For many years, people were afraid of fats, and some still avoid them. It was believed that if they were overweight, they were to blame. And many people of the older generation probably still remember about fears of cholesterol. From the article you can find out what fats (lipids) are, what they are, how much you should consume, and much more. Only verified information for you.
What are fats?
Fats are complex organic compounds of the lipid class.
This is one of the three macronutrients we need for life. The other two are proteins and carbohydrates .
Dietary fats that a person receives from food, as well as those synthesized in the body, are divided into three classes :
- Triglycerides. More than 90% of fats are triglycerides, consisting of glycerol and three fatty acid residues. They perform many functions in the human body. More on this below.
- Phospholipids are similar in structure to triglycerides. But they have phosphoric acid instead of one of the fatty acids. They are soluble in water and fat. Primarily responsible for the plasticity of cell membranes.
- Sterols. The most famous representative of sterols is cholesterol. Cholesterol comes from food and is also synthesized in the human body. It is needed for the formation of bile, the synthesis of vitamin D and some hormones. Gives rigidity and stability to cell membranes.
Many people believe that cholesterol is to blame for all cardiovascular diseases. However, this is not quite true. There is not only “bad” cholesterol (low density), but also “good” (high density). It is important to maintain the necessary balance between these two types of cholesterol. You can find out your cholesterol level, as well as the ratio of different types, using a lipid profile analysis.
The main factors that contribute to high cholesterol are heredity, excess weight, excessive consumption of saturated and trans fats, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Cheese
Cheese is incredibly nutritious. This makes sense considering that an entire glass of milk is used to produce one dense piece of cheese. Cheese is an excellent source of calcium, vitamin B12, phosphorus and selenium, and contains all sorts of other nutrients (41).
It is also very rich in protein - 100 grams of cheese can contain between 20 and 40 grams of high-quality protein. Cheese, like other high-fat dairy products, also contains powerful fatty acids that have been linked to a variety of health benefits, including a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes (42).
You can learn more about the beneficial properties of cheese and the possible harm from consuming it on this page - Cheese: benefits and harm for the human body.
Summary:
Cheese is incredibly nutritious. Just one piece contains as many nutrients as a glass of milk. It is an excellent source of vitamins, minerals, quality proteins and healthy fats.
The importance of fats in the human body
Numerous studies have shown how important fats are in human nutrition.
The fats we consume vary greatly in their effects. Some species really should be limited. Others, on the contrary, are very important for health. Why are they needed anyway?
Lipids are an important source of energy . The energy value of 1 g of fat is 9 kcal. This means that it contains twice as much energy as carbohydrates (1 g - 4 kcal).
It is lipids that make up more than 80% of the energy reserves in the body. But this is not their only function.
Functions of fats
- Provide thermal insulation, protecting the body from the cold.
- They produce hormones that regulate appetite and affect other organs and tissues.
- They slow down the digestion process, as a result we do not feel hungry for a long time.
- They add flavor and aroma to food; it’s not for nothing that we all love fatty foods to one degree or another.
- Fats contain fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K).
- They serve as building material for our body.
- They are an indispensable participant in many metabolic processes, for example, cholesterol metabolism.
Thus, the benefits are great, and you should not give up fats under any circumstances.
Low-calorie food - good or bad?
Why should you avoid foods that are very low in body fat? Many people do not tolerate this type of diet for long because they consider low-fat meals to be tasteless and full of restrictions. The fact is that fat significantly slows down digestion; many diets based on eating low-fat foods force a person to fight hunger all day long.
Dietary fat plays a crucial role in metabolism - each gram contains 9 kilocalories. This calorie content is life-saving in cases where there is not enough food; it is very important for people who are not able to absorb large amounts of food.
Types of fats
There are saturated and unsaturated fats (fatty acids).
Saturated fats
They are solid at room temperature (except coconut and palm oils). The main source is animal products:
- red meat (pork, beef, etc.) and lard;
- dairy products (especially cheeses and butter);
Some vegetable oils:
- coconut and palm.
Saturated fats increase the risk of cholesterol deposits in the walls of blood vessels. At the same time, they provide the body with energy . The main thing is not to abuse it. Everything needs moderation.
The human body can synthesize saturated fatty acids on its own.
Trans fats
Trans fats are a type of unsaturated fat. We define them in a separate group, because they are obtained by hydrogenation of cheap vegetable oils . During complex chemical reactions, unsaturated fats become saturated.
These oils hold their shape well and provide a pleasant taste; baked goods with trans fats are stored well and remain fresh for a long time. The saddest thing is that thanks to this hydrogenation, changes occur in the molecules of initially harmless vegetable fats, turning them into extremely dangerous ones .
