohydrates, simple carbohydrates are added - lactose or milk sugar.
A bad combination is combining carbohydrates with proteins and fats.
You should not eat meat products, both animals and birds (for example, sausages or cutlets), together with pasta. Fish is also not suitable. You can prepare a vegetable sauce for pasta, for example from tomatoes. Vegetables are ideal for fish, both fresh (in the form of salad) and baked or boiled (except potatoes, beets). You can also eat vegetables in any form with meat.
Poultry and eggs go well with vegetables. An omelet with vegetables or herbs is ideal for eating in the morning. Asparagus, spinach, lettuce, chard go well with meat. Vegetables and herbs go well with vegetable oils - sunflower, olive and others.
Often fruits are combined with dairy products - kefir, cottage cheese, yogurt, cream, sour cream. The fruit also goes well with nuts and seeds. It is not recommended to mix sour and sweet fruits; you should eat sour and sweet fruits separately.
You need to be very careful when combining carbohydrate foods. For example, the combination of starch and sucrose is not very successful. The breakdown of starch begins directly in the mouth and ends in the stomach. And the digestion of sugars begins only in the small intestine.
Starch will be digested first, and sucrose at the same time will cause fermentation in the stomach. Starchy foods are recommended to be consumed separately from other foods and during the daytime. Potatoes are recommended to be consumed together with pumpkin, cauliflower, carrots, and eggplants. The main condition is the exclusion of foods containing sugar.
Bread, no matter what flour it is baked from, is recommended to be consumed separately from other food products. It does not combine with jams, preserves, or butter. Flour products should be consumed separately from other products, due to the fact that baked goods themselves are quite high in calories. Combinations of dough products with eggs, meat and any other proteins are especially “dangerous”.
Bad food combinations are:
- joint consumption of cereals with tomatoes, since oxalic acid from tomatoes inhibits the absorption of starch;
- porridge should not be eaten together with fermented milk products due to differences in the duration of digestion;
- legumes (beans, peas) are not recommended to be consumed with fish due to different digestion times, but beans can be baked with vegetables;
- bread is not compatible with fermented milk products also due to different digestion times;
- It is not recommended to drink rye bread with coffee, because the substances contained in this drink interfere with the absorption of nutritional components from the bread.
Any sweets (cakes, chocolate, caramel and cakes) are recommended to be consumed as a separate dish (as dessert) and no more than 3-4 times a week.
Chocolate should not be consumed together with alcoholic beverages, because chocolate promotes the outflow of bile, and alcohol, on the contrary, prevents its release, resulting in spasm of the sphincter (passage into the duodenum) and acute pancreatitis.
The list of foods containing carbohydrates is very long. The vast majority of food products contain both simple and slow carbohydrates. These nutrients are essential for human health.
Why product compatibility is important
Products that are compatible with each other contribute to the complete absorption of beneficial microelements found in this food.
Each product has a specific chemical composition, which determines its digestibility in the human body. All products are divided into quickly and slowly digested.
If you eat food with different “speeds” of digestion, there will be a delay in the body of fast foods.
Be sure to read: Low-carb foods, no-carb menu for weight loss
Also, each food group requires its own environment in the stomach. For example, for chicken meat it should be acidic, and for mashed potatoes it should be alkaline.
Carbohydrate foods are best combined with fats, vegetables, and herbs. This combination is safe for the body and does not lead to food fermentation.
Scientist William Hay proved that when simultaneous consumption of protein foods and carbohydrate foods, the alkaline environment interacts with the acidic one, as a result of which they neutralize each other.
With this process, 40% of the food remains undigested.
What foods don't go together?
Separate nutrition will greatly simplify the functioning of the human body and improve health.
Nutritionists have identified several groups of incompatible foods:
- Foods high in protein and flour products.
- Proteins of plant origin and proteins of animal origin.
- Pastries and fruits.
- Flour products and dairy products.
- Proteins and milk.
Thus, tea cannot be combined with milk, since the proteins contained in milk prevent the absorption of the beneficial properties of tea.
Avoid combining cheese with meat.
Precautionary measures
Easily digestible carbohydrates have almost no value for our body, and are even dangerous to some extent.
Excessive consumption of carbohydrates contained in foods can adversely affect your health:
- Hormonal imbalances. It has a detrimental effect on the functioning of the pancreas and adrenal glands. Foods containing fast carbohydrates provoke an energy surge, followed by fatigue and wear and tear of the endocrine system.
- Changes in intestinal microflora. Each person maintains a balance in the digestive system between beneficial microorganisms and fungal ones. When the latter begin to suppress the former, this can lead to a decrease in immunity and the occurrence of fungal diseases.
- Empty calories. These organic substances hardly replenish the reserves of useful elements in the body and contain a huge amount of empty calories, which are transformed into fat cells.
- Insulin surge. Due to the fact that this type of carbohydrate consists mainly of various sugars, this leads to an instant release of a hormone such as insulin. An excess of this substance helps slow down the process of fat breakdown; moreover, it “helps” their formation. This hormone causes a feeling in the human body that is a little like euphoria, but after a few hours it passes and insulin starvation sets in - the body begins to “ask” to replenish its reserves with foods that contain fast carbohydrates.
Let's get to know carbohydrates in more detail
Carbohydrates are organic nutrients needed by the body as the main source of energy. The amount of carbohydrates consumed should be directly related to the amount of physical activity a person does, since unspent energy turns into fat and increases cholesterol.
- Providing the body with energy.
- Participation in brain activity.
- Strengthening the immune system.
Based on the breakdown process, carbohydrates are divided into complex and fast (easily digestible). Complex carbohydrates include polysaccharides based on starch and cellulose. They are contained in some vegetables (carrots, potatoes), grains and legumes, and nuts. They improve digestion and help relieve hunger for a long time.
Fast carbohydrates include monosaccharides and disaccharides based on glucose, fructose, lactose and galactose. They are found in milk, sweets, fruits and some vegetables. The breakdown of this type of carbohydrate occurs very quickly and with little physical activity the blood sugar level rises, which then drops sharply and hunger returns.