Knee pain may occur with movement (walking or bending). When the load on the knee is reduced, in many cases the pain goes away. But after some time, the pain usually occurs again. Quite often, people get used to the fact that they have painful knees, trying to limit movement and load, but this is the wrong way. Many knee conditions develop gradually over years, and if left untreated, symptoms will worsen over time, robbing a person of their quality of life and freedom of movement.
Discomfort in the knee area
Knee pain when squatting and standing is one of the most common complaints of patients when visiting a doctor. The resulting discomfort is often attributed by experts to excessive stress placed on the knee joints. Deciding what to do about this problem and what treatment is required is necessary only after identifying the root cause. Otherwise, your knees will continue to hurt when squats.
The main factors for such discomfort may be incorrectly performed strength exercises, for example, squats with a barbell. Long-standing knee injuries can also contribute to pain when squatting and standing up. But even in the presence of these two factors, degenerative phenomena of the joints cannot be ruled out - they may be the answer to the question, why do my knees hurt when squatting and standing up?
The knee joint is a complex joint that is based on the principles of operation of hinge mechanisms. During movement, it is the knee joint that receives the main load. The main work when standing up, while running, jumping and walking is done by the knee.
Gradually, the knee joint wears out - first there is a crunching sensation, then a slight nagging pain, and periodic sharp pain. As a signal of the need to consult a traumatologist, constant acute pain occurs in the knee, which can only be relieved with medications. It becomes painful for a person to sit down, walk, or otherwise work with the affected leg. As a result, the joint is completely destroyed and the person becomes disabled.
To avoid disability, you need to be a little attentive to your own body and the signals it gives. If your knees hurt, you need to do the following:
- Calculate when your knees hurt the most - after squats or jumps, walking or running.
- Determine the nature of the pain syndrome - nagging pain, stabbing, pulsating.
- Finding out the average duration – it hurts for a couple of seconds, a minute, an hour.
In the case where pain is caused by physical exercise, you should pay attention to the following parameters:
- fidelity to the technique of performing exercises;
- correct positioning of the legs and distribution of loads;
- intensity of load on the knee joint.
When it’s not a matter of technique or correct position, but of excessive loads, you should think about what to replace squats with.
- Knees hurt when squatting and standing up: causes, treatment
Read about Bubnovsky’s advice for knee pain here.
If the unpleasant sensations in the area of the knee joint do not depend on the load, then you should go to the doctor. When it hurts to kneel, or after squats or when squatting, the knee or both hurt, it is also advisable to visit a doctor, who will determine the nature of the root cause.
Which doctor should I contact for knee pain?
With knee pain, it is best to consult an orthopedic traumatologist or surgeon. In case of chronic knee pain, help can be provided by a rheumatologist. In order to relieve pain, people also consult a physiotherapist, massage therapist or chiropractor.
Diagnosis
If a specialized specialist complains of pain in the knee joint during flexion and extension, he conducts an initial examination of the patient. The initial examination includes the following procedures:
- patient interview;
- viewing a medical record;
- visual inspection;
- palpation;
- issuing referrals for tests and research.
As part of a diagnostic examination, the patient is required to follow the doctor’s instructions - tests and studies guarantee the truth of the diagnosis and the correctness of treatment tactics. As usual, the list of necessary diagnostic measures is as follows:
- blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- X-ray examination;
- MRI;
- CT;
- Ultrasound;
- arthroscopy of the knee joint.
The last type of study is invasive and is prescribed exclusively when other methods are powerless or there is suspicion of a serious pathology of the knee joint.
Relief of pain until a definitive diagnosis is made
It may take some time for the attending physician to receive the results of studies and tests, as well as make a final diagnosis based on the data obtained. During this period, you should take care of the sore joint and reduce the load on it.
Important! If you need to move, it is advisable to fix the joint with an elastic bandage.
If there is such an opportunity, then provide complete rest to the knee joint. In order to reduce pain, it is possible to use the following medications and traditional medicine recipes:
- Knee pain when squatting and standing up
- compresses and bandages on the knee;
- local painkillers;
- warming ointments;
- massages (with extreme caution);
- relaxing baths with salts, essential oils and herbs.
For people who cannot even temporarily give up sports, swimming is the best way out of the situation. It will not put such a significant load on the joint, but at the same time it requires significant muscle work.
