In this article we will tell you:
- Description and functions of carbohydrates
- Main types of carbohydrates
- Glucose metabolism, its regulation
- Symptoms of high insulin
- The harm of fructose and corn syrup
- Laboratory diagnostics of carbohydrate metabolism
- Red list of products
A couple of decades ago, a loud recognition came to the world stage: cholesterol is an enemy for the human body. Hundreds, if not thousands of articles in scientific and popular journals spoke about the need for its elimination. Marketing quickly changed to follow new trends: low-fat products began to appear on supermarket shelves.
Time passes - and fashion tirelessly follows it. Science does not stand still, and now new contradictory conclusions have come to the forefront: carbohydrates are now in the focus of attention of doctors and, in general, people who are conscious of their nutrition. Keto, paleo, LCHF (low carb, high fat) - these new low-carb diets are gaining more and more popularity. So where is the truth? Let's figure it out and separate the zebra's black stripes from the white ones.
Not banned, but under suspicion
Numerous popular diets have developed in most of us a disdainful and even sharply negative attitude towards carbohydrate-containing foods.
There are methods that are based on the consumption of foods low in sugars, and there are those in which they are completely prohibited because they cause a sharp increase in body weight. But is this really so and why can’t we completely give up bread, corn, legumes, and sweet fruits, if we believe the statement that they are so harmful? In order to tell which foods are those that contain simple and complex carbohydrates, we must explain the nature of the compounds themselves, which nutritionists are afraid of.
So, we have before us organic substances that have a number of properties:
- Perform energetic and structural functions.
- They are part of complex proteins.
- They cannot be synthesized by the body - we get them exclusively from food.
Products related to essential sources of carbohydrates, a list of which we will give later, are divided into those that contain lighter and more complex compounds. We will tell you more about them below.
Simple or fast
This group includes compounds that contain 1-2 molecules. These substances are divided into 2 types.
Monosaccharides
During hydrolysis, their structure does not undergo changes - they do not break down into simpler components. Distinctive features: sweetness, rapid dissolution in water.
This group includes:
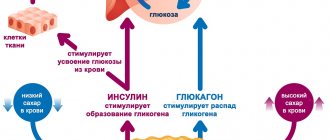
- Glucose is the most common light carbohydrate, which is rich in berries and fruits. The second name for this compound is dextrose. Its remains are building material for more complex substances (such as glycogen and starch). There is also glucose in sucrose. This is a valuable source of energy, without which the heart, brain and many tissues would be left without nutrition. Its absorption is impossible without the participation of insulin, a hormone that regulates carbohydrate metabolism. The consequence of its insufficient production is the development of diabetes.
- Galactose is also a simple sugar and is found in dairy products and some energy drinks. The substance in question is formed as a result of the hydrolysis of lactose, and in the liver it is converted into the already described glucose.
- Fructose is another monosaccharide. It is not involved in replenishing glycogen reserves, is absorbed more slowly, and acts as one of the main ingredients in sports drinks and nutrition. This is the sweetest of sugars and is best obtained from fruits and berries. An excess of this substance can lead to problems with the heart, liver, and the development of metabolic syndrome - metabolic disorders.
Disaccharides
These polyfunctional compounds consist of 2 molecules of simple substances, which were mentioned above. The most famous of them:
- Lactose – found in milk and dairy products, plays an important role in the development of a child and is the main component of baby food. Cleavage occurs in the gastrointestinal tract under the influence of the enzyme lactase. In adults, lactase activity is lower than in children. This leads to the formation of intolerance to whole milk.
- Maltose – This variety is rarely seen in its free form. Most often it is presented in grains of barley, rye, products made from malt, and molasses. Also present in tomatoes and some plants.
- Sucrose is a combination of glucose and fructose, one of the most effective immunosuppressants. This substance does not exist in nature. It was synthesized artificially - in man-made beets and sugar cane.
Expert opinion
Smirnov Viktor Petrovich Dietitian, Samara
All slow polysaccharides and their representatives are truly “long-range artillery” and lead to long-term saturation of the body. Of these, the table shows not only exogenous, but also endogenous carbohydrates, which are practically not found in products; they cannot be found on sale in their pure form. This is animal starch - glycogen. After eating, it is formed in our liver, into which glucose enters under the influence of insulin. In glycogen, sugar is stored in the form of condensed glucose residues. Glycogen in our body is the first “accumulator” of energy and, gradually breaking down again into glucose under the influence of the counter-insular hormone glucagon, ensures its concentration in the blood plasma. It is on the first and even the second day of complete fasting that all adequate carbohydrate consumption, including for the functioning of the brain and myocardium, is ensured due to the slow breakdown of glycogen. And only on the third or fourth day of fasting does an acidotic crisis begin, when the body begins to look for other metabolic pathways, activating lipolysis, or the breakdown of fats. Other types of slow carbohydrates are also irreplaceable, and especially pectins and fiber. Fiber differs from all carbohydrates in that at first glance it is a ballast substance: it is not nutritious, since it is not absorbed by the body. But it is fiber that binds various exotoxins and radionuclides, prevents dysbiosis, stimulates peristalsis and is very useful in the fight against atonic constipation.