Trans fats are often linked to diabetes, strokes, heart attacks and even cancer . WHO recommends limiting them to a minimum. In some European countries their use is completely prohibited or severely limited.
What foods contain trans fats:
- margarine, spreads, cooking oil;
- most baked goods (cookies, waffles, cakes, pastries, etc.);
- chips and crackers;
- frozen meals;
- chocolates, bars, almost all chocolates;
- many dairy products;
- some sausages;
- all fast food.
The list may be incomplete, because manufacturers add hydrogenated oils everywhere and carefully hide it.
Almost 50% of foods sold in supermarkets contain trans fats.
Why not replace trans fats with something healthier?
The fact is that they are very cheap, and it is not possible to replace them without a significant increase in price in any country in the world. However, some countries are finding a solution for themselves.
In addition, trans fats are formed during frying as a result of prolonged high heating of vegetable oils .
A certain amount of trans fats is also found in common foods - meat and milk. However, their content in such products is so insignificant that there is no need to limit yourself in milk and meat.
Doctors recommend consuming up to 7 g of trans fats per day . Therefore, it is advisable to exclude industrial sweets, fast food and some other products. Or at least carefully read the ingredients on the product label. They are hidden under the phrases: “Partially hydrogenated vegetable fat”, “vegetable oils”, etc.
Monounsaturated fats
This includes omega 9 fatty acids, the main of which is oleic acid. It is also partially synthesized in the human body.
Sources:
- Vegetable oils (olive, sunflower, soybean, rapeseed, sesame, walnut, flaxseed, etc.).
- Avocado.
- Nuts and seeds.
- Chicken, red meat.
Omega 9 has a beneficial effect on cardiovascular health and can increase “good” cholesterol . Although for this it is important to reduce the consumption of saturated fats and replace them with unsaturated ones.
Research is currently ongoing to determine the benefits of monounsaturated acids for human health. The benefits of oils have been proven for a long time, but the benefits of these acids contained in meat are still in doubt among scientists.
Polyunsaturated fats
This includes the most beneficial essential omega 3 and 6 fatty acids. They are not synthesized in the body and must be obtained from food.
Perform essential functions in the body. A number of biologically active substances are produced from them. Therefore, they are necessary for normal metabolism.
Sources:
- Fatty fish, seafood.
- Fish fat.
- Vegetable oils (olive, sunflower, corn, rapeseed and others).
- Nuts, seeds.
Remember which foods contain healthy fats .
Polyunsaturated fatty acids:
- reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases (strokes, heart attacks, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease), diabetes;
- lower “bad” cholesterol and increase “good” cholesterol;
- have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
A little about the complex
Essential fatty acids include linoleic and linolenic acids. Linoleic acid and arachidonic acid formed in our body from it belong to omega 6 fatty acids.
Linolenic acid and its metabolic products, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), are omega 3 fatty acids. Only small amounts of EPA and DHA can be formed from linolenic acid.
However, eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid can be obtained by consuming fish or fish oil.
A deficiency of essential acids can lead to diseases of the cardiovascular system and premature aging.
Sources of Selected Fatty Acids
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | Main food sources |
| ω-6 | |
| Linoleic | Vegetable oil, nuts, seeds |
| ω-3 | |
| Linolenic | Flaxseed oil, soybean oil, flax seeds, walnuts, broccoli, Brussels sprouts |
| Eicosapentaenoic, docosahexaenoic | Fish, fish oil |
Omega 3
Separately, I would like to talk about the benefits of omega-3, eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids, which can only be obtained with fish and fish oil.
Proven to perform the following tasks:
- acts as a prevention of heart attacks and strokes;
- prevents arrhythmias, slows down the number of heart contractions;
- reduces heart failure;
- prevents thrombosis;
- used in the treatment of depression;
- reduces insulin resistance, thereby preventing diabetes and oncology;
- has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Which is better, fish or supplements?
Doctors recommend eating fish several times a week. The best source of Omega 3 is fatty sea fish that live in cold waters. Therefore, it is better to give preference to sardines, herring, salmon, tuna, mackerel, and capelin. There is much less of it in squid and white sea fish, such as cod.
If you are unwilling or unable to eat fish regularly, it is advisable to take fish oil or an Omega-3 supplement directly.
There are 3 supplements on the market:
- Fish oil , which is sold in pharmacies, usually contains both omega 3 and 6, as well as some vitamins. It should be used for vitamin deficiencies, or as a source of small amounts of essential fatty acids. Fish oil is most often prescribed to children.
- For adults, omega 3 or omega 3, 6, 9 . Moreover, omega - 3, 6, 9 is most often taken by athletes who completely exclude all fats from their diet. An ordinary person does not need such a supplement. Why?
Because the ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 in your diet is extremely important.
