Slow
Good or slow carbohydrates are foods with a low glycemic index. Characteristics of this energy group:
- presence of vitamins, fiber and minerals
- chemical structure that speeds up metabolism
- prolonged digestion
- slow release of calories
The good ones, also known as complex compounds, are found in whole grains, unprocessed rice, cereals, nuts, seeds, vegetables and fruits.
Which carbohydrates are needed for weight gain and which for weight loss? How to use them correctly
For sports purposes, both types of carbohydrates are important - each of them has its own role and benefits (portion sizes, calorie content and product quality also need to be taken into account):
Gaining muscle mass:
- fast carbohydrates - consume half an hour before and after training. In the first case, you will spend them faster than they have time to be deposited in fat, in the second, they will go straight to replenish glycogen reserves in the muscles (no need to worry about excess weight);
- slow carbohydrates – consume 1-2 hours before and after training. In the first case, the energy will last until the end of the session, in the second, the muscles will also recover and grow, but more slowly.
Weight loss:
- fast carbohydrates - you shouldn’t give them up completely, especially when losing weight - this can lead to breakdowns;
- Slow carbohydrates – save you from overeating and are not stored in reserve. While they are digesting, you feel full.
Fast
Bad or fast carbohydrates are a nutritional group with a high glycemic index and properties:
- digest very quickly
- cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels
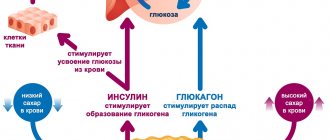
- provoke a sharp release of insulin
- lead to the deposition of adipose tissue
Sources of fast or simple carbohydrates are foods that are pre-processed, lack fiber, and have low nutritional value.
Fast carbohydrates, list of products:
- pasta made from soft wheat varieties
- potatoes, white bread, pastries
- confectionery - cakes and desserts
- muesli, cereal, white rice, popcorn, sugar
- instant porridge and puree, honey
- yoghurts and curds with additives
- jam, chips, lemonades, sweet drinks, juices
A carbohydrate-balanced menu consists mainly of foods including:
- dark flour
- fruits and vegetables
In this case, the processes of lipogenesis - that is, the formation and deposition of fat in the body are under control.
Foods with easily digestible carbohydrates should be avoided:
- made from white flour
- semolina-type cereals
- with added sugar
Remember - simple carbohydrates are a calorie bomb devoid of nutrients.
Back to contents
Useful properties of cereals
- Cereals
- one of the first complementary foods that a child is introduced to. They not only serve as excellent sources of energy (in addition to mother's milk), but also cover some of the growing body's needs for minerals and elements - in particular, iron.
In addition, their introduction also contributes to the active development of “adult” intestinal microflora: the population of bacteroids, one of the main representatives of gram-negative bacteria, increases. This is ensured, according to scientists, by the content in grain crops of a significant proportion of complex carbohydrates, which our microscopic residents ferment with the formation of biologically active compounds.
The use of cereals as complementary foods is also due to their pleasant, mild taste combined with a semi-solid consistency - these properties help the baby transition from liquid breast milk to a new food for him.
- The effects of biological compounds concentrated in cereals have a wide range of directions: many of them have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunostimulating effects, and also regulate the expression of some important genes. Some of them also have potentially protective mechanisms against many serious pathologies: cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases.
- Effect on the composition of the intestinal microbiota. This issue, it must be said, still remains quite controversial, and there is a lot of disagreement among scientists regarding which types of grain affect which bacteria.
For example, recent studies have shown that breakfast cereals made from whole grain wheat have a prebiotic effect - in other words, they are in some way food for our normal flora, actively stimulating its growth. At the same time, consumption of rye bread, no less rich in dietary fiber, did not affect the composition of the microbiota in adult volunteers suffering from metabolic syndrome: a complex of diseases including arterial hypertension, blood lipid disorders, insulin resistance, and obesity.
Interestingly, a 6-week diet in which overweight patients added whole grain rye and wheat to their diet also did not produce significant results: despite slightly improved markers of gut health, there were no changes in the fecal microbiota.