Complex and slow
These polyfunctional compounds have several chains of monosaccharide molecules in their structure. These include:
- Starch
- there is a lot of it in whole grain bread, various cereals, rice, potatoes, and legumes. There are 4 types of this complex carbohydrate found in nature. The first can be found in beans, peas, lentils, and chickpeas. It is distinguished by its resistance to digestion and its connection with fiber. The second type is found in potatoes and corn that have not undergone heat treatment, and in bananas and greens. The third is found in the same potatoes, boiled or fried, and in rice. The fourth is the brainchild of chemical processing. It is not found in natural food. Particularly useful is resistant starch, which is a breeding ground for bacteria that help our intestines work properly and smoothly. The main task of a modern person who wants to improve their health is to learn to distinguish a resistant substance from a regular one, which is rich in food stuffed with refined carbohydrates.
- Fiber
is valuable coarse fiber that is found in fruits, vegetables, cereals, nuts, and beans. They carefully cleanse the intestines, remove waste and toxins, help reduce cholesterol levels in the blood, and also slow down the absorption of glucose. We know that eating fiber in your diet is the key to keeping you full for longer. And if we are full, we will not need high-calorie and sugary snacks that lead to weight gain.
- Glycogen
is glucose molecules assembled into a single chain, an excess of monosaccharide that enters the blood. They are deposited in the liver and muscle tissue. If you play sports, you know that a lack of glycogen leads to feelings of fatigue, weakness, and physical exhaustion. That is why, before a long workout, you need to eat something light, but filling and healthy - for example, a medium-ripe banana, a salad of berries and fruits.
Since realizing the importance of multifunctional compounds, we have been concerned with the question of which foods contain carbohydrates. Increased interest is associated with conversations about the dangers of mono- and disaccharides. Are they really that dangerous and why are they called the enemies of a slim figure? Let's look into this further.
Carbohydrate diet for a week
The weekly diet includes the same products and provides three meals a day. However, if it is difficult for you to maintain long periods of time between meals, you can divide breakfast and lunch into two parts and give yourself snacks.
Day 1: egg and salad with spinach and tomato; vegetable stew, sliced green vegetables with butter; grilled chicken and salad with herbs.
2nd day: omelette, grapefruit; oven-baked meat with green beans; braised cabbage.
Day 3: yogurt with whole grain bread; lentil soup; meat stewed with mushrooms, leafy greens.
4th day: sandwich of rye bread and cheese; a piece of baked fish, a portion of brown rice; squid salad.
5th day: cottage cheese with dried fruits or nuts; steamed pollock and tomato juice; zucchini stewed with garlic.
6th day: tomatoes, 2 eggs; pea soup with croutons; stew with meat, green vegetable mix.
7th day: cottage cheese and apple; cabbage salad, boiled potatoes; fish stewed with vegetables.
Slowly but surely: how our weight depends on our diet
Why are some substances called fast? All because of the speed with which they are absorbed by our body. In the case of glucose and fructose, this is almost instantaneous absorption, which is accompanied by a sharp increase in blood sugar levels and the instant production of the hormone insulin. It works to reduce the jumping indicator, turning energy into fat deposits. Sometimes this results in a condition characterized as carbohydrate starvation, which occurs in diabetes and hypoglycemia.
To prevent a sharp drop in blood sugar, we eat foods high in simple carbohydrates, after which everything repeats according to the usual pattern - a jump in glucose, a rapid decline, increased appetite. It turns out that we ourselves are dooming ourselves to obesity and related problems.
That is why foods with mono- and disaccharides should be entered into the body in limited quantities, both during weight loss and when gaining muscle mass in the gym.
But this does not mean that fast organic substances are deadly. They cause the least harm in the first half of the day, before 16:00. During this period, we are less likely to process them into fat.
If you have diabetes, you should only include foods with a low glycemic index in your diet. GI is a measure of the speed at which compounds entering our body are broken down and absorbed. The higher the value for a particular product, the more your blood sugar will rise after eating it. The highest GI is:
- cakes, confectionery;
- dates;
- fast food (burgers, French fries);
- chocolate;
- sauces from the store;
- sweet fruits.
Products with slow and complex carbohydrates are listed in the table - you can immediately see what can help you lose weight, and what it is better to stay away from.
The first column contains high GI foods. Its consumption in large quantities is undesirable, as it causes a rapid increase in blood glucose. But some items should not be crossed off from the menu. For example, you can afford both melon and banana - but the bananas should not be overripe, and you need to eat both in the first half of the day. We have already written about the benefits of honey in a recent article. Let us repeat once again - a couple of teaspoons of herbal tea a day will not make you fat if you eat right. But it is better to replace white bread with whole grain bread or baked from amaranth flour, jam - with a sugar-free dietary analog presented in our catalog.