The optimal ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 should be, according to various sources, from 1:2 to 1:4. However, in the diet of most people the ratio is 1:20 or more towards omega - 6. After all, as you remember, omega - 6 is found in vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, avocados, etc. Every person consumes these to one degree or another products.
Excess omega 6 can lead to increased blood clotting, blood clots, heart attacks and strokes. It is recommended to add omega-3 to the diet and reduce omega-6.
Therefore, it is omega-3 fatty acids that enter your body and it is recommended to eat fish a couple of times a week. Or Omega-3 supplement in capsules.
Nowadays there is a huge selection of fish oil on sale, both in liquid form and in capsules. You need to be very serious about choosing a brand, because you need a high-quality drug.
I recommend paying attention to this premium Omega 3 at an affordable price . It is manufactured under strict quality control. This brand of fish oil is tested to be free of heavy metals, mercury, and other harmful substances.
Eggs
Whole eggs were considered unhealthy because the yolks were high in cholesterol and fat. In fact, one egg contains 212 mg of cholesterol, which is 71% of the recommended daily intake. Additionally, 62% of calories from whole eggs come from fat (8).
However, new research has shown that the cholesterol in eggs does not affect blood cholesterol levels, at least in most people (9).
In fact, eggs are among the most nutrient-dense foods on the planet. They are rich in vitamins and minerals, and contain almost all the nutrients we need.
Eggs even contain eye-protecting, powerful antioxidants and are high in choline, an important brain nutrient that 90% of people don't get enough from food (10, 11).
Eggs are also a food that helps you lose weight. They're filling and high in protein, the most important nutrient for weight loss (12).
Despite the high fat content, people who replace breakfast cereals with eggs end up consuming fewer calories and losing weight (13, 14).
The best eggs are fortified with omega-3 fatty acids or homemade. Don't shy away from eating the yolk, as it contains almost all the nutrients.
Summary:
Whole eggs are some of the most nutrient-dense foods on the planet. Although high in fat and cholesterol, they are incredibly nutritious and healthy.
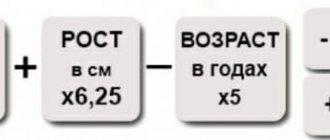
How much fat do you need per day
The food must contain fats. A deficiency, as well as an excess, can lead to serious consequences. The daily need for fats, like other nutrients, depends on your age, gender, health, physical activity, and climatic conditions.
The recommended ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates can be seen in the chart.
The World Health Organization recommends no more than 30% of daily calories from fat.
It is important to maintain the ratio of different types:
- saturated - up to 10% (that is, no more than ⅓ of the total amount of fat consumed);
- monounsaturated - 10% (⅓ of the total);
- polyunsaturated - 5–10% (up to ⅓ of the total);
- trans fats - less than 1%.
Thus, WHO recommends giving preference to unsaturated fats, avoiding saturated fats, and eliminating trans fats.
The exact amount of fat is calculated individually.
As an example, I give calculations for men and women 30 years old, of average height with low activity.
In the case of weight gain, average activity was taken (3 workouts per week).
See table below.
| 50–55 kg | 55–60 kg | 60–65 kg | 65–70 kg | 70–75 kg | 75–80 kg | |
| Men | ||||||
| Weight loss | 44 | 45 | 47 | 48 | 50 | 51 |
| Weight maintenance | 55 | 57 | 59 | 61 | 63 | 64 |
| Muscle gain | 81 | 83 | 86 | 89 | 92 | 95 |
| Women | ||||||
| Weight loss | 37 | 38 | 40 | 42 | 43 | 45 |
| Weight maintenance | 46 | 48 | 50 | 52 | 54 | 56 |
| Muscle gain | 68 | 70 | 73 | 76 | 79 | 82 |
Types of fatty acids and why they are needed
There are two types of fatty acids: linoleic and alpha-linoleic. Fatty acids are important components of cell membranes; they are converted into chemical regulators that affect blood clotting, dilation of blood vessels, etc. Their deficiency in children is characterized by slow growth, decreased immune function, and the appearance of rashes. Sometimes this leads to vision problems and nerve disorders.
Proteins are also required for proper development. Without them, the immune system cannot properly protect the body from bacteria and viruses. That's why it's so important to eat foods rich in fats and proteins.