Treatment
Once a diagnosis has been made, and the pain in the knee area is the result of an illness or serious injury, there is no way to get by with general measures. How to treat knees if they hurt when squatting and standing up? In addition to the main treatment prescribed by a specialized specialist, he can recommend the following auxiliary measures to the patient:
- If an injury is detected, the knee joint should not be strained. All sports and any intense movements are prohibited. This is necessary to prevent consequences and complications.
- If arthritis has been diagnosed, non-steroidal drugs are prescribed as an analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug.
- If you have gout, it is recommended to review your diet and exclude from it those foods that have a fairly high content of purine bases.
- In the absence of deformations and degradation of cartilage tissue, as well as neoplasms in the joint area, exercise therapy is recommended.
All of these measures cannot be prescribed independently, since some of the measures aimed at improving the condition may have the opposite effect.
Important! After performing physical therapy exercises, rest is required. In the event that pain occurs in the affected area when performing an exercise, you should abandon it completely.
Pain in the knee joint: treatment at the Yusupov Hospital
The main goals for the treatment of pain in the knee joint, which the doctors at the Yusupov Hospital Therapy Clinic set for themselves, are the following:
- eliminate swelling;
- relieve the patient from discomfort;
- restore the functions of the knee joint;
- prevent new attacks.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics are used to relieve pain. The use of warming and distracting ointments, as well as restorative drugs, is effective.
In the remission stage, patients are prescribed the use of physiotherapeutic techniques, massages, and therapeutic exercises.
In the absence of effectiveness from conservative therapy, specialists, taking into account all the pros and cons, consider the advisability of surgical treatment.
In addition, there are a number of traditional medicine that help reduce pain, but their use must first be discussed with specialists who monitor the progress of treatment aimed at eliminating pain in the knee joint. How to treat this pathology should only be decided by an experienced, highly qualified doctor who is familiar with the patient’s research results, the individual characteristics of his body and many other important nuances.
Preventive measures and prophylaxis
To prevent any damage to the joints of the lower extremities, as well as to reduce the likelihood of inflammation, common sense should be used. This is required not only in everyday life, but also when playing sports. If you have non-recurrent pain, you can try to get rid of it by following these instructions:
- Before any physical exercise, a warm-up is required.
- After performing exercises, your knees need rest and relaxation.
- When performing squats, the technique of their execution must be ideal.
- If pain occurs, you need to reduce the intensity of the exercise - this will prevent injury and deformation of the joint.
- Avoid hypothermia of joints.
- Treat all diseases in a timely manner.
- Eat a balanced diet and keep your weight under control.
Such measures will help to avoid unwanted processes in the joints in youth and reduce their likelihood in old age.
If the meniscus is not completely torn, then such an injury is similar to a bruise
After a few weeks, the bruising will disappear. When the gap in the cartilage widens, severe pain will appear, and there is a high probability that the meniscus will rupture completely. When you sit down and stand up, you experience pain. In most cases, the injury is treated conservatively. The leg is immobilized, the inflammatory process with pain is eliminated. In severe cases, surgery is indicated.
The knee joints are protected from injury by the patellas, which is why the kneecaps are often injured. When a person falls or hits himself, there is a high probability that he will break a bone and a crack will appear. If the patella is fractured, the shape of the joint changes, becoming painful and swollen. In fractures with displaced bone fragments, soft tissue structures with ligaments and tendons are injured.
If there is a crack on the patella, then the person can move independently for a long period; when squatting, the knee will hurt and ache. In case of a crack in the kneecap and a fracture without displaced bone fragments, the lower limb is fixed with a plaster bandage. According to indications, the patella is surgically restored using a wire. During the rehabilitation period, the joint is not loaded, and its mobility will gradually be restored.
The joint is intact and mobile thanks to ligaments. They are injured when a person falls, hits, or moves carelessly. Ligaments can:
- Partially rupture. It will seem to the person that they are stretched (the ligament is not elastic). There is pain in the knees when squatting and standing up.
- Suffer from an incomplete rupture, when the fiber structure of the ligament is severely damaged, but is still intact. The pain syndrome is provoked by any physical activity: when squats, when the patient gets up, walks.
- Break completely. Motor activity is impossible; it is difficult for the patient to move the lower limb.
If the internal collateral ligament is damaged, the pain inside the knee will intensify when the shin area is retracted outward when I stand up or squat. If the lateral collateral ligament is damaged, the outer side of the knee is painful, and the discomfort will increase when the lower leg moves inward after squats. If the pain is in the center of the knee, then the person’s cruciate ligaments are affected.