Above we gave a list of complex and fast carbohydrates, told what these products are, what their benefits and harms are. Next, we will talk in more detail about those compounds that will help us lose weight, provided that we create a balanced menu and maintain a healthy lifestyle. But before that, we’ll answer the question of why you can’t plan your diet without fiber and starch.
Why do we need sugar in the body?
Carbohydrates are required by the body to maintain energy. It produces approximately 60% of its energy from mono- and polysaccharides. And the rest is fats and proteins.
Please note: It should be noted that fast carbohydrates immediately return lost energy, but they themselves are quickly consumed and then the body signals for supplementation. Then polysaccharides come into play, they feed the body with fuel slowly but for a long time. The body especially requires heavy carbohydrates for those who do not like to sit in one place.
To feel energetic and not suffer from hunger, the ratio of carbohydrates should be as follows:
- polysaccharides – 70%;
- monosaccharides – 25%;
- fiber – 5% of the total amount of carbohydrates required.
This combination will allow you to save energy for sports and at the same time stabilize constant weight loss.
Video
The role of polysaccharides
Our body needs useful multifunctional compounds - without them it will not be able to function properly:
- They serve as the main source of energy - if you refuse carbohydrate foods, you will feel tired, lethargic, and lack of strength.
- Directly associated with proteins - if the necessary substances do not enter the blood, the body cannot use the protein obtained from food for further work. All he can do is take what has already become building material for muscles. Gluconeogenesis (that’s what this process is called) leads to a decrease in the volume of muscle tissue, and this is fraught with a slowdown in metabolism - a change that is unacceptable when losing weight.
- They normalize the state of the nervous system - it has been proven that a low-carbohydrate diet is dangerous for our brain - it helps to reduce mental acuity.
- Helps avoid hypoglycemia - or a condition when blood sugar levels drop to a critical level. Symptoms: weakness, pallor, dizziness, fainting, hunger.
List of weight loss foods containing complex carbohydrates
- Grapefruits - it is better to take ripe fruit with bright red pulp. This is a great light and healthy snack.
- Tomatoes - tomatoes inhibit the production of the hormone responsible for appetite and perfectly cleanse not only the intestines, but also the blood vessels.
- Apples - contain many vitamins, minerals and plant fibers that remove waste and toxins.
- Spinach – you can use it not only for salad, but also for smoothies and dietary puree soup.
- Brown rice is relatively low in calories and rich in healthy carbohydrates.
- Quinoa is an Indian grain loved by many vegetarians. It can be added to warm salads and toppings.
- Variegated beans - rich in antioxidants, protein, essential minerals, folic acid, fiber. Include beans in your diet, and you will never have problems with your heart and blood vessels.
All of these foods contain “good” carbohydrates, essential for gaining muscle mass and losing weight, which are sometimes called “long” carbohydrates (however, this is a misnomer). They should definitely be on your menu. Try to eat more vegetables, less flour, but do not forget that our body needs energy replenishment.
If you are just starting to get acquainted with proper nutrition, open the Di&Di Corporation catalog. Everything you see in it is made from natural ingredients based on Jerusalem artichoke, stevia, and amaranth. This food is suitable for those who want to become slimmer, as well as for diabetics and celiac disease patients.
Minuses
Enlarge image
There are only three disadvantages:
- The need to prepare food. It will no longer be possible to intercept something on the run. For the most part, foods based on complex carbohydrates need to be combined and cooked in order to achieve sufficient nutritional value and provide the body with everything it needs.
- Slowly meets the body's energy needs. When you urgently need a boost of energy, complex carbohydrates are not helpful.
- During pregnancy, if there are no complications, an enhanced balanced diet is prescribed, where the percentage of simple substances may be higher than usual. In addition, vitamins for pregnant women are prescribed. Everything in order to consistently cover the needs of the expectant mother’s body.
These features must be taken into account when organizing the diet.
What foods provide the lowest amount of carbohydrates?
- Zucchini will be an excellent addition to lean meat dishes.
- Cauliflower – Like broccoli, it is high in antioxidants. And it will also be an excellent replacement for the usual mashed potatoes.
- Swiss chard – rich in potassium, reduces the risk of developing heart and vascular diseases. It can be added to salads and steamed.
- Mushrooms are another well-known guest on our list with products containing few carbohydrates and without them at all. It doesn’t matter what you choose - champignons, honey mushrooms, and chanterelles are incredibly healthy and help strengthen the immune system.
- Celery - This green is 95% water, so when you add it to salads, you can be sure that you won't gain an ounce. Celery contains vitamin K, which promotes the absorption of calcium and strengthens nails.
- Apricots contain a lot of beta-carotene, a substance that stimulates brain function better than any medicine.
Foods high in healthy carbohydrates, with the slowest absorption rate and low glycemic index are a rich topic that would be enough for more than one article. But we have already come to the end and want to remind you: without a proper diet and physical activity, you will not be able to lose weight. Plan your diet wisely and do not rush to get rid of foods rich in fiber and starch - you will still need them.
Author: Di&Di Corporation