This got doctors thinking about the synergy between fiber and other biological compounds found in whole grains: experiments clearly demonstrated that the health benefits to the human body went beyond dietary fiber alone.
Consumption of whole grains has been shown in numerous studies to be associated with a significant reduction in the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, colorectal cancer, and cardiovascular pathologies. In addition, it correlated with improvement (in adulthood) of cognitive functions: learning, memory, concentration.
All these effects are associated mainly with some protective mechanisms that cereal crops are capable of providing. In particular, we are talking about inhibiting inflammatory processes, maintaining intestinal health, improving the lipid spectrum of the blood and enhancing the insulin response.
For example, 44 overweight Iranian girls (aged 8 to 15 years) showed significant changes in a panel of inflammatory biomarkers (consisting of C-reactive protein, serum amyloid, and A, leptin, intercellular adhesion molecules-1).
Study
: Infant Cereals: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Opportunities for Whole Grains, Dietary Effects on Microbiota—New Trends with Gluten-Free or Paleo Diet
Is it right to give up carbohydrate-containing foods?
Sometimes, people, in pursuit of good shape, decide to avoid eating any carbohydrates. But, this is a bad choice.
- Low-energy nutrition is of the ketogenic type. A lack of energy substances in the diet leads to the process of ketosis - fat burning, during which ketone substances enter the blood. These are toxins, in particular, depressing brain functions.
- In addition, the body increases the production of hormones - norepinephrine, adrenaline and glucagon. These compounds are useful in the short term, but on an ongoing basis lead to exhaustion of the body and endocrine disruption.
- Another unpleasant aspect of a low-carbohydrate diet is hypercholesterolemia with rapid vascular damage and the risk of conditions such as stroke or heart attack.
- Just 3-4 months of eating without plant fiber will cause gastrointestinal problems - vomiting, constipation or nausea. Additionally, a deficiency of vitamins B, C and A will form, the body will become acidic, the nervous system will become hyperactive, and the urinary system will react with gout.
- Separately, disorders of calcium phosphate, hemoglobin and glucose metabolism may develop. That is, a person will become acquainted with type 2 diabetes, osteoporosis or osteopenia.
Therefore, the right choice would be a healthy diet rich in slow carbohydrates.
Back to contents
Buckwheat porridge against diseases of the circulatory system
Buckwheat porridge is a true favorite of all athletes who are trying to build muscle mass. This high-calorie, but nutritious porridge helps to quickly increase muscle size, maintain strength and health of the body. It contains:
- carbohydrates - 17.1 g;
- proteins – 3.2 g;
- fats – 0.8 g;
- vitamin E – 6.7 mg;
- vitamin PP – 4.2 mg;
- iron – 6.7 mg;
- magnesium – 200 mg;
- calcium – 20 mg.
This porridge has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the circulatory system. Iron is necessary for the formation of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in our body. Vitamin P strengthens the walls of blood vessels.
In addition, it lowers cholesterol levels, can stabilize the amount of glucose in the blood, strengthens hair and nails, and relieves stress.
In our country, it is customary to eat buckwheat porridge with meat. Buckwheat dishes can be extremely varied and tasty. Some simply boil it in water and then serve it with beef stroganoff, others stew it in the oven or pour it with milk.
When and how to consume carbohydrate-containing foods?
There are general rules for consuming energy products.
In the morning
You can use small amounts of fast carbohydrates, which will help your brain work intensively and will be a good way to start the day energetically. In the morning it is recommended:
- jam, marmalade or honey
- sweetened yoghurts
- cereal with dried fruits
And also, carbohydrates in porridges - semolina, millet, oatmeal with the addition of fruit.
Dinner
Must include complex carbohydrates:
- whole grain bread
- durum wheat pastes
- dark pasta and brown rice
In addition, fruits or vegetables in salads, side dishes and fresh.
Evening
Starting from 18-19 hours, it is recommended to eat only protein foods with the addition of lettuce or vegetables, except potatoes and legumes.
Depending on daily activity, when an energetic period is replaced by a measured period, it is necessary to reduce the amount of carbohydrates in the diet.