After sitting, when the patient has to get up or sit down, the pain will intensify. If the ligament is not completely torn, then a rigid bandage is applied from the ankle to the femoral area. When it ruptures completely, surgery is required, after which a plaster cast is applied. During the rehabilitation period, exercise therapy (physical therapy) is used.
Tendons have low elasticity; they are attached to bone and muscle tissue. Tendons are more likely to be damaged in patients suffering from pathological changes in the muscles, as well as in people involved in sports. The quadriceps tendon is most commonly injured. When such a muscle is tense, the leg is bent at the knee joint, the tendon is injured.
When tendons are injured, pain is localized above the knee above the patella
A frequent complaint from a patient over 50 years old: “I can’t get on my knee after I squat, when I straighten my leg, my knee hurts.” If the tendon is not completely torn, the cast should be worn for 3 to 6 weeks. If the rupture is complete, the tendon is sutured and the leg is in a cast. During the rehabilitation period, a complex of exercise therapy with massage is recommended.
Injuries during sports occur because a person:
- Didn't warm up enough before doing gymnastics.
- Squatted incorrectly if the knee joints protruded beyond the level of the fingers of the lower extremities.
- Lifted a heavy barbell while squatting.
- He fell and got injured.
With chronic pathological changes in the knee joints, it is difficult for a person to determine the cause of pain. Arthritis of the knees (gonitis) often occurs chronically. Any joint inflammation can be infectious or non-infectious. The non-infectious form is caused by impaired metabolism, injury, excess body weight, and pregnancy.
The affected joint tissues are enlarged, swollen, and the person experiences pain during physical activity. If joint inflammation is not treated, the destructive processes of bone and cartilage tissue will intensify. In rheumatoid arthritis, the joint is chronically inflamed, the pathology is caused by impaired metabolism. When a person wakes up, aching pain occurs, and it is difficult for the patient to sit down.
In the future, due to rheumatoid arthritis, all joint tissues will begin to hurt, and nodes will appear under the skin
Joint inflammation caused by infection will occur due to the fact that the patient was bitten by ticks or the infectious process was introduced from the urinary organs. The patient is weakened, he has hyperthermia, the knee joints are hot on palpation, and purulent contents can accumulate in them. How to treat arthritis?
Therapeutic measures depend on the genesis of the inflammatory process. Pathogenic bacteria are eliminated with the help of antibacterial drugs. Symptomatic treatment is used: pain is eliminated, inflammation is relieved, a cold or warm compress is applied externally. If the patient is overweight, then you need to get rid of it, and it is also better to say goodbye to bad habits forever.
Physical activity should be moderate, and you should eat a balanced diet.
With arthrosis, the trophism of the joints is impaired, gradual destruction of cartilage occurs, which becomes thinner, and the joints gradually lose function. Arthrosis changes develop due to:
People who spend a lot of time on their knees are prone to inflammation of the prepatellar bursa, located in the center of the joint under the kneecap.
If the nerves are pinched or inflamed, the pain will occur suddenly. After a person has trained, his joint may hurt. When you change position, the pain may disappear, which signals a pinched nerve. Inflammation of the sciatic nerve is most often observed; an inflammatory process in the femoral, breech, and gluteal nerves can also be observed.
The inflammatory process is promoted by excess weight, pathological processes in muscle tissue, old injuries, and exposure to low temperatures. Treatment is aimed at eliminating pain and inflammation; physiotherapeutic procedures, exercise therapy, and massage are used.
A doctor will help determine the cause of knee pain.
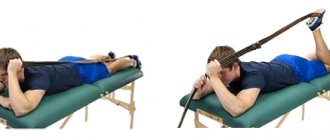
Exercise therapy is used after the exacerbation has been eliminated, and the exercises are monitored by a specialist. Set of exercises:
- You need to lie on your back, bend your legs, imitate riding a bicycle for 2 minutes, then rest for 1 minute.
- The starting position is the same. The legs are straight, positioned above the floor surface, alternately crossed, imitating the movements of scissors.
- Sit on the floor, stretch your legs forward, relax one by one, strain your thumbs forward and back.
Unconventional methods are used in addition to the main treatment; before using them, you should consult a specialist. Take 15 golden mustache leaves, they need to be crushed. Insist for 2 weeks in a dark, cool place. Apply externally as a rub. Honey with mustard, soda and salt are mixed in the same ratio. Apply externally to the affected area before going to bed, fix it with film, and wash the area in the morning.