Foods rich in fats
The table lists the foods that contain the most fat without taking into account the health benefits. Give preference to the useful ones.
| Food products | Fats (g) per 100 g of product |
| Vegetable oil | 99,9 |
| Pork lard | 99 |
| Ghee | 98 |
| Butter | 82 |
| Margarine | 82 |
| Pecan | 72 |
| Mayonnaise | 67 |
| Pine nut | 68 |
| Cod liver (canned) | 65 |
| Walnut, hazelnut | 61 |
| Sunflower seeds | 60 |
| Raw smoked sausage | 57 |
| Pork is fatty | 50 |
| Peanut | 50 |
| Pork is fatty | 50 |
| Goose, duck | 38 |
| Chocolate | 35 |
| Pork lean | 33 |
| Sprats (canned) | 32 |
| Cheese | 30–50 |
| Mackerel | 25 |
| Sausages | 24–30 |
| Saira | 23 |
| Natural pink salmon (canned) | 22 |
| Sardines in oil | 20 |
| Iwasi herring | 17 |
| Chum salmon caviar | 13 |
| Beef | 12 |
| Chicken egg | 11 |
| Sardines | 10 |
| Mackerel | 9 |
| Lean herring | 7 |
Beneficial features
Fats are involved in almost all the most important processes in the human body. With their help, hormones are synthesized, new cellular structures are formed, and fat-soluble vitamins are better absorbed. If there is not enough fat, vitamin deficiency develops, which means the risk of skin diseases and rickets increases.
In addition, fats protect the body from freezing and serve as a source of energy that is stored in the body “just in case.” When a person is forced to starve, is cold, or is under extreme stress, these substances come to the rescue.
Vegetable fats are used not only in cooking, but also in the medical field. They are digested much faster and easier than animal products. On their basis, ointments, massage products, and preparations in capsules for oral administration are made.
What other benefits do vegetable fats bring:
- prevent blood clots and surges in blood pressure;
- stops skin aging processes;
- normalizes the production of female hormones;
- help strengthen the immune defense, which means they help to quickly cope with colds and other diseases;
- improve metabolism, restore full digestion.
Manufacturing
In fact, there are two ways to obtain vegetable fats: pressing and extraction. Industrial volumes and sanitary standards require a long, multi-stage cycle, during which most oils lose their natural value. This is due to the fact that by removing harmful components, it is impossible to separate them from beneficial substances. Because of this, there is constant debate about what type of production and what degree of purification is most beneficial. A simplified production cycle looks like this:
- Processing and purification of raw materials. Grain products are cleaned of debris, husks, and leaves. The hard inner kernels are crushed and fried to a certain degree. For soft fruits (for example, olives), only grinding is used.
- Oil release. When using mechanical extraction, the entire process consists of applying pressure to the raw material mass until the oil is released. For extraction, a special solvent is used, which is mixed with the raw material. After some time it is pumped out. Further operations are specific to each individual crop. The resulting product can already be eaten, but the taste and smell are far from store standards.
- Filtration and settling. For example, for olive oil, this is the last stage of production.
- Refining – removal of mineral and organic substances. The procedure is aimed at improving the taste and technological qualities of the oil. At the same time, refining removes many beneficial vitamins, minerals, phosphatides, and fatty acids. At the same time, oil hydration occurs.
Sunflower oil during pregnancy
It is important for expectant mothers to properly balance their diet for the full development of the baby. After eliminating many foods, pregnant women often develop problems with the gastrointestinal tract, teeth, hair, and nails deteriorate. Constipation is associated with changes in lifestyle and the rhythm of the body's functioning: low mobility, additional weight, change in diet. In order to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, it is recommended to take 2-3 tablespoons of sunflower oil per day (you can simply add it to salads, rather than drink it in its pure form).
Saturation with vitamins A, B and E and additional minerals will improve the condition of nails, hair and teeth. It is important to remember that such a product should be used only in its original form without any heat treatment. In this case, it will help solve cosmetic problems, get rid of constipation and heartburn. The only obstacle to the use of sunflower oil is individual intolerance.
Contraindications
It is not recommended to eat unrefined oil after improper storage or heat treatment: during the frying process, the constituent substances are modified into trans fats (it is better to prepare salads based on it). Vegetable fats in large quantities are contraindicated for those suffering from cholelithiasis. If you have regular diarrhea, the oil should be limited due to its stable laxative effect. If a person decides to replace animal oils with vegetable oils, one should consult a gastroenterologist and nutritionist.
Compound
The composition of vegetable fat directly depends on the source plant. The composition contains mandatory components that form the oil structure of the product. The main thing that needs to be mentioned is: do not believe advertising and branding that claims to remove cholesterol from the product, because it is not found in vegetable oils.
The saturation of natural non-animal fats with vitamins and microelements after the production cycle is artificial. The basic composition of any vegetable oil looks like this:
- unsaturated fatty acids: butyric, caproic, caprylic, decenoic, lauric, myristic, palmitic, stearic, linoleic, nervonic, arachidic, etc.;
- wax;
- phospholipids;
- sterols;
- glycerol;
- vitamins, minerals, microelements.