Back to contents
Dietary intake of complex carbohydrates for men and women
Calculating the norm of consumption of complex carbohydrates for men and women depends on age, initial weight, daily activity, and most importantly, on the goal.
Norm for women
For women who want to lose weight, the following daily norms of slowly digestible carbohydrates are determined:
- With an initial weight of 50-55 kg - 110 g.
- Weight 60-65 kg - 140 g.
- Weight 70-75 kg - 160 g.
- Initial weight 80-85 kg - 170 g.
To maintain optimal weight, slightly different daily intakes of complex carbohydrates are recommended:
- Weight 50-55 kg - 140 g.
- Weight 60-65 kg - 160 g.
- Weight 70-75 kg - 190 g.
- Weight 80-85 kg - 210 g.
If a woman’s goal is to gain weight, the daily intake of complex carbohydrates should be increased:
- Initial weight 50-55 kg - 190 g.
- Weight 60-65 kg - 240 g.
- Weight 70-75 kg - 250 g.
- Weight 80-85 kg - 260 g.
Norm for men
For men, the daily intake of complex carbohydrates is slightly higher, and they also depend on the goal and initial body weight.
If you want to lose weight, a man is shown the following daily carbohydrate intake:
- Initial weight 50-55 kg - 165 g.
- Weight 60-65 kg - 170 g.
- Weight 70-75 kg - 175 g.
- Weight 80-85 kg - 185 g.
To maintain optimal body weight in men, other daily dosages of complex polysaccharides have been determined:
- Initial weight 50-55 kg - 220 g.
- Weight 60-65 kg - 235 g.
- Weight 70-75 kg - 245 g.
- Weight 80-85 kg - 265 g.
To increase weight, men are recommended to increase the dose of carbohydrates per day:
- Initial weight 50-55 kg - 280 g.
- Weight 60-65 kg - 295 g.
- Weight 70-75 kg - 310 g.
- Weight 80-85 kg - 320 g.
To avoid mistakes, calorie calculations and menu planning taking into account complex carbohydrates should be carried out by a nutritionist based on the initial parameters.
Why is sugar dangerous?
If we can say about slow carbohydrates that these are natural fruits and whole grains, then among fast carbohydrates the most useless carbohydrate is sugar. The product has no nutritional value and is considered the drug of the century for a number of reasons.
Sugar:
- Stimulates the formation of beta-endorphins.
- Gives the illusion of stress relief, briefly improving mood.
- It produces biochemical dependence in people.
- It affects the brain in a way similar to opioid intoxication because it stimulates the same receptors that respond to morphine, heroin and codeine.
After eating sweets, people feel calm. They quickly get used to the cake = happiness scheme. As a result, they become dependent.
Excess sugar, as the most prominent representative of bad carbohydrates, leads to:
- hypertension, irritability, hyperactivity
- decreased mental functions, cancer pathology
- suppression of the immune system, accelerated aging
- slowing down recovery processes
Not everyone consciously chooses to abuse simple carbohydrates. Therefore, it is useful to know where sugar is hidden in hidden form.
Back to contents
Quinoa
Although technically classified as a pseudocereal, quinoa is often cooked and eaten as a grain ().
Quinoa is rich in beneficial antioxidants and polyphenols, which may help reduce inflammation and protect against chronic diseases (, ,).
It's also relatively low in carbs, with just 34 grams of net carbs in a 185-gram serving of cooked quinoa ().
Quinoa is also one of the few sources of complete plant-based protein, meaning that it contains all nine essential amino acids that the body needs to get from food sources ().
In addition, quinoa is rich in other key nutrients, including manganese, magnesium, phosphorus, copper and folate ().
Summary:
A 185-gram serving of cooked quinoa contains 34 grams of net carbs. This grain is also rich in antioxidants and contains all nine essential amino acids that your body needs.