Take a teaspoon of willow bark with birch leaves and calendula flowers. Pour a glass of boiling water and leave for at least 12 hours. Take 100 g 3 times a day 60 minutes before meals. If a person suffers from gout, then nettle juice, which is taken 1 teaspoon 3 times a day, will help him.
To prevent your knees from hurting, you need to warm up before doing gymnastics, and after physical education you should rest. If a person has done a warm-up, his microcirculation will improve and the joint will be abundantly lubricated with fluid. It is required to eat a balanced diet of natural food, drink at least 2 liters of water per day, adhere to a healthy lifestyle, control body weight, not be dependent on addictions, and not be overcooled.
There is no need to endure pain in the knee joints, otherwise the pathological process will become chronic. You can strengthen your joints with foods rich in vitamin D. They eat mushrooms, herbs, eggs, dairy products, and fish with liver. There is a lot of vitamin A in vegetable oil, rosehip oil, sea buckthorn oil, carrots, and pumpkin.
It is important to remember that if pain occurs in the knee joints, you should not treat it yourself, you should seek medical help. The doctor will help establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, choosing the correct dosage of drugs. Self-medication will lead to negative consequences due to which a person may become disabled.
You can also read: Is cracking your fingers harmful?
What to do if your knees hurt after training: causes and best ways to get rid of pain
Strength training, morning jogging, cycling, football, basketball are good for health, help strengthen the muscle corset, and help keep the whole body in good shape. But not the joints. These structural elements of the musculoskeletal system sometimes experience excessive stress during intense training. Short-term pain that quickly disappears after a good stretch is usually provoked by lactic acid. It accumulates in the muscles, but a feeling of discomfort occurs in the joints. If your knees hurt for a long time after training, then a thorough diagnosis is necessary. The examination cannot be postponed, especially if the intensity of the pain syndrome gradually increases. There is a possibility of an inflammatory or degenerative process developing in the knee joint. Then you will have to forget about training until you fully recover. Otherwise, increased physical activity will cause rapid progression of joint pathology. It is the knee joints that most often hurt after training due to the impact of static and dynamic loads on them. When performing exercises, changes occur in the muscular-ligamentous apparatus or osteo-articular elements. For example, when lifting a barbell, a person’s ligaments undergo a certain test of strength and elasticity. They stretch and then take an anatomically correct position. If the nature of the changes is temporary, then pain in the knee joints is considered normal. Under what conditions can discomfort after training be considered natural and does not require seeking medical help:
- slight, short-lived painful sensations occur due to an increase in the concentration of lactic acid in the muscle fibers. It is formed during anaerobic glycolysis and is excreted from the body within a few hours. The rate of lactic acid metabolism depends on the athlete’s muscle training. To speed up its elimination, stretching exercises, massage, and short rest are practiced;
- There is a dull aching pain that does not last long. It is not localized to a specific point, but spreads to the entire knee. Typically, such sensations are experienced by athletes who lift heavy weights or engage in freestyle wrestling. The dull nature of the pain syndrome is explained by temporary compression of the knee joint. Discomfort also occurs as the body naturally ages. With age, an insufficient amount of collagen is produced, which is responsible for the elasticity of connective joint structures. Their tensile strength decreases, so exposure to previous loads can cause microtrauma to hyaline cartilage. In the future, this can lead to the development of gonarthrosis - a severe pathology that is difficult to treat. If after 40-45 years of age athletes experience knee pain more often and more intensely after training, then it’s time to reconsider their regimen and reduce the load.
Pathological causes of pain
Pain is a protective reaction of the body to the influence of external or internal damaging factors. There are many pathological causes of discomfort and they are very diverse. Experienced sports doctors are able to make a diagnosis based on a person’s complaints and external examination. To confirm it, instrumental studies are prescribed. The most informative are radiography, arthroscopy, MRI, CT. The type of sport the patient is involved in becomes a definite clue for the doctor.
Run
People start running to lose weight, prolong youth, and improve their overall health. After the first lessons, even under the guidance of an experienced instructor, pain occurs in the knees. Over time, they disappear, as the strength and elasticity of ligaments, tendons, and muscles increases significantly. But, if the intensity of uncomfortable sensations increases in a runner, then the development of pathology can be assumed. Why do my knees hurt after training?
- traumatic injury to the meniscus. If the loads are distributed incorrectly when jogging, the lower leg may rotate poorly relative to the hip. The nature of the pain that occurs is sharp, acute. The main symptoms of meniscus injury are extensive swelling, increased severity of discomfort during palpation and during movement;
- luxation of the patella. Displacement of the kneecap occurs after a fall with the knee resting or a strong blow. The pain is sharp, but disappears quickly. After contacting a doctor, therapy takes only a few days. If an athlete neglects medical care, then a habitual dislocation of the knee joint gradually develops;
- Chondromalacia patella is a pathological condition in which the cartilage of the posterior surface of the patella is destroyed. After a run, there is a nagging pain that disappears only after a long rest. It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor to stop the degenerative-dystrophic process.
Runners often go to the emergency room when they have damaged ankle ligaments or partial rupture of the Achilles tendon during a sudden start. But with excessive loads, the ligamentous-tendon apparatus of the knee is also injured. Despite adequate therapy, joint pain sometimes occurs after training.
Lifting barbells, dumbbells
These are the most traumatic sports for knee joints that experience excessive stress. At the end of their career, professional athletes often experience problems due to microtrauma of hyaline cartilage, leading to the development of gonarthrosis. The leading symptom of this type of osteoarthritis is pain that increases with flexion and extension of the joint. If your joints hurt after training, doctors suspect the following pathologies:
- arthrosis of the knee, various forms of arthritis. Their development is indicated by long-lasting discomfort and the appearance of crepitus - a crunching sound during squats;
- Osgood-Schlatter disease is an aseptic destruction of the tuberosity and nucleus of the tibia. The disease is usually diagnosed in young athletes.
After lifting heavy objects, pain in the knees occurs due to previous injuries: damage to the meniscus, rupture of one of the cruciate ligaments.
Strands are formed in the connective tissue structures, reducing the functional activity of the joint and causing its instability. Race walking and cycling
When walking and pedaling a bicycle, the knee joints move monotonously, and this is a common cause of damage to any joint. When your knee hurts after a workout, and this condition lasts for at least an hour, this may be a clinical manifestation of the following pathologies:
- Osteoarthritis is a recurrent disease accompanied by the gradual destruction of cartilage tissue. To stabilize the joint, the body starts the process of formation of osteophytes (growth of the edges of bone plates). While walking, they compress sensitive nerve roots, causing severe pain. Discomfort in the knees after training is also explained by injury to nearby soft tissues;
- gouty, rheumatoid, psoriatic arthritis. Pain after walking or cycling may indicate an inflammatory process developing in the joints. If no treatment was carried out at this stage, then soon you will have to forget about training forever. Destruction of hyaline cartilage will begin, which ends with disability;
- osteochondritis dissecans - aseptic necrosis, leading to the separation of a small section of cartilage from the underlying bone and its displacement into the joint cavity. As a result, a loose intra-articular body is formed, causing pain during and after walking.
Acute pain syndrome is a sign of a knee injury, after which any movement becomes impossible.
Discomfort in the joint area of low intensity is felt due to previous injury. For example, if the synovial capsule was damaged after a fall, then during the healing process, areas of fibrous tissue may form on it. With this type of injury, the athlete needs to dose the load on the knee. Basic methods for pain relief
Pain that occurs due to natural causes is easy to eliminate. This is usually done by stroking the knee and then vigorously rubbing it. There is an intense rush of blood to the structural elements of the joint, muscle spasm is eliminated, and the elimination of lactic acid is accelerated. Professional athletes know well what to do if their knees hurt after training:
- straighten up, place your hands on your sides, rise up, focusing on the toes of first one, then the other leg. Shake your feet vigorously and roll onto your heels. Perform exercises 20 times in 2-3 approaches;
- legs spread wide and slightly bent, arms position is arbitrary. Sway gently from side to side to warm up. Then do shallow lunges, using both knees;
- stand up straight, straighten your back, move your legs back one at a time and use your hands to pull your feet towards your buttocks. Perform the exercise 10-15 times in 3 approaches.
Sometimes painful sensations persist even after knee massage and physical therapy. Sports doctors have various types of gels and ointments with a cooling effect. Typically, their main ingredients are menthol and camphor. They act on the receptors of subcutaneous tissue, exhibiting analgesic, distracting, and locally irritating activity. After applying the ointment or gel, a pleasant feeling of coolness occurs, and the discomfort completely disappears. What else can you do if your knee joints hurt after training:
- use cold compresses. Cooling helps reduce the intensity of discomfort. A bag of ice cubes wrapped in thick cloth is applied to the knees for 10-15 minutes;
- rest for 30-60 minutes. You can simply lie down or sit down and put your feet on a pillow or put them on a low stool;
- secure the knee with an elastic bandage. To do this, use a narrow bandage of medium or high stretch, which is wrapped around the knee several times. Pharmacies and medical equipment stores sell sports bandages that are comfortable to wear and do not restrict movement. Sports doctors recommend using them during training to reduce the likelihood of injury.
What to do when joints hurt after training is decided only by a doctor after carrying out diagnostic measures. If the results of instrumental studies do not reveal degenerative tissue degeneration, then wearing soft bandages and a good warm-up before training will help eliminate discomfort in the knees. And if developing articular pathology is detected, long-term therapy with chondroprotectors, analgesics, and NSAIDs is required.
Video on the topic
Knee-joint
The knee is a joint that allows the leg to bend, provides stability to the body and supports all of its weight. Thanks to the knee, activities such as walking, running, turning, jumping and squatting are possible.
This work is ensured by several components:
- bones;
- cartilage tissue;
- muscles and ligaments;
- tendons.
No. 1. Injuries
Acute or chronic injury is a common cause of knee pain. According to some studies, the knee is the joint most often subject to injury. The very anatomical structure of the knee and its functions predispose to the development of injuries, which can disrupt its functioning and, accordingly, cause pain.
The appearance of such symptoms indicates damage to one of three ligaments:
- anterior and posterior cruciate;
- medial collateral.
Such injuries occur in athletes, especially track and field athletes. But this does not mean that non-professional athletes are out of the risk zone. Incorrect running technique is one of the causes of ligament damage and joint pain, which is typical for non-professional athletes.
Football and other contact sports with a ball can cause injuries such as direct blows to the knee. Some injuries may be so severe that they require surgery.
Despite the fact that this injury is serious, it is, unfortunately, not uncommon. Pain can occur not only in the acute period, but also persist in the future.
A fracture can affect several bones, including the kneecap. At risk are older patients and those suffering from degenerative diseases. In this case, a fracture can form even with minor injuries and everyday activities.
No. 2. Bursitis
This is an inflammation of the joint capsule of the joint. Anatomically, they are designed to soften the work of the joint and allow the ligaments to easily slide over the component parts of the joint.
Sudden impacts, chronic injuries and irritations can damage this joint capsule, which leads to inflammation.
Characteristic symptoms of inflammation will be: swelling, pain, stiffness of movement, and the knee becomes hot to the touch.
Treatment is prescribed individually, but more often it comes down to taking anti-inflammatory medications; rest for the knee and the absence of a traumatic agent are also necessary.
No. 3. Dislocations
Patella dislocations are also common, which is accompanied by severe and acute pain. When seeking medical help, the doctor can easily return the patella to its place, however, visual examination methods are mandatory.
Radiography allows you to identify possible fractures and, based on this, develop treatment tactics. In severe cases, surgery may be required to prevent further dislocations.
No. 4. Degenerative changes in tissues
Osteoarthritis is a common problem and degenerative tissue disorder. A decrease in the volume of cartilage and surrounding tissues is the cause of pain, stiffness of movement and dysfunction of the joint.
Such changes are more associated with the aging process: it occurs in 10% of men and 13% of women aged 55-65 years.
No. 5. Rheumatoid diseases
These are inflammatory autoimmune diseases in which the target organ is the joints. Their own immune system perceives them as enemies and attacks.
Characteristic symptoms of the disease include: swelling, severe pain in the joints; if left untreated, bone erosion and joint deformation may occur.
There is no specific treatment for rheumatoid arthritis, but depending on the clinical picture, the doctor may prescribe a number of medications:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- corticosteroids;
- biological agents and antirheumatic drugs;
- painkillers and others.
This is a very painful form of arthritis. Characteristic symptoms include: severe swelling, stiffness of movement, severe pain, etc. Their appearance is associated with the accumulation of uric acid in the joint; taking anti-inflammatory drugs or other treatments helps break down these chemicals.
No. 7. Infections
Even after a scratch in the knee area, the infection can spread to underlying structures, including the joint. The spread of infection can also occur through the blood and lymph flow. In weakened patients with immunodeficiency, this condition can be dangerous and pose a threat to the patient's health.
Discomfort in the knee brings a lot of inconvenience. The causes of discomfort range from physiological factors to pathology. Such manifestations should not be ignored. Treatment for pain depends on what causes it. It is important to see a doctor in time. Painful discomfort in the knees manifests itself when at rest and in motion; it hurts under the knee when squatting. This article will discuss this type of discomfort.
What to do?
If you have knee pain, treatment should be carried out by a doctor. However, everyone should be able to react competently and provide first aid in case of injury to the designated area, because the salvation of the kneecap itself may depend on this.
So, it is necessary to completely immobilize the affected limb along with the joint and apply a cold compress to it, and then seek qualified medical help by calling an ambulance.
The specialist will first conduct an examination and prescribe medications to relieve pain in the back or front of the knee, after which treatment will be carried out depending on the cause of the discomfort.
Varieties of arthritis are treated with drugs that relieve inflammation and kill germs. They are prescribed exclusively by a doctor. Arthrosis requires heat, so experts prescribe warming herbal compresses and ointments to patients that increase the protective properties of cartilage.
JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Rotyberg) has the most advanced equipment that allows for a quick and accurate examination of the knee joints. Medical center specialists will perform the necessary diagnostics and then prescribe the required treatment.
To get help at the highest level, just make an appointment with a therapist who will determine the exact cause of the pain. Also in our clinic in the center of Moscow, the best traumatologists, rheumatologists, surgeons and neurologists await you.
You can make an appointment by calling 24 hours a day or using the feedback form on the clinic’s official website. The medical center is located at Moscow, 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10. Geographically, we are located near the Mayakovskaya, Belorusskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Chekhovskaya, Tverskaya metro stations.
Characteristics of pain syndrome
The knee is subject to stress and suffers from discomfort; the reasons for this condition are ambiguous. Distribution area:
- below the knee
- above the knee
- under the knee
- in the knee joints
Knee pain syndrome
The character is varied:
- acute (sudden and short-term)
- chronic (permanent)
- sharp
- aching
- stabbing
Inconveniences may occur:
- when bending
- during extension
- during flexion and extension
- when walking
- in a calm state
Often there is pain behind the knee when squatting. If you have symptoms, consult your doctor. They will help you: rheumatologist, physiotherapist, traumatologist, orthopedist, massage therapist, chiropractor. After tests and examination, the diagnosis will be clear. Doctors will diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Pain behind the knee when squatting
If there is pain behind the knee when squatting, then this may be either a violation of the structure of the ligamentous apparatus or a sign of compression of the sciatic nerve at the point of its bifurcation into the tibial and peroneal branches.
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs in people who are engaged in sedentary work and do not pay due attention to the ergonomics of their workplace. When pressure is applied to the popliteal area by sitting in a chair, blood circulation is disrupted and primary ischemia of the sciatic nerve occurs. This manifests itself in the form of pain. The differential clinical sign is a feeling of numbness in the area of the legs and feet.
Damage to the posterior cruciate ligament can also cause significant pain when squatting. It will be stronger when doing squats. And when you get up, the discomfort will decrease. Associated clinical signs: pain on palpation of the posterior surface of the knee joint, swelling and hyperemia of the skin.
Physiological factors
There are a number of factors that are not pathological.
Knee-joint
If these factors are present, the diagnosis is obvious. See a doctor for treatment.
- Damage. Common causes of knee pain. The results of injuries, bruises, dislocations, sprains, serious fractures. After violations, pain syndrome appears. Unbearable pain, accompanied by swelling and bruising. After injury, numbness and tingling are possible. In case of serious injuries, deformation of the knee joint and bending cannot be ruled out. Some injuries result in disability.
- Excessive loads. After systematic stress on the knee, discomfort is a common occurrence. The result of the action is injury. Legs need rest. Do gymnastics and massage, relieving your lower limbs from overwork. Measured, balanced loads are the key to a healthy knee joint.
- Excess weight is also a cause of discomfort. Excess weight puts pressure on the lower limbs. The knees are the first to suffer. It hurts people to walk, bend and straighten their legs. Difficulty standing. Overweight
- Wearing the wrong shoes. If the shoes are uncomfortable, expect lower extremity discomfort. The lower part of the knee is often affected. Look at comfort, then at beauty. Then the leg will not need treatment.
- Improper execution of exercises. The causes of discomfort are negligence, leading to unpleasant consequences. A considerable number of athletes and training enthusiasts have injuries. It is important to adhere to the technique of performing the exercises. The exercises should be done correctly. Beginners and amateurs need instructions from a trainer.
Athletes with barbells often suffer from knee pain. Barbell training should be done responsibly. Incorrect technique for squatting with weights leads to dire consequences. Beginners need to follow the instructions of the trainer. Do barbell exercises correctly.
Injuries during training occur as a result of setting records. The desire to sit down an incredible number of times per approach will not lead to good results. Expect unpleasant discomfort and pain.
- Lack of physical activity. If a person moves little, “does not knead his bones,” the functioning of the joints, including the knee, is disrupted.
- Poor nutrition. Eating more than normal leads to osteoarthritis.
As a result, the knees hurt when squatting. These factors are not considered diseases. The manifestation of these factors requires consultation with a doctor. When it comes to injuries, you can’t hesitate.
After childbirth, knee joints hurt when squatting
Many women after childbirth have pain in their knees when squatting - this is not a natural process. It is worth paying close attention to the appearance of this symptom. If it lasts longer than 7 days, then you need to consult an orthopedist as soon as possible.
The fact is that the joints of the knees hurt when squatting after pregnancy due to the total destruction of the synovial cartilaginous layer. In the process of bearing a baby, the expectant mother’s body gives the fetus some of the nutrients, minerals and trace elements. Especially if a woman has problems with the large intestine or she lives in a region where there is insufficient sunlight and, as a result, she does not produce the required amount of vitamin D. Such women experience total osteoporosis. It is expressed in the destruction of tooth enamel and bone loss. First of all, the so-called loaded articular surfaces are affected. In conditions when extreme body weight increases (due to a growing abdomen) and bone tissue destruction occurs, the process of sclerosis of the articular end plates begins. They become thinner, deformed and lose the ability to provide diffuse nutrition to the cartilaginous synovial layer. It, in turn, is also destroyed, which causes the development of deforming osteoarthritis in a short time at a fairly young age.
It is necessary to consult an orthopedist or chiropractor and undergo a course of rehabilitation or restorative treatment. In advanced cases, such a disease can only be treated with surgery.
As a symptom of a disease
When there is no reason for unpleasant sensations, pain is constantly bothering you - this is a reason to think about the presence of pathology. A professional will answer the question. Having determined the disorder, he will prescribe treatment to eliminate the disease.
Similar sensations in the knee joint are symptoms of diseases:
Intervertebral hernia. Characterized by radiating pain extending above the knee. Treatment consists of correcting disorders of the source of the disease, the spine.
Osteoarthritis. Destruction of the joint structure. Pain appears during movements. A characteristic symptom is increased in the morning, weakened in the evening. Accompanied by a crunch in the knee. A good solution is physical therapy. Which needs to be done systematically.
Necrosis of the tuberosity. Boys aged 11-15 years suffer. Chronic pain is characteristic.
Bursitis. Inflammatory process. There is joint swelling and decreased activity.
Baker's cyst. There is discomfort in the popliteal area.
Gonarthrosis. The condition of the cartilage worsens. Pain under the knee when squatting.
Osguth-Schlatter disease. Discomfort when bending the leg. Affects the tibia. Occurs after an injury; an unexplained occurrence is possible. May become chronic.
Osguth-Schlatter disease
Arthrosis. Manifests itself during movement, extension, squatting. Accompanied by a crunch. In the initial stages, you can cope with special exercises. In its advanced form, it manifests itself in unbearable pain syndromes that do not allow movement.
Prevention and risk reduction when running
Almost every athlete can encounter a situation where their knee hurts after a run. However, if you approach the organization of training with caution, you can avoid such problems. Professionals recommend:
- Get tested in advance. You can consult a doctor for disease prevention if you plan to run. The specialist will prescribe the necessary tests and give recommendations. If diseases are observed, the doctor will prescribe treatment, after which it will be possible to start running after a while. In rare cases, you will have to forget about running.
- Contact your coach. He will help you choose sports shoes and create an exercise plan. Periodization and level of loads must be thoughtful. Otherwise, overtraining and inflammation cannot be avoided.
- Choose a suitable place to run. A road with many potholes and uneven spots is clearly not suitable for a beginner. If there is no suitable place for running, then it is better to exercise on a treadmill.
Beginners can start at a sports club on a treadmill under the supervision of an experienced trainer. If you experience problems with your knees during such exercises, you should definitely consult a doctor. Diseases of this kind are best treated in the early stages, because at a later stage they are difficult to treat. Sometimes advanced diseases have to be treated with radical methods.
How long might it take for therapy? It depends on the severity of the disease, the individual characteristics of the patient, and heredity. The doctor will indicate more precise dates after the diagnosis.