Healthy foods with bad ingredients
Diet cereals and candies are simply a trap for buyers, as they contain hefty doses of sugar. It's useful to know that this ingredient is also hidden in unsweetened foods:
- ketchup and salad sauces
- canned meat and fish
- peanut butter
- all types of bread
- yoghurts, muesli, cereal bars
- sausages and sausages
How can I find the information on the label? Read the section “Carbohydrates”, where the explanation “Including sugar” follows. On average, 150 grams of sugar-containing, although unsweetened, products contain up to 2 teaspoons of sugar. Healthy chocolate or cereal contains up to 3-5 spoons per 150 grams.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that nutritionists recommend paying attention not only to the amount of carbohydrates, but also to the presence of fats in foods, since the combination of sugar and fat has a particularly adverse effect on the health of the body.
Back to contents
Rice porridge protects the gastrointestinal tract
Rice is a unique product that is the basis of many dishes in Eastern countries and an ingredient in exquisite culinary masterpieces. Its calorie content directly depends on the method of preparation. Porridge with water contains only 89 kcal, and with milk 101. It contains:
- fat – 1 g;
- protein – 7 g;
- starch – 73 g;
- carbohydrates – 1.1 g;
- dietary fiber – 0.4 g;
- vitamin PP – 1.6 mg;
- vitamin H – 3.5 mcg;
- iron – 1 mg;
- potassium – 100 mg;
- iodine – 1.4 mg.
Thanks to this composition, rice porridge is an indispensable element of the diet for people suffering from various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, especially those prone to diarrhea. In addition, rice is an effective adsorbent, which makes it recommended for weight loss, removal of waste and toxins, and also as a remedy for bad breath. Nutritionists also advise vegetarians to supplement their diet with rice porridge, since its proteins are similar in structure to animal ones.
Rice porridge is rich in iodine, which also allows it to be recommended as a preventive measure for thyroid diseases. It can strengthen the nervous system and relieve insomnia. Like many cereals, rice is rich in potassium and iron, which has a beneficial effect on the condition of nails, hair and skin.
Rice is a product that allows you to prepare a wide variety of dishes. Supplement it with seafood, meat, vegetables or cook it with milk, then your meal will be definitely satisfying, tasty and healthy.
Summarize
- While many low-carb diets do not exclude grains, many varieties are suitable for a healthy, controlled carbohydrate diet.
- In fact, many types of grains are high in fiber and low in net carbohydrates, which is the amount of carbohydrates the body actually digests.
- For best results, be sure to choose whole grain varieties and avoid highly processed or refined grains whenever possible.
The article was prepared by experts for informational purposes only. It should not be used as a guide for treating medical conditions and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. In case of illness or any symptoms, you should always consult a doctor and not self-medicate.
Tags: carbohydrates
About the author: Alexander Fedorov
Candidate of Biological Sciences, biologist, nutrition expert. Graduated from Stavropol State University with a degree in Biology at the Faculty of Biology and Chemistry.
- Related Posts
- Which rice is the healthiest for the human body?
- Oats: benefits and harms for the human body
- What are the benefits of wheat? Benefits and harm to the body
« Previous entry
Wild rice
Wild rice is a grain obtained from the Tsitsaniya genus of herbaceous plants.
Compared to other types of rice, wild rice contains significantly fewer carbohydrates, with 32 grams of net carbohydrates in every 165-gram serving of cooked wild rice ().
Additionally, wild rice is rich in health-promoting antioxidants.
One review found that phenolic compounds found in wild rice have 10 times more antioxidant activity than those found in white rice ().
What's more, wild rice is an excellent source of a number of other nutrients, including zinc, vitamin B6 and folate ().
Summary:
Wild rice is lower in carbohydrates than other types of rice, with 32 grams of net carbs per 165-gram serving. It is also rich in antioxidants, as well as zinc, vitamin B6 and folate.
Carbohydrate diet for weight loss
The principle of the carbohydrate diet is quite simple: it is necessary to control the amount of sugar consumed in food so as not to cause excess unspent energy, which will subsequently settle in the form of fat deposits.
In no case should you skip main meals, since a prolonged lack of fuel will give the body a signal to store it for future use. And this, again, is excess weight.
Choose foods with low and medium GI more often, limit the consumption of ordinary sugar and other sweets, and increase physical activity.
At first, a special table of fast and slow carbohydrates will help, and over time, taking care of your health will become an invariable part of your